

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Prospective Students
- Postgraduate Study
- Department of Sociology
- Our History
- Job Vacancies
- Green Team overview
- Everyday Tips for the Office
- Environmental Action Plan
- Green Travel
- Green Cambridge
- Green Seminar Series
- Alumni overview
- Help support the Department of Sociology
- Alumni Benefits
- Alumni Events
- Academic Staff
- Affiliated Staff
- Postdoctoral and Research Staff
- Postgraduate Students
- Emeritus Academics
- Administrative Staff overview
- Paulina Baltsoukou
- Lara Gisborne
- Lucy O'Connor
- Lisa Watson
- Abigail Youngman
- Yvonne Frankfurth
- Yvonne Martin-Portugues
- Ellen Munnelly
- Lucian Stephenson
- Undergraduates overview
- Part I overview
- Supervisions
- One-Year Part II
- Undergraduate Teaching FAQs
- Postgraduates overview
- Library Services
- Resources & Training
- Support & Wellbeing
- Cambridge University Sociology Society (SocSoc)
- Generative AI and your learning
- Why study Sociology?
- Undergraduate Study overview
- Course Structure
- Applying to Sociology
- Fees and Funding
- Guidance for Teachers
- Preparing for Interview
- Student Testimonials
- Support and Services
- Postgraduate Study overview
- Choosing a Supervisor
- Applications overview
- Postgraduate FAQs
Visiting Scholars
- Outreach & Open Days
- Y10-13 Photography Competition
- Events overview
- News overview
- Decolonise Sociology ↗
- Applications
- Undergraduate Study

PhD in Sociology
The PhD in Sociology offers a world-class programme of research study in sociology supervised by experts in their respective fields. The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2024 . And the QS World University rankings list our departments as 2nd out of over 500 Sociology Departments across the world in 2023.
In the first year you are encouraged to take research methods courses offered by the Department and the Social Science Research Methods Programme (SSRMP) to build the methodological grounding of your individual research projects.
The Department also offers a programme of seminars covering transferable skills such as academic writing, presentation skills and in-depth information about how to progress the PhD and the academic career. PhD students are supported by their supervisor and a faculty adviser.
Watch our open day video
The Programme
The course aims to provide all students with the skills they need to be professional researchers and academics. There is an organised programme of courses for first-year PhD students, which has three major components:
- Basic academic and research skills, designed to provide the essential tools of academic work
- The core training programme, which covers issues of social science research in general
- Issues of research specific to particular disciplines or areas of interest, and research design, including the integration of methodological, theoretical and substantive issues
The standard period for PhDs is 3-4 years full-time or 5-7 years part-time. Click here for further information about part-time PhD studies .
Meet our Candidates
What you can do with your phd.
Students who complete graduate programmes in Sociology have the opportunity to develop the analytical and writing skills to help them succeed in academia but also in careers such as health and social care, marketing and public relations, politics, and education, amongst others.
Postgraduate Prospectus

The PG prospectus details all the courses on offer at Cambridge, as well as introducing the different Colleges and describing the admissions process.
The Department of Sociology University of Cambridge Free School Lane Cambridge CB2 3RQ
Tel: 01223 (3)34520
Contact: [email protected]
Privacy notice & cookie policies.
Website Updates
Profile Update Form
Research Project Form
Event Promotion Form
Tweet Request Form
Useful Information
Annual Reports
Equipment for Loan
Digital Editorial Guidelines
IT Services Guide
twitterrrr.png

facebook_logo_square.png

117156_media_512x512.png

768px-youtube_play_button_square_2013-2017.svg_.png
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
Our cookies
We use cookies for three reasons: to give you the best experience on PGS, to make sure the PGS ads you see on other sites are relevant , and to measure website usage. Some of these cookies are necessary to help the site work properly and can’t be switched off. Cookies also support us to provide our services for free, and by click on “Accept” below, you are agreeing to our use of cookies .You can manage your preferences now or at any time.
Privacy overview
We use cookies, which are small text files placed on your computer, to allow the site to work for you, improve your user experience, to provide us with information about how our site is used, and to deliver personalised ads which help fund our work and deliver our service to you for free.
The information does not usually directly identify you, but it can give you a more personalised web experience.
You can accept all, or else manage cookies individually. However, blocking some types of cookies may affect your experience of the site and the services we are able to offer.
You can change your cookies preference at any time by visiting our Cookies Notice page. Please remember to clear your browsing data and cookies when you change your cookies preferences. This will remove all cookies previously placed on your browser.
For more detailed information about the cookies we use, or how to clear your browser cookies data see our Cookies Notice
Manage consent preferences
Strictly necessary cookies
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and cannot be switched off in our systems.
They are essential for you to browse the website and use its features.
You can set your browser to block or alert you about these cookies, but some parts of the site will not then work. We can’t identify you from these cookies.
Functional cookies
These help us personalise our sites for you by remembering your preferences and settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers, whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, then these services may not function properly.
Performance cookies
These cookies allow us to count visits and see where our traffic comes from, so we can measure and improve the performance of our site. They help us to know which pages are popular and see how visitors move around the site. The cookies cannot directly identify any individual users.
If you do not allow these cookies we will not know when you have visited our site and will not be able to improve its performance for you.
Marketing cookies
These cookies may be set through our site by social media services or our advertising partners. Social media cookies enable you to share our content with your friends and networks. They can track your browser across other sites and build up a profile of your interests. If you do not allow these cookies you may not be able to see or use the content sharing tools.
Advertising cookies may be used to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant adverts on other sites. They do not store directly personal information, but work by uniquely identifying your browser and internet device. If you do not allow these cookies, you will still see ads, but they won’t be tailored to your interests.
PhD in Sociology
University of cambridge, different course options.
- Key information
Course Summary
Tuition fees, entry requirements, similar courses at different universities, key information data source : idp connect, qualification type.
PhD/DPhil - Doctor of Philosophy
Subject areas
Course type.
The PhD in Sociology offers a world-class programme of a research study in sociology supervised by world-renowned experts in their fields.
The course aims to provide all students with the skills they need to be professional researchers and academics. There is an organised programme of courses for first-year PhD students, which has three major components: Basic academic and research skills, designed to provide the essential tools of academic work. The core training programme, which covers issues of social science research in general; Issues of research specific to particular disciplines or areas of interest, and research design, including the integration of methodological, theoretical and substantive issues.
You will be expected to participate fully in the core training programme, and in the departmental seminar series. At the beginning of your third term, your progress is examined on the basis of a 10,000-word piece of written work to determine whether you can proceed to a full programme of PhD research.
Part-time PhD studies are possible for home/EU students only. Part-time applicants must contact a potential supervisor before applying.
UK fees Course fees for UK students
For this course (per year)
International fees Course fees for EU and international students
Applicants for this course should have achieved a UK Masters (Merit).
Criminology with Forensic Psychology MSc
Middlesex university, criminology ma, ma applied criminology, youth and criminal justice, ma in criminal justice and crime control, university of hull, phd sociology and anthropology and gender studies.

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges and Departments
- Email and phone search
- Give to Cambridge
- Museums and collections
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Postgraduate events
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
Topic description and stories

Tales from the edge of modern fertilities
A major research project sees sociologists situated at emerging hot spots of reproductive change, investigating the new ‘haves and have-nots’ in our...

'Lab in your phone' lets you play the scientific life
A unique, free new game – “part Sims, part Tamagotchi” – lets players inhabit a stem cell researcher as they rise through the ranks: growing cells...
Postgraduate Pioneers 2017 #4
With our Postgraduate Open Day fast-approaching (3 November), we introduce five PhD students who are already making waves at Cambridge.

'Precarious scheduling' at work affects over four million people in UK – far more than just zero-hours
Analysis of EU survey data suggests millions in UK may suffer anxiety as a result of unpredictable management-imposed flexible working hours...

Database protecting UK migrants in EU from Brexit ‘misinformation’ to be built by Cambridge researchers
Urgent requirement for channels of timely and reliable information to be developed targeting UK-born people living on the continent, say researchers...
Where the river meets the sea: the making of ethical decisions
What is our place in the natural world – and how do we feel about the scientific advances that are changing the way we live? In her book Making a...

Financial cycles of acquisitions and ‘buybacks’ threaten public access to breakthrough drugs
An analysis of a new drug’s journey to market, published today in the BMJ, shines a light on financial practices that see some major pharmaceutical...

Study finds little change in the IMF’s policy advice, despite rhetoric of reform
Researchers describe IMF as having an “escalating commitment to hypocrisy”, as study reveals that strict lending conditions have returned to pre-...

Flexible hours 'controlled by management' cause stress and damage home lives of low-paid workers
Researcher Alex Wood calls on new DWP Minister Stephen Crabb to acknowledge distinction between flexible scheduling controlled by managers to...

Predicting gentrification through social networking data
Data from location-based social networks may be able to predict when a neighbourhood will go through the process of gentrification, by identifying...

Opinion: Here’s how tweets and check-ins can be used to spot early signs of gentrification
Desislava Hristova (Computer Laboratory) discusses how data from location-based social networks can be used to predict when a neighbourhood will go...

IMF lending undermined healthcare provision in Ebola-stricken West Africa
Researchers criticise reforms advocated by IMF for chronically under-funded and insufficiently staffed health systems in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra...

Connect with us

© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility statement
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Cambridge University Press & Assessment
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Land use changes in the environs of Moscow

Related Papers
Eurasian Geography and Economics
Grigory Ioffe
komal choudhary
This study illustrates the spatio-temporal dynamics of urban growth and land use changes in Samara city, Russia from 1975 to 2015. Landsat satellite imageries of five different time periods from 1975 to 2015 were acquired and quantify the changes with the help of ArcGIS 10.1 Software. By applying classification methods to the satellite images four main types of land use were extracted: water, built-up, forest and grassland. Then, the area coverage for all the land use types at different points in time were measured and coupled with population data. The results demonstrate that, over the entire study period, population was increased from 1146 thousand people to 1244 thousand from 1975 to 1990 but later on first reduce and then increase again, now 1173 thousand population. Builtup area is also change according to population. The present study revealed an increase in built-up by 37.01% from 1975 to 1995, than reduce -88.83% till 2005 and an increase by 39.16% from 2005 to 2015, along w...
Elena Milanova
Land use/Cover Change in Russia within the context of global challenges. The paper presents the results of a research project on Land Use/Cover Change (LUCC) in Russia in relations with global problems (climate change, environment and biodiversity degradation). The research was carried out at the Faculty of Geography, Moscow State University on the basis of the combination of remote sensing and in-field data of different spatial and temporal resolution. The original methodology of present-day landscape interpretation for land cover change study has been used. In Russia the major driver of land use/land cover change is agriculture. About twenty years ago the reforms of Russian agriculture were started. Agricultural lands in many regions were dramatically impacted by changed management practices, resulted in accelerated erosion and reduced biodiversity. Between the natural factors that shape agriculture in Russia, climate is the most important one. The study of long-term and short-ter...
Annals of The Association of American Geographers
Land use and land cover change is a complex process, driven by both natural and anthropogenic transformations (Fig. 1). In Russia, the major driver of land use / land cover change is agriculture. It has taken centuries of farming to create the existing spatial distribution of agricultural lands. Modernization of Russian agriculture started fifteen years ago. It has brought little change in land cover, except in the regions with marginal agriculture, where many fields were abandoned. However, in some regions, agricultural lands were dramatically impacted by changed management practices, resulting in accelerating erosion and reduced biodiversity. In other regions, federal support and private investments in the agricultural sector, especially those made by major oil and financial companies, has resulted in a certain land recovery. Between the natural factors that shape the agriculture in Russia, climate is the most important one. In the North European and most of the Asian part of the ...
Ekonomika poljoprivrede
Vasilii Erokhin
Journal of Rural Studies
judith pallot
In recent decades, Russia has experienced substantial transformations in agricultural land tenure. Post-Soviet reforms have shaped land distribution patterns but the impacts of these on agricultural use of land remain under-investigated. On a regional scale, there is still a knowledge gap in terms of knowing to what extent the variations in the compositions of agricultural land funds may be explained by changes in the acreage of other land categories. Using a case analysis of 82 of Russia’s territories from 2010 to 2018, the authors attempted to study the structural variations by picturing the compositions of regional land funds and mapping agricultural land distributions based on ranking “land activity”. Correlation analysis of centered log-ratio transformed compositional data revealed that in agriculture-oriented regions, the proportion of cropland was depressed by agriculture-to-urban and agriculture-to-industry land loss. In urbanized territories, the compositions of agricultura...
Open Geosciences
Alexey Naumov
Despite harsh climate, agriculture on the northern margins of Russia still remains the backbone of food security. Historically, in both regions studied in this article – the Republic of Karelia and the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) – agricultural activities as dairy farming and even cropping were well adapted to local conditions including traditional activities such as horse breeding typical for Yakutia. Using three different sources of information – official statistics, expert interviews, and field observations – allowed us to draw a conclusion that there are both similarities and differences in agricultural development and land use of these two studied regions. The differences arise from agro-climate conditions, settlement history, specialization, and spatial pattern of economy. In both regions, farming is concentrated within the areas with most suitable natural conditions. Yet, even there, agricultural land use is shrinking, especially in Karelia. Both regions are prone to being af...
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Former UCD Ph.D. elected into the National Academy of Science
- by Joanna I Kaminski
- May 10, 2024

School of Criminology
In memory of Robert M. Gordon
- Administration and Staff
- Criminology Faculty
- Applied Legal Studies Faculty
- Adjunct Professors & Associate members
- Emeritus & retired faculty
- In Memoriam
- Visiting Faculty & Term Lecturers
- Director's Welcome
- Why study criminology
- Honours Program
- Post Baccalaureate Diploma Programs
- Second Degree Option
- Directed Readings and Directed Studies
- Application Process
- Placement Opportunities
- Guidelines for Field Placement Descriptions
- Responsibility of the Agency Field Supervisor
- Advising FAQ
- Contact an Advisor
- Sample Course Plan A (3 Term)
- Sample Course Plan B (2 Term)
- Sample Course Plan C (Lighter Option)
- Program Completion Check Sheets
- Alumni Testimonials
- Graduate Director's Welcome
- Faculty & Administration
- Program Overview
- BC Notaries Public
- Research group
- Alumni Profiles
- Graduate Students' Association
- MA Students
- PHD Students
- Upcoming Thesis Defence
- Research Clusters
- Institute & Centres
- Research Connections
- Presentations & Videos
- Student Association (CSA)
- Publications
- The Founding Family
- Annual Forum
- Annual Lecture and Dialogue Series
- The Ting Ocassional Forums
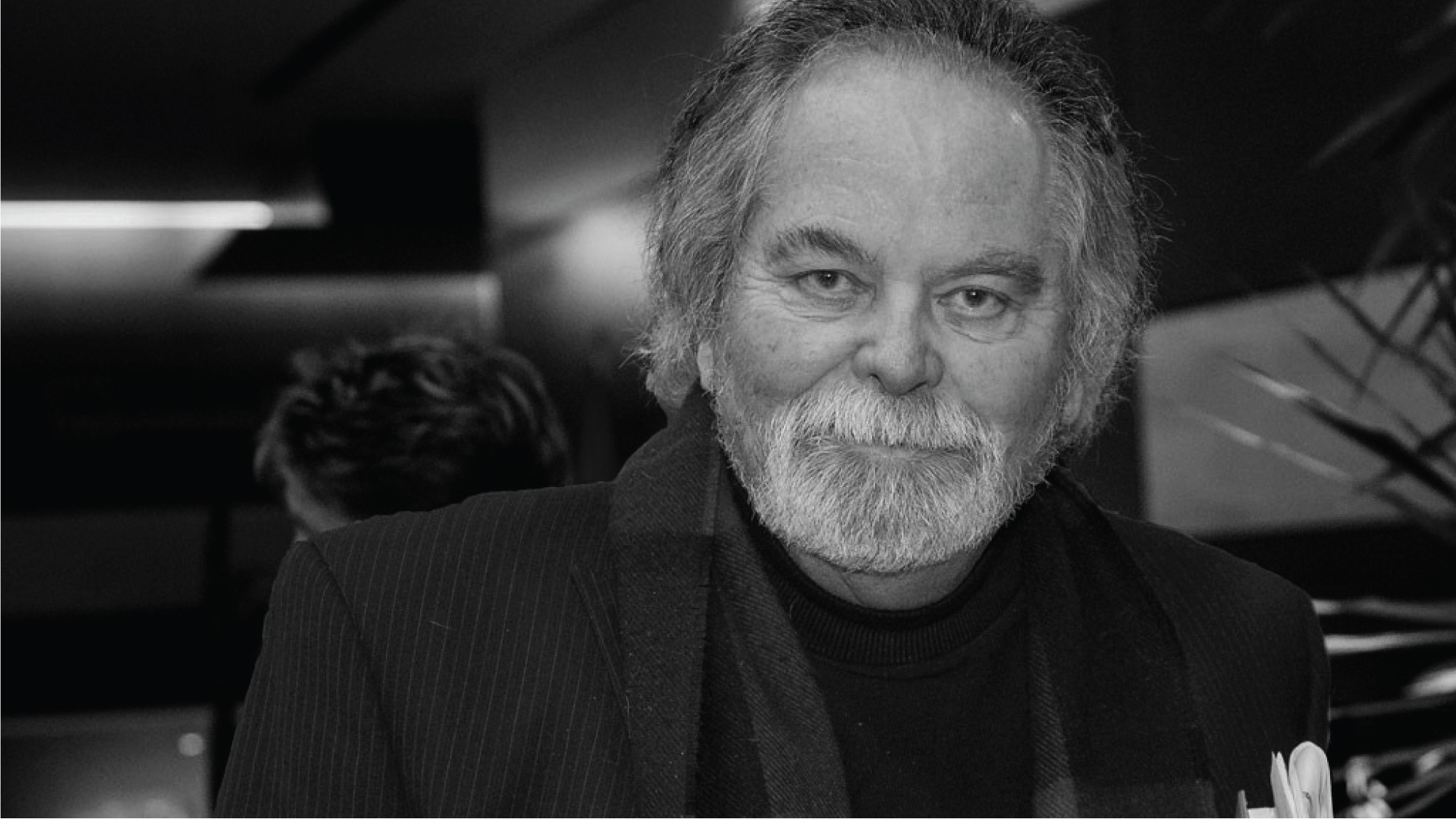

The School of Criminology is deeply saddened to announce the passing of professor emeritus Robert Gordon on April 25, 2024. Rob was a key figure in shaping the School as it is today and his contributions will be felt for years to come.
Known affectionally by some as “the captain”, Rob held several pivotal roles during his time at Simon Fraser University, including a six-year stint as associate dean of the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences (FASS), and 15 years as the director of the School of Criminology . He was also a founding director of the International Cybercrime Research Centre , co-founder of the Centre for Restorative Justice, and a member of the Board of Directors of the Institute for Forensic Research.
As associate dean, Rob was instrumental in the start-up of the FASS One program for first-year students and shepherded the creation of the Department of World Languages and Literatures . He also designed, implemented and directed the University’s highly-renowned Master of Arts in Applied Legal Studies program.
Outside SFU, Rob was a consultant to different levels of government in Canada and beyond, serving on advisory boards and panels dealing with a range of legal and criminal issues, such as adult guardianship, adult protection, and mental health law. Rob worked tirelessly for many years in drafting legislation in B.C., Yukon, and other Canadian jurisdictions, as well as working on similar reforms in Eastern Europe on behalf of the Council of Europe. In 2013, the Governor General of Canada awarded him the Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal for his work on these issues.
He was also a prolific writer, having authored numerous books, book chapters, journal articles, and official reports on youth crime and youth gangs, adult guardianship law, adult protection law, health law, the abuse and neglect of the elderly, and restorative justice. He was a member of several professional associations including the American Society of Criminology and the Western Society of Criminology .
Well-known as British Columbia’s go-to expert for analysis on crime and policing, Rob became a sought-after voice for all major Canadian and international news outlets over the years. Whether he was out on his tractor or taking a well-deserved vacation, Rob was always quick to pick up the phone or return an email when a reporter contacted him. With more than 1,500 media mentions, he received his first SFU Newsmaker Award in 2007 and a Lifetime Achievement Award later in 2023 .
Although he will be deeply missed, Rob Gordon's contributions to the School of Criminology and Simon Fraser University will keep his spirit alive. We extend our thoughts and heartfelt condolences to professor Gordon's family and friends during this difficult time.
Tribute messages
The memory of Robert Gordon will be cherished by those who knew him, including his colleagues, students, and friends. If you wish to share a message of condolence, please send an email to [email protected]
It is with deep and heartfelt sadness that I learned of the passing of Dr. Rob Gordon. While Rob was a great scholar, commentator and a person who provided great service to SFU, what I will remember most about Rob was the great down-to-earth human being he was. Rob was a great friend to me and the SFU Surrey campus. In meetings and gatherings, he would make us laugh, he would hold us accountable and he would pat you on the back when he saw a job well done. Rob may be gone but his legacy and influence will forever be with me.
Steve Dooley, Executive Director, SFU Surrey.
Though I only knew Professor Gordon superficially, his kindness, warmth and sincerity were immediately palpable. His vocational and allied accomplishments speak for themselves. Certainly, his rich legacy and proactive ambitions live on in those many students and colleagues whose studies and work he helped shape and enrich.
Gary Brown, former SFU Distance Education student
I had the good fortune of knowing Rob when we were fledgeling graduate students in sociology at the University of British Columbia in the early 1980s. I was amazed that he could fit his frame into a tiny midget MG sports car! There was more amazement to follow.
Rob demonstrated his leadership skills throughout the program, whether representing the departmental graduate students’ association, standing on principle for students, staff and students alike, encouraging us by example, and generous sharing of his time and skills. He and I were office mates, drawing on one another’s humour, problem-solving, and shared commitment to seeing this doctoral program through.
We had a good fortune of securing tenure-track positions at SFU, thereby continuing our close friendship as colleagues from any decades. Once again, Rob stepped up as a leader in many roles, most significantly IMHO as a longtime Director of the School of Criminology. Devoted husband, father, colleague and friend, he has left a formidable legacy for the School and many other sectors. I will miss his friendship and comradeship.
Brian Burtch, professor emeritus, Criminology, and former associate member, Gender, Sexuality, and Women Studies, SFU
Rob Gordon was a force to be reckoned with in so many ways. In addition to being a dedicated teacher, prolific scholar and omnipresent media commentator, he was a major contributor to the life of SFU in his multiple roles as an academic administrator, member of the Senate and other bodies, and institutional sage. As President, I could always count on Rob for insight and advice which he dispensed with good humour and generosity. And while he took it upon himself to jokingly refer to me as “boss,” I never doubted who in the university truly merited the right to be called “captain.”
Andrew Petter, CM, OBC, KC, president emeritus, professor emeritus, School of Public Policy, Simon Fraser University
I send my condolences to Rob’s family, friends and colleagues. I worked with him for many years when I was dean and vice-president academic, and he contributed so much to SFU. Beyond his research and teaching he gave his time selflessly to collegial governance of the School of Criminology and FASS, as well as his work in Senate. He was very influential in developing and administering policy in areas of student discipline. Rob exemplified SFU’s commitment to the broader community and it sometimes seemed that he was CBC’s resident broadcaster on crime.
Rob was a wonderful person to work with. He was thoughtful and thorough and tried to see all sides of an issue. His kindness shone through his rather gruff exterior. He had a great sense of humour and approached running a university with a twinkle in his eye and a kindly mockery of the foibles of senior administrators.
Jon Driver, professor emeritus, Department of Archaeology
I am so sorry to hear of Rob Gordon’s passing, and my heartful condolences go out to his family, friends, colleagues and all those whose lives he touched. Over the years I relied on Rob’s wise counsel, and I was fortunate enough to work on the foundation he laid across so many programs and activities in FASS. Rob had a way of cutting to the heart of an issue (there is NO space), but always with humour and never unkindly. Rob was also a leader in my hometown, New Westminster, where his legacy lives on various civic and charitable organizations. Cheers Rob, and thank you.
Peter Hall, vice-provost and associate vice-president, academic, professor of urban studies, SFU
As the director of the then-World Literature Program and the founding Chair of WLL, I benefited from Associate Dean Gordon’s support over several years. Without his ongoing help in merging the Language Training Institute and the World Literature Program, we wouldn’t have the lovely department we have today. His support was invaluable to the department, and to me personally, and I’ll never forget it.
Melek Ortabasi, associate dean, undergraduate programs, teaching and learning, and student experience, Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences
Such a loss. I can only fathom the amount of students and colleagues that feel this. I can still remember his voice so clearly and the accompanying eyebrow lift. He trusted my abilities, my intelligence and my commitment to the school. For that, I am forever grateful. Condolences to family and friends. His light will never dim and his voice echoing wisdom and confidence never waiver.
Jacqueline Faubert, PhD Crim
I was very saddened and shocked to learn of Rob Gordon's death. The notion of a world without Rob in it had never occurred to me, to be honest.
Always larger than life, Rob made a big impression when we first met at one of the annual gatherings of the Western deans' group. We had many memorable conversations over the years, particularly around the never-dull topic of academic integrity.
My condolences to Rob's friends and family. I had not seen him in a while and now I'm really going to miss him.
Julia Denholm, dean, Lifelong Learning, Simon Fraser University
Rob Gordon was a true character. You sensed his presence when he entered a room. Larger than life, with piercing eyes, Rob was a man of great impression. During meetings and discussions, Rob was candid and pragmatic yet respectful and personable. Some individuals were ruffled by his no-nonsense, honest approach. When placed in command, he was an outstanding "Captain" navigating many stormy seas and troubled waters with ease. The School of Criminology was very fortunate to have him at the helm for so many years.
He gave so much of his time and energy into fostering positive change. Rob really put his heart into the organization and.....into people. He cared. His influence was great and I know he will missed by many.
Rick Parent, police officer and associate professor (ret.), School of Criminