
Home > ECONOMICS > UER

Most Popular Papers *
The Role of Entrepreneurship in Economic Growth Daniel Smith
The Strength of Religious Beliefs is Important for Subjective Well-Being Enrique Colón-Bacó
Impact of Exchange Rate Regimes on Economic Growth Brigitta Jakob
The Impact of Sustainability Reporting on Firm Profitability Lancee L. Whetman
Do Mandatory Minimums Increase Racial Disparities in Federal Criminal Sentencing? Caroline Gillette
A Data Analysis of the World Happiness Index and its Relation to the North-South Divide Charles Alba
Impact of Privatization on Economic Growth Adnan Filipovic
Does the Economy Determine the President? A Regression Model For Predicting US Presidential Elections Roy K. Roth
Determinants of Bank Profitability in Ukraine Antonina Davydenko
Crisis: Capitalism, Economics and the Environment Raj Navanit Patel Mr
* Based on the average number of full-text downloads per day since the paper was posted. » Updated as of 05/06/24.
- Journal Home
- About This Journal
- Journal FAQ
- Most Popular Papers
- Receive Email Notices or RSS
Advanced Search
- Economics Department
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Economics Research Paper

This sample economics research paper features: 7800 words (approx. 26 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 36 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
Evolutionary Economics Research Paper
Introduction, relationship between theories of biological and sociocultural evolution, the scope and methods of evolutionary economics, marxist models of evolution, original institutional economics, the new institutional economics, whither evolutionary economics.
- Bibliography
More Economics Research Papers:
- Budget Research Paper
- Cost-Benefit Analysis Research Paper
- Economic History Research Paper
- Fiscal Policy Research Paper
- Labor Market Research Paper
Evolutionary economics has gained increasing acceptance as a field of economics that focuses on change over time in the process of material provisioning (production, distribution, and consumption) and the social institutions that surround that process. It is closely related to, and often draws on research in, other disciplines such as economic sociology, economic anthropology, and international political economy. It has important implications for many other fields in economics, including, but not limited to, growth theory, economic development, economic history, political economy, history of thought, gender economics, industrial organization, the study of business cycles, and financial crises.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Historically, evolutionary economics was the province of critics of the mainstream, neoclassical tradition. Both Marxist and original institutional economists (OIE) have long asserted the importance and relevance of understanding change over time and critiqued the standard competitive model for its abstract, ahistorical, and static focus. In recent years, however, the rise of the new institutional economics (NIE) as well as game theory has resulted in wider acceptance of evolutionary explanations by the mainstream (Hodgson, 2007b, pp. 1-15; North, 1990). Consequently, it is now possible to identify three major traditions in evolutionary economics: the Marxist (Sherman, 2006), the OIE (Hodgson, 2004), and the NIE (North, 1990). Each of these major traditions encompasses multiple strands within it. As a general rule, Marxists and OIEs seek to replace the standard competitive model of mainstream economics, while NIEs seek to complement the standard competitive model, although the growing acceptance of game theory may make this less of an important distinction. Despite their differences, it is possible to identify some common themes that are shared by each of these disparate traditions. For example, authors in each tradition have exhibited a concern with how the interaction of technology, social institutions, and ideologies leads to changes in economic and social organization over time.
The goal of this research paper is to introduce the reader to a few of the major concerns, themes, and important authors of each respective tradition. In doing so, it will first address some general issues in evolutionary economics, including its relationship to evolutionary biology as well as some conceptual, definitional, and taxonomic issues. It will then proceed to provide a brief overview of the evolution of each respective tradition. Unfortunately, the length of this research paper precludes discussion of many worthy contributions to each tradition as well as important topics that can and should be addressed by evolutionary economics. For example, space does not permit a discussion of how evolutionary economics could be applied to gender economics or how economists who write on gender often incorporate the contributions of evolutionary economists. Nor will this research paper attempt to assess the extent of empirical or conceptual progress in evolutionary economics within or between respective traditions. In addition, the reader should be aware that evolutionary economics itself is an evolving field and that the boundaries between the three traditions are often fluid.
General Issues in Evolutionary Economics
Taken at face value, the word evolution simply means change. But Darwin’s theory of gradual (step-by-step) evolution by variation of inherited characteristics and natural selection (differential survival based on the level of adaptation) removed both theological and teleological explanations from the process of biological evolution and placed humans firmly in the natural world. The modern neo-Darwinian synthetic theory of evolution combines Darwin’s focus on gradual (step-by-step) change based on variation of inherited characteristics and natural selection with modern population genetics. Both Darwin’s original theory and the modern synthetic theory of evolution explain change within a species, the rise of new species, and the more dramatic kinds of change such as the rise of mammals, primates, and eventually human beings as a result of the same step-by-step process (Mayr, 2001, 2004).
At the risk of oversimplifying slightly, it should be noted that the neo-Darwinian synthesis formulated by Thedosius Dobzhansky and Ernst Mayr in the 1950s has given rise to two sometimes opposing strands within the overarching frame of the synthesis (Mayr, 2004, pp. 133-138). One strand, exemplified by Richard Dawkins, who has written many widely read books on evolution, focuses on the role of genes in building organisms and on the tendency of natural selection to result in highly adapted organisms. This approach is sometimes referred to as the strong adaptationist program in evolutionary biology. It is closely related to fields such as sociobiology and evolutionary psychology, which explain many human behaviors in terms of their evolutionary origins.
Other evolutionary biologists have de-emphasized the role of natural selection and emphasize the importance of understanding biological evolution in terms of emergence, chance, path dependence, satisficing, and punctuated equilibrium. Richard Lewontin and the late Stephen J. Gould are two widely read authors who have advocated this position. Both Gould and Lewontin have been strongly critical of biologically based explanations for human behavior.
Although these two differing approaches to evolution are sometime viewed as rivals, they are in actuality complementary to each other. It is important to understand both aspects of biological evolution. In addition, biological evolution is a very complex process, and evolutionary biologists continue to push their field forward. Contemporary research in evolutionary biology focuses on the important interactions between genes, organisms, and their interaction with the environment in the process of development. Evolutionary biologists have also become more aware of the importance of lateral gene transfer and endo-symbiosis in bacteria evolution. However, there is still widespread consensus among evolutionary biologists that the synthetic theory of evolution is a true theory. Evolutionary biologists reject theories that incorporate teleological explanations or inheritance of acquired characteristics because these theories have been discredited empirically. Evolutionary biologists reject theories that are premised on or seek to find evidence of supernatural design as this adds nothing to the explanation and draws the focus of science away from understanding and explaining natural law.
Evolutionary economists often draw on and incorporate concepts developed by evolutionary biologists to explain how economic evolution occurs. For example, many evolutionary economists view economic evolution as a nondirected step-by-step process that is non-teleological (it lacks a specific goal or predetermined endpoint). Many, although not necessarily all, evolutionary economists agree that humans have at least some genetically based cognitive and social predispositions that are a result of genetic evolution. Some examples include the ability to learn a language, to learn social norms, to cooperate in groups, and to develop complex tool kits with which to transform nature into useable goods and services. In addition, the use of the Darwinian concepts of inheritance, variation, and selection as analogs to explain outcomes is pervasive in evolutionary economics. Evolutionary economists also distinguish between specific or microevolution (change that occurs within a sociocultural system) and general or macroevolution (change from one sociocultural system to another).
Some evolutionary economists view the market as natural and as an extended phenotype. Other evolutionary economists argue that evolutionary economics should be viewed as a generalization of the Darwinian concepts of variation, inheritance, and natural selection with each case specifying additional, relevant detail (Hodgson, 2007a; Hodgson & Knudsen, 2006). Others have argued that while Darwinian concepts often provide useful analogies for understanding sociocultural evolution, aspects of sociocultural evolution are distinctly non-Darwinian (Poirot, 2007). For example, in at least some instances, social and economic evolution results from the conscious decisions of groups of purposive agents who intentionally design or redesign human institutions. Also, in the process of socio-cultural evolution, we can pass on cultural traits that we acquire through the process of learning. Biological evolution results in a branching pattern and barriers between different species. But human cultures can always learn from each other. The more emphasis that is placed on purposive design of social institutions and cultural learning as well as the abruptness (instead of the step-by-step nature) of social change, the less Darwinian a model of sociocultural evolution becomes. However, it would be difficult to identify anyone today who argued for a strong teleological concept of sociocultural evolution or who sought to explain sociocultural evolution in terms of divine or supernatural intervention.
Two other important concepts borrowed from the natural sciences, emergence and complexity, also play a key role in evolutionary economics. Emergence means that an observed system results from the complex interaction of the components of the subsystems. This process of interaction gives rise to patterns that would not be predicted from and cannot be reduced to the behaviors of the individual components. However, understanding the system still requires an understanding of its components and the interaction of the components. So it is important to understand what individuals do. And it is also important to understand how individual choices and habits interact with social institutions in a dynamic way. It is often easier to think in mechanical terms. But if we are careless with mechanical analogies, then we can be easily misled.
This raises the question of what it is that evolves in sociocultural evolution. In evolutionary biology, selection takes place at multiple levels but logically requires changes in the gene pool of a population over time (Mayr, 2004, pp. 133-158). This has led some evolutionary economists to suggest that institutions and/or organizational routines provide us with an analog to the gene. Others argue that there is not a precise analog. To understand this debate, we first have to understand what an institution is.
It is popular to define institutions as “rules of the game.” This is a good start, but it confuses the function of institutions with a definition of institutions. A more extensive definition of institution defines an institution as any instituted process, or in other words a shared, learned, ordered, patterned, and ongoing way of thinking, feeling, and acting. Institutions may be tacit and informal or highly organized and structured. By this latter definition, modern firms, medieval manors, technology, nation-states, political ideologies, and even technology are all institutions. In other words, virtually everything that humans do is an instituted process. Institutions are component parts of a sociocultural system.
But to just call everything an “institution” can make it difficult to conduct analysis. So it is useful to draw a distinction between entities such as social ideologies (e.g., Calvinism and democracy), social institutions (e.g., class, caste, kinship, the family, the nation-state), organizations (e.g., the modern firm, the International Monetary Fund, the medieval manor), organizational routines of actors within specific organizations, and technology (the combined set of knowledge, practices, and tool kits used in production). So in that sense, everything in sociocultural systems is constantly evolving. There is no precise analog in sociocultural evolution to the gene pool of a population.
As suggested above, social institutions are part of more general wholes, which it is convenient to term sociocultural systems. A sociocultural system includes the direct patterns of interaction of a society with the ecosystem (its subsistence strategy, technology, and demographic patterns), its social institutions, and its patterns of abstract meaning and value. Many anthropologists classify sociocultural systems by their scale, complexity, and the amount of energy captured by their subsistence strategy. Standard classification includes bands, tribes, chiefdoms, agrarian states, and industrial states, each of which corresponds roughly to subsistence strategies of foraging, horticulture, pastoralism and fishing, settled agriculture, and modern industrial technology. This classification system provides a useful scheme with which to understand the rise of large agrarian empires in the neolithic era and, ultimately, the Industrial Revolution in northwestern Europe. It also provides a useful classificatory schema with which to understand the interaction of multiple kinds of contemporary societies in a globalizing world. However, care must be taken to emphasize the multilinear and dynamic nature of socio-cultural evolution rather than rigidly applying these concepts as a universal and unilinear schema (e.g., see Harris, 1997; Wolf, 1982).
The evolutionary biologist Ernst Mayr (2004) argued that biologists who study genetic evolution ask “why” questions while biologists who study things such as biochemistry ask “how” questions. Similarly, many mainstream economists ask “how” questions while evolutionary economists ask “why” questions. While the study of evolutionary economics does not preclude the use of formal mathematical models or quantification, most of its practitioners employ qualitative and interpretive methods. Also, as suggested above, some evolutionary biologists focus on changes that occur at the level of species, while others focus on more dramatic kinds of change. Similarly, evolutionary economists are interested in the study of sociocultural evolution on a grand scale, such as the rise of agrarian empires or modern capitalism, as well more specific, micro-level evolution such as changes in the organizational routines of individual firms.
Consequently, the kinds of issues that evolutionary economists are interested in overlap with the focus of other social sciences and even, in some instances, with the fields of ecology and evolutionary biology. Evolutionary economics reflects a tendency to counter the fragmentation of political economy into disparate social sciences that occurred in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Evolutionary economists, like their counterparts in economic sociology, economic anthropology, and political economy, focus more directly on those institutions with the strongest, most immediate, direct relevance to the process of material provisioning. So there may still be a need for some division of labor in the social sciences. What is of direct relevance will vary according to what is being analyzed in any particular study. An economic historian studying the rise of capitalism may, following Weber, find an understanding of Calvinist theology to be essential. Someone studying financial innovation in twenty-first-century industrialized societies would most likely find the religious affiliation of modern banking executives to be of little interest or relevance.
Research Traditions in Evolutionary Economics
Evolutionary economics is composed of three rival but sometimes overlapping major traditions: the Marxist, the OIE, and the NIE. While there is some degree of ideological overlap between the schools, each of the respective schools tends to share a common overarching ideology. Marxists seek to replace capitalism, OIEs seek to reform capitalism, and NIEs generally view capitalism as beneficent. This is not, notably, to argue that the ideology necessarily determines the empirical and theoretical analysis. Also, as previously noted, Marxists and OIEs seek to replace the standard competitive model while NIEs seek to complement the standard model. However, the reader should be aware that the boundary between the three traditions is often fuzzy, and there is sometimes overlap between the three traditions. Similarly, each of these three schools is composed of multiple strands and has undergone significant change over time.
The remainder of this research paper will focus on outlining in very broad terms a few of the significant themes and concerns of each respective tradition, how these traditions have changed over time, and the contributions of a few representative authors of each of the three traditions. The reader may note that despite the differences between the traditions, there is a strong interest in all three in understanding how technology, social institutions, and cognitive models interact in the process of sociocultural evolution. The division made between the three traditions may be of greater interest and relevance in the United States, where there is a strong correlation between specific organizations and schools of thought. For example, the Association for Evolutionary Economics (AFEE) has been the primary promoter of OIE in the United States. In contrast, the European Association for Evolutionary Political Economy (EAEPE) has a much wider umbrella. So there may be hope someday for a grand synthesis of the three respective traditions.
There are, of course, many different Marxist and quasiMarxist models of sociocultural evolution. For the purposes of this research paper, it is convenient to make the differentia specifica of a Marxist model of sociocultural evolution a focus on class struggle: the conflict between social groups defined in terms of differential access to the productive resources of a given society (Dugger & Sherman, 2000). This way of understanding sociocultural evolution is often referred to as historical materialism. While Darwinian reasoning may at times be employed in Marxist theories of sociocultural evolution, Marxists have generally emphasized the non-Darwinian aspects of sociocultural evolution as well as sharp discontinuities between human and infrahuman species. At the same time, it is hard to think of any academic Marxists writing today who would advocate Lysenkoism or Lamarckian theories of inheritance as valid explanatory concepts for understanding genetic evolution.
To understand historical materialism, we must begin with Marx’s concept of the mode of production (for extended discussions, see Wolf, 1982, chap. 3, and also Fusfeld, 1977). A mode of production includes the techno-environmental relationships (e.g., agriculture based on a plough or factories using steam engines) and the social relationships of production (e.g., warlords and peasants or factory owners and workers) or, in Marxist jargon, the forces of production and the social relations of production, respectively. These relationships between groups of people in Marx’s view are characterized by unequal relations of power, domination, subordination, and exploitation. This gives rise to social conflict over the terms of access to and the distribution of the productive resources of society. Social conflict requires the creation of a coercive entity to enforce the interests of the dominant social class (i.e., a state). In addition, human beings develop complex ideologies with which to justify their positions. Thus, the entire civilization (or what above is termed a sociocultural system) rests on a given mode of production, with the mode of production distinguished by the primary means of mobilizing labor (e.g., slavery, serfdom, wage labor).
In his analysis of Western history, Marx distinguished between the primitive commune, the slave mode of production of the ancient Roman Empire, the Germanic mode of production, the feudal mode of production of medieval Europe, and the modern capitalist mode of production. In analyzing Western history, Marx argued that each successive mode of production had produced technological advance, thus elevating the material level of human existence.
Capitalism, in Marx’s view, is qualitatively different from extended commodity production. Capitalism requires that land, labor, and capital are fully treated as commodities. This means that labor is “free” in the sense of not being legally bound to perform labor for the dominant class and “free” in the sense that it has no claim to the resources needed to produce goods and services. Therefore, capital is used as a means to finance innovation in production, and labor is compelled by economic circumstances to sell its labor power. Because capitalism promotes endless accumulation of capital, it is thus far the most successful in a material sense. However, the dynamic of capitalist accumulation gives rise to periodic crises, and it is therefore unstable. In addition, it is often destructive of human relationships. So a relationship of apparent freedom is in actuality a relationship of power, subordination, and domination that will give rise to social conflict. The only way to end this conflict, in Marx’s view, is to redesign social institutions so as to pro-mote both development of the forces of production and social cooperation (i.e., replace capitalism with socialism). There is disagreement among scholars who study Marx as to whether Marx thought that the triumph of socialism over capitalism was inevitable.
Insofar as one seeks to explain the historical origins of capitalism and the Industrial Revolution, two historical epochs are of particular relevance. Marxist historians and Marxist economists (and many others) with a particular interest in economic history thus often refer to two transitions (one from antiquity to feudalism and the other from feudalism to capitalism) as giving rise to modern capitalism. Howard Sherman (1995, 2006), a well-known Marxist economist, has summarized and synthesized much of this existing literature.
Sherman traces Western economic history from tribal organization through the rise of modern capitalism. Sherman is a materialist who analyzes societies by starting with the material base of human existence and examines the interaction between technology, economic institutions, social institutions, and ideologies. Technology and technological innovation as well as social conflict between classes are key variables in Sherman’s analysis. But overall, Sherman’s schema is holistic and interactive, rather than mechanical or reductionist.
In analyzing the breakdown of feudalism, Sherman focuses on the tripartite class conflict between peasants, nobles, and monarchs and the ability of each of the respective classes to force an outcome on the other classes. As a consequence of this conflict, a new pattern of relationships based on private property and production for profit in a market, as well as increasingly organized around new sources of mechanical power, gave rise to a unique and extremely productive system referred to as capitalism. This system of production encourages constant cost cutting, innovation, and capital accumulation, thus leading to the potential for the progressive material elevation of human society.
However, capitalist society is still riven by conflict between property-less workers and property-owning capitalists. Because the capitalist has a monopoly over the productive resources of society, the capitalist is still able to compel the worker to produce a surplus for the capitalist. This creates social conflict between the capitalist and worker and also forces the capitalist into an ultimately self-defeating boom-and-bust cycle of rising profits and increasing concentrations of capital, followed by falling rates of profit, leading to cycles of recession and crisis. The institutional structure of capitalism also magnifies other social conflicts and problems such as environmental degradation and destruction, as well as relations between racial and ethnic groups and genders. The solution to this social conflict, in Sherman’s view, is to replace the institutions of capitalism with economic democracy (i.e., democratic socialism).
Sherman, who has long been a critic of Stalinist-style socialism, also extends his analysis to change in Russia and the Soviet Union. The October Revolution of 1917 occurred because neither the czar nor the Mensheviks were able to satisfy the material aspirations of the vast majority of Russians. But industrialization in the Soviet Union became a nondemocratic, elite-directed process due primarily to the particular circumstances surrounding the Bolshevik Revolution, the ensuing civil war, and the problems of the New Economic Policy. In time, factions among the elites developed as the Soviet economy proved unable to satisfy the material aspirations of the majority of the Soviet population. This created new pressure for change as elites were able to capture this process. Due also to pressure from the West, change in the former Soviet Union took the direction of restoring capitalism rather than developing greater economic democracy.
It should be noted that the standard Marxist model of historical materialism focuses on the ability of capitalism to elevate the material capacity of human societies. This focus has been challenged by the rise of world systems and dependency theory. Theorists who follow this line of thinking focus on the uneven nature of development and the tendency of core economies to place boundaries on the development of formerly colonized areas of the world. Some theorists in this tradition have been justly accused of having a rather muddled conception of the term capitalism, insofar as they claim inspiration from Marx. The late Eric Wolf (1982), a well-known economic anthropologist, resolved many of these conceptual issues in his book Europe and the People Without History. So rather than assume that capitalism leads uniformly to material progress, Wolf extended the historical materialist model to analyze the process of uneven development in the world system as a whole. In their textbook on economic development, James Cypher and James Dietz (2004) provide an excellent history and exposition of classical Marxism, dependency theory, and extended analysis and discussion of the new institutional economics, original institutional economics, and modernization theory.
