Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples

What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

How to Write a Complete Literature Review for Your Thesis/Dissertation

A literature review critically evaluates and synthesizes existing research and scholarly publications on a specific topic or research question. Its goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on the topic, identify gaps in the literature, and highlight areas for future research. A well-conducted literature review is an essential component of research because it helps to establish the research context, justify the need for the study, and guide the development of research questions or hypotheses.
The literature review of your thesis/dissertation is a very significant part of your paper. It provides readers with an understanding of previously published research in relation to your topic. It also highlights where your research fits into the existing literature. In other words, it provides valuable context for your readers about the field as a whole and the specific topic you have chosen to cover in your thesis/dissertation.
Literature reviews: An overview
A literature review does not only summarize what has been written about a topic already: it also offers a critical analysis of the existing literature.
Literature reviews can take different forms depending on what type of research you are doing and what your field of research is about. Literature reviews are a key part of the majority of academic articles or theses, and can even be written as articles all on their own. A literature review does not only summarize what has been written about a topic already: it also offers a critical analysis of the existing literature. In other words, you, the author, offer your analysis or critique on what has been written already. A literature review, however, should not just be a description of what has been written or a set of summaries.
The idea of reviewing and analyzing all the research that has been done on a topic can sound overwhelming; however, the task is easier than it sounds. This is also a vital step in performing the work necessary to write a good thesis. As you prepare and write your literature review, you will select and filter which sources are relevant to your work and which are not. As you review the literature, you will develop a clear understanding of the work that has come before you. This will enable you to write about it in such a way that you clearly demonstrate how you arrived at your own thesis statement or hypothesis.
A literature review can be quite short (5% of a paper) or quite long (30% of a paper) depending on the type of paper. For a thesis/dissertation, a literature review may be a full chapter, and is usually at least 10-20% of your paper.
Types of literature reviews
There are different types of literature reviews and the type you choose will be determined by the topic you are researching. Four common types of literature reviews are summarized below, but there are also other types that may be preferable depending on your thesis topic.
Chronological
This type of literature review organizes sources and their ideas by the date of publication. For example, if you are writing about chronic Lyme disease, you would start with articles describing and identifying Lyme disease (1970s), then describe initial treatments and discoveries (1980s), increased prevalence of Lyme disease and rise of people with chronic Lyme disease (2000s), and finally discuss the current controversies and treatments (2010s).
This type is often used in social science papers such as political science or public policy. They focus on specific trends in a field and can still include a chronological component. For example, you could write about changes in approaches to early childhood education by discussing the rise and fall in popularity of public preschool, highlighting relevant case studies, and presenting arguments that there is no need for schooling so early. This is often used to highlight competing schools of thought in a field.
Methodological
This focuses less on what is said in different sources and more on how previous research has been performed. For example, a methodological review of the treatment of chronic Lyme disease might reveal that previous studies which relied solely on laboratory tests dismissed persistent Lyme symptoms as “all in the patients’ heads,” while studies that focused on interviewing patients as well as doctors classified the disease as an unidentified syndrome. Methodological studies can highlight how approaches to research have changed over time and how the approaches used in research influence the results.
Theoretical
Theoretical literature reviews are often found in fields like philosophy or humanities, but are also prevalent in social sciences. They review existing theories and their relationships, as well as what has been tested and what has not. This kind of review is quite useful in demonstrating where existing theories fall short in describing a particular phenomenon in the field.
Structuring your literature review
A literature review is usually a chapter in your thesis/dissertation and as such generally includes an introduction, main body, and conclusion. The introduction will explain:
- The type of literature review you have performed
- Why you have chosen to perform that type of literature review
- Your criteria for selecting sources
Your main body will be the actual literature review, which we will discuss further in the next section. In your conclusion, you will summarize the major arguments that you have highlighted in your literature review and center your own research among them. The conclusion of the literature review should explain why your research study is necessary (what gap in the literature it fulfils) to lead smoothly into your next thesis chapter.
How do I review the literature?
An easy way to find relevant sources is to look at the citations of papers you find that are on the topic you want to research.
Before you write a literature review, you need to:
- Become familiar with the literature
- Select which sources are relevant to your thesis topic
- Organize your sources
- Choose the type of literature review you will write
- Arrange your notes to reflect the type of literature review
How do you become familiar with the literature?
If you aren’t sure where to start, try going to Google Scholar and typing in some keywords about your topic. For example, if you’re researching chronic Lyme disease, you could type in keywords such as “chronic Lyme” “post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome” and “Lyme disease treatment” to see what results show up. As you search, you will be able to identify more keywords that are relevant to what you want to search. Making a list of these keywords can help you as you engage in this task. When you find an article that looks promising, copy the citation information from Google Scholar and save it in a file or use a reference manager like Mendeley . You will thank yourself for this later. You can then search your academic institution’s online library to download the article.
An easy way to find relevant sources is to look at the citations of papers you find that are on the topic you want to research. If you aren’t sure whether an article or paper you are reading is reputable , you can check its citation metrics using Google Scholar, which can tell you how many other people cited a particular source. Generally, it holds true that the more highly cited a source is, the more reliable and useful it is. Of course, your citation sources don’t need to be limited to journal articles. Books , news articles , interviews, and other sources are all acceptable .
Finally, as you read through sources and organize them, you will want to take notes. Don’t just save an article and hope you’ll remember why you did. Jot down a few sentences about the main argument of this source and why/how it is relevant to your research study. Once you have done this, you will want to go ahead and organize your sources in an order that reflects the type of literature review you have chosen to do. For example, if you are doing a thematic review, you should organize sources by a theme or type of argument. If you are doing a historical review, you would organize them in chronological order.
Writing the literature review
As you write your literature review, you will want to walk the reader through what has happened in the literature review and offer your analysis of it.
Now that you’ve reviewed the literature, taken notes, organized your sources and your notes, you are ready to begin! As we mentioned above, a literature review needs an introduction and a conclusion. As you write your literature review, you will want to walk the reader through what has happened in the literature review and offer your analysis of it. For example, you could say “while Yue and Xu argue that Lyme disease is a bacterial infection and should not result in symptoms resembling post-viral syndromes, others such as Scott and Zebrowski have noted the strong similarities between patients with chronic Lyme disease and the newly emerging group of COVID long-haulers. Scott and Zebrowski appear to be at the forefront of the changing perspective on chronic Lyme disease as newer evidence supports their position.”
Your literature review will include the ideas of many other people, but it should not be a lengthy chapter directly quoting other papers. You should instead paraphrase what others say. Of course you can use some quotes! They are not off limits. Short quotes like “Marx said ‘religion is the opiate of the masses’ while Mao Zedong said ‘religion is poison’” is fine. Longer blocks of text should be used only when necessary and properly indicated within the text .
Now you are ready to write your thesis literature review! Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis, where to find the best thesis editing services, and more about thesis editing and proofreading services .
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Checklist for writing a literature review
Below is a list of points to remember when writing your literature review. These will help you make sure that your literature review is thorough and properly structured.
Do a thorough review of the sources in your field that are relevant to your thesis topic.
Make sure your sources are reliable and high-quality.
Take detailed notes and maintain an organized list of your sources.
Cover a wide variety of viewpoints, not just those that support or agree with your argument. Make it clear what controversies and unsettled point of views exist.
Make sure your literature review chapter has a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion.
Use quotes sparingly.
What is a literature review? +
A literature review is a summary of the major studies and sources related to your topic that already exist and provides critical analysis of these sources. A literature review is not a bibliography or a list of sources. It is written in a narrative format.
e.g. “Clowes and McKnight (2002) argue that chronic Lyme disease is analogous to post-viral syndrome.”
What kinds of sources can be included in a literature review? +
Anything you can cite in an academic paper can be included in a literature review. This includes journal articles, books, news sources, interviews, and so on. You should not include Wikipedia or your Uncle Bob as a source in the literature review (unless your Uncle Bob is a recognized expert in your topic!).
Do I really have to write a literature review? +
A literature review is part of most social science or natural science theses/dissertations. your institutional requirements inform you to, then you have to write a literature review. If you are writing a thesis/dissertation in humanities or in another field where the structure does not mandate a literature review, you may be able to skip it. Always check with your advisor and your institution about the requirements of your thesis/dissertation structure.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide and Examples
Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Chapter Summary
Chapter summary is a brief overview of the key points or events covered in a specific chapter of a book, academic paper, or other written work. It typically includes a concise description of the main ideas, arguments, or themes explored in the chapter, as well as any important supporting details or evidence .
Chapter summaries are often used as study aids, providing readers with a quick way to review and understand the content of a particular section of a longer work. They may also be included as part of a book’s table of contents or used as a promotional tool to entice potential readers.
How to Write Chapter Summary
Writing a chapter summary involves condensing the content of a chapter into a shorter, more concise form while still retaining its essential meaning. Here are some steps to help you write a chapter summary:
- Read the chapter carefully: Before summarizing a chapter, it is important to read it thoroughly to ensure that you understand the main ideas and points being made.
- Identify the main ideas: Identify the main ideas and arguments that the chapter is presenting. These may be explicit, or they may be implicit and require some interpretation on your part.
- Make notes: Take notes while reading to help you keep track of the main ideas and arguments. Write down key phrases, important quotes, and any examples or evidence that support the main points.
- Create an outline : Once you have identified the main ideas and arguments, create an outline for your summary. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure that you include all the important points.
- Write the summary : Using your notes and outline, write a summary of the chapter. Start with a brief introduction that provides context for the chapter, then summarize the main ideas and arguments, and end with a conclusion that ties everything together.
- Edit and revise: After you have written the summary, review it carefully to ensure that it is accurate and concise. Make any necessary edits or revisions to improve the clarity and readability of the summary.
- Check for plagiarism : Finally, check your summary for plagiarism. Make sure that you have not copied any content directly from the chapter without proper citation.
Chapter Summary in Research Paper
In a Research Paper , a Chapter Summary is a brief description of the main points or findings covered in a particular chapter. The summary is typically included at the beginning or end of each chapter and serves as a guide for the reader to quickly understand the content of that chapter.
Here is an example of a chapter summary from a research paper on climate change:
Chapter 2: The Science of Climate Change
In this chapter, we provide an overview of the scientific consensus on climate change. We begin by discussing the greenhouse effect and the role of greenhouse gases in trapping heat in the atmosphere. We then review the evidence for climate change, including temperature records, sea level rise, and changes in the behavior of plants and animals. Finally, we examine the potential impacts of climate change on human society and the natural world. Overall, this chapter provides a foundation for understanding the scientific basis for climate change and the urgency of taking action to address this global challenge.
Chapter Summary in Thesis
In a Thesis , the Chapter Summary is a section that provides a brief overview of the main points covered in each chapter of the thesis. It is usually included at the beginning or end of each chapter and is intended to help the reader understand the key concepts and ideas presented in the chapter.
For example, in a thesis on computer science field, a chapter summary for a chapter on “Machine Learning Algorithms” might include:
Chapter 3: Machine Learning Algorithms
This chapter explores the use of machine learning algorithms in solving complex problems in computer science. We begin by discussing the basics of machine learning, including supervised and unsupervised learning, as well as different types of algorithms such as decision trees, neural networks, and support vector machines. We then present a case study on the application of machine learning algorithms in image recognition, demonstrating how these algorithms can improve accuracy and reduce error rates. Finally, we discuss the limitations and challenges of using machine learning algorithms, including issues of bias and overfitting. Overall, this chapter highlights the potential of machine learning algorithms to revolutionize the field of computer science and drive innovation in a wide range of industries.
Examples of Chapter Summary
Some Examples of Chapter Summary are as follows:
Research Title: “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: A Review of the Literature”
Chapter Summary:
Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research problem, which is the impact of social media on mental health. It presents the purpose of the study, the research questions, and the methodology used to conduct the research.
Research Title : “The Effects of Exercise on Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis”
Chapter 2: Literature Review
This chapter reviews the existing literature on the effects of exercise on cognitive functioning in older adults. It provides an overview of the theoretical framework and previous research findings related to the topic. The chapter concludes with a summary of the research gaps and limitations.
Research Title: “The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership Effectiveness: A Case Study of Successful Business Leaders”
Chapter 3: Methodology
This chapter presents the research methodology used in the study, which is a case study approach. It describes the selection criteria for the participants and the data collection methods used. The chapter also provides a detailed explanation of the data analysis techniques used in the study.
Research Title: “Factors Influencing Employee Engagement in the Workplace: A Systematic Review”
Chapter 4: Results and Discussion
This chapter presents the findings of the systematic review on the factors influencing employee engagement in the workplace. It provides a detailed analysis of the results, including the strengths and limitations of the studies reviewed. The chapter also discusses the implications of the findings for practice and future research.
Purpose of Chapter Summary
Some Purposes of the Chapter Summary are as follows:
- Comprehension : A chapter summary can help readers understand the main points of a chapter or book. It can help readers remember important details, keep track of the plot or argument, and connect the key ideas.
- Review : A chapter summary can be a useful tool for reviewing the material covered in a chapter. It can help readers review the content quickly and efficiently, and it can also serve as a reference for future study.
- Study aid: A chapter summary can be used as a study aid, especially for students who are preparing for exams or writing papers. It can help students organize their thoughts and focus on the most important information.
- Teaching tool: A chapter summary can be a useful teaching tool for educators. It can help teachers introduce key concepts and ideas, facilitate class discussion, and assess student understanding.
- Communication : A chapter summary can be used as a way to communicate the main ideas of a chapter or book to others. It can be used in presentations, reports, and other forms of communication to convey important information quickly and concisely.
- Time-saving : A chapter summary can save time for busy readers who may not have the time to read an entire book or chapter in detail. By providing a brief overview of the main points, a chapter summary can help readers determine whether a book or chapter is worth further reading.
- Accessibility : A chapter summary can make complex or technical information more accessible to a wider audience. It can help break down complex ideas into simpler terms and provide a clear and concise explanation of key concepts.
- Analysis : A chapter summary can be used as a starting point for analysis and discussion. It can help readers identify themes, motifs, and other literary devices used in the chapter or book, and it can serve as a jumping-off point for further analysis.
- Personal growth : A chapter summary can be used for personal growth and development. It can help readers gain new insights, learn new skills, and develop a deeper understanding of the world around them.
When to Write Chapter Summary
Chapter summaries are usually written after you have finished reading a chapter or a book. Writing a chapter summary can be useful for several reasons, including:
- Retention : Summarizing a chapter helps you to better retain the information you have read.
- Studying : Chapter summaries can be a useful study tool when preparing for exams or writing papers.
- Review : When you need to review a book or chapter quickly, a summary can help you to refresh your memory.
- Analysis : Summarizing a chapter can help you to identify the main themes and ideas of a book, which can be useful when analyzing it.
Advantages of Chapter Summary
Chapter summaries have several advantages:
- Helps with retention : Summarizing the key points of a chapter can help you remember important information better. By condensing the information, you can identify the main ideas and focus on the most relevant points.
- Saves time : Instead of re-reading the entire chapter when you need to review information, a summary can help you quickly refresh your memory. It can also save time during note-taking and studying.
- Provides an overview : A summary can give you a quick overview of the chapter’s content and help you identify the main themes and ideas. This can help you understand the broader context of the material.
- Helps with comprehension : Summarizing the content of a chapter can help you better understand the material. It can also help you identify any areas where you might need more clarification or further study.
- Useful for review: Chapter summaries can be a useful review tool before exams or when writing papers. They can help you organize your thoughts and review key concepts and ideas.
- Facilitates discussion: When working in a group, chapter summaries can help facilitate discussion and ensure that everyone is on the same page. It can also help to identify areas of confusion or disagreement.
- Supports active reading : Creating a summary requires active reading, which means that you are engaging with the material and thinking critically about it. This can help you develop stronger reading and critical thinking skills.
- Enables comparison : When reading multiple sources on a topic, creating summaries of each chapter can help you compare and contrast the information presented. This can help you identify differences and similarities in the arguments and ideas presented.
- Helpful for long texts: In longer books or texts, chapter summaries can be especially helpful. They can help you break down the material into manageable chunks and make it easier to digest.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?
Reflecting on and Comparing Your Data, Recognising the Strengths and Limitations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
409 Accesses
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with subsections and paragraphs. We also present a list of points to do and avoid when writing the discussion together with a Discussion chapter checklist.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Braun V, Clarke V (2013) Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. SAGE Publications, London
Google Scholar
McGregor SLT (2018) Understanding and evaluating research: a critical guide. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA
Book Google Scholar
PLOS (2023) Author resources. How to write discussions and conclusions. Accessed Mar 3, 2023, from https://plos.org/resource/how-to-write-conclusions/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Cottrell S (2017) Critical thinking skills: effective analysis, argument and reflection, 3rd edn. Palgrave, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Welcome to Chapter 2
How to Critically Analyze Sources
Learning about synthesis analysis, chapter 2 webinars.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Library Guide: Research Process This link opens in a new window
- ASC Guide: Outlining and Annotating This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Copyright Information This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Need help ask us.

- Research Process An introduction to the research process.
- Determining Information Needs A Review Scholarly Journals and Other Information Sources.
- Evaluating Information Sources This page explains how to evaluate the sources of information you locate in your searches.
- Video: Doctoral Level Critique in the Literature Review This video provides doctoral candidates an overview of the importance of doctoral-level critique in the Literature Review in Chapter 2 of their dissertation.
What D oes Synthesis and Analysis Mean?
Synthesis: the combination of ideas to

- show commonalities or patterns
Analysis: a detailed examination
- of elements, ideas, or the structure of something
- can be a basis for discussion or interpretation
Synthesis and Analysis: combine and examine ideas to
- show how commonalities, patterns, and elements fit together
- form a unified point for a theory, discussion, or interpretation
- develop an informed evaluation of the idea by presenting several different viewpoints and/or ideas
- Article Spreadsheet Example (Article Organization Matrix) Use this spreadsheet to help you organize your articles as you research your topic.
Was this resource helpful?
- Next: Library Guide: Research Process >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2023 11:59 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1007176

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
When you need an introduction for a literature review, what to include in a literature review introduction, examples of literature review introductions, steps to write your own literature review introduction.
A literature review is a comprehensive examination of the international academic literature concerning a particular topic. It involves summarizing published works, theories, and concepts while also highlighting gaps and offering critical reflections.
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
Instead, you should always offer some form of introduction to orient the reader and clarify what they can expect.
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
- Academic literature review papers: When your literature review constitutes the entirety of an academic review paper, a more substantial introduction is necessary. This introduction should resemble the standard introduction found in regular academic papers.
- Literature review section in an academic paper or essay: While this section tends to be brief, it’s important to precede the detailed literature review with a few introductory sentences. This helps orient the reader before delving into the literature itself.
- Literature review chapter or section in your thesis/dissertation: Every thesis and dissertation includes a literature review component, which also requires a concise introduction to set the stage for the subsequent review.
You may also like: How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Here’s a structured breakdown based on length and the necessary information:
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
- The research problem: Clearly articulate the problem or question that your literature review aims to address.
- The research gap: Highlight the existing gaps, limitations, or unresolved aspects within the current body of literature related to the research problem.
- The research relevance: Explain why the chosen research problem and its subsequent investigation through a literature review are significant and relevant in your academic field.
- The literature review method: If applicable, describe the methodology employed in your literature review, especially if it is a systematic review or follows a specific research framework.
- The main findings or insights of the literature review: Summarize the key discoveries, insights, or trends that have emerged from your comprehensive review of the literature.
- The main argument of the literature review: Conclude the introduction by outlining the primary argument or statement that your literature review will substantiate, linking it to the research problem and relevance you’ve established.
- Preview of the literature review’s structure: Offer a glimpse into the organization of the literature review paper, acting as a guide for the reader. This overview outlines the subsequent sections of the paper and provides an understanding of what to anticipate.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will provide a clear and structured overview of what readers can expect in your literature review paper.
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
Most academic articles or essays incorporate regular literature review sections, often placed after the introduction. These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper.
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
- An introduction to the topic: When delving into the academic literature on a specific topic, it’s important to provide a smooth transition that aids the reader in comprehending why certain aspects will be discussed within your literature review.
- The core argument: While literature review sections primarily synthesize the work of other scholars, they should consistently connect to your central argument. This central argument serves as the crux of your message or the key takeaway you want your readers to retain. By positioning it at the outset of the literature review section and systematically substantiating it with evidence, you not only enhance reader comprehension but also elevate overall readability. This primary argument can typically be distilled into 1-2 succinct sentences.
In some cases, you might include:
- Methodology: Details about the methodology used, but only if your literature review employed a specialized method. If your approach involved a broader overview without a systematic methodology, you can omit this section, thereby conserving word count.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will effectively integrate your literature review into the broader context of your academic paper or essay. This will, in turn, assist your reader in seamlessly following your overarching line of argumentation.
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
The literature review typically constitutes a distinct chapter within a thesis or dissertation. Often, it is Chapter 2 of a thesis or dissertation.
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
- Purpose of the literature review and its relevance to the thesis/dissertation research: Explain the broader objectives of the literature review within the context of your research and how it contributes to your thesis or dissertation. Essentially, you’re telling the reader why this literature review is important and how it fits into the larger scope of your academic work.
- Primary argument: Succinctly communicate what you aim to prove, explain, or explore through the review of existing literature. This statement helps guide the reader’s understanding of the review’s purpose and what to expect from it.
- Preview of the literature review’s content: Provide a brief overview of the topics or themes that your literature review will cover. It’s like a roadmap for the reader, outlining the main areas of focus within the review. This preview can help the reader anticipate the structure and organization of your literature review.
- Methodology: If your literature review involved a specific research method, such as a systematic review or meta-analysis, you should briefly describe that methodology. However, this is not always necessary, especially if your literature review is more of a narrative synthesis without a distinct research method.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will empower your literature review to play a pivotal role in your thesis or dissertation research. It will accomplish this by integrating your research into the broader academic literature and providing a solid theoretical foundation for your work.
Comprehending the art of crafting your own literature review introduction becomes significantly more accessible when you have concrete examples to examine. Here, you will find several examples that meet, or in most cases, adhere to the criteria described earlier.
Example 1: An effective introduction for an academic literature review paper
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.

The entire introduction spans 611 words and is divided into five paragraphs. In this introduction, the authors accomplish the following:
- In the first paragraph, the authors introduce the broader topic of the literature review, which focuses on innovation and its significance in the context of economic competition. They underscore the importance of this topic, highlighting its relevance for both researchers and policymakers.
- In the second paragraph, the authors narrow down their focus to emphasize the specific role of culture in relation to innovation.
- In the third paragraph, the authors identify research gaps, noting that existing studies are often fragmented and disconnected. They then emphasize the value of conducting a systematic literature review to enhance our understanding of the topic.
- In the fourth paragraph, the authors introduce their specific objectives and explain how their insights can benefit other researchers and business practitioners.
- In the fifth and final paragraph, the authors provide an overview of the paper’s organization and structure.
In summary, this introduction stands as a solid example. While the authors deviate from previewing their key findings (which is a common practice at least in the social sciences), they do effectively cover all the other previously mentioned points.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
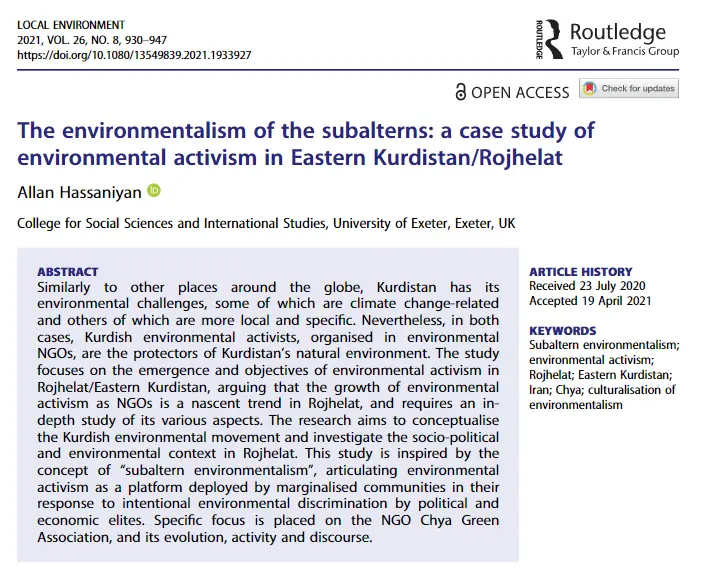
The paper begins with a general introduction and then proceeds to the literature review, designated by the authors as their conceptual framework. Of particular interest is the first paragraph of this conceptual framework, comprising 142 words across five sentences:
“ A peripheral and marginalised nationality within a multinational though-Persian dominated Iranian society, the Kurdish people of Iranian Kurdistan (a region referred by the Kurds as Rojhelat/Eastern Kurdi-stan) have since the early twentieth century been subject to multifaceted and systematic discriminatory and exclusionary state policy in Iran. This condition has left a population of 12–15 million Kurds in Iran suffering from structural inequalities, disenfranchisement and deprivation. Mismanagement of Kurdistan’s natural resources and the degradation of its natural environmental are among examples of this disenfranchisement. As asserted by Julian Agyeman (2005), structural inequalities that sustain the domination of political and economic elites often simultaneously result in environmental degradation, injustice and discrimination against subaltern communities. This study argues that the environmental struggle in Eastern Kurdistan can be asserted as a (sub)element of the Kurdish liberation movement in Iran. Conceptually this research is inspired by and has been conducted through the lens of ‘subalternity’ ” ( Hassaniyan, 2021, p. 931 ).
In this first paragraph, the author is doing the following:
- The author contextualises the research
- The author links the research focus to the international literature on structural inequalities
- The author clearly presents the argument of the research
- The author clarifies how the research is inspired by and uses the concept of ‘subalternity’.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
While introductions to a literature review section aren’t always required to offer the same level of study context detail as demonstrated here, this introduction serves as a commendable model for orienting the reader within the literature review. It effectively underscores the literature review’s significance within the context of the study being conducted.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
The introduction to a literature review chapter can vary in length, depending largely on the overall length of the literature review chapter itself. For example, a master’s thesis typically features a more concise literature review, thus necessitating a shorter introduction. In contrast, a Ph.D. thesis, with its more extensive literature review, often includes a more detailed introduction.
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
The first example is “Benchmarking Asymmetrical Heating Models of Spider Pulsar Companions” by P. Sun, a master’s thesis completed at the University of Manchester on January 9, 2024. The author, P. Sun, introduces the literature review chapter very briefly but effectively:

PhD thesis literature review chapter introduction
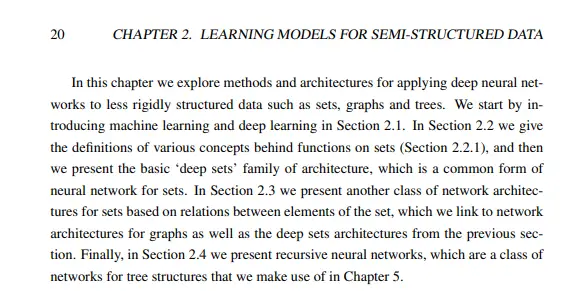
The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester . In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the final paragraph serving as an overview of the chapter’s structure:
PhD thesis literature review introduction
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.

Having absorbed all of this information, let’s recap the essential steps and offer a succinct guide on how to proceed with creating your literature review introduction:
- Contextualize your review : Begin by clearly identifying the academic context in which your literature review resides and determining the necessary information to include.
- Outline your structure : Develop a structured outline for your literature review, highlighting the essential information you plan to incorporate in your introduction.
- Literature review process : Conduct a rigorous literature review, reviewing and analyzing relevant sources.
- Summarize and abstract : After completing the review, synthesize the findings and abstract key insights, trends, and knowledge gaps from the literature.
- Craft the introduction : Write your literature review introduction with meticulous attention to the seamless integration of your review into the larger context of your work. Ensure that your introduction effectively elucidates your rationale for the chosen review topics and the underlying reasons guiding your selection.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The best answers to "What are your plans for the future?"
10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles.

10 key skills of successful master’s students


How to write effective cover letters for a paper submission

Dealing with failure as a PhD student

Reject decisions: Sample peer review comments and examples
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Advertisement
Supported by
‘The Strangers: Chapter 1’ Review: Crowded House
A reboot of the 2008 home invasion film “The Strangers” brings back masked assailants and brutal violence but leaves originality behind.
- Share full article

By Erik Piepenburg
The key to a terrific scary home invasion horror movie is not just how domesticity gets breached but why. It’s great to have a determined aggressor, sympathetic victims and a brutal invasion that’s contained and sustained. But to what end?
Yet some of the best home invasion films — “Funny Games,” “Them” — don’t supply easy answers. “The Strangers,” Bryan Bertino’s terrifying 2008 thriller starring Liv Tyler and Scott Speedman as a couple under siege, didn’t either. It kept the invaders’ motives and their identities mysterious, amping up the devil-you-don’t-know terrors with a sense of randomness that was despairing. The premise and execution were simple. The payoff was a gut punch.
On its face, “The Strangers: Chapter 1,” the first of three new films in a “Strangers” reboot from the director Renny Harlin (“ A Nightmare on Elm Street 4: The Dream Master ”), checks all the same boxes. But the hapless script — written by Alan R. Cohen and Alan Freedland and based on the original — offers nothing fresh in a tiring 91 minutes, and nothing daring to justify a new “Strangers” film, let alone a new series, especially when Bertino’s formidable film is streaming on Max .
This new tale begins with Maya (Madelaine Petsch) and her boyfriend, Ryan (Froy Gutierrez), taking a fifth anniversary road trip through the Pacific Northwest. When their car breaks down in a rural Oregon town, they meet a seen-it-before who’s who of horror movie yokeldom: unsmiling boys, sweaty bumpkin mechanics, a diner waitress whose eyes scream “run, if you know what’s good.”
As Maya and Ryan wait for their car to be fixed, they decide to spend the night at a secluded rental cabin. Under darkness there’s a knock at the door and, true to the home invasion formula, our leading sweethearts get terrorized until dawn inside the cabin and through the woods by a trio of assailants with big weapons and indefinite end goals. They have face coverings too, making menace out of the same blank-faced creepiness the villains embodied in the original film and its 2018 sequel.
Harlin is known for action films, including “Die Hard 2,” and those chops come in handy here, especially when he’s left hanging by a sleepy middle section of frantic chases and failed attacks that feel like padding. Cat-and-mouse games can be compelling, but here , like a “Tom and Jerry” marathon, they get repetitive, dulling the impact of the violence. Petsch and Gutierrez have sufficient enough rapport, and border on sharing a couple’s chemistry as the final stretch comes to a too-predictable conclusion.
The film’s few thrilling moments have little to do with blood and guts and more with the juxtaposition of dread and song, as when Joanna Newsom’s lilting hymn “Sprout and the Bean” and Twisted Sister’s power anthem “We’re Not Gonna Take It” pop up unexpectedly to disorient the action. These and other oddball musical interludes provide too-fleeting hints of what might have been had this film sought a novel household takeover, not the same old.
The Strangers: Chapter 1 Rated R for heaps of ruthless violence and general despair. Running time: 1 hour 31 minutes. In theaters.
Explore More in TV and Movies
Not sure what to watch next we can help..
Season 49 of “Saturday Night Live” has ended. Here’s a look back at its most memorable monologues, sketches, product parodies and impressions .
“Megalopolis,” the first film from the director Francis Ford Coppola in 13 years, premiered at the Cannes Film Festival. Here’s what to know .
Why is the “Planet of the Apes” franchise so gripping and effective? Because it doesn’t monkey around, our movie critic writes .
Luke Newton has been in the sexy Netflix hit “Bridgerton” from the start. But a new season will be his first as co-lead — or chief hunk .
If you are overwhelmed by the endless options, don’t despair — we put together the best offerings on Netflix , Max , Disney+ , Amazon Prime and Hulu to make choosing your next binge a little easier.
Sign up for our Watching newsletter to get recommendations on the best films and TV shows to stream and watch, delivered to your inbox.
- Cast & crew
- User reviews
Horizon: An American Saga - Chapter 1

Chronicles a multi-faceted, 15-year span of pre-and post-Civil War expansion and settlement of the American west. Chronicles a multi-faceted, 15-year span of pre-and post-Civil War expansion and settlement of the American west. Chronicles a multi-faceted, 15-year span of pre-and post-Civil War expansion and settlement of the American west.
- Kevin Costner
- Sienna Miller
- 5 User reviews
- 15 Critic reviews
- 50 Metascore

- Hayes Ellison

- Frances Kittredge

- Hugh Proctor

- Diamond Kittredge

- Colonel Houghton

- Owen Kittredge

- First Lt. Trent Gephardt

- Walter Childs

- Sgt. Major Riordan

- Caleb Sykes

- Roland Bailey

- Matthew Van Weyden

- All cast & crew
- Production, box office & more at IMDbPro
The Big List of Summer Movies

More like this

Did you know
- Trivia Kevin Costner 's first directorial effort since Open Range (2003) .
- Connections Featured in The Project: Episode dated 21 May 2024 (2024)
User reviews 5
- May 24, 2024
The 2024 Festival Films You Need to Know

- When will Horizon: An American Saga - Chapter 1 be released? Powered by Alexa
- June 28, 2024 (United States)
- United States
- Horizon: An American Saga
- New Line Cinema
- Territory Pictures Entertainment
- Warner Bros.
- See more company credits at IMDbPro
- $100,000,000 (estimated)
Technical specs
- Runtime 3 hours 1 minute
- Dolby Digital
- Dolby Atmos
Related news
Contribute to this page.

- See more gaps
- Learn more about contributing
More to explore

Recently viewed
site categories
Patton oswalt’s ‘parks and recreation’ rant was copied by disney’s ‘book of boba fett’, breaking news.
‘Horizon: An American Saga’ Review: Kevin Costner’s Chapter 1 (Of 4) Sets Stage For Epic Story Of American West And Its Complicated History – Cannes Film Festival
By Pete Hammond
Pete Hammond
Awards Columnist/Chief Film Critic
More Stories By Pete
- Cannes Film Festival 2024: All Of Deadline’s Movie Reviews
- 1964 Palme d’Or Winner ‘The Umbrellas Of Cherbourg’ Celebrates 60th In Cannes With Special Screening & Two New Documentaries – Cannes Film Festival
- ‘The Count Of Monte-Cristo’ Review: Sumptuous And Thrilling French Version Of Classic Revenge Tale Feels New All Over Again – Cannes Film Festival

Related Stories

Kevin Costner’s ‘Horizon: An American Saga’ Gets 11-Minute Ovation At Its Cannes World Premiere

Kevin Costner Reveals The Epic Journey Of His Cannes Western ‘Horizon’ And Has His Say On ‘Yellowstone’ Rancor
Running three hours, this film, scheduled for release by New Line and Warner Bros on June 28, is just “Chapter 1”, first of an unusual planned series of four separate films (not sequels) continuing the massive story, with Chapter 2 already in the can and scheduled for an August 16 release, and Chapter 3 reportedly going before the cameras imminently. Of course this multi-part saga is not unusual for television, where it thrives in the limited series form, but for movies it is virtually unheard of — along with the fact that its star/director, who has been dreaming of this in various forms since 1988, is largely footing the bill.
RELATED: ‘Horizon: An American Saga’ Cannes Film Festival Premiere Photos: Kevin Costner, Sienna Miller Luke Wilson & More
RELATED: ‘Furiosa: A Mad Max Saga’ Review: Chris Hemsworth And Anya Taylor-Joy Take Dystopian Franchise To New Levels
But nothing on this scale has ever been attempted for this kind of release pattern on the big screen, and I would say, at least based on the first part with its huge cast of characters and storylines woven in and out, Costner’s biggest influence may have in fact been 1963’s Cinerama production of How the West Was Won. I know from multiple interviews in the past, including mine, Costner has always noted the impact seeing that film (nominated for Best Picture and winner of three Oscars including Best Original Screenplay) with his father made a lifelong impression on him. It similarly traversed many years, characters and story arcs like Horizon does but was just one long, reserved seat movie event. Horizon has four times its spirit at the very least.
RELATED: Kevin Costner, Sienna Miller, Luke Wilson & Cast Talk ‘Horizon’: “We Can’t Be Consumed With Making Our Pile Of Money Bigger As Much As Our Heart Full” – Cannes Studio
Spanning about 15 years from the end of the Civil War (a factor but not the focus here), Horizon is about the expansion and settlement of the American West, those brave white people who made their way on horse and wagon trains to the promise of a new life. Literally. In the movie Horizon is the name of a basically suburban dream. Flyers are continually seen urging people to come West. “If you want a farm or home the best thing in the West is the town of Horizon. Best grazing land in the world, the richest land, premium virgin land with pure and abundant water, temperate climate, and excellent health,” it advertises to potential settlers.
What it doesn’t say is it is also the home of American Indians, our Native Americans, many who are understandably not too keen about this development on what they consider their territory, and that it could also be a dangerous proposition. But this is a film about Manifest Destiny, and therein will lie many of the complications for these (many) people we meet along the way. And of course in different parts of the world this concept makes this movie still relevant, even as it is told as a piece of our history.
It is clear from this Chapter 1 that Costner, who co-wrote the script with Jon Baird and a story from Mark Kasdan, is interested again in this conundrum with the Indigenous population, just as he was in Dances With Wolves in going for a much deeper and complex study than what Hollywood largely did for decades in its treatment of the American Indian on film. And coming on the heels of another film that premiered in Cannes last year, Martin Scorsese’s Killers of the Flower Moon, it will be interesting to see how it all plays out in the upcoming chapters . In this one the table is set and we meet a lot of the key players, with the emphasis on those white settlers who made their way west as the Civil War had ravaged the Union, but with the promise of changing times giving hope.
Chief among the settlers is Costner’s character, Hayes Ellison, a lone wolf type who would like to keep to himself but keeps getting drawn into things he would rather avoid. He has survival and fighting skills that will come in handy, especially in some confrontations with very bad guys who are making trouble, notably the outlaw Sykes family.
This is a huge cast, but Costner tries to get them all introduced here including the intriguing Sam Worthington character of First Lt. Trent Gephardt, a soldier stationed at Fort Gallant but a guy with questions about himself and where he is going in this new world. Danny Huston’s sympathetic Col. Houghton has his hands full with the emerging droves of settlers, but knows there will be no way to stop, or possibly protect them when they get to Horizon. And you can count in Michael Rooker’s Sgt Major Riordan, who has the same concerns at Gallant.
Others include Luke Wilson’s good but reluctant leader of a wagon train, chosen against his will but trying to live up to the challenge, and Will Patton, a widower still recovering from the Civil War and accompanying his three daughters for a better shot at life.
The Native Americans are authentically cast, as you might expect in any movie from the filmmaker of Dances With Wolves. Standouts include Owen Crow Shoe as Pionsenay, an Apache warrior who is confused and frustrated with clashes with the settlers and none too pleased at this development, as opposed to brother Taklishim (a fine Tatanka Means) who is siding with their father, the Chief, in trying to be non-confrontational. Liluye (an excellent Wase Winyan Chief) is also his wife and mother of their baby, but she seems to have more fortitude and actually believes they should, like her brother-in-law, be resisting the rise of the settlers rather than sitting idly by.
Giovanni Ribisi, Glynn Turman, Tom Payne, Kathleen Quinlan, Angus MacFayden and countless others also pop in and out, some with perhaps more to do in ensuing chapters. There are more than 170 speaking roles in the series which is being shot on locations in Utah, with stunning cinematography by J. Michael Muro who captures the grandeur of the Old West in style. Other shout-outs go to Derek R. Hill’s authentic production design and John Debney’s stirring score.
For Costner, this is an impressive beginning, with the promise of more to come. It even ends with a montage of scenes from the second film coming in August, much like you might see if this were a television production, something it is defiantly not. With Horizon: An American Saga, Costner is just trying to keep the American Western alive, but he may, with this innovative roll of the dice, also be trying to keep theaters alive at the same time, that is if there is still an appetite for Westerns. Hopefully there is.
Title: Horizon: An American Saga Distributor: Warner Bros Festival: Cannes (Out of Competition) Release date: June 28, 2024 Director: Kevin Costner Screenwriters: Kevin Costner, Jon Baird Cast: Kevin Costner, Sienna Miller, Sam Worthington, Jena Malone, Danny Huston, Luke Wilson, Michael Rooker, Will Patton, Owen Crow Shoe, Tatanka Means, Wase Winyan Chief, Jamie Campbell Bower, Isabelle Fuhrman, Jon Beavers Rating: R Running time: 3 hr 1 min
Must Read Stories
‘seed of the sacred fig’ premiere & review; un certain regard, doc awards.

Trump Files Cease & Desist To Halt Release Of ‘Apprentice’; Producers React
‘count of monte cristo’ producer on lessons learned & future plans, more sit-downs set for june as iatse & amptp continue contract talks.
Subscribe to Deadline Breaking News Alerts and keep your inbox happy.
Read More About:
15 comments.
Deadline is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Deadline Hollywood, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
‘Horizon: An American Saga — Chapter 1’ Review: Sprawling Yet Thinly Spread, the First Part of Kevin Costner’s Western Epic Feels Like the Set-Up for a TV Miniseries
It's set in 1859 and has a few vivid characters, from settlers to Native Americans, but the films jumps around too much and explains too little.
By Owen Gleiberman
Owen Gleiberman
Chief Film Critic
- ‘Ernest Cole: Lost and Found’ Review: Raoul Peck’s Documentary Rediscovers the Fearless Photographer of South African Apartheid 3 days ago
- ‘Armand’ Review: An Accusation at a Primary School Results in a Drama So Convoluted It’s Claustrophobic 4 days ago
- ‘The Shrouds’ Review: David Cronenberg Makes a Movie About Grief — and Body Horror, and Digital Gravestones — That in Its Somber Way Verges on Self-Parody 5 days ago

Arriving in the middle of the art smorgasbord that’s the Cannes Film Festival , a three-hour Western directed by Kevin Costner sounded like it might be just the ticket for a perfect night of counterprogramming: a grandly scaled slice of neo-classical Hollywood. That, after all, describes the other two Westerns Costner has directed (“Dances with Wolves” and “Open Range”), as well as his quirky sci-fi pseudo-Western “The Postman.” There’s no question that “ Horizon: An American Saga — Chapter 1 ,” Costner’s fourth outing as a director, gives off some of that traditional flavor.
Popular on Variety
And that feels like a major disappointment. As a stand-alone film (which it isn’t, but let’s pretend for a moment), “Horizon” is by turns convoluted, ambitious, intriguing, and meandering. But it’s never quite moving. It’s too busy laying down narrative tracks and hammering out the minutiae of situations that don’t feel like they’re leading anywhere special.
Costner, to his credit, wants to nudge the Western away from a white hat/black hat mythology that’s now outdated. He wants shades of gray, and characters we can’t pigeonhole as heroes or villains (though there are a few of those). But too often the action feels hurried, both overstaged and underscripted. One of the key locales is the settlement of Horizon, advertised on handbills — a place that’s not quite a place yet, because when people show up to settle there they tend to get killed by the local Apache. We see an Apache raid that ends up in apocalyptic fire, and experience it from inside the home of Frances Kittredge ( Sienna Miller ) and her daughter, Elizabeth (Georgia MacPhail), the two of whom hide in a hole under the living room, which is so airtight that they have to poke a rifle out of the ground and use the gun barrel as a breathing tube. That’s a vivid detail, and then Frances loses her husband and son. But it’s jarring to take this all in before we’ve even had a sense of who this family is.
The Native characters are the attackers, but we see several extended scenes from their point-of-view. They are never “the other,” the simple enemy. That said, there are two speeches in the movie, one by an Apache war chief (Gregory Cruz) and one by a U.S. cavalry officer (Danny Huston), that address the fundamental issue of the Indigenous tribes trying to stop what they call the “white-eye” settlers who’ve invaded their land. And both speeches, weirdly, make the same point: that even if the Native people are justified, and even if they keep trying to fight the settlers, they’re doomed to lose. The settlers will keep coming. History is not on the Natives’ side. This seems an awfully definitive vision to hold in 1859. And while Costner doesn’t seem unsympathetic to his Native characters, it’s not clear, as of now, how much they’ll take on a life of their own.
There are also scenes set on a covered-wagon trail that center on the Proctors, an effete English couple who’ve joined the Westward movement. They have a very naïve and almost charmingly entitled attitude (they don’t realize that they have to work, too — that the other settlers are not their servants), but Matthew Van Weyden, the leader of the wagon train, sets them straight. He’s played by Luke Wilson, who is very good, shaking off any semblance of his usual irony. Meanwhile, Frances and her daughter wind up being taken care of at a U.S. Army encampment, where First Lieutenant Trent Gephart (Sam Worthington) attracts Frances’ attention by being both handsome and too gentlemanly for his own good.
A few of these characters are interesting; none of them are memorable. “Horizon” is no “Lonesome Dove,” though Costner tries, and mostly succeeds, at setting aside Western clichés about what towns really looked like, and how frontier life worked. The real problem is the script (by Costner and Jon Baird), which is shapeless. It doesn’t weave these stories together; it stacks them next to each other like a series of cabooses. Yet I think the idea is that the design of it all will come into focus as we see “Horizon: An American Saga — Chapter 2” (later this year), and then, at some point, “Chapter 3” (which is now scheduled) and maybe, if all goes according to plan, more chapters. I seriously hope not. I’m not sure how much juice there is to squeeze out of these characters, but even if there is some I don’t want to see movies turn into television. Just about every Western of the studio era came in at two hours or less, and so did most of the revisionist Westerns (and some of those were complicated ). There’s a reason for that. It’s all the time they needed.
Reviewed at Cannes Film Festival (Out of Competition), May 19, 2024. MPAA Rating: R. Running time: 181 MIN.
- Production: A Warner Bros. Pictures release of a New Line Cinema, Territory Pictures production. Producers: Kevin Costner, Howard Kaplan, Mark Gillard. Executive producers: Robert J. Scannell, Danny Peykoff, Marc DeBevoise, Armyan Bernstein, Rod Lake, Charlie Lyons, Barry M. Berg.
- Crew: Director: Kevin Costner. Screenplay: Jon Baird, Kevin Costner. Camera: J. Michael Muro. Editor: Miklos Wright. Music: John Debney.
- With: Kevin Costner, Sienna Miller, Sam Worthington, Jena Malone, Owen Crow Shoe, Tatanka Means, Ella Hunt, Tim Guinee, Giovanni Ribisi, Danny Huston, Colin Cunningham, Scott Haze, Tom Payne, Abby Lee, Michael Rooker, Will Patton.
More From Our Brands
See rush’s geddy lee and alex lifeson cover gordon lightfoot song at toronto tribute concert, dodgers star shohei ohtani scores a socal estate for $7.8 million, juan soto open to all suitors, but few teams can afford him, the best loofahs and body scrubbers, according to dermatologists, lanterns: damon lindelof among writers of dc’s green lantern series, james gunn confirms, verify it's you, please log in.
Is Fortnite down? What to know about the update to Chapter 5 Season 3, 'Wrecked'
Fortnite servers are offline Friday morning as the game updates to version 30.00, or Chapter 5, Season 3.
Here's what we know.
When will Fortnite servers be back up?
According to Epic Games , Fortnite is offline for scheduled maintenance. Servers are expected to be back online at 8 a.m. ET.
According to Downdetector, which tracks internet outages based on user submissions, less than 100 people are reporting issues as of about 6:30 a.m. Reports peaked with 345 outages at about 2 a.m.
What's new in Fortnite Chapter 5 Season 3, 'Wrecked'
The latest season gives "serious apocalypse vibes," according to Esports.gg , and brings with it the return of modable vehicles along with new weapons, new locations and new Medallions, among others.
Men's Journal says the new season brings the Wrecked Battle Pass, focused on the Wasteland Warriors. New locations include a new biome called the wasteland, "after a big sandstorm rolled through and transformed the area into a Mad Max-inspired sandscape."
Cookie banner
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our site, show personalized content and targeted ads, analyze site traffic, and understand where our audiences come from. To learn more or opt-out, read our Cookie Policy . Please also read our Privacy Notice and Terms of Use , which became effective December 20, 2019.
By choosing I Accept , you consent to our use of cookies and other tracking technologies.
Follow The Ringer online:
- Follow The Ringer on Twitter
- Follow The Ringer on Instagram
- Follow The Ringer on Youtube
Site search
- Diss Track Rankings
- What to Watch
- Bill Simmons Podcast
- 24 Question Party People
- 60 Songs That Explain the ’90s
- Against All Odds
- Bachelor Party
- The Bakari Sellers Podcast
- Beyond the Arc
- The Big Picture
- Black Girl Songbook
- Book of Basketball 2.0
- Boom/Bust: HQ Trivia
- Counter Pressed
- The Dave Chang Show
- East Coast Bias
- Every Single Album: Taylor Swift
- Extra Point Taken
- Fairway Rollin’
- Fantasy Football Show
- The Fozcast
- The Full Go
- Gambling Show
- Gene and Roger
- Higher Learning
- The Hottest Take
- Jam Session
- Just Like Us
- Larry Wilmore: Black on the Air
- Last Song Standing
- The Local Angle
- Masked Man Show
- The Mismatch
- Mint Edition
- Morally Corrupt Bravo Show
- New York, New York
- Off the Pike
- One Shining Podcast
- Philly Special
- Plain English
- The Pod Has Spoken
- The Press Box
- The Prestige TV Podcast
- Recipe Club
- The Rewatchables
- Ringer Dish
- The Ringer-Verse
- The Ripple Effect
- The Rugby Pod
- The Ryen Russillo Podcast
- Sports Cards Nonsense
- Slow News Day
- Speidi’s 16th Minute
- Somebody’s Gotta Win
- Sports Card Nonsense
- This Blew Up
- Trial by Content
- Wednesday Worldwide
- What If? The Len Bias Story
- Wrighty’s House
- Wrestling Show
- Latest Episodes
- All Podcasts
Filed under:
- Pop Culture
Kevin Costner Wills His Own ‘Yellowstone’ Into Existence With ‘Horizon: An American Saga’
Going full Francis Ford Coppola and producing an epic passion project at great cost to himself, Costner attempts a classical Western that could use a modern update
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Kevin Costner Wills His Own ‘Yellowstone’ Into Existence With ‘Horizon: An American Saga’
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73367693/HorizonAAS_WarnerBrosPictures_Ringer.0.jpg)
There might not be a more appropriate and straightforward way to open an American Western than with a scene of a white settler tracing the foundations of the house he wants to build on some seemingly available plot of land. The colonial question at the heart of the genre is thus immediately introduced in Horizon: An American Saga—Chapter 1 , the first film in Kevin Costner’s epic four-movie series (the second installment has already been shot) that he produced ( at great cost to himself ), cowrote, directed, and starred in. Costner’s perspective on that question, however, isn’t entirely clear in that opening sequence, but it does end with the settler and his young child being killed by Apaches who are defending their territory, highlighting their rightful anger. In this sequence, a rousing old-fashioned score, plenty of cross-fades, and an orange sunset give the brutal encounter the look of a monumental, foundational, almost elemental event, like a big bang—a natural, terribly meaningful catastrophe.
The Ringer ’s Streaming Guide

There’s a lot of TV out there. We want to help: Every week, we’ll tell you the best and most urgent shows to stream so you can stay on top of the ever-expanding heap of Peak TV.
It is through such small yet symbolic stories that Costner starts to paint his very large and detailed picture of pre– and post–Civil War America. Jumping from one setting to another, the filmmaker introduces us to various archetypes of the American West, from the English settlers too posh and sophisticated to do any work while traveling on the Santa Fe Trail (Ella Hunt and Tom Payne), to the housewife with a dark secret (Jena Malone) and her naive husband (Michael Angarano) hoping to get rich through gold, to the foulmouthed sex worker (Abbey Lee) whom everyone despises, except for the hero (Costner, naturally), who finds himself protecting her. In a series of extended vignettes, their personal dramas unfold and sometimes intersect, with occasional time jumps to speed things up and show the consequences of their decisions. None of these stories are particularly original or compelling, retreading old tropes and recalling television both visually and structurally. (It’s hard not to think of Yellowstone , the Western series starring Costner; it was during that show’s hiatus that he made this film.) For instance, the past of the housewife, Ellen, comes back to haunt her when we learn that she once was a sex worker herself and killed a powerful criminal who had abused her: The idea that the Wild West allowed for self-reinvention but was also fueled by the exploitation of women is a staple of the genre—and could still be interesting to explore—but Costner struggles to keep all his plates spinning at once, offering only a quick glance at one prototypical story before moving on to the next one. Instead of making us feel the unbearable weight of history through this amalgamation of survival tales—or creating at least a sense of time and place—this first “episode” indeed functions as a technically efficient but not very appealing series pilot, setting the scene but not giving its protagonists enough room for us to get invested in them.
Making an American Western in 2024 means coming after a long line of films, the first succession of which established the genre’s often white supremacist and pro-colonial codes. Later, revisionist Westerns adapted these tropes to suit different eras, taking into account changing mentalities about the romanticization of America’s violent past and materialistic tendencies (think of The Wild Bunch and its explosive, balletic, devastating gunfights, or the spaghetti Western For a Few Dollars More ), and, eventually, the oppressed were put at the center of the narrative, be they women or Indigenous people themselves. ( Killers of the Flower Moon is the most recent example, but Soldier Blue from 1970 may be the most strident.) Costner, however, doesn’t seem all that interested in looking back with a critical eye, and he’s also not trying to tell a story about the past that could be relevant today. Instead, he’s aiming for the timelessness of myth and adopts a centrist approach: Colonialism was an unstoppable engine that everyone, Indigenous or white, was simply caught up in. After a deadly Apache attack, First Lieutenant Trent Gephardt (Sam Worthington, who seems determined to act in projects that will be made over several years or decades of his life ) has to remind the surviving white settlers that this land is not, in fact, simply where they live, but that it belongs to Indigenous people; still, the pioneers refuse to leave. Costner spends time on the unwelcome inhabitants and their sorrow and helplessness but also cuts to the Apaches—they, too, are having internal disagreements about whether this attack was ultimately necessary. Yet if these two points of view could allow for some interesting ambiguity, revealing the moral dilemmas and doubts of people on both sides, in Costner’s vision, the two parties are stuck in a dynamic that is completely outside their control and has a will of its own—rather than one born of the colonizers’ endless thirst for more land. (Costner’s production company is in fact called Territory Pictures Entertainment.) No one is really responsible. Playing a blasé colonel, Danny Huston puts it bluntly: “Let this place do what it’s done since time immemorial.” But isn’t this time still relatively fresh in the Apaches’ memory?
This idea of a manifest destiny that pushes for colonization, whether its participants approve of it or not, appears as much in the film’s aesthetics as it does in its narrative. Costner’s camera repeatedly focuses on and emphasizes old-fashioned and at times offensive clichés of the genre: a dying white man refusing to let an Apache take his violin, thus defending civilization against barbarism until his last breath; a priest solemnly digging graves for fallen pilgrims on Apache ground; men working hard to build infrastructure where there was once only nature; a teenage son choosing to fight back against the Indigenous alongside his father rather than hiding with his mother and sister. To quote Vampire Weekend : “Untrue, unkind, and unnatural, how the cruel, with time, becomes classical.” If his old-school conservatism wasn’t apparent enough, the filmmaker also gives his actors cheesy dialogue that even John Wayne couldn’t have made cool. (“It’s what drove us across the ocean to this country in the first place: hope.”) Whether they’re full of threat or flirtatious (as between Sienna Miller’s widow, Frances Kittredge, and Gephardt), conversations tend to be tedious exchanges of witty comebacks, with no one saying what they really mean until they’ve exhausted all possible innuendos and the scene just cries out for a resolution—an unintentional parody of the typically charming repartee of the best cowboys of the silver screen, from Wayne to Jimmy Stewart to Montgomery Clift. So far in the film series, only Luke Wilson and Michael Rooker come across as believable men of the time, the former thanks to his Southern drawl and natural ease, the latter because of his ability to find depth and emotion in the otherwise one-dimensional, obedient, and kind sergeant he must play.
But what about Costner the actor? Naturally, he plays the strong, silent type—always his strongest suit—as Hayes Ellison, a straight shooter who accidentally gets involved in the revenge campaign that threatens Ellen because of her past rebellion. Although he only appears after about an hour of exposition, the humility of that delay vanishes almost instantaneously. As he gets off his horse, Marigold (the sex worker played by Lee) lays eyes on him and, for no apparent reason other than the fact that he’s the film’s protagonist, decides to try seducing him again and again—despite his repeated rejection and almost offensive disinterest—instead of trying her luck with any of the other men who just got into town. In one of the film’s most successful and enjoyable scenes, however, Ellison lets Marigold do all the talking, his silence pushing her to almost turn double entendres into just plain sex talk. Here, Lee is showing much more range and playfulness than she’s ever had the chance to as an actress, so it’s particularly disappointing that Costner later gives the two of them a completely lifeless and preposterous sex scene in which she tells him, word for word, “You just lay there,” and he does so, looking almost bored as this beautiful woman half his age does all the work.
With its hubris, traditionalism, and sprawling, messy structure, Horizon feels like a relic of the 1990s, back when Costner was at his peak and he could indeed almost just lay there and be perceived as the masculine ideal. There is still a chance that Chapter 2 will reveal a deeper questioning of the American past and, by the same token, the more toxic aspects of masculinity tied to colonialism and violence. Still, considering how far and with how much conviction Costner has pushed it here, it seems unlikely that the cheesy style of this opus will be abandoned for something that’s more grounded and that spends less time glorifying both its star and conservative ideas of property, national identity, women, and progress. After all, the horizon always appears to stay at the same place.
Next Up In Movies
Everyone hates ticketmaster, but is it a monopoly, ‘furiosa: a mad max saga’.
- ‘Furiosa’ Is Here! Witness It!
- Netflix’s Plan for ‘3 Body Problem,’ Apple Music’s 100 Best Albums, and ‘Top Chef’
- Mallory Rubin on ‘Avengers: Endgame’
- ‘Furiosa: A Mad Max Saga’ Is All Muscle Memory
Sign up for the The Ringer Newsletter
Thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.

Luka Doncic Broke Down the Wolves. Then He Ripped Their Hearts Out.
The Dallas Mavericks star finished Game 2 with a stone-cold game-winner. But he won it with every pass, drive, and read that came before.

Are Luka and Kyrie the Best Duo in the NBA? Plus, Reminiscing on LeBron’s Best Years.
Austin and Pausha also discuss the Pacers’ Game 2 loss and the dominant Tatum-Brown duo

RANGERS TIE THE SERIES AT 1
JJ recaps the Rangers’ 2-1 win over the Florida Panthers, plus hot Yankees bats and Mets struggles

Something About Her Finally Opens! Plus ‘Summer House’ and ‘The Valley.’
Rachel Lindsay and Jodi Walker also talk the torso-themed ‘Summer House’ reunion looks, Amir’s demand that his girlfriend be part of Summer House: Martha’s Vineyard, and Something About Her’s grand opening

Matt is joined by Puck’s Eriq Gardner to discuss the U.S. government’s monopoly lawsuit against Ticketmaster and Live Nation

The Midnight Boys return to the wasteland and dive into their thoughts on the madcap epic that is ‘Furiosa: A Mad Max Saga’

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How To Structure Your Literature Review. Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components - an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Let's take a closer look at each of these. 1: The Introduction Section
The Review must include the following (this is a ready-made outline): 1. Introduction and thesis: In the introduction summarize the topic of the chapter and tell how it relates to this course. Also state the thesis of the chapter—the author's primary point/conclusions in the chapter. 2.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The key here is to focus first on the literature relevant to the puzzle. In this example, the tokenism literature sets up a puzzle derived from a theory and contradictory empirical evidence. Let's consider what each of these means... The literature(s) from which you develop the theoretical/empirical puzzle that drives your research question.
If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you've come to the right place.. In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction.We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template.
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review can be quite short (5% of a paper) or quite long (30% of a paper) depending on the type of paper. For a thesis/dissertation, a literature review may be a full chapter, and is usually at least 10-20% of your paper.
First, remember that this is the first chapter, and you can use it to "sell" your research story to the reader of your dissertation. Crafting a snappy, interesting introduction, and putting effort into explaining the rationale of the study is key to creating this interest in your readers. Fig. 6.1.
Chapter 2: The Literature Review . A literature review is a section of your thesis or dissertation in which you discuss previous research on your subject. Following your Chapter 1, your literature review begins as you try to answer your larger research question: Who has looked at what, why, and what have they found? ...
Chapter 1. A Complete Dissertation 7 purpose, or it does not stand alone as a document. Chapter 2: Literature Review This chapter situates the study in the con-text of previous research and scholarly mate - rial pertaining to the topic, presents a critical synthesis of empirical literature according to relevant themes or variables, justifies how
Chapter Summary in Thesis. In a Thesis, the Chapter Summary is a section that provides a brief overview of the main points covered in each chapter of the thesis. It is usually included at the beginning or end of each chapter and is intended to help the reader understand the key concepts and ideas presented in the chapter. ... Useful for review ...
Slide 1. Mainly Chapter 2 of a doctoral dissertation. An exhaustive exposition of the literature sources (especially methods and findings) that a researcher consulted in order to understand and investigate his or her research problem. Built from the annotated bibliography assignment (#4) from the Methods of Inquiry (MOI) course.
Every chapter that you have written so far has a base of some sort. The literature review is the theoretical base for your research project. Based on previous research, you built an argument that details why your research is worth performing, you may have identified gaps in knowledge, and you constructed an aim, objectives, and hypotheses.
Example: Mix of different constructions Chapter 2 contains a review of the relevant literature that I used for the purposes of this paper. The methods used in the study are then described in Chapter 3, after which the results are presented and discussed in Chapter 4. Sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline
17. CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW. There is substantial research on STEM and women, in large part due to studies that the U.S. government has funded, and continues to fund, including substantive data collection related to recruiting women into STEM professions and the barriers to progress. The majority of published works include a focus toward ...
Chapter 2 covers the literature review. It provides a detailed analysis of the theory/conceptual framework used in the study. In addition, chapter 2 offers a thorough synthesis of the available, current, scholarly literature on all aspects of the topic, including all points of view.
PhD thesis literature review chapter introduction . The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester. In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis).The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others, "standing on the shoulders of giants", as Newton put it.The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.. Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure ...
A thesis is built up of a series of chapters that construct a substantiated and convincing response to the research question (s). Typically, a thesis contains the following chapters: an introduction; a literature review; a description of methodology; a report and discussion of results; and a conclusion. A thesis may have five to eight chapters ...
CHAPTER 2: Literature Review. This chapter will explore the literature that is relevant to understanding the development of, and interpreting the results of this convergent study. The first two parts of this review of the literature will describe two types of research: research on teaching and research on teachers' conceptions.
Sue's example illustrates that carrying out a comprehensive literature review is a required step in any research project. First, a researcher cannot conduct the study. 1. without gaining a deep understanding of the research topic and learning from the work of other scholars and researchers in the field (Creswell, 2018).
The payoff was a gut punch. On its face, "The Strangers: Chapter 1," the first of three new films in a "Strangers" reboot from the director Renny Harlin (" A Nightmare on Elm Street 4 ...
Horizon: An American Saga - Chapter 1: Directed by Kevin Costner. With Kevin Costner, Abbey Lee, Sienna Miller, Dale Dickey. Chronicles a multi-faceted, 15-year span of pre-and post-Civil War expansion and settlement of the American west.
With Horizon: An American Saga, Costner is just trying to keep the American Western alive, but he may, with this innovative roll of the dice, also be trying to keep theaters alive at the same time ...
'Horizon: An American Saga — Chapter 1' Review: Sprawling Yet Thinly Spread, the First Part of Kevin Costner's Western Epic Feels Like the Set-Up for a TV Miniseries
Fortnite servers are offline Friday morning as the game updates to version 30.00, or Chapter 5, Season 3. Here's what we know. According to Epic Games, Fortnite is offline for scheduled ...
Now, it appears Furiosa: A Mad Max Saga is going to underperform as well, coming in well below the $40-45 million projections ahead of summer. Furiosa appears headed for a finish barely north of ...
Kevin Costner Wills His Own 'Yellowstone' Into Existence With 'Horizon: An American Saga'. Going full Francis Ford Coppola and producing an epic passion project at great cost to himself ...