Thorstein Veblen (1898) was the founder of OIE, and his influence on OIE continues to be prevalent (Hodgson, 2004). Veblen was strongly influenced by Darwin’s theory of biological evolution and held evolutionary science as the standard for the social sciences, including economics, to emulate. He was also deeply influenced by the evolutionary epistemology of the American pragmatists Charles Saunders Peirce and John Dewey. In addition, he incorporated the contrasting positions of nineteenth-century evolutionist anthropology, as exhibited by the work of Tylor and Morgan, and the historical particularism of Franz Boas. Although he was strongly critical of Marx and of Marxism, there are both parallels as well as differences in the writings of Marx and Veblen.
Like Marx, Veblen focused on the importance of understanding the interaction of changes in technology, social institutions, and social ideologies as well as social conflict. Veblen also had a stage theory of history, which he borrowed from the prevailing anthropological schemas of his day. However, where Marx focuses on concepts such as class and mode of production, Veblen focuses on instituted processes and the conflicts created by vested interests seeking to reinforce invidious distinctions. Veblen’s model of sociocultural evolution is a conflict model in that it focuses broadly on social conflict that arises in the struggle for access to power, prestige, and property. But it is not a class-based model in the sense that Marxists use class.
In “Why Is Economics Not an Evolutionary Science?” (1898) and in “The Preconceptions of Economic Science” (1899) , Veblen developed a critique of the mainstream economics of his day. In developing this critique, Veblen was critical of the abstract and a priori nature of much of mainstream economic analysis. In articulating this point, he contrasted the “a priori method” with the “matter of fact method.” This particular aspect of Veblen’s criticism has often led some to view both Veblen and later OIEs as “atheoretical.” But this misses the point for at least two reasons.
Veblen did not eschew theoretical analysis per se. He was however, critical of theory that divorced itself from understanding actual, real-world processes of material provisioning. But most important, in Veblen’s view, economics was not up to the standards of evolutionary science because economics continued to implicitly embrace the concepts of natural price and natural law by focusing on economics as the study of economizing behavior and the adjustment of markets to equilibrium. In contrast, Veblen argued that the process of material provisioning entailed a constant process of adaptation to the physical and social environment through the adjustment of institutions or deeply ingrained social habits based on instinct. Veblen’s understanding of the term institution was broad enough to encompass any instituted process. Yet he drew a sharp distinction between institutions and technology. He was sharply critical of the former and strongly in favor of the latter.
When Veblen wrote about deep-seated and persistent social habits developing on the basis of genetically based instincts, he did in fact appear to mean something similar to contemporary theories of gene-culture evolution. Social habits are not consciously thought-through, purposive behaviors—they develop out of the complex “reflex arc” of enculturation based on genetically based propensities to act in the presence of environmental stimuli. Instincts are acquired through genetic evolution and social habits through enculturation. Both are inherited, vary in nature, and may therefore be selected for or against in the process of sociocultural evolution (Hodgson, 2004, Part III). However, Veblen also borrowed from Dewey a view of socialization in which individuals are active participants in socialization, a concept that was later more clearly articulated by Meade. In addition, Veblen also emphasized the ability of humans to conceptualize and engage in purposive behavior.
Veblen drew a sharp dichotomy between the instinct of workmanship and the instinct of predation. He associated the instinct of workmanship with a focus on adaptive, problem-solving, tinkering, and innovative behavior. In contrast, he associated predation with a focus on brute force, ceremonial displays of power, emulative behavior, conspicuous consumption, financial speculation, and the power of vested interests. Veblen argued that the instinct of workmanship arose in the primitive stage of human history (roughly corresponding to what contemporary anthropologists would term bands and tribes) and that the instinct of predation emerged during the stage of barbarism (roughly corresponding to the rise of chiefdoms). These instincts gave rise to deep-seated social habits. Both instincts continued to be present during the rise of civilization (agrarian states) and persisted in modern civilization (industrial states). But because modern civilization is based on the rise and extensive application of machine technology, further progress would require the triumph of the instinct of workmanship over the instinct of predation.
But in Veblen’s view, there was no reason to expect this would necessarily occur. Vested interests were often capable of instituting their power to reinforce the instinct of predation. Hence, institutions often served to encapsulate and reinforce the instinct of predation. The behaviors of predation were primarily exhibited by the new “leisure class” or, in other words, the robber barons of the late nineteenth century. In contrast, workmen and engineers often exhibited the instinct of workmanship. Consequently, Veblen tended to view institutions in general as change inhibiting and the instinct of workmanship as change promoting.
In later works, Veblen extended this kind of analysis to study other topics such as changes in firm organization and the business cycle. Veblen argued that as modern firms became larger and more monopolistic, a permanent leisure class arose, thus displacing technological thinking among this new class. In addition, increasing amounts of time and energy were channeled into financial speculation, leading to repeated financial crises. Emulative behavior in the form of conspicuous consumption and ceremonial displays of patriotism and militarism served to reinforce the instinct of predation. In his analysis of the rise of militarism in Prussia, Veblen noted the socially devastating impact of the triumph of the instinct of predation. Thus, Veblen tended to identify institutions with imbecilic behaviors that serve to block the triumph of technological innovations.
Veblen’s focus on the conflict between the instinct of workmanship and predatory and pecuniary instincts is often referred to as the instrumental-ceremonial dichotomy. Ayres (1938) in particular reinforced the tendency of the OIE to focus on the past binding and ceremonial aspects of institutions and on the scientific and progressive nature of instrumental reasoning. This dichotomy was, at one point in time, a core proposition of the OIE.
Most contemporary OIEs, however, recognize and accept that at least some institutions can promote and facilitate progressive change and that technology itself is an institution. This rethinking of the ceremonial-instrumental dichotomy is also reflected in the incorporation of Karl Polanyi’s (1944) dichotomy between habitation and improvement. Polanyi noted that the need for social pro-tection may actually serve a noninvidious purpose. Some improvements destroy livelihoods and reinforce invidious distinctions while others promote the life process. So the distinction might better be thought of in terms of “invidious versus noninvidious.”
One OIE who had a more positive understanding of the role of institutions is J. R. Commons (Commons, 1970; Wunder & Kemp, 2008). Commons in particular focused on the need for order in society and thus addressed the evolution of legal systems and the state. Commons’s theory is primarily microevolutionary insofar as he focuses on the evolution of legal arrangements and shifting power alignments in modern industrial states. Commons is not as critical of existing arrangements as Veblen. Institutions, including the state, in Commons’s view, are clearly both necessary and potentially beneficial. For example, with the rise of big business, labor conflict, and the problems inherent in the business cycle, there is a need for a strong state to manage this conflict. At the same time, Commons developed a theory of the business cycle that has strong elements in common with some of Keynes’s analysis.
The Veblenian strand as expressed by Commons is, by the standards of American politics, moderately left of center in that it expresses support for much of the regulatory framework and expanded role of government in managing the business cycle that came out of the New Deal and the publication of Keynes’s (1936) The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Not surprisingly, a number of OIE economists have begun to attempt to synthesize OIE and Keynes, relying to a large degree on the work of Hyman Minsky (1982). This project, often referred to as PKI (post-Keynesian institutionalism), is microevolution-ary in nature in that it focuses on the problems of financial instability created by financial innovation and deregulation. The goal of PKI is wisely managed capitalism (Whalen, 2008). PKI clearly has a focus on the possibility of designing effective institutions, which logically implies that at least some institutions can embody instrumental reasoning.
In contrast to the direction taken by some OIEs, Hodgson (2004) has argued that Veblen’s focus on technological thinking and the Commons-Ayres trend in OIE was a wrong turn for OIE. He has sought to revivify OIE by reinterpreting Veblenian economics as generalized Darwinism. Generalized Darwinism, according to Hodgson, generalizes the basic principles of Darwin’s biological theory of evolution (inheritance, variation, and selection) to sociocultural evolution. In Hodgson’s view, the mechanisms of inheritance, variation, and selection are not just analogies or metaphors to explain outcomes in social evolution—they are ontological principles that describe any entity that evolves. As noted above, because institutions and organizational routines are inherited through cultural learning and vary, they are subject to selection. Social evolution is therefore a special case of the more general case of evolution.
However, Hodgson (2004) also acknowledges that human agents are purposive and that culture is an emergent phenomenon. So Hodgson is not seeking to biologize social inequality or to reduce the social sciences to genetic principles such as inclusive fitness. Indeed, as Hodgson states, “more is needed” than just the principles of inheritance, variation, and natural selection. This would appear to be an understanding of how social institutions, in concert with instincts and human agency, generate outcomes in a complex, emergent process of social evolution. To this end, Hodgson has incorporated some elements of structure agency theory into his analysis.
Hodgson’s program could be taken as an injunction to OIEs to build models of change that incorporate both Darwinian principles as well as more complex concepts of structure and agency. Hodgson has used this model to explain how changes in firm organization can be selected for or against by changes in market structure. So there are strong parallels between the work of Hodgson and that of Nelson and Winter (1982), who could notably be placed in either the OIE or NIE camp. As noted in the preceding section, Hodgson’s view of evolutionary economics as “generalized Darwinism” is controversial, even among his fellow OIEs.
One competing strand of Veblenian economics is the radical strand as advocated by Bill Dugger (Dugger & Sherman, 2000). Dugger focuses on the role of technology, instrumental reasoning, and institutions as providing the capacity for improving the material condition of humans. The full application of instrumental reasoning, however, in Dugger’s view is blocked by the key institutions of capitalism. These institutions are reinforced by ceremonial myths. Dugger also puts more emphasis on the social and ideological implications of the respective traditions and has been sharply critical of the NIE. He has also notably been instrumental in promoting dialogue between Marxists and OIEs and has often copublished works on sociocultural evolution with Howard Sherman. Dugger also tends to emphasize the non-Darwinian nature of sociocultural evolution.
It can be fairly argued that Adam Smith was the first evolutionary economist, even though his contributions predate any significant consideration of biological evolution by naturalists. Adam Smith provides an account of how an increasingly complex society arises out of the natural propensity of humans to truck, barter, and exchange (Fusfeld, 1977; Smith, 1776/1937). Ironically, some of Smith’s concerns with specialization and division of labor, as well as the writings of another political economist, Thomas Malthus, influenced Darwin. Many Social Darwinists in the late nineteenth century drew on Darwinian reasoning to explain how competitive markets work and to justify social inequality. Some twentieth-century theorists such as Frederick Hayek and Larry Arnhart have tended to view the market as a natural outgrowth of human genetic endowments.
Taken as a whole, however, evolutionary explanations fell out of favor among economists in the twentieth century. In the late nineteenth century, the social sciences became increasingly fragmented, and the new field of economics increasingly lost its evolutionary focus. With the triumph of the standard competitive model in the mid-twentieth century, economics became narrowly focused on providing formal mathematical proofs of narrowly defined “how” questions. However, there are some signs that the standard competitive model is in the process of being displaced by game theory. There is also widespread recognition that it is necessary to supplement the standard competitive model with an evolutionary account. These developments have led to an increased acceptance of evolutionary explanations among mainstream economists and renewed attention to the importance of institutions in framing economic outcomes.
Some strands of the NIE, particularly the version espoused by Coase (1974) and Williamson (1985), view institutions primarily as providing “solutions” to the problems of asymmetric information and transactions costs. This strand of NIE does not significantly challenge the standard competitive model or its underlying behavioral assumptions. To the contrary, it is a complement to the standard competitive model. It is also to a large degree a micro-oriented theory of sociocultural evolution.
A more dynamic view of economic evolution is that of Joseph Schumpeter (1908, 1950). Schumpeter focused on the individual entrepreneur and his role in promoting technological innovation. This technological innovation disturbs the equilibrium and leads to gales of creative destruction. However, with the rise of the modern, bureaucratically organized firm, the role of the entrepreneur was lessened, leading to a static and moribund organization. Schumpeter thought that this would eventually lead to the destruction of capitalism, an outcome that, in contrast to Marx, Schumpeter viewed in a negative way. Schumpeter, however, drew a strong distinction between statics, exemplified by the Walrasian model of his day, and dynamics, exemplified by theories of economic evolution. Thus, “dynamics” was intended to complement “statics” (Andersen, 2008). Many contemporary mainstream models of economic growth, often referred to as new growth theory, explicitly incorporate Schumpeterian analysis.
Some of the richness of Schumpeter’s focus on technological innovation as gales of creative destruction has been recaptured by the economic historian Joel Mokyr (1990) in his masterful work on technological progress. Mokyr adapts Gould’s concept of “punctuated equilibrium” to the history of technology. He also draws a distinction between invention (the rise of new techniques and processes) and innovation (the spread of these new techniques). The Industrial Revolution, in Mokyr’s view, is ongoing but is nevertheless a clear instance of a dramatic change in technological and social organization. Similarly, the work of Nelson and Winter (1982), previously cited, which acknowledges the contributions of Veblen, can also be considered neo-Schumpeterian. There are, it should be noted, significant parallels between Marx, Schumpeter, and Veblen, as well as differences.
The most prominent and most successful NIE, of course, is Douglas North. North’s career has spanned several decades, during which his contributions to multiple fields in economics have been voluminous. Notably, North’s own views themselves have undergone significant evolution. North’s (1981) earlier work on economic evolution was an application of the work of Coase (1974) and Williamson (1985) to the problem of economic evolution and did not significantly challenge the standard competitive model. North viewed economic evolution as taking place due to changing resource constraints in response to the growth in population as rational agents calculated the marginal costs and marginal benefits of shifting from foraging to farming.
North’s later work (1990, 1991, 1994), however, has challenged many aspects of the standard competitive model. North has focused specifically on the role institutions play in cognitive framing of decision making. Notably, North has explicitly abandoned the theory of strong rational choice in favor of models of human behavior that focus on the limited ability of humans to obtain, process, and act on information. In most textbook models of market behavior, price is the primary means of providing information. But in North’s view of markets, information encompasses much more than price. In addition, norms, values, and ideology can blunt the ability of humans to obtain and interpret some information. North is not arguing that humans are “irrational” as his approach still logically implies some degree of calculation and conscious decision making based on self-interest. But he has abandoned the strong view of rationality, which implies humans are lightning rods of hedonic calculation. In that sense, his view of human behavior is much closer to that of the Austrians in focusing on the purposiveness of human behavior.
For the most part, North tends to see institutions as constraints on human action, though he acknowledges that institutions can provide incentives both in terms of the things we actually do, as well as the things that we do not do. Thus, institutions that reward innovative behavior, risk seeking, and trade will lead to efficient outcomes. Institutions that reward rent seeking and prohibit innovation and trade will lead to inefficient outcomes. Once an institutional structure is set, there is a strong degree of inertia that perpetuates the existing institutional structure. In other words, evolutionary paths, in North’s view, tend to be path dependent. Clearly, the kinds of institutions in North’s view that promote efficient outcomes are those that clearly define the rules of the game in favor of the operation of markets. This does not necessarily imply laissez-faire as the state may still be necessary to perform multiple functions. It does serve to distinguish between states, such as Great Britain in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries or South Korea in the past several decades, that were able to define an institutional framework that promoted innovation and growth as opposed to states such as Spain in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries or in the Congo (Zaire) today that destroy any incentive for innovation and economic growth.
This raises two very interesting questions. How does a particular type of path become established, and how does it change? North’s explanation is one that is rooted in a metaphor of variation and selection. Greater variation will allow for a higher probability that a particular path will be successful. Greater centralization will reduce variation and increase the chances that the state will adopt or promote institutions that blunt technological and social innovation. North explains the greater success of Europe versus the rest of the world as a result of the relative decentralization of Europe in the early modern period. Arbitrary authoritarian states that destroyed incentives for growth such as Spain existed. But Spain was unable to impose its will on Europe or on the emerging world market. Consequently, this enabled states such as England, where the power of the Crown became limited as Parliament enacted laws to protect commercial interests and innovation, to industrialize rapidly and emerge as world leaders. These contrasting paths were transferred to the New World. The United States inherited and successfully modified the institutional framework of Britain and therefore developed. Latin America inherited and failed to successfully modify the institutional frame-work of absolutist Spain and developed much more slowly.
Evolutionary economics clearly has a future. Economists in general are becoming more attuned to the importance of understanding how humans organize the economy through institutions and how institutions change over time. This entails extensive borrowing of concepts from evolutionary biology and a reconsideration of the underlying behavioral assumptions of mainstream economics. Understanding how institutions permit or inhibit changes in technology, as well as how changes in technology in turn require changes in institutions, is a concern of all three schools of evolutionary economics. As NIE economists push the boundaries of the mainstream, at least some have increasingly asked heterodox questions, and a few have been willing to acknowledge heterodox contributions. Some Marxist and OIE scholars have also begun to note that at least some versions of NIE, if not necessarily entirely new, are at least genuinely institutional and evolutionary. Any grand synthesis seems distant, but there is at least a basis for further argumentation and even dialogue.
Bibliography:
- Andersen, E. S. (2008). Appraising Schumpeter’s “essence” after 100 years: From Walrasian economics to evolutionary economics. In K. K. Puranam & R. Kumar Jain B. (Eds.), Evolutionary economics. Hyderabad, India: ICFAI University Press.
- Ayres, C. (1938). The problem of economic order. New York: Farrar and Rinehart.
- Coase, R. H. (1974). The new institutional economics. Journal of Institutional and Theoretical Economics, 140, 229-231.
- Commons, J. R. (1970). The economics ofcollective action. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
- Cypher, J., & Dietz, J. (2004). The process of economic development. London: Routledge.
- Dugger, B. (1988). Radical institutionalism: Basic concepts. Review of Radical Political Economics, 20, 1-20.
- Dugger, B. (1995). Veblenian institutionalism. Journal of Economic Issues, 29, 1013-1027.
- Dugger, B., & Sherman, H. (Eds.). (2000). Reclaiming evolution: A dialogue between Marxism and institutionalism on social change. London: Routledge.
- Dugger, B., & Sherman, H. (Eds.). (2003). Evolutionary theory in the social sciences: Vol. 1. Early foundations and later contributions. London: Routledge.
- Fusfeld, D. R. (1977). The development of economic institutions. Journal of Economic Issues, 11, 743-784.
- Harris, M. (1997). Culture, people, nature (7th ed.). New York: Addison Wesley Longman.
- Hodgson, G. M. (2004). The evolution of institutional economics: Agency, structure and Darwinism in American institutionalism. London: Routledge.
- Hodgson, G. M. (Ed.). (2007a). The evolution of economic institutions: A critical reader. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
- Hodgson, G. M. (2007b). Introduction. In G. M. Hodgson (Ed.), The evolution of economic institutions: A critical reader (pp. 1-15). Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
- Hodgson, G. M., & Knudsen, T. (2006). Why we need a generalized Darwinism and why a generalized Darwinism is not enough. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, 61, 1-19.
- Keynes, J. M. (1936). The general theory of employment, interest and money. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Mayr, E. (2001). What evolution is. New York: Basic Books.
- Mayr, E. (2004). What makes biology unique? Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Minsky, H. (1982). Can “it” happen again? Essays on instability and finance. Armonk, NY: M. E. Sharpe. Mokyr, J. (1990). The lever of riches: Technological creativity and economic progress. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Nelson, R. R., & Winter, S. G. (1982). An evolutionary theory of economic change. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- North, D. (1981). Structure and change in economic history. New York: W. W. Norton.
- North, D. (1990). Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- North, D. (1991). Institutions. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 5, 97-112.
- North, D. (1994). Economic performance through time. American Economic Review, 84, 359-367.
- Poirot, C. S. (2007). How can institutional economics be an evolutionary science? Journal of Economic Issues, 51, 155-179.
- Polanyi, K. (1944). The great transformation. New York: Farrar and Rinehart. Schumpeter, J. (1908). Das Wesen und der Haupterhault der theoretischen Nationolokonomie [The nature and essence of theoretical economics]. Leipzig, Germany: Dunckerund Humboldt.
- Schumpeter, J. (1950). Capitalism, socialism and democracy (3rd ed.). New York: Harper.
- Sherman, H. (1995). Reinventing Marxism. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Sherman, H. (2006). How society makes itself. New York: M. E. Sharpe.
- Smith, A. (1937). An enquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations. New York: Modern Library. (Original work published 1776)
- Veblen, T. (1898). Why is economics not an evolutionary science? Quarterly Journal of Economics, 12, 373-397.
- Veblen, T. (1899). The preconceptions of economic science. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 13, 121-150.
- Whalen, C. J. (2008). Toward wisely managed capitalism: Post-Keynesianism and the creative state. Forum for Social Economics, 37, 43-60.
- Williamson, O. E. (1985). The economic institutions of capitalism. New York: Free Press.
- Wolf, E. (1982). Europe and the people without history. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Wunder, T., & Kemp, T. (2008). Institutionalism and the state: Founding fathers re-examined. Forum for Social Economics, 37, 27-42.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Jump to navigation
Search form

- History of Women Faculty in Economics
- Chairs & Managers
- Research Centers
- Publications
- Year-end letter: Berkeley Economics
- Faculty Profiles
- In Memoriam
- Graduate Program
- Current Students
- Graduate Profiles
- 2023-2024 Job Market Candidates
- 2023-2024 Ph.D. Job Market Infopage
Undergraduate Program
- Course Enrollment
- Prospective Majors
- Current Majors
- Student Organizations
- Commencement
- Course List
- This Week's Seminars
- Next Week's Seminars
- Spring 2024 Economics Classes
- Summer 2024 Economics Classes
- Charter Hill Society for Economics
- Submit a note
- Alumni Notes

Economics Undergraduate Honors Theses
Examples of honors theses written by economics undergraduate students.
Posted with permission of the author. © 2019-2022 by the individual author. All rights reserved.
- "The Causal Effect of ACA Subsidies on Insurance Coverage Status Among California Adults" - William Vereyken
- "Economic Impacts of Immigration Detention Centers Built Between 1990-2016 on U.S. Commuting Zones" - Ekaterina Yudina
Spring/Summer 2022
- "The Impact of Indiv. Mandate on High-Income, Non-elderly Indiv. Health Insurance Coverage Rates and Racial/Ethnic Disparities" - YeJin Ahn
- "An Economic Analysis of the 1997 Amhara Land Redistribution in Ethiopia" - Ezana Anley
- "Affirmative Action's Effect on Educational and Wage Outcomes for Underrepresented Minorities" - Vishnu G. Arul
- "Are the Effects of Racism Really That Black and White? A Study on the Effect Racism Has on the Productivity of Black Footballers in the Premier League" - Advik Banerjee
- "An Empirical Analysis of Industrial Concentration and Prices: Can We Blame Inflation on Corporate Greed?" - Anton Bobrov
- "Tax Revenue Cyclicality and Income Inequality: Evidence from U.S. Counties From 1989 to 2019" - Yiyang Chen
- "The Impact of Economic Opportunities on African American Migration Patterns in Oakland" - Fernando Cheung
- "Impact of Tech Companies on Wages in the Local Economy" - Niki Collette
- "Warm Welcome: Evidence for Weather-based Projection Bias in College Choice" - Maria Cullen
- "Impact of the Belt and Road Initiative on Bilateral Trade with China" - Pedro de Marcos
- "Renaissance of the Black Homeowner: Impact Evaluation of Michigan's Renaissance Zones" - Rupsha Debnath
- "Lockdown Blues: The Effect of Social Norms on the Psychological Cost of Unemployment During the COVID-19 Pandemic" - Dylan Hallahan
- "How Education Affects Health Outcomes Across Genders" - Jessica Li
- "Is Increasing Diversity Inclusion Effective in Improving Companies' Performance in the Financial Services Industry?" - Miranda Li
- "The Future Financial Status of the Social Security Program" - Chloe Manouchehri
- "Does Recreational Marijuana Legalization Affect Hard-Drug Use? - Evidence from Cocaine Prevalence and Treatment Admissions" - Arthur Weiss
- "Relationship Between Economic Status and Money Spent on Private Education Leading to Economic Inequality in South Korea" - Jiho Lee
- "The Impact of Migrant Remittances on Rural Labor Supply: Evidence from Nepal" - Amanda Wong
- "Confirmation Bias: The Role of Messages and Messengers" - Hongyu (Randol) Yao
Spring 2021
- "Gender Equality and Economic Growth: Solving the Asian Puzzle" - Zoya Ali
- "Women in STEM: Moving Up or Falling Off the Academic Career Ladder?" - Sophia J. Bai
- "Time Dependence in Okun's Law at the State Level" - Sarah Baig
- "Labor Regulation and the Impact on Firm Behavior in India" - Vatsal Bajaj
- "Gender Representation in Academia: Evidence from the Italian Education System Reform" - Oyundari Batbayar
- "Money & Marriage on the Elementary Mind: A High-Level Analysis of Inequitable Child Development in LA County" - Matthew J. Chang
- "Unanticipated Unemployment Rate News on the Stock Market" - David Chi
- "Should Physicians Be More Collaborative? Determining the Relationship Between Patient Participation and Treatment Plan Confidence Across a Spectrum of Illness Severity in the State of California" - Saif Chowdhury
- "Modeling Optimal Investment and Greenhouse Gas Abatement in the Presence of Technology Spillovers" - Sabrina Chui
- "Understanding the Influence of Marginal Income Tax Rates on Retirement Investment Habits" - Daniel Cohen
- "Infrastructure in India's Internal War: A District-Level Analysis of the Naxalite-Maoist Conflict" - Krunal Desai
- "Do Eucalyptus Trees Increase Wildfires?" - Lila Englander
- "Understanding the Labor Outcomes of Hurricane Sandy" - Kevin Fang
- "Does TikTok Show Viewers the Content Relevant to them?" - Ekaterina Fedorova
- "The Impact of the Affordable Care Act Dependent Care Provision on Long-term Young Adult Labor Market Choices" - Anne Fogarty
- "Orchestra Sex Disparity: Experimental Evidence from Audience Members" - Richard Gong
- "The Big Three Medical Price Indexes: A Comparative Review and Analysis" - Robert Hovakimyan
- "Effect of Value-Added-Services on Customer Reviews in a Platform Marketplace" - Shankar Krishnan
- "COVID19 Recession: Gender Layoff Gap Explodes" - Ember Lin-Sperry
- "The Gender Wage Gap in China: Learning from Recent Longitudinal Data" - Donghe Lyu
- "Local Graduation Policies as a Tool for Increasing College Eligibility: Evidence from Los Angeles" - Dan L. Ma
- "Trust in Government and Lockdown Compliance in Sub-Saharan Africa" - Charles McMurry
- "I Do (or Don't): The Impact of Same-Sex Marriage Laws on International Tourism" - Oliver McNeil
- "International Shipping Consequences of a Navigable Arctic" - Jack Melin
- "Investigating Dollar Invoicing Trends Using United Kingdom Export Data" - Aneesh Nathani
- "Micro-Level Impact of Initial Public Offerings on Bay Area Housing Inflation" - Mina Nezam-Mafi
- "Explaining EU's Oil Dependency Through the Response of the Portuguese Sector Indexes to Brent Oil Prices Fluctuations" - Pedro S. Nunes
- "Dynamic Incentives and Effort Provision in Professional Tennis Tournaments" - Ruiwen Pan
- "Examining the Effects of Minimum Wage Laws on Part-Time Employment" - Odysseus Pyrinis
- "The Great Indian Identity Crisis? Exclusions & Intersectionality in the Indian Aadhaar System" - Aditi Ramakrishnan
- "The 'Clutch Gene' Myth: An Analysis of Late-Game Shooting Performance in the NBA" - Can Sarioz
- "Estimating the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Jobs Within the Healthcare Industry" - Sidharth Satya
- "Factors Influencing Telehealth Utilization: Evidence from California" - Emily Schultz
- "Cash and Conflict: Evidence from the Indian Banknote Demonetization" - Nachiket Shah
- "Determinants of the Number of Anti-Government Demonstrations: Evidence from OECD Countries" - Nina Singiri
- "Hygiene Heroes: A Process Evaluation of Promoting Hygiene Practices in Tamil Nadu Schools" - Malika Sugathapala
- "Exploring the Labour Patterns of Women and Mothers Through the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Impact of School Closures and a New Kind of Recession" - Renee Isabel Utter
- "How Have Socioeconomic Achievement Determinants Changed in the Past Decade for First-Generation Chinese Immigrants in the U.S." - Haolin Wang
- "The Impact of Quarantining on School Enrollment: Evidence from the Ebola Epidemic in Sierra Leone" - David Willigrod
- "Weeding out Needy Households and Welcoming the Better Off? Impacts of Transactional Barriers on SNAP Participation Rates" - Kevin Woo
- "Are Soccer Teams Being Inefficient? An Analysis of Sunk Cost Fallacy and Recency Bias Using Transfer Fee" - Junru Lyu
- "The Effects of Access to Family Planning Facilities on Female Labor Market Outcomes" - Marcus Sander
- "Macroeconomic Volatility at the Zero Lower Bound: Evidence from the OECD" - Anthony Swaminathan
- "How are Society's Conditions and Demographics Related to the Popularity of Chief Executive Carrie Lam and the Hong Kong Government" - Peter To
Spring/Summer 2020
- "Parental Involvement: The Differential Impacts of Consent and Notice Requirements for Minors' Abortions" - Angela Ames
- "Examining Local Price Levels and Income Distribution Over Time" - Josh Archer
- "Estimating the Effect of Grandparent Death on Fertility" - Jason Chen
- "Democracy in the Face of COVID-19: Have Less Democratic Countries Been More Effective at Preventing the Spread of This Pandemic ?" - Yi Chen
- "Understanding the Effects of Conditional Cash Transfers on Indigenous People in Mexico" - Arushi Desai
- "Microfinance and Payday Lending: Are they Solving a Problem or Creating One?" - Sophia Faulkner
- "The Risk-Taking Channel of Monetary Policy and Foreign Banks" - Noah Forougi
- "Ride of Die? Metropolitan Bikeshare Systems and Pollution" - Sean Furuta
- "Internet's Important Involvement in Information Industry Integration in Idaho, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana (and others): How the emerging internet affected the economic geography of the information industry" - Keming (Alex) Gao
- "The Relationship between Economic Crises and Long-Run Wealth Inequality" - Renuka Garg
- "Voter Bias in the Associated Press College Football Poll : Reconducting a 2009 study with new data in a $1 Billion-dollar industry that has seen significant changes in the past decade" - Brent Hensley
- "Monopsony Exploitation in Major League Baseball: Using Wins Above Replacement to Estimate Marginal Revenue Product" - Jacob C. Hyman
- "The Relationship Between Currency Substitution and Exchange Rate Volatility" - Jewon Ju
- "Efficiency, Bias, and Decisions: Observations from a Sports Betting Exchange" - Alexander Kan
- "The Effect of Medicaid Expansion on Substance Use Disorder Treatment Utilization: Evidence from the Affordable Care Act" - Christy Kang
- "Analyzing the Relationship between Personal Income Tax Progressivity and Income Inequality" - Gevorg Khandamiryan
- "The Effects of Occupancy Taxes on the Short-Term Rental Market: Evidence from Boston" - Alan Liang
- "Corporate Types and Bank Lending in Contractionary Era: Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies" - Zishen Liu
- "Financial Constraints on Student Learning: An Analysis of How Financial Stress Influences Cognitive Function in Children" - Simone Matecna
- "The Effect of Workplace Inspections on Employment and Sales - A Regression Discontinuity Analysis" - Jeseo Park
- "Lending Sociodynamics, Economic Instability, and the U.S. Farm Credit Crisis" - Erfan Samaei
- "The Effect of Intangible Assets on Value Added: Evidence from microdata across small and large firms in Europe" - Tamara Sequeira
- "Price Efficiency Differences Between Public and Private Utilities: An Empirical Analysis of US Electric Utilities" - Yechan Shin
- "Effect of Campus Shootings on Academic Achievement: Examination of 2014 Isla Vista Killings" - Min Joo (Julie) Song
- "First-Degree Price Discrimination: Evidence from Informal Markets in India" - Rishab Srivastava
- "Who Benefits From Gentrification? A Case Study of Oregon Public High Schools" - Namrata Subramanian
- "Estimating the Economic Impacts of Wealth Taxation in France" - Jeffrey Suzuki
- "Transit-Oriented Development or Transit-Oriented Displacement? Evaluating the Sorting Effect of Public Transportation in Los Angeles County" - Yeeling Tse
- "How State Abortion Policy Restrictiveness is Associated with Unintended Pregnancy Outcomes in the United States from 2014-2018" - Ruhee Wadhwania
- "Global Food Security and the El Niño-Southern Oscillation" - Aidan Wang
- "The Relationship Between Pharmaceutical R&D Spending and NME Development" - Taylor Wang
- "The Role of Individual Risk Attitude in Occupational Inheritance" - Yi Wang
- "Labor Market Segmentation: Evidence from U.S. Janitorial Jobs Advertised in English and Spanish" - Zijun Xu
- "Bias on the Brain: How Patient Gender Influences Use of Emergency Room Diagnostic Imaging" - Abigail Zhong
- "Age Effects, Irrationality and Excessive Risk-Taking in Supposedly Expert Agents" - William Aldred
- "Pricing Disparities for Minority Communities in Chicago: Rideshares and Taxis" - Matthew Cleveland
- "Where My Negros At? Evaluating the Effects of Banning Affirmative Action on Black College Enrollment" - Ellie Koepplinger
- "Race and Recession: How Minorities May Affect Downturns" - Alexander Szarka
- "Understanding the Effects of Canadian International Food Aid on Production and Trade" - Patrick D. Tagari
- "Urban Property Rights and Labor Supply in Peru: Heterogeneity Analysis by Gender and Educational Attainment" - Juan Sebastián Rozo Vásquez
- "Effect of High-Speed Rail on City Tourism Revenue in China: A Perspective on Spatial Connectivity" - Lingyun Xiao
Archives (2009-2019)
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Stockholm University, Department of Economics
Research papers in economics.
- Publisher Info
- Serial Info
Corrections
Contact information of stockholm university, department of economics, serial information, impact factors.
- Simple ( last 10 years )
- Recursive ( 10 )
- Discounted ( 10 )
- Recursive discounted ( 10 )
- H-Index ( 10 )
- Euclid ( 10 )
- Aggregate ( 10 )
- By citations
- By downloads (last 12 months)
More services and features
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
ECON 4370: Econometrics
- Data & Statistics
- Finding Articles
- Guides and Examples for How to Write an Econometric Analysis Paper
Guides and Examples of econometrics paper for undergrads
- Econometric Analysis Undergraduate Research Papers: Georgia Tech Library
- Format for an Econometrics Paper: Skidmore College
- Research Paper in Introductory Econometrics: Carleton College
- Writing in Economics: Duke University
- The Young Economist’s Short Guide to Writing Economic Research: Pomona College
- << Previous: Finding Articles
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 10:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.trinity.edu/4370econometrics

Economics Examples
Here are examples of undergraduate research experiences in the social sciences that you can use as models for developing your own. You can also consider perusing examples from a wider range of disciplines . Each example includes learning goals, a context for use, a description of project needs, tips related to structuring and supporting the exercise, and means of assessment. Rather than search these by economic subject matter, consider and compare them as examples of forms of undergraduate research--remember that the goal of undergraduate research is the creation of knowledge. A project in, say, urban economics, may have a structure that lends itself well to an udnergradaute reearch experiences on a topic in an altogether different field.
Remember that some of the pedagogical practices described in other parts of Starting Point can be developed as undergraduate research experiences as well. Others can be considered supporting structures for undergraduate research.
Want to contribute your own example? Follow these steps for submitting an activity to Starting Point .
Jump to: Class-based Activities * Class-based Research Projects * Capstone Experiences * Student/Faculty Collaborative Research
Class-based Activities
Naturalististic Observation
- Taking Risks While Driving: Are There Sex Differences? - This example, developed for psychology, describes a study of the hypothesis that there are sex differences in risk-taking. Design ideas from this naturalistic obervation approach to undergraduate research can serve as the inspiration for similar tests of other hypotheses in economics.
Quantitative Writing Assignments
Experiments
- Who Gets Help? - This example from psychology describes a field experiment of the hypothesis that able-bodied individuals receive less help than those perceived to have an injury. The field experiment approach is one that can be considered in economics as well.
Back to Top
Class-based Research Projects
Term papers and assignments.
- A Survey Paper: Topics in Economic Growth and Development - This assignment helps students develop deeper understanding of a topic that could potentially lead to the development of a thesis proposal. It does not require them to complete an entire research project, but only asks them to develop a feasible research question based on a review of the literature.
- Term Assignment: Family Economy of 19th Century Industrial Workers - This project, originally designed for a quantitative methods course for graduate students in history, consists of a set of assignments, distributed throughout the semester, that together move students through the steps of an empirical analysis. It is appropriate in courses where students will be able to use multiple regression by the end of the semester.
- A Research Paper in Experimental Economics - In teams, students complete original research in experimental economics.
- Replicating the Results of Famous Empirical Papers - This project provides an example of how students can engage in research by replicating and extending the methods and results of famous empirical papers (here, Solow (1957)).
- Independent Term Paper I: Independent Research Paper in Introductory Econometrics - This example describes one way to design an independent research experience for an introductory econometrics course. It is one that includes the preparation of a research proposal shared with others in the class as well as a paper presentation at the end of the semester.
- Independent Term Paper II: Research on Economics of Population - Here, students prepare an empirical term paper with the assistance of weekly computer labs and structured problem sets. This assignment is an example of one in which the dataset is chosen by the instructor, but the research question is developed and explored by the student.
- Using Economic Theory to Predict Outcomes - Students apply stylized facts from the literature to a model, here the Solow model.
Service Learning, Community-based Learning, and Campus-based Learning
- Using Census Data to Identify a Town's Housing Needs - In this service learning project for an elective course, students and faculty help a local non-profit identify area U.S. Census tracts most in need of its assistance in promoting decent and affordable homeownership. It serves as an example of an undergraduate research experience in which the research process is facilitated by a mixture of assignments, some requiring full-class collaboration and consensus, and others requiring small group and individual work.
- The Effects of Condemned/Restored Homes on Surrounding Property Values - Here, students help a non-profit and their college's city understand some of neighborhood effects of condemned/restored homes. It is another example of a project mixing class decision-making with small group and individual activities.
Independent Capstone and Honors Research Experiences
- Economics Senior Thesis I - This is an example of a 2-semester (total 4 credit hour) senior capstone experience in which the first semester culminates in a research proposal and independent research is conducted in the second semester. A grading rubric is included.
- Economics Senior Thesis II: The Effect of Race and Ethnicity on High School Graduation Rates in Florida - This is an example of an independent empirical research project. It includes tips on providing the mentoring, structure, and support necessary for independent work, and discusses the importance of developing a "research contract" with students. This project can be modified to be a group project.
- Economic Senior Thesis III: Independent Capstone Project Predictors of Student Success in College - This is another example of an independent empirical research project. Like the previous one, it is full of tips on providing the mentoring, structure, and support for independent work, and discusses the value of a "research contract." This project can be modified to be a group project.
- Economics Honors Thesis I: Three Semester Economics Honors Thesis - This is an example of a comprehensive program for scaffolding independent research. It is designed for honors students, but can be modified for any independent research project in economics. A grading rubric is included.
Student/Faculty Collaborative Research
Summer research experiences.
- Summer Undergraduate Research Experience I - This example provides a framework for conducting summer undergraduate research with a student, with the ultimate goal being a faculty-student co-authored publication in a peer reviewed journal. A sample summer research grant proposal is included, along with a link to one such co-authored article.
« Previous Page Next Page »
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Economics →

- 11 Apr 2024
- In Practice
Why Progress on Immigration Might Soften Labor Pains
Long-term labor shortages continue to stoke debates about immigration policy in the United States. We asked Harvard Business School faculty members to discuss what's at stake for companies facing talent needs, and the potential scenarios on the horizon.

- 01 Apr 2024
Navigating the Mood of Customers Weary of Price Hikes
Price increases might be tempering after historic surges, but companies continue to wrestle with pinched consumers. Alexander MacKay, Chiara Farronato, and Emily Williams make sense of the economic whiplash of inflation and offer insights for business leaders trying to find equilibrium.

- 29 Jan 2024
- Research & Ideas
Do Disasters Rally Support for Climate Action? It's Complicated.
Reactions to devastating wildfires in the Amazon show the contrasting realities for people living in areas vulnerable to climate change. Research by Paula Rettl illustrates the political ramifications that arise as people weigh the economic tradeoffs of natural disasters.

- 10 Jan 2024
Technology and COVID Upended Tipping Norms. Will Consumers Keep Paying?
When COVID pushed service-based businesses to the brink, tipping became a way for customers to show their appreciation. Now that the pandemic is over, new technologies have enabled companies to maintain and expand the use of digital payment nudges, says Jill Avery.

- 17 Aug 2023
‘Not a Bunch of Weirdos’: Why Mainstream Investors Buy Crypto
Bitcoin might seem like the preferred tender of conspiracy theorists and criminals, but everyday investors are increasingly embracing crypto. A study of 59 million consumers by Marco Di Maggio and colleagues paints a shockingly ordinary picture of today's cryptocurrency buyer. What do they stand to gain?

- 15 Aug 2023
Why Giving to Others Makes Us Happy
Giving to others is also good for the giver. A research paper by Ashley Whillans and colleagues identifies three circumstances in which spending money on other people can boost happiness.

- 13 Mar 2023
What Would It Take to Unlock Microfinance's Full Potential?
Microfinance has been seen as a vehicle for economic mobility in developing countries, but the results have been mixed. Research by Natalia Rigol and Ben Roth probes how different lending approaches might serve entrepreneurs better.

- 23 Jan 2023
After High-Profile Failures, Can Investors Still Trust Credit Ratings?
Rating agencies, such as Standard & Poor’s and Moody's, have been criticized for not warning investors of risks that led to major financial catastrophes. But an analysis of thousands of ratings by Anywhere Sikochi and colleagues suggests that agencies have learned from past mistakes.

- 29 Nov 2022
How Much More Would Holiday Shoppers Pay to Wear Something Rare?
Economic worries will make pricing strategy even more critical this holiday season. Research by Chiara Farronato reveals the value that hip consumers see in hard-to-find products. Are companies simply making too many goods?

- 21 Nov 2022
Buy Now, Pay Later: How Retail's Hot Feature Hurts Low-Income Shoppers
More consumers may opt to "buy now, pay later" this holiday season, but what happens if they can't make that last payment? Research by Marco Di Maggio and Emily Williams highlights the risks of these financing services, especially for lower-income shoppers.

- 01 Sep 2022
- What Do You Think?
Is It Time to Consider Lifting Tariffs on Chinese Imports?
Many of the tariffs levied by the Trump administration on Chinese goods remain in place. James Heskett weighs whether the US should prioritize renegotiating trade agreements with China, and what it would take to move on from the trade war. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 05 Jul 2022
Have We Seen the Peak of Just-in-Time Inventory Management?
Toyota and other companies have harnessed just-in-time inventory management to cut logistics costs and boost service. That is, until COVID-19 roiled global supply chains. Will we ever get back to the days of tighter inventory control? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 09 Mar 2022
War in Ukraine: Soaring Gas Prices and the Return of Stagflation?
With nothing left to lose, Russia's invasion of Ukraine will likely intensify, roiling energy markets further and raising questions about the future of globalization, says Rawi Abdelal. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 10 Feb 2022
Why Are Prices So High Right Now—and Will They Ever Return to Normal?
And when will sold-out products return to store shelves? The answers aren't so straightforward. Research by Alberto Cavallo probes the complex interplay of product shortages, prices, and inflation. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 11 Jan 2022
- Cold Call Podcast
Can Entrepreneurs and Governments Team Up to Solve Big Problems?
In 2017, Shield AI’s quadcopter, with no pilot and no flight plan, could clear a building and outpace human warfighters by almost five minutes. It was evidence that autonomous robots could help protect civilian and service member lives. But was it also evidence that Shield AI—a startup barely two years past founding—could ask their newest potential customer, the US government, for a large contract for a system of coordinated, exploring robots? Or would it scare them away? Harvard Business School professor Mitch Weiss and Brandon Tseng, Shield AI’s CGO and co-founder, discuss these and other challenges entrepreneurs face when working with the public sector, and how investing in new ideas can enable entrepreneurs and governments to join forces and solve big problems in the case, “Shield AI.” Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 06 May 2021
How Four Women Made Miami More Equitable for Startups
A case study by Rosabeth Moss Kanter examines what it takes to break gender barriers and build thriving businesses in an emerging startup hub. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 20 Apr 2021
- Working Paper Summaries
The Emergence of Mafia-like Business Systems in China
This study sheds light on the political pathology of fraudulent, illegal, and corrupt business practices. Features of the Chinese system—including regulatory gaps, a lack of formal means of property protection, and pervasive uncertainty—seem to facilitate the rise of mafia systems.
- 02 Feb 2021
Nonprofits in Good Times and Bad Times
Tax returns from millions of US nonprofits reveal that charities do not expand during bad times, when need is the greatest. Although they are able to smooth the swings of their activities more than for-profit organizations, nonprofits exhibit substantial sensitivity to economic cycles.

- 01 Feb 2021
Has the New Economy Finally Arrived?
Economists have long tied low unemployment to inflation. James Heskett considers whether the US economic policy of the past four years has shaken those assumptions. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 06 Jan 2021
Aggregate Advertising Expenditure in the US Economy: What's Up? Is It Real?
We analyze total United States advertising spending from 1960 to 2018. In nominal terms, the elasticity of annual advertising outlays with respect to gross domestic product appears to have increased substantially beginning in the late 1990s, roughly coinciding with the dramatic growth of internet-based advertising.
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Methods Used in Economic Research: An Empirical Study of Trends and Levels
The methods used in economic research are analyzed on a sample of all 3,415 regular research papers published in 10 general interest journals every 5th year from 1997 to 2017. The papers are classified into three main groups by method: theory, experiments, and empirics. The theory and empirics groups are almost equally large. Most empiric papers use the classical method, which derives an operational model from theory and runs regressions. The number of papers published increases by 3.3% p.a. Two trends are highly significant: The fraction of theoretical papers has fallen by 26 pp (percentage points), while the fraction of papers using the classical method has increased by 15 pp. Economic theory predicts that such papers exaggerate, and the papers that have been analyzed by meta-analysis confirm the prediction. It is discussed if other methods have smaller problems.
1 Introduction
This paper studies the pattern in the research methods in economics by a sample of 3,415 regular papers published in the years 1997, 2002, 2007, 2012, and 2017 in 10 journals. The analysis builds on the beliefs that truth exists, but it is difficult to find, and that all the methods listed in the next paragraph have problems as discussed in Sections 2 and 4. Hereby I do not imply that all – or even most – papers have these problems, but we rarely know how serious it is when we read a paper. A key aspect of the problem is that a “perfect” study is very demanding and requires far too much space to report, especially if the paper looks for usable results. Thus, each paper is just one look at an aspect of the problem analyzed. Only when many studies using different methods reach a joint finding, we can trust that it is true.
Section 2 discusses the classification of papers by method into three main categories: (M1) Theory , with three subgroups: (M1.1) economic theory, (M1.2) statistical methods, and (M1.3) surveys. (M2) Experiments , with two subgroups: (M2.1) lab experiments and (M2.2) natural experiments. (M3) Empirics , with three subgroups: (M3.1) descriptive, (M3.2) classical empirics, and (M3.3) newer empirics. More than 90% of the papers are easy to classify, but a stochastic element enters in the classification of the rest. Thus, the study has some – hopefully random – measurement errors.
Section 3 discusses the sample of journals chosen. The choice has been limited by the following main criteria: It should be good journals below the top ten A-journals, i.e., my article covers B-journals, which are the journals where most research economists publish. It should be general interest journals, and the journals should be so different that it is likely that patterns that generalize across these journals apply to more (most?) journals. The Appendix gives some crude counts of researchers, departments, and journals. It assesses that there are about 150 B-level journals, but less than half meet the criteria, so I have selected about 15% of the possible ones. This is the most problematic element in the study. If the reader accepts my choice, the paper tells an interesting story about economic research.
All B-level journals try hard to have a serious refereeing process. If our selection is representative, the 150 journals have increased the annual number of papers published from about 7,500 in 1997 to about 14,000 papers in 2017, giving about 200,000 papers for the period. Thus, the B-level dominates our science. Our sample is about 6% for the years covered, but less than 2% of all papers published in B-journals in the period. However, it is a larger fraction of the papers in general interest journals.
It is impossible for anyone to read more than a small fraction of this flood of papers. Consequently, researchers compete for space in journals and for attention from the readers, as measured in the form of citations. It should be uncontroversial that papers that hold a clear message are easier to publish and get more citations. Thus, an element of sales promotion may enter papers in the form of exaggeration , which is a joint problem for all eight methods. This is in accordance with economic theory that predicts that rational researchers report exaggerated results; see Paldam ( 2016 , 2018 ). For empirical papers, meta-methods exist to summarize the results from many papers, notably papers using regressions. Section 4.4 reports that meta-studies find that exaggeration is common.
The empirical literature surveying the use of research methods is quite small, as I have found two articles only: Hamermesh ( 2013 ) covers 748 articles in 6 years a decade apart studies in three A-journals using a slightly different classification of methods, [1] while my study covers B-journals. Angrist, Azoulay, Ellison, Hill, and Lu ( 2017 ) use a machine-learning classification of 134,000 papers in 80 journals to look at the three main methods. My study subdivide the three categories into eight. The machine-learning algorithm is only sketched, so the paper is difficult to replicate, but it is surely a major effort. A key result in both articles is the strong decrease of theory in economic publications. This finding is confirmed, and it is shown that the corresponding increase in empirical articles is concentrated on the classical method.
I have tried to explain what I have done, so that everything is easy to replicate, in full or for one journal or one year. The coding of each article is available at least for the next five years. I should add that I have been in economic research for half a century. Some of the assessments in the paper will reflect my observations/experience during this period (indicated as my assessments). This especially applies to the judgements expressed in Section 4.
2 The eight categories
Table 1 reports that the annual number of papers in the ten journals has increased 1.9 times, or by 3.3% per year. The Appendix gives the full counts per category, journal, and year. By looking at data over two decades, I study how economic research develops. The increase in the production of papers is caused by two factors: The increase in the number of researchers. The increasing importance of publications for the careers of researchers.
The 3,415 papers
2.1 (M1) Theory: subgroups (M1.1) to (M1.3)
Table 2 lists the groups and main numbers discussed in the rest of the paper. Section 2.1 discusses (M1) theory. Section 2.2 covers (M2) experimental methods, while Section 2.3 looks at (M3) empirical methods using statistical inference from data.
The 3,415 papers – fractions in percent
The change of the fractions from 1997 to 2017 in percentage points
Note: Section 3.4 tests if the pattern observed in Table 3 is statistically significant. The Appendix reports the full data.
2.1.1 (M1.1) Economic theory
Papers are where the main content is the development of a theoretical model. The ideal theory paper presents a (simple) new model that recasts the way we look at something important. Such papers are rare and obtain large numbers of citations. Most theoretical papers present variants of known models and obtain few citations.
In a few papers, the analysis is verbal, but more than 95% rely on mathematics, though the technical level differs. Theory papers may start by a descriptive introduction giving the stylized fact the model explains, but the bulk of the paper is the formal analysis, building a model and deriving proofs of some propositions from the model. It is often demonstrated how the model works by a set of simulations, including a calibration made to look realistic. However, the calibrations differ greatly by the efforts made to reach realism. Often, the simulations are in lieu of an analytical solution or just an illustration suggesting the magnitudes of the results reached.
Theoretical papers suffer from the problem known as T-hacking , [2] where the able author by a careful selection of assumptions can tailor the theory to give the results desired. Thus, the proofs made from the model may represent the ability and preferences of the researcher rather than the properties of the economy.
2.1.2 (M1.2) Statistical method
Papers reporting new estimators and tests are published in a handful of specialized journals in econometrics and mathematical statistics – such journals are not included. In our general interest journals, some papers compare estimators on actual data sets. If the demonstration of a methodological improvement is the main feature of the paper, it belongs to (M1.2), but if the economic interpretation is the main point of the paper, it belongs to (M3.2) or (M3.3). [3]
Some papers, including a special issue of Empirical Economics (vol. 53–1), deal with forecasting models. Such models normally have a weak relation to economic theory. They are sometimes justified precisely because of their eclectic nature. They are classified as either (M1.2) or (M3.1), depending upon the focus. It appears that different methods work better on different data sets, and perhaps a trade-off exists between the user-friendliness of the model and the improvement reached.
2.1.3 (M1.3) Surveys
When the literature in a certain field becomes substantial, it normally presents a motley picture with an amazing variation, especially when different schools exist in the field. Thus, a survey is needed, and our sample contains 68 survey articles. They are of two types, where the second type is still rare:
2.1.3.1 (M1.3.1) Assessed surveys
Here, the author reads the papers and assesses what the most reliable results are. Such assessments require judgement that is often quite difficult to distinguish from priors, even for the author of the survey.
2.1.3.2 (M1.3.2) Meta-studies
They are quantitative surveys of estimates of parameters claimed to be the same. Over the two decades from 1997 to 2017, about 500 meta-studies have been made in economics. Our sample includes five, which is 0.15%. [4] Meta-analysis has two levels: The basic level collects and codes the estimates and studies their distribution. This is a rather objective exercise where results seem to replicate rather well. [5] The second level analyzes the variation between the results. This is less objective. The papers analyzed by meta-studies are empirical studies using method (M3.2), though a few use estimates from (M3.1) and (M3.3).
2.2 (M2) Experimental methods: subgroups (M2.1) and (M2.2)
Experiments are of three distinct types, where the last two are rare, so they are lumped together. They are taking place in real life.
2.2.1 (M2.1) Lab experiments
The sample had 1.9% papers using this method in 1997, and it has expanded to 9.7% in 2017. It is a technique that is much easier to apply to micro- than to macroeconomics, so it has spread unequally in the 10 journals, and many experiments are reported in a couple of special journals that are not included in our sample.
Most of these experiments take place in a laboratory, where the subjects communicate with a computer, giving a controlled, but artificial, environment. [6] A number of subjects are told a (more or less abstract) story and paid to react in either of a number of possible ways. A great deal of ingenuity has gone into the construction of such experiments and in the methods used to analyze the results. Lab experiments do allow studies of behavior that are hard to analyze in any other way, and they frequently show sides of human behavior that are difficult to rationalize by economic theory. It appears that such demonstration is a strong argument for the publication of a study.
However, everything is artificial – even the payment. In some cases, the stories told are so elaborate and abstract that framing must be a substantial risk; [7] see Levitt and List ( 2007 ) for a lucid summary, and Bergh and Wichardt ( 2018 ) for a striking example. In addition, experiments cost money, which limits the number of subjects. It is also worth pointing to the difference between expressive and real behavior. It is typically much cheaper for the subject to “express” nice behavior in a lab than to be nice in the real world.
(M2.2) Event studies are studies of real world experiments. They are of two types:
(M2.2.1) Field experiments analyze cases where some people get a certain treatment and others do not. The “gold standard” for such experiments is double blind random sampling, where everything (but the result!) is preannounced; see Christensen and Miguel ( 2018 ). Experiments with humans require permission from the relevant authorities, and the experiment takes time too. In the process, things may happen that compromise the strict rules of the standard. [8] Controlled experiments are expensive, as they require a team of researchers. Our sample of papers contains no study that fulfills the gold standard requirements, but there are a few less stringent studies of real life experiments.
(M2.2.2) Natural experiments take advantage of a discontinuity in the environment, i.e., the period before and after an (unpredicted) change of a law, an earthquake, etc. Methods have been developed to find the effect of the discontinuity. Often, such studies look like (M3.2) classical studies with many controls that may or may not belong. Thus, the problems discussed under (M3.2) will also apply.
2.3 (M3) Empirical methods: subgroups (M3.1) to (M3.3)
The remaining methods are studies making inference from “real” data, which are data samples where the researcher chooses the sample, but has no control over the data generating process.
(M3.1) Descriptive studies are deductive. The researcher describes the data aiming at finding structures that tell a story, which can be interpreted. The findings may call for a formal test. If one clean test follows from the description, [9] the paper is classified under (M3.1). If a more elaborate regression analysis is used, it is classified as (M3.2). Descriptive studies often contain a great deal of theory.
Some descriptive studies present a new data set developed by the author to analyze a debated issue. In these cases, it is often possible to make a clean test, so to the extent that biases sneak in, they are hidden in the details of the assessments made when the data are compiled.
(M3.2) Classical empirics has three steps: It starts by a theory, which is developed into an operational model. Then it presents the data set, and finally it runs regressions.
The significance levels of the t -ratios on the coefficient estimated assume that the regression is the first meeting of the estimation model and the data. We all know that this is rarely the case; see also point (m1) in Section 4.4. In practice, the classical method is often just a presentation technique. The great virtue of the method is that it can be applied to real problems outside academia. The relevance comes with a price: The method is quite flexible as many choices have to be made, and they often give different results. Preferences and interests, as discussed in Sections 4.3 and 4.4 below, notably as point (m2), may affect these choices.
(M3.3) Newer empirics . Partly as a reaction to the problems of (M3.2), the last 3–4 decades have seen a whole set of newer empirical techniques. [10] They include different types of VARs, Bayesian techniques, causality/co-integration tests, Kalman Filters, hazard functions, etc. I have found 162 (or 4.7%) papers where these techniques are the main ones used. The fraction was highest in 1997. Since then it has varied, but with no trend.
I think that the main reason for the lack of success for the new empirics is that it is quite bulky to report a careful set of co-integration tests or VARs, and they often show results that are far from useful in the sense that they are unclear and difficult to interpret. With some introduction and discussion, there is not much space left in the article. Therefore, we are dealing with a cookbook that makes for rather dull dishes, which are difficult to sell in the market.
Note the contrast between (M3.2) and (M3.3): (M3.2) makes it possible to write papers that are too good, while (M3.3) often makes them too dull. This contributes to explain why (M3.2) is getting (even) more popular and the lack of success of (M3.3), but then, it is arguable that it is more dangerous to act on exaggerated results than on results that are weak.
3 The 10 journals
The 10 journals chosen are: (J1) Can [Canadian Journal of Economics], (J2) Emp [Empirical Economics], (J3) EER [European Economic Review], (J4) EJPE [European Journal of Political Economy], (J5) JEBO [Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization], (J6) Inter [Journal of International Economics], (J7) Macro [Journal of Macroeconomics], (J8) Kyklos, (J9) PuCh [Public Choice], and (J10) SJE [Scandinavian Journal of Economics].
Section 3.1 discusses the choice of journals, while Section 3.2 considers how journals deal with the pressure for publication. Section 3.3 shows the marked difference in publication profile of the journals, and Section 3.4 tests if the trends in methods are significant.
3.1 The selection of journals
They should be general interest journals – methodological journals are excluded. By general interest, I mean that they bring papers where an executive summary may interest policymakers and people in general. (ii) They should be journals in English (the Canadian Journal includes one paper in French), which are open to researchers from all countries, so that the majority of the authors are from outside the country of the journal. [11] (iii) They should be sufficiently different so that it is likely that patterns, which apply to these journals, tell a believable story about economic research. Note that (i) and (iii) require some compromises, as is evident in the choice of (J2), (J6), (J7), and (J8) ( Table 4 ).
The 10 journals covered
Note. Growth is the average annual growth from 1997 to 2017 in the number of papers published.
Methodological journals are excluded, as they are not interesting to outsiders. However, new methods are developed to be used in general interest journals. From studies of citations, we know that useful methodological papers are highly cited. If they remain unused, we presume that it is because they are useless, though, of course, there may be a long lag.
The choice of journals may contain some subjectivity, but I think that they are sufficiently diverse so that patterns that generalize across these journals will also generalize across a broader range of good journals.
The papers included are the regular research articles. Consequently, I exclude short notes to other papers and book reviews, [12] except for a few article-long discussions of controversial books.
3.2 Creating space in journals
As mentioned in the introduction, the annual production of research papers in economics has now reached about 1,000 papers in top journals, and about 14,000 papers in the group of good journals. [13] The production has grown with 3.3% per year, and thus it has doubled the last twenty years. The hard-working researcher will read less than 100 papers a year. I know of no signs that this number is increasing. Thus, the upward trend in publication must be due to the large increase in the importance of publications for the careers of researchers, which has greatly increased the production of papers. There has also been a large increase in the number of researches, but as citations are increasingly skewed toward the top journals (see Heckman & Moktan, 2018 ), it has not increased demand for papers correspondingly. The pressures from the supply side have caused journals to look for ways to create space.
Book reviews have dropped to less than 1/3. Perhaps, it also indicates that economists read fewer books than they used to. Journals have increasingly come to use smaller fonts and larger pages, allowing more words per page. The journals from North-Holland Elsevier have managed to cram almost two old pages into one new one. [14] This makes it easier to publish papers, while they become harder to read.
Many journals have changed their numbering system for the annual issues, making it less transparent how much they publish. Only three – Canadian Economic Journal, Kyklos, and Scandinavian Journal of Economics – have kept the schedule of publishing one volume of four issues per year. It gives about 40 papers per year. Public Choice has a (fairly) consistent system with four volumes of two double issues per year – this gives about 100 papers. The remaining journals have changed their numbering system and increased the number of papers published per year – often dramatically.
Thus, I assess the wave of publications is caused by the increased supply of papers and not to the demand for reading material. Consequently, the study confirms and updates the observation by Temple ( 1918 , p. 242): “… as the world gets older the more people are inclined to write but the less they are inclined to read.”
3.3 How different are the journals?
The appendix reports the counts for each year and journal of the research methods. From these counts, a set of χ 2 -scores is calculated for the three main groups of methods – they are reported in Table 5 . It gives the χ 2 -test comparing the profile of each journal to the one of the other nine journals taken to be the theoretical distribution.
The methodological profile of the journals – χ 2 -scores for main groups
Note: The χ 2 -scores are calculated relative to all other journals. The sign (+) or (−) indicates if the journal has too many or too few papers relatively in the category. The P -values for the χ 2 (3)-test always reject that the journal has the same methodological profile as the other nine journals.
The test rejects that the distribution is the same as the average for any of the journals. The closest to the average is the EJPE and Public Choice. The two most deviating scores are for the most micro-oriented journal JEBO, which brings many experimental papers, and of course, Empirical Economics, which brings many empirical papers.
3.4 Trends in the use of the methods
Table 3 already gave an impression of the main trends in the methods preferred by economists. I now test if these impressions are statistically significant. The tests have to be tailored to disregard three differences between the journals: their methodological profiles, the number of papers they publish, and the trend in the number. Table 6 reports a set of distribution free tests, which overcome these differences. The tests are done on the shares of each research method for each journal. As the data cover five years, it gives 10 pairs of years to compare. [15] The three trend-scores in the []-brackets count how often the shares go up, down, or stay the same in the 10 cases. This is the count done for a Kendall rank correlation comparing the five shares with a positive trend (such as 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5).
Trend-scores and tests for the eight subgroups of methods across the 10 journals
Note: The three trend-scores in each [ I 1 , I 2 , I 3 ]-bracket are a Kendall-count over all 10 combinations of years. I 1 counts how often the share goes up. I 2 counts when the share goes down, and I 3 counts the number of ties. Most ties occur when there are no observations either year. Thus, I 1 + I 2 + I 3 = 10. The tests are two-sided binominal tests disregarding the zeroes. The test results in bold are significant at the 5% level.
The first set of trend-scores for (M1.1) and (J1) is [1, 9, 0]. It means that 1 of the 10 share-pairs increases, while nine decrease and no ties are found. The two-sided binominal test is 2%, so it is unlikely to happen. Nine of the ten journals in the (M1.1)-column have a majority of falling shares. The important point is that the counts in one column can be added – as is done in the all-row; this gives a powerful trend test that disregards differences between journals and the number of papers published. ( Table A1 )
Four of the trend-tests are significant: The fall in theoretical papers and the rise in classical papers. There is also a rise in the share of stat method and event studies. It is surprising that there is no trend in the number of experimental studies, but see Table A2 (in Appendix).

4 An attempt to interpret the pattern found
The development in the methods pursued by researchers in economics is a reaction to the demand and supply forces on the market for economic papers. As already argued, it seems that a key factor is the increasing production of papers.
The shares add to 100, so the decline of one method means that the others rise. Section 4.1 looks at the biggest change – the reduction in theory papers. Section 4.2 discusses the rise in two new categories. Section 4.3 considers the large increase in the classical method, while Section 4.4 looks at what we know about that method from meta-analysis.
4.1 The decline of theory: economics suffers from theory fatigue [16]
The papers in economic theory have dropped from 59.5 to 33.6% – this is the largest change for any of the eight subgroups. [17] It is highly significant in the trend test. I attribute this drop to theory fatigue.
As mentioned in Section 2.1, the ideal theory paper presents a (simple) new model that recasts the way we look at something important. However, most theory papers are less exciting: They start from the standard model and argue that a well-known conclusion reached from the model hinges upon a debatable assumption – if it changes, so does the conclusion. Such papers are useful. From a literature on one main model, the profession learns its strengths and weaknesses. It appears that no generally accepted method exists to summarize this knowledge in a systematic way, though many thoughtful summaries have appeared.
I think that there is a deeper problem explaining theory fatigue. It is that many theoretical papers are quite unconvincing. Granted that the calculations are done right, believability hinges on the realism of the assumptions at the start and of the results presented at the end. In order for a model to convince, it should (at least) demonstrate the realism of either the assumptions or the outcome. [18] If both ends appear to hang in the air, it becomes a game giving little new knowledge about the world, however skillfully played.
The theory fatigue has caused a demand for simulations demonstrating that the models can mimic something in the world. Kydland and Prescott pioneered calibration methods (see their 1991 ). Calibrations may be carefully done, but it often appears like a numerical solution of a model that is too complex to allow an analytical solution.
4.2 Two examples of waves: one that is still rising and another that is fizzling out
When a new method of gaining insights in the economy first appears, it is surrounded by doubts, but it also promises a high marginal productivity of knowledge. Gradually the doubts subside, and many researchers enter the field. After some time this will cause the marginal productivity of the method to fall, and it becomes less interesting. The eight methods include two newer ones: Lab experiments and newer stats. [19]
It is not surprising that papers with lab experiments are increasing, though it did take a long time: The seminal paper presenting the technique was Smith ( 1962 ), but only a handful of papers are from the 1960s. Charles Plott organized the first experimental lab 10 years later – this created a new standard for experiments, but required an investment in a lab and some staff. Labs became more common in the 1990s as PCs got cheaper and software was developed to handle experiments, but only 1.9% of the papers in the 10 journals reported lab experiments in 1997. This has now increased to 9.7%, so the wave is still rising. The trend in experiments is concentrated in a few journals, so the trend test in Table 6 is insignificant, but it is significant in the Appendix Table A2 , where it is done on the sum of articles irrespective of the journal.
In addition to the rising share of lab experiment papers in some journals, the journal Experimental Economics was started in 1998, where it published 281 pages in three issues. In 2017, it had reached 1,006 pages in four issues, [20] which is an annual increase of 6.5%.
Compared with the success of experimental economics, the motley category of newer empirics has had a more modest success, as the fraction of papers in the 5 years are 5.8, 5.2, 3.5, 5.4, and 4.2, which has no trend. Newer stats also require investment, but mainly in human capital. [21] Some of the papers using the classical methodology contain a table with Dickey-Fuller tests or some eigenvalues of the data matrix, but they are normally peripheral to the analysis. A couple of papers use Kalman filters, and a dozen papers use Bayesian VARs. However, it is clear that the newer empirics have made little headway into our sample of general interest journals.
4.3 The steady rise of the classical method: flexibility rewarded
The typical classical paper provides estimates of a key effect that decision-makers outside academia want to know. This makes the paper policy relevant right from the start, and in many cases, it is possible to write a one page executive summary to the said decision-makers.
The three-step convention (see Section 2.3) is often followed rather loosely. The estimation model is nearly always much simpler than the theory. Thus, while the model can be derived from a theory, the reverse does not apply. Sometimes, the model seems to follow straight from common sense, and if the link from the theory to the model is thin, it begs the question: Is the theory really necessary? In such cases, it is hard to be convinced that the tests “confirm” the theory, but then, of course, tests only say that the data do not reject the theory.
The classical method is often only a presentation devise. Think of a researcher who has reached a nice publishable result through a long and tortuous path, including some failed attempts to find such results. It is not possible to describe that path within the severely limited space of an article. In addition, such a presentation would be rather dull to read, and none of us likes to talk about wasted efforts that in hindsight seem a bit silly. Here, the classical method becomes a convenient presentation device.
The biggest source of variation in the results is the choice of control/modifier variables. All datasets presumably contain some general and some special information, where the latter depends on the circumstances prevailing when the data were compiled. The regression should be controlled for these circumstances in order to reach the general result. Such ceteris paribus controls are not part of the theory, so many possible controls may be added. The ones chosen for publication often appear to be the ones delivering the “right” results by the priors of the researcher. The justification for their inclusion is often thin, and if two-stage regressions are used, the first stage instruments often have an even thinner justification.
Thus, the classical method is rather malleable to the preferences and interests of researchers and sponsors. This means that some papers using the classical technique are not what they pretend, as already pointed out by Leamer ( 1983 ), see also Paldam ( 2018 ) for new references and theory. The fact that data mining is tempting suggests that it is often possible to reach smashing results, making the paper nice to read. This may be precisely why it is cited.
Many papers using the classical method throw in some bits of exotic statistics technique to demonstrate the robustness of the result and the ability of the researcher. This presumably helps to generate credibility.
4.4 Knowledge about classical papers reached from meta-studies
Individual studies using the classical method often look better than they are, and thus they are more uncertain than they appear, but we may think of the value of convergence for large N s (number of observations) as the truth. The exaggeration is largest in the beginning of a new literature, but gradually it becomes smaller. Thus, the classical method does generate truth when the effect searched for has been studied from many sides. The word research does mean that the search has to be repeated! It is highly risky to trust a few papers only.
Meta-analysis has found other results such as: Results in top journals do not stand out. It is necessary to look at many journals, as many papers on the same effect are needed. Little of the large variation between results is due to the choice of estimators.
A similar development should occur also for experimental economics. Experiments fall in families: A large number cover prisoner’s dilemma games, but there are also many studies of dictator games, auction games, etc. Surveys summarizing what we have learned about these games seem highly needed. Assessed summaries of old experiments are common, notably in introductions to papers reporting new ones. It should be possible to extract the knowledge reached by sets of related lab experiments in a quantitative way, by some sort of meta-technique, but this has barely started. The first pioneering meta-studies of lab experiments do find the usual wide variation of results from seemingly closely related experiments. [25] A recent large-scale replicability study by Camerer et al. ( 2018 ) finds that published experiments in the high quality journal Nature and Science exaggerate by a factor two just like regression studies using the classical method.
5 Conclusion
The study presents evidence that over the last 20 years economic research has moved away from theory towards empirical work using the classical method.
From the eighties onward, there has been a steady stream of papers pointing out that the classical method suffers from excess flexibility. It does deliver relevant results, but they tend to be too good. [26] While, increasingly, we know the size of the problems of the classical method, systematic knowledge about the problems of the other methods is weaker. It is possible that the problems are smaller, but we do not know.
Therefore, it is clear that obtaining solid knowledge about the size of an important effect requires a great deal of papers analyzing many aspects of the effect and a careful quantitative survey. It is a well-known principle in the harder sciences that results need repeated independent replication to be truly trustworthy. In economics, this is only accepted in principle.
The classical method of empirical research is gradually winning, and this is a fine development: It does give answers to important policy questions. These answers are highly variable and often exaggerated, but through the efforts of many competing researchers, solid knowledge will gradually emerge.
Home page: http://www.martin.paldam.dk
Acknowledgments
The paper has been presented at the 2018 MAER-Net Colloquium in Melbourne, the Kiel Aarhus workshop in 2018, and at the European Public Choice 2019 Meeting in Jerusalem. I am grateful for all comments, especially from Chris Doucouliagos, Eelke de Jong, and Bob Reed. In addition, I thank the referees for constructive advice.
Conflict of interest: Author states no conflict of interest.
Appendix: Two tables and some assessments of the size of the profession
The text needs some numbers to assess the representativity of the results reached. These numbers just need to be orders of magnitude. I use the standard three-level classification in A, B, and C of researchers, departments, and journals. The connections between the three categories are dynamic and rely on complex sorting mechanisms. In an international setting, it matters that researchers have preferences for countries, notably their own. The relation between the three categories has a stochastic element.
The World of Learning organization reports on 36,000 universities, colleges, and other institutes of tertiary education and research. Many of these institutions are mainly engaged in undergraduate teaching, and some are quite modest. If half of these institutions have a program in economics, with a staff of at least five, the total stock of academic economists is 100,000, of which most are at the C-level.
The A-level of about 500 tenured researchers working at the top ten universities (mainly) publishes in the top 10 journals that bring less than 1,000 papers per year; [27] see Heckman and Moktan (2020). They (mainly) cite each other, but they greatly influence other researchers. [28] The B-level consists of about 15–20,000 researchers who work at 4–500 research universities, with graduate programs and ambitions to publish. They (mainly) publish in the next level of about 150 journals. [29] In addition, there are at least another 1,000 institutions that strive to move up in the hierarchy.
The counts for each of the 10 journals
Counts, shares, and changes for all ten journals for subgroups
Note: The trend-scores are calculated as in Table 6 . Compared to the results in Table 6 , the results are similar, but the power is less than before. However, note that the results in Column (M2.1) dealing with experiments are stronger in Table A2 . This has to do with the way missing observations are treated in the test.
Angrist, J. , Azoulay, P. , Ellison, G. , Hill, R. , & Lu, S. F. (2017). Economic research evolves: Fields and styles. American Economic Review (Papers & Proceedings), 107, 293–297. 10.1257/aer.p20171117 Search in Google Scholar
Bergh, A. , & Wichardt, P. C. (2018). Mine, ours or yours? Unintended framing effects in dictator games (INF Working Papers, No 1205). Research Institute of Industrial Econ, Stockholm. München: CESifo. 10.2139/ssrn.3208589 Search in Google Scholar
Brodeur, A. , Cook, N. , & Heyes, A. (2020). Methods matter: p-Hacking and publication bias in causal analysis in economics. American Economic Review, 110(11), 3634–3660. 10.1257/aer.20190687 Search in Google Scholar
Camerer, C. F. , Dreber, A. , Holzmaster, F. , Ho, T.-H. , Huber, J. , Johannesson, M. , … Wu, H. (27 August 2018). Nature Human Behaviour. https://www.nature.com/articles/M2.11562-018-0399-z Search in Google Scholar
Card, D. , & DellaVigna, A. (2013). Nine facts about top journals in economics. Journal of Economic Literature, 51, 144–161 10.3386/w18665 Search in Google Scholar
Christensen, G. , & Miguel, E. (2018). Transparency, reproducibility, and the credibility of economics research. Journal of Economic Literature, 56, 920–980 10.3386/w22989 Search in Google Scholar
Doucouliagos, H. , Paldam, M. , & Stanley, T. D. (2018). Skating on thin evidence: Implications for public policy. European Journal of Political Economy, 54, 16–25 10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2018.03.004 Search in Google Scholar
Engel, C. (2011). Dictator games: A meta study. Experimental Economics, 14, 583–610 10.1007/s10683-011-9283-7 Search in Google Scholar
Fiala, L. , & Suentes, S. (2017). Transparency and cooperation in repeated dilemma games: A meta study. Experimental Economics, 20, 755–771 10.1007/s10683-017-9517-4 Search in Google Scholar
Friedman, M. (1953). Essays in positive economics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. Search in Google Scholar
Hamermesh, D. (2013). Six decades of top economics publishing: Who and how? Journal of Economic Literature, 51, 162–172 10.3386/w18635 Search in Google Scholar
Heckman, J. J. , & Moktan, S. (2018). Publishing and promotion in economics: The tyranny of the top five. Journal of Economic Literature, 51, 419–470 10.3386/w25093 Search in Google Scholar
Ioannidis, J. P. A. , Stanley, T. D. , & Doucouliagos, H. (2017). The power of bias in economics research. Economic Journal, 127, F236–F265 10.1111/ecoj.12461 Search in Google Scholar
Johansen, S. , & Juselius, K. (1990). Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration – with application to the demand for money. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 52, 169–210 10.1111/j.1468-0084.1990.mp52002003.x Search in Google Scholar
Justman, M. (2018). Randomized controlled trials informing public policy: Lessons from the project STAR and class size reduction. European Journal of Political Economy, 54, 167–174 10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2018.04.005 Search in Google Scholar
Kydland, F. , & Prescott, E. C. (1991). The econometrics of the general equilibrium approach to business cycles. Scandinavian Journal of Economics, 93, 161–178 10.2307/3440324 Search in Google Scholar
Leamer, E. E. (1983). Let’s take the con out of econometrics. American Economic Review, 73, 31–43 Search in Google Scholar
Levitt, S. D. , & List, J. A. (2007). On the generalizability of lab behaviour to the field. Canadian Journal of Economics, 40, 347–370 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.00412.x Search in Google Scholar
Paldam, M. (April 14th 2015). Meta-analysis in a nutshell: Techniques and general findings. Economics. The Open-Access, Open-Assessment E-Journal, 9, 1–4 10.5018/economics-ejournal.ja.2015-11 Search in Google Scholar
Paldam, M. (2016). Simulating an empirical paper by the rational economist. Empirical Economics, 50, 1383–1407 10.1007/s00181-015-0971-6 Search in Google Scholar
Paldam, M. (2018). A model of the representative economist, as researcher and policy advisor. European Journal of Political Economy, 54, 6–15 10.1016/j.ejpoleco.2018.03.005 Search in Google Scholar
Smith, V. (1962). An experimental study of competitive market behavior. Journal of Political Economy, 70, 111–137 10.1017/CBO9780511528354.003 Search in Google Scholar
Stanley, T. D. , & Doucouliagos, H. (2012). Meta-regression analysis in economics and business. Abingdon: Routledge. 10.4324/9780203111710 Search in Google Scholar
Temple, C. L. (1918). Native races and their rulers; sketches and studies of official life and administrative problems in Nigeria. Cape Town: Argus Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Martin Paldam, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
- Supplementary material
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Journal and Issue
Articles in the same issue.
How to Write Economics Research Paper: Ultimate Guide

Everything You Need to Know about Economics Research Paper
Whether you are a student, a doctor, or a dancer, we have all engaged in economic activities. Bartering or exchanging money for food and services has been a part of human life for millennia, and we are proud heirs of the tradition.
As society grows, economic issues become bigger, and they call for research and study. We debate whether certain economic systems are the best fit, whether we should have a shared currency, how cryptocurrencies can revolutionize modern economics, etc. Such an inquiry aims to find solutions to the economic crises humanity faces. Poverty, famine, and homelessness are some of the major problems experienced by millions around the world.
Professional researchers and students write research papers for economics to share their analysis and findings about the major economic topics, trends, policies, or theories. Some academics prefer to work with primary data, such as surveys or experiments, while others analyze secondary data, such as historical records or existing statistics.
This article will explore the steps to writing an exceptional economics research paper. Below you will find an ultimate economics research paper outline and plenty of topics to explore in your study. Our thoughtful essay service team has also prepared a research paper economics sample to simplify your writing process.
Economics Research Paper Example
Just as we promised in the beginning, our writers took the extra mile and wrote an economics research paper example for you. Check out what makes an essay exceptional and how the paper ensures the readers stay engaged all the way through. Explore the structure, format, and language with which our writers achieve the main purpose of economics research papers.
How to Write an Economics Research Paper: Easy Steps
Our professional dissertation writers know the six holy elements of crafting a compelling economics paper, do you?
Let's put the writing aside for a second and take time to learn how to write an economics research paper. We have prepared an ultimate guide with easy steps for you to impress the reader. Remember, a strong foundation and compatible building blocks keep the skyscrapers standing tall.
Economics Research Paper Outline
First, you need to master the structure of an economics research paper. Often students skip this part leading to a mess of information that is not readable or understandable, and hours of work go in vain. To avoid such problems below, we discuss six holy elements of an excellent economics paper.
.webp)
Introduction - To impress the reader, start by offering a relevant and cutting-edge topic. There are endless amounts of research paper topics in economics; choose the one you feel passionate about and make it interesting for the audience.
Literature Review - Take your time to research information around the chosen topic. Sometimes our beliefs and prejudices blur our judgment, but we must remain unbiased. Secondary sources are there to guide you in the right direction.
Methods/data - describe the methodologies with which you plan to explore the topic and provide conclusions. Here you need to formulate your thesis and describe the data you gathered.
Results - Don't shy away from charts and graphs when presenting your study results. They are a great way to visualize large amounts of information.
Discussion - you can and need to challenge the methods you used for the research paper for economics. Credibility is as important as air when it comes to economic research.
Conclusion - Shortly restate your findings. Use clear and concise sentences. Emphasize why your study is important and what some questions are for future research.
Creating an Economics Research Paper Introduction
By an unwritten rule, an introduction is the first element of the economics research paper format. It aims to provide an overview of your study, explain its importance, explain why people should spend time thinking about the issue, and explain what value your research adds to the conversation.
Ensure that your introduction includes the research hypothesis and the objectives you aim to cover in your research paper economics study. You must also provide background information and a brief overview of your findings. Be sharp and stick to the point. The goal is to give the audience a clear understanding of what the paper is about and what problems it could solve.
Our team of custom research paper writing services can free you from worrying about writing a compelling introduction or providing a thorough statistical analysis. Let us know what is required, and we will return with an A+ essay.
Discussing the Existing Literature Review for Your Economics Research Paper
Everything in life has its context, and economic events are no exception to the rule. Before you start discussing your results, it is appropriate to provide a piece of background information, what we know from previous studies, and how that knowledge relates to your thesis statement.
According to the economics research paper outline, an introduction should be followed by a literature review section. Besides establishing the state of knowledge around the topic, the literature review can help you and the audience identify gaps, highlight the parts where further research is needed and put your research question in the larger scheme of things.
Literature reviews should include a critical analysis of relevant literature, reports, policy documents, etc. It should provide an evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of each source, showing gaps in information and proving the importance of your scholarly work.
We know this is a lot. If you prefer learning by example, our professional writers have crafted an economics research paper example for you. You can find it below.
Explaining the Methodology for Your Economics Research Paper
For your hard labor to be appreciated, your study must be credible. Readers must be able to see where you derived your conclusions from. This is why explaining the methodologies and techniques used is such an important section of the economics research paper outline.
Research methodologies for economics are various, and you need to be aware of which one could be the best fit for your study. Not every topic can be examined with identical tools; you need to find the one that helps you provide unbiased, trustworthy results.
Here you can find some research methodologies that could be useful for your research paper for economics:
.webp)
Econometric Analysis : Use of statistical techniques to analyze economic data and test hypotheses.
Experimental Design : Conducting controlled experiments to test economic theories
Case Study : An in-depth analysis of a particular case
Historical Analysis : Use of historical data and documents to analyze economic trends
Mathematical Modeling : Use of math models to analyze economic behavior and predict outcomes
Are You Struggling With Academic Writing?
Let our economics essay writing service remove all your academic stress and get you at the top of your class!
Presenting the Results in Your Economics Research Paper
Even though every section in the outline is equally important, the part where you present the results is the most interesting and anticipated. Here you need to get creative and focus on delivering the main points. Avoid passive voice; instead, take ownership of your work, rely on yourself, and use active voice. Use the following paragraphs to impress your audience.
The way you present the results depends on the type of data you collected and the analytical techniques you used. Some research papers need a numerical answer, and others focus on ideas.
Below you can see several techniques you can use in the results section of your economics research paper:
Tables : Effective way to present numerical data. Tables can be used to present descriptive statistics, regression results, and other types of quantitative data.
Figures : Effective way to demonstrate relationships between variables and trends over time.
Narrative Forms : Effective way to analyze non-numerical data such as surveys, interviews, or case studies.
Reviewing the Findings for Economics Research Paper
Our guide on how to write an economics research paper is nearing its end. Before concluding, you need to review the results of your study. This step might seem unnecessary, but it's vital for economics writing.
A critical analysis of one's writing can validate the research results even more. It is an excellent way to find out whether the original hypothesis is now supported by data. Reviewing can also help you identify the strength and weaknesses of the study, including the limitations in data or methods used.
It will also help you write a more comprehensive conclusion. Reviewing and interpreting the results will help you link the findings of your research paper for economics to the broader picture and also identify areas for further research.
Concluding Your Economics Research Paper
Like other disciplines, the economics research paper format also requires a comprehensive conclusion. Remember conclusion is not where you introduce new ideas; you simply have to restate your findings in a slightly different manner.
Explain the reasoning behind the results, and make it intuitive and engaging. Discuss what mechanisms could drive them and what obstacles you had to overcome during research. Let the reader know if there were any limitations to your approach.
Remember that other scholars will use your report as a secondary source just like you used other researchers' concepts and ideas, so make room and give enough time for future research and policy implications.
We understand that college is hard and following an economics research paper outline is not the easiest job. All you have to write to our college essay writing service and expert writers will come back with research writing that will put you at the top of your class.
30 Research Paper Topics in Economics
The tips above will help you write an excellent economics research paper. Now you have to select a cutting-edge topic. Below you will find the hottest economics topics for research paper:
- The benefits and drawbacks of a carbon tax
- The toll of immigration on economics
- The impact of AI on employment and wages
- Private insurance VS universal coverage
- The benefits and drawbacks of Free Trade Agreements
- The role of government in the Economy: Keynesian VS Neoliberal perspectives
- Should education be free?
- The impact of income inequality economic growth
- The cost of an aging population
- The role of big tech in economics
- The impact of covid-19 on the global economy
- Universal Basic Income: Does it fix poverty?
- The gig economy: a new threat to traditional employment
- Crime economics: the costs of punishment and rehabilitation
- Bioeconomy: Pros and cons of biodegradable plastics
- Small governments with big impact: Benefits of minimalist economic policy
- Silicon Valley and the Tech industry: Is it innovation or monopoly?
- Does Apple Inc. hold a monopoly in the tech business?
- The role of the economic model in policy discussion and decision-making
- The contribution of abstract economic models to real-world analysis and policy-making
- Describing the quality of life: Measuring economic and social well-being beyond GDP
- The role of abstract economic concepts in shaping policy and practice
- Subjectivity in economics paper: Can there be a single 'correct' answer to economic questions?
- The future of economics papers: embracing interdisciplinary approaches and open access publishing
- Social entrepreneurship: Innovations in Economic and Social Development
- Social welfare policies and economic outcomes
- The impact of tech companies on small business growth
- The economics of consumer behavior: links between consumer decisions and economics outcomes
- The economics of customer satisfaction: the drivers of loyalty and retention
- The economics of social influence: Social networks and decision-making
A Brief Afterword
Writing economics research papers is a lot of work. You must plan, research and analyze excessively to achieve the best quality. You'll need to find an attention-grabbing research question, come up with a methodology, and turn complex ideas into one paragraph.
But writing research could be much easier. All you have to say is, ' write paper for me ,' and our team of professionals will take care of the rest. You can relax while we select the best research topic and turn dense ideas into short sentences, honoring the process and structure of economic research. A+ is just a click away!
Is College Stressing You Out?
Our finance essay writing service can help you achieve your academic goals

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
%20(3).webp)
The Young Economist’s Short Guide to Writing Economic Research
Attributes of writing economics.
- The discourse is often mathematical, with lots of formulas, lemmas, and proofs.
- Writing styles vary widely. Some authors are very dry and technical while a few are quite eloquent.
Economics writing is different from many other types of writing. It is essentially technical, and the primary goal is to achieve clarity. A clear presentation will allow the strength of your underlying analysis and the quality of your research to shine through.
Unlike prose writing in other disciplines, economics research takes time. Successful papers are not cranked out the night before a due date.
General Guidelines for Quality Research
Getting started.
The hardest part of any writing assignment is starting. Economics research usually begins with a strong understanding of literature, and papers require a section that summarizes and applies previous literature to what the paper at hand. This is the best way to start.
Your writing will demonstrate that you understand the findings that relate to the topic.
Economists use the first few paragraphs to set up research questions and the model and data they use to think about it. Sure, it can be dry, but this format ensures the write and reader have strong grasp on the subject and structure of the work that follows.
Clear and Concise Work
Clarity is hard to achieve, but revising and reworking a paper ensures it is easy to read
- Organize your ideas into an argument with the help of an outline.
- Define the important terms you will use
- State your hypothesis and proceed deductively to reach your conclusions
- Avoid excess verbiage
- Edit yourself, remove what is not needed, and keep revising until you get down to a simple, efficient way of communicating
- Use the active voice
- Put statements in positive form
- Omit needless words (concise writing is clear writing)
- In summaries, generally stick to one tense
Time Management
Poor time management can wreck the best-planned papers. Deadlines are key to successful research papers.
- Start the project by finding your topic
- Begin your research
- Start and outline
- Write a draft
- Revise and polish
The Language of Economic Analysis
Economic theory has become very mathematical. Most PhD students are mathematicians, not simply economics majors. This means most quality economic research requires a strong use of mathematical language. Economic analysis is characterized by the use of models, simplified representations of how economic phenomena work. A model’s predictions about the future or the past are essentially empirical hypotheses. Since economics is not easily tested in controlled experiments, research requires data from the real world (census reports, balance sheets), and statistical methods (regressions and econometrics) to test the predictive power of models and hypotheses based on those models.
The Writing Process
Finding a topic.
There are a million ways to find a topic. It may be that you are writing for a specific subfield of economics, so topics are limited and thus easier to pick. However, must research starts organically, from passive reading or striking news articles. Make sure to find something that interests you. Be sure to find a niche and make a contribution to the subfield.
You will also need a project that can be done within the parameters of the assignment (length, due date, access to research materials). A profoundly interesting topic may not be manageable given the time and other constraints you face. The key is to just be practical.
Be sure to start your research as soon as possible. Your topic will evolve along the way, and the question you begin with may become less interesting as new information draws you in other directions. It is perfectly fine to shape your topic based on available data, but don’t get caught up in endlessly revising topics.
Finding and Using Sources
There are two types of economic sources: empirical data (information that is or can be easily translated into numerical form), and academic literature (books and articles that help you organize your ideas).
Economic data is compiled into a number of useful secondary sources:
- Economic Report of the President
- Statistical Abstract of the United States
- National Longitudinal Survey
- Census data
- Academic journals
The Outline
A good outline acts as an agenda for the things you want to accomplish:
- Introduction: Pose an interesting question or problem
- Literature Review: Survey the literature on your topic
- Methods/Data: Formulate your hypothesis and describe your data
- Results: Present your results with the help of graphs and charts
- Discussion: Critique your method and/or discuss any policy implications
- Conclusions: Summarize what you have done; pose questions for further research
Writing a Literature Review
The literature review demonstrates your familiarity with scholarly work on your topic and lays the foundations for your paper. The particular issues you intent to raise, the terms you will employ, and the approach you will take should be defined with reference to previous scholarly works.
Presenting a Hypothesis
Formulate a question, problem or conjecture, and describe the approach you will take to answer, solve, or test it. In presenting your hypothesis, you need to discuss the data set you are using and the type of regression you will run. You should say where you found the data, and use a table, graph, or simple statistics to summarize them. In term papers, it may not be possible to reach conclusive results. Don’t be afraid to state this clearly and accurately. It is okay to have an inconclusive paper, but it is not okay to make overly broad and unsupported statements.
Presenting Results
There are essentially two decisions to make: (1) How many empirical results should be presented, and (2) How should these results be described in the text?
- Focus only on what is important and be as clear as possible. Both smart and dumb readers will appreciate you pointing things out directly and clearly.
- Less is usually more: Reporting a small group of relevant results is better than covering every possible statistical analysis that could be made on the data.
- Clearly and precisely describe your tables, graphs, and figures in the text of your results section. The first and last sentence in a paragraph describing a result should be “big picture” statements, describing how the results in the table, graph or figure fit into the overall theme of the paper.
Discussing Results
The key to discussing results is to stay clear of making value judgments, and rely instead on economic facts and analyses. It is not the job of an economist to draw policy conclusions, even if the research supports strong evidence in a particular direction.
Referencing Sources
As with any research paper, source referencing depends on the will of a professor a discourse community. However, economists generally use soft references in the literature review section and then cite sources in conventional formats at the end of papers.
This guide was made possible by the excellent work of Robert Neugeboren and Mireille Jacobson of Harvard University and Paul Dudenhefer of Duke University.
Mailing Address
Pomona College 333 N. College Way Claremont , CA 91711
Get in touch
Give back to pomona.
Part of The Claremont Colleges
Research Paper
Category: economics research paper examples.

Economics is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers.
Readers interested in learning about economic analysis of a topic or issue as well as students developing research papers will find sample research papers on various economic topics. And economists seeking to learn about extensions of analysis into new areas or about new approaches will benefit from research papers on cutting-edge topics. The collection of economics research paper examples below provide a good place to begin researching or studying a topic in economics.

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Examples
Research Paper Examples on Economics
A solution to inequality and poverty: effects of innovation and government policy on global economy.
Gunter & Van der Hoeven (2004) state that there is a general agreement that in the case of economic growth, the advantages thereof mainly depend on the sharing of the income generated by it. Furthermore, they say there is “some general agreement today that growth and equity need not be contradictory goals. Most economists also agree that there is no...
Words: 1955 | Pages: 9
How Law of Supply and Law of Demand Correspond With Eachother?
Introduction Supply and demand are the basic and most essential concepts of economics. They provide the stamina of a market in an economy. Demand is a term used to describe the amount of commodity or service needed by buyers in the market. It refers to the quantity of a commodity or service individuals are willing and able to pay for...
Words: 1630 | Pages: 7
Problems that Nurses Face in Their Work Place
A nurse is a professional that deals with managing of patient’s health care. It requires sacrifice and dedication to ensure the patients get quality healthcare. However, it is a profession faced by many challenges in the course of duty (Corsaro, 2011). One ought to deal with these challenges in a professional way to ensure efficient health care is always provided...
Words: 1331 | Pages: 6
Counterfeit Products in the Apparel and Textile Industry
Introduction Counterfeiting is creating or designing an exact imitation of something valuable with an anticipated outcome that is intended to defraud or deceive. In other words, counterfeiting is finally a violation of the legal rights of a proprietor of intellectual belonging. It includes any goods not leaving out the packaging, which conveys unauthorized trademark alike to the brand with valid...
Words: 1596 | Pages: 7
Campaign Financing
Campaign financing refers to raising of funds with a goal of promoting political parties, candidates or policies during elections, party organization, party actions, ingenuities and reforms. Though most campaign expenditure is privately funded, public financing is accessible for succeeding presidential candidates of the United States in the general elections and primaries. Political campaigns have numerous spending responsibilities such as political...
Words: 3348 | Pages: 14
Effects of E-Commerce to the Motor Vehicle Industry in Japan
Research proposal on information technology Introduction The field of technology has witnessed enormous changes over the past decades. Notably, technology has been growing at a high speed with its impacts been evident in the various sectors of the economy. Major sectors that have greatly been impacted by technology include; education and research, trade and industry and communication. Most importantly, great...
Words: 413 | Pages: 2
A Study of the Natural Gas Industry’s Marketization Process – Models, Trajectory and Policy Instruments
Abstract Since the mid-1980s, the structure of the natural gas industry has evolved dramatically. About a hundred years ago, the structure of the natural gas industry was less complex with few options for natural gas delivery. Natural gas has become increasingly fashionable in recent years. This paper analyzes the policy instruments in four typical countries in order to identify similar...
Words: 3404 | Pages: 15
Analysis of the Democratic and Participatory Budgeting
Section 1.0 Introduction Since the Congo picked up freedom in 1960, progressions have been associated with being fixed to ethnic conflicts, uniquely the political and social transformations. In 1959 when the nation was still under the control of the frontier force, rough conflicts contradicted the inhabitants of the Pool locale to those in the northern areas (Ulimwengu 2009). This contention...
Words: 2336 | Pages: 10
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
Are Markups Driving the Ups and Downs of Inflation?

Download PDF (158 KB)
FRBSF Economic Letter 2024-12 | May 13, 2024
How much impact have price markups for goods and services had on the recent surge and the subsequent decline of inflation? Since 2021, markups have risen substantially in a few industries such as motor vehicles and petroleum. However, aggregate markups—which are more relevant for overall inflation—have generally remained flat, in line with previous economic recoveries over the past three decades. These patterns suggest that markup fluctuations have not been a main driver of the ups and downs of inflation during the post-pandemic recovery.
In the recovery from the pandemic, U.S. inflation surged to a peak of over 7% in June 2022 and has since declined to 2.7% in March 2024, as measured by the 12-month change in the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index. What factors have been driving the ups and downs of inflation? Production costs are traditionally considered a main contributor, particularly costs stemming from fluctuations in demand for and supply of goods and services. As demand for their products rises, companies need to hire more workers and buy more intermediate goods, pushing up production costs. Supply chain disruptions can also push up the cost of production. Firms may pass on all or part of the cost increases to consumers by raising prices. Thus, an important theoretical linkage runs from cost increases to inflation. Likewise, decreases in costs should lead to disinflation.
Labor costs are an important factor of production costs and are often useful for gauging inflationary pressures. However, during the post-pandemic surge in inflation, nominal wages rose more slowly than prices, such that real labor costs were falling until early 2023. By contrast, disruptions to global supply chains pushed up intermediate goods costs, contributing to the surge in inflation (see, for example, Liu and Nguyen 2023). However, supply chains have more direct impacts on goods inflation than on services inflation, which also rose substantially.
In this Economic Letter , we consider another factor that might drive inflation fluctuations: changes in firms’ pricing power and markups. An increase in pricing power would be reflected in price-cost markups, leading to higher inflation; likewise, a decline in pricing power and markups could alleviate inflation pressures. We use industry-level measures of markups to trace their evolving impact on inflation during the current expansion. We find that markups rose substantially in some sectors, such as the motor vehicles industry. However, the aggregate markup across all sectors of the economy, which is more relevant for inflation, has stayed essentially flat during the post-pandemic recovery. This is broadly in line with patterns during previous business cycle recoveries. Overall, our analysis suggests that fluctuations in markups were not a main driver of the post-pandemic surge in inflation, nor of the recent disinflation that started in mid-2022.
Potential drivers of inflation: Production costs and markups
To support households and businesses during the pandemic, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate target to essentially zero, and the federal government provided large fiscal transfers and increased unemployment benefits. These policies boosted demand for goods and services, especially as the economy recovered from the depth of the pandemic.
The increase in overall demand, combined with supply shortages, boosted the costs of production, contributing to the surge in inflation during the post-pandemic recovery. Although labor costs account for a large part of firms’ total production costs, real labor costs were falling between early 2021 and mid-2022 such that the increases in prices outpaced those in nominal wages. This makes it unlikely that labor costs were driving the surge in inflation.
Instead, we focus on another potential alternative driver of inflation that resulted from firms’ ability to adjust prices, known as pricing power. As demand for goods surged early in the post-pandemic recovery, companies may have had a greater ability to raise their prices above their production costs, a gap known as markups. Following a sharp drop in spending at the height of the pandemic, people may have become eager to resume normal spending patterns and hence more tolerant to price increases than in the past. In fact, growth of nonfinancial corporate profits accelerated in the early part of the recovery (see Figure 1), suggesting that companies had increased pricing power. Some studies have pointed to the strong growth in nonfinancial corporate profits in 2021 as evidence that increased markups have contributed to inflation (see, for example, Weber and Wasmer 2023). However, the figure also shows that growth in corporate profits is typically volatile. Corporate profits tend to rise in the early stages of economic recoveries. Data for the current recovery show that the increase in corporate profits is not particularly pronounced compared with previous recoveries.
Figure 1 Profit growth for nonfinancial businesses
More importantly, corporate profits are an imperfect measure of a firm’s pricing power because several other factors can drive changes in profitability. For instance, much of the recent rise in corporate profits can be attributed to lower business taxes and higher subsidies from pandemic-related government support, as well as lower net interest payments due to monetary policy accommodation (Pallazzo 2023).
Instead of relying on profits as a measure of pricing power, we construct direct measures of markups based on standard economic models. Theory suggests that companies set prices as a markup over variable production costs, and that markup can be inferred from the share of a firm’s revenue spent on a given variable production factor, such as labor or intermediate goods. Over the period of data we use, we assume that the specific proportion of a company’s production costs going toward inputs does not change. If the share of a firm’s revenue used for inputs falls, it would imply a rise in the firm’s price-cost margin or markup. In our main analysis, we use industry-level data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) to compute markups based on the share of revenue spent on intermediate inputs. Our results are similar if we instead use the share of revenue going toward labor costs.
We compare the evolution of markups to that of prices, as measured by the PCE price index, since the recovery from the pandemic. In constructing this price index, the BEA takes into account changes in product characteristics (for instance, size) that could otherwise bias the inflation measure by comparing the prices of inherently different products over time. Similarly, based upon standard economic theory, our markup measure implicitly captures changes in those characteristics (see, for example, Aghion et al. 2023).
The post-pandemic evolution of markups
We examine the evolution of markups in each industry since the third quarter of 2020, the start of the post-pandemic recovery. Figure 2 shows that some sectors, such as the motor vehicles and petroleum industries, experienced large cumulative increases in markups during the recovery. Markups also rose substantially in general merchandise, such as department stores, and for other services, such as repair and maintenance, personal care, and laundry services. Since the start of the expansion, markups in those industries rose by over 10%—comparable in size to the cumulative increases over the same period in the core PCE price index, which excludes volatile food and energy components. However, the surge in inflation through June 2022 was broad based, with prices also rising substantially outside of these sectors. Thus, understanding the importance of markups for driving inflation requires a macroeconomic perspective that examines the evolution of aggregate markups across all sectors of the economy.
Figure 2 Cumulative changes in markups for salient industries
The role of aggregate markups in the economy
To assess how much markup changes contribute to movements in inflation more broadly, we use our industry-level measurements to calculate an aggregate markup at the macroeconomic level. We aggregate the cumulative changes in industry markups, applying two different weighting methods, as displayed in Figure 3. In the first method (green line), we match our industry categories to the spending categories in the core PCE price index for ease of comparison; we then use the PCE weights for each category to compute the aggregate markup. Alternatively, we use each industry’s cost weights to compute the aggregate markup (blue line). Regardless of the weighting method, Figure 3 shows that aggregate markups have stayed essentially flat since the start of the recovery, while the core PCE price index (gray line) rose by more than 10%. Thus, changes in markups are not likely to be the main driver of inflation during the recovery, which aligns with results from Glover, Mustre-del-Río, and von Ende-Becker (2023) and Hornstein (2023) using different methodologies or data. Markups also have not played much of a role in the slowing of inflation since the summer of 2022.
Figure 3 Cumulative changes in aggregate markups and prices
Moreover, the path of aggregate markups over the past three years is not unusual compared with previous recoveries. Figure 4 shows the cumulative changes in aggregate markups since the start of the current recovery (dark blue line), alongside aggregate markups following the 1991 (green line), 2001 (yellow line), and 2008 (light blue line) recessions. Aggregate markups have stayed roughly constant throughout all four recoveries.
Figure 4 Cumulative changes of aggregate markups in recoveries
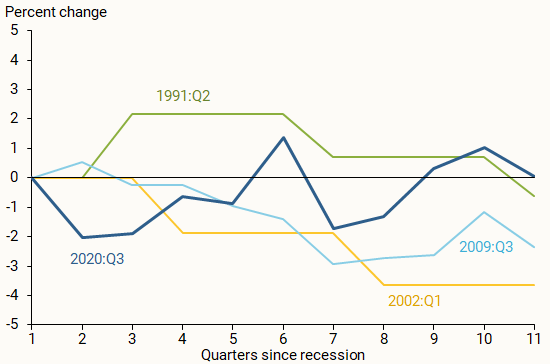
Firms’ pricing power may change over time, resulting in markup fluctuations. In this Letter , we examine whether increases in markups played an important role during the inflation surge between early 2021 and mid-2022 and if declines in markups have contributed to disinflation since then. Using industry-level data, we show that markups did rise substantially in a few important sectors, such as motor vehicles and petroleum products. However, aggregate markups—the more relevant measure for overall inflation—have stayed essentially flat since the start of the recovery. As such, rising markups have not been a main driver of the recent surge and subsequent decline in inflation during the current recovery.
Aghion, Philippe, Antonin Bergeaud, Timo Boppart, Peter J. Klenow, and Huiyu Li. 2023. “A Theory of Falling Growth and Rising Rents.” Review of Economic Studies 90(6), pp.2,675-2,702.
Glover, Andrew, José Mustre-del-Río, and Alice von Ende-Becker. 2023. “ How Much Have Record Corporate Profits Contributed to Recent Inflation? ” FRB Kansas City Economic Review 108(1).
Hornstein, Andreas. 2023. “ Profits and Inflation in the Time of Covid .” FRB Richmond Economic Brief 23-38 (November).
Liu, Zheng, and Thuy Lan Nguyen. 2023. “ Global Supply Chain Pressures and U.S. Inflation .” FRBSF Economic Letter 2023-14 (June 20).
Palazzo, Berardino. 2023. “ Corporate Profits in the Aftermath of COVID-19 .” FEDS Notes , Federal Reserve Board of Governors, September 8.
Weber, Isabella M. and Evan Wasner. 2023. “Sellers’ Inflation, Profits and Conflict: Why Can Large Firms Hike Prices in an Emergency?” Review of Keynesian Economics 11(2), pp. 183-213.
Opinions expressed in FRBSF Economic Letter do not necessarily reflect the views of the management of the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco or of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. This publication is edited by Anita Todd and Karen Barnes. Permission to reprint portions of articles or whole articles must be obtained in writing. Please send editorial comments and requests for reprint permission to [email protected]
The Effects of Mental Health Interventions on Labor Market Outcomes in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Mental health conditions are prevalent but rarely treated in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Little is known about how these conditions affect economic participation. This paper shows that treating mental health conditions substantially improves recipients’ capacity to work in these contexts. First, we perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) ever conducted that evaluate treatments for mental ill-health and measure economic outcomes in LMICs. On average, treating common mental disorders like depression with psychotherapy improves an aggregate of labor market outcomes made up of employment, time spent working, capacity to work and job search by 0.16 standard deviations. Treating severe mental disorders, like schizophrenia, improves the aggregate by 0.30 standard deviations, but effects are noisily estimated. Second, we build a new dataset, pooling all available microdata from RCTs using the most common trial design: studies of psychotherapy in LMICs that treated depression and measured days participants were unable to work in the past month. We observe comparable treatment effects on mental health and work outcomes in this sub-sample of highly similar studies. We also show evidence consistent with mental health being the mechanism through which psychotherapy improves work outcomes.
The three authors listed first (Crick Lund, Kate Orkin, and Marc Witte) are jointly the first author. This study was funded by the Wellspring Philanthropic Fund. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
Vikram Patel acknowledges research support from the NIMH, Wellcome Trust, Grand Challenges Canada and the Medical Research Council. He also receives funding from the Lone Star Prize and serves as a consultant to Modern Health and Johnson & Johnson.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
- data appendix
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

Female labor force participation
Across the globe, women face inferior income opportunities compared with men. Women are less likely to work for income or actively seek work. The global labor force participation rate for women is just over 50% compared to 80% for men. Women are less likely to work in formal employment and have fewer opportunities for business expansion or career progression. When women do work, they earn less. Emerging evidence from recent household survey data suggests that these gender gaps are heightened due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Women’s work and GDP
Women’s work is posited to be related to development through the process of economic transformation.
Levels of female labor force participation are high for the poorest economies generally, where agriculture is the dominant sector and women often participate in small-holder agricultural work. Women’s participation in the workforce is lower in middle-income economies which have much smaller shares of agricultural activities. Finally, among high-income economies, female labor force participation is again higher, accompanied by a shift towards a service sector-based economy and higher education levels among women.
This describes the posited U-shaped relationship between development (proxied by GDP per capita) and female labor force participation where women’s work participation is high for the poorest economies, lower for middle income economies, and then rises again among high income economies.
This theory of the U-shape is observed globally across economies of different income levels. But this global picture may be misleading. As more recent studies have found, this pattern does not hold within regions or when looking within a specific economy over time as their income levels rise.
In no region do we observe a U-shape pattern in female participation and GDP per capita over the past three decades.
Structural transformation, declining fertility, and increasing female education in many parts of the world have not resulted in significant increases in women’s participation as was theorized. Rather, rigid historic, economic, and social structures and norms factor into stagnant female labor force participation.
Historical view of women’s participation and GDP
Taking a historical view of female participation and GDP, we ask another question: Do lower income economies today have levels of participation that mirror levels that high-income economies had decades earlier?
The answer is no.
This suggests that the relationship of female labor force participation to GDP for lower-income economies today is different than was the case decades past. This could be driven by numerous factors -- changing social norms, demographics, technology, urbanization, to name a few possible drivers.
Gendered patterns in type of employment
Gender equality is not just about equal access to jobs but also equal access for men and women to good jobs. The type of work that women do can be very different from the type of work that men do. Here we divide work into two broad categories: vulnerable work and wage work.
The Gender gap in vulnerable and wage work by GDP per capita
Vulnerable employment is closely related to GDP per capita. Economies with high rates of vulnerable employment are low-income contexts with a large agricultural sector. In these economies, women tend to make up the higher share of the vulnerably employed. As economy income levels rise, the gender gap also flips, with men being more likely to be in vulnerable work when they have a job than women.
From COVID-19 crisis to recovery
The COVID-19 crisis has exacerbated these gender gaps in employment. Although comprehensive official statistics from labor force surveys are not yet available for all economies, emerging studies have consistently documented that working women are taking a harder hit from the crisis. Different patterns by sector and vulnerable work do not explain this. That is, this result is not driven by the sectors in which women work or their higher rates of vulnerable work—within specific work categories, women fared worse than men in terms of COVID-19 impacts on jobs.
Among other explanations is that women have borne the brunt of the increase in the demand for care work (especially for children). A strong and inclusive recovery will require efforts which address this and other underlying drivers of gender gaps in employment opportunities.
- Research and Publications
- Projects and Operations
- Privacy Notice
- Site Accessibility
- Access to Information
- REPORT FRAUD OR CORRUPTION

Department of Agricultural, Food, and Resource Economics Innovation Lab for Food Security Policy, Research, Capacity and Influence

Effect of Pesticide Use on Crop Production and Food Security in Uganda
May 14, 2024 - Linda Nakato, Umar Kabanda, Pauline Nakitende, Tess Lallemant & Milu Muyanga
The increasing pest proliferation has continued to cause a serious threat to food security in Uganda. This study explores the impact of pesticide adoption on food security in Uganda. Specifically, it seeks to assess whether the use of pesticides ensures food security, with crop productivity serving as an intervening variable. Employing the control function approach with fixed effects estimation on a dataset comprising 1,656 households spanning the periods 2013/2014, 2016/2015, and 2018/19 to 2019/20 obtained from the Uganda National Panel Survey, the study reveals several determinants influencing pesticide use in Uganda. The findings also highlight that the adoption of pesticides demonstrates a positive influence on crop productivity. However, when assessed through indicators such as Food Consumption Score (FCS), Minimum Acceptable Household Food Consumption (MAHFP), and Household Dietary Diversity Score (HDDS) at the pre-harvest stage, the results do not indicate a statistically significant correlation of pesticide use and food security outcomes. Consequently, beyond enhanced crop productivity and the pre-harvest activities focused on in the study, it is imperative to consider the post-harvest application of pesticides to comprehensively explain how pesticide use effects food security in Uganda. Based on the positive link between pesticides and crop productivity, its recommended that government should increase awareness on and access of insecticides among farmers. Given that insects are the main pests damaging crops in Uganda. It is also important for Uganda to reform and reactive a regulatory framework having a licensing system to regulate private local market dealers’ sale of pesticides. Given that the majority of the households purchase their pesticides from private traders in the local/village market. This approach might improve the quality of pesticide purchased by farmers and, increase pesticide use to diversify produce of more nutritious foods, to ultimately enhance access and nutrient intake per meal in Uganda.
Pesticide use, crop productivity, food security.
DOWNLOAD FILE
Tags: prci research paper
new - method size: 1 - Random key: 0, method: personalized - key: 0
You Might Also Be Interested In
STAAARS+ RFP webinar Sept 14 2022
Published on September 15, 2022
PRCI STAAARS+ Teams Presentation Video 2022
Published on July 26, 2022

Scoping Study of Agriculture Development Strategy of Nepal (ADS) (Five-year achievements)
Published on February 1, 2023
Sugarcane Production and Food Security in Uganda
Published on September 1, 2023
Institutional Arrangements Between Sugarcane Growers and Millers in Uganda and Implications for Grower Productivity and Profitability

Rwanda Natural Forest Cover Dynamics between 2015 and 2020
Published on June 19, 2023
Accessibility Questions:
For questions about accessibility and/or if you need additional accommodations for a specific document, please send an email to ANR Communications & Marketing at [email protected] .
- prci research paper,
- innovation lab for food security policy research capacity & influence

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sharpening your economics writing skills is crucial in communicating top-notch research effectively. Remember, your paper's impact may suffer if your writing is: • grammatically flawed, • unclear, or • excessively journalistic. Writing an economics paper without proper grammar is like balancing an economic model on a
What Is An Economics Research Paper? How Does One Write An Economics Research Paper? Summary Reminders for Next Week Theoretical Research Papers Example 2 (Baliga and Ely 2010): Reasonable assumptions: The interrogator only has a finite period of time to interrogate and/or torture the prisoner. The longer a prisoner goes without confessing ...
Most Popular Papers *. PDF. The Role of Entrepreneurship in Economic Growth. Daniel Smith. PDF. The Strength of Religious Beliefs is Important for Subjective Well-Being. Enrique Colón-Bacó. PDF. Impact of Exchange Rate Regimes on Economic Growth.
Economics Research 1 Writing and Research Opportunities in the Concentration 1 Plan of this Guide 3 ... economics papers don't just "happen" without time spent on preparation; you cannot hide a lack of research, ... for example, the following excerpt from a student's short response paper: In the beginning of the 1980's, the problem of ...
This sample economics research paper features: 7800 words (approx. 26 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 36 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help.
II, "Researching Economic Topics," tries to explain the scholarly and analytical approach behind economics papers. The third part, "Genres of Economics Writing," briefly surveys some of the kinds of papers and essays economists write. It is in the fourth part, "Writing Economics," that the manual homes in on discipline-specific writing.
to succeed as a writer of economics and offers an overview of the writing process from beginning to end. Chapter 2 describes the basic methods economists use to analyze data and communicate their ideas. Chapter 3 offers suggestions for finding and focusing your topic, including standard economic sources and techniques for doing economic research.
I have no disclosures to report. The research did not receive funding from external sources. The views expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research. NBER working papers are circulated for discussion and comment purposes. They have not been peer-
Determining the Relationship Between Patient Participation and Treatment Plan Confidence Across a Spectrum of Illness Severity in the State of California" - Saif Chowdhury. "Modeling Optimal Investment and Greenhouse Gas Abatement in the Presence of Technology Spillovers" - Sabrina Chui. "Understanding the Influence of Marginal Income Tax Rates ...
by Berg, Heléne. 2018:4 The Stockholm School in a New Age - Erik Lundberg and the Swedish Model. by Erixon, Lennart. 2018:3 Politicians' Payments in a Proportional Party System. by Berg, Helene. 2018:2 The Relative Skill Demand of Superstar Firms and Aggregate Implications. by Akerman, Anders.
Guides and Examples of econometrics paper for undergrads ... Georgia Tech Library. Format for an Econometrics Paper: Skidmore College. Research Paper in Introductory Econometrics: Carleton College. Writing in Economics: Duke University. The Young Economist's Short Guide to Writing Economic Research: Pomona College << Previous: Finding ...
A Research Paper in Experimental Economics- In teams, students complete original research in experimental economics. Replicating the Results of Famous Empirical Papers - This project provides an example of how students can engage in research by replicating and extending the methods and results of famous empirical papers (here, Solow (1957)).
This study sheds light on the political pathology of fraudulent, illegal, and corrupt business practices. Features of the Chinese system—including regulatory gaps, a lack of formal means of property protection, and pervasive uncertainty—seem to facilitate the rise of mafia systems. 02 Feb 2021. Working Paper Summaries.
The methods used in economic research are analyzed on a sample of all 3,415 regular research papers published in 10 general interest journals every 5th year from 1997 to 2017. The papers are classified into three main groups by method: theory, experiments, and empirics. The theory and empirics groups are almost equally large. Most empiric papers use the classical method, which derives an ...
Economics Research Paper Example. Just as we promised in the beginning, our writers took the extra mile and wrote an economics research paper example for you. Check out what makes an essay exceptional and how the paper ensures the readers stay engaged all the way through. Explore the structure, format, and language with which our writers ...
Economics research usually begins with a strong understanding of literature, and papers require a section that summarizes and applies previous literature to what the paper at hand. This is the best way to start. ... As with any research paper, source referencing depends on the will of a professor a discourse community. However, economists ...
About the journal. Established in 1947, Research in Economics is one of the oldest general-interest economics journals in the world and the main one among those based in Italy. The purpose of the journal is to select original theoretical and empirical articles that will have high impact on the debate in the social …. View full aims & scope.
When I read economics research papers, I look for the author's ability to motivate an interesting question using economic logic, critically analyze the past literature, and recognize empirical problems as they arise. Your research paper should also highlight a central novelty related to existing ... example, Oster (2012) starts her abstract ...
For example, a paper on, say, the impact of a particular change in the minimum wage ... • Indicate briefly the research that has been done on the topic • Identify a gap, problem, controversy, etc., in the existing research ... The Conclusion sections of economics papers are the least standardized, and are an often neglected
Five-page review of literature relevant to research paper topic due at the beginning of class. •March 20. Five-page description of model or data to be used in research paper due at the beginning of class. •April 10. Five-page summary of research paper results due at the beginning of class. •May 1. Completed research paper (drawing on but
Economics Research Paper Examples. Economics is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their ...
Research Paper Examples on Economics A Solution To Inequality And Poverty: Effects Of Innovation And Government Policy On Global Economy. Gunter & Van der Hoeven (2004) state that there is a general agreement that in the case of economic growth, the advantages thereof mainly depend on the sharing of the income generated by it.
Founded in 1920, the NBER is a private, non-profit, non-partisan organization dedicated to conducting economic research and to disseminating research findings among academics, public policy makers, and business professionals.
Working Paper 32452 DOI 10.3386/w32452 Issue Date May 2024. In this review, we argue that access to financial advice and the quality of this advice is shaped by a broad array of demand-side and supply-side constraints. While the literature has predominantly focused on conflicts of interest between advisors and clients, we highlight that the ...
How much impact have price markups for goods and services had on the recent surge and the subsequent decline of inflation? Since 2021, markups have risen substantially in a few industries such as motor vehicles and petroleum. However, aggregate markups—which are more relevant for overall inflation—have generally remained flat, in line with previous economic recoveries over the past three ...
Implications for Policy and Future Research: The paper's findings directly affect policy formulation aimed at maximising the benefits of FDI on economic growth and employment generation. Furthermore, by identifying areas for future research, such as the role of selective FDI policies and judicial controls, the paper paves the way for ...
How to Write an Economics Research Paper. To write an economics research paper: 1 Go step by step. As with all large projects, a research paper is much more manageable when broken down into smaller tasks. 2 The first step: Identify an interesting, specific, economic. question.
This paper shows that treating mental health conditions substantially improves recipients' capacity to work in these contexts. First, we perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) ever conducted that evaluate treatments for mental ill-health and measure economic outcomes in LMICs.
Women's work and GDP. Women's work is posited to be related to development through the process of economic transformation. Levels of female labor force participation are high for the poorest economies generally, where agriculture is the dominant sector and women often participate in small-holder agricultural work.
Study in Uganda explores pesticide impact on food security: boosts crop yield but not pre-harvest food security. Post-harvest use, regulation, and diversified nutrition recommended for better outcomes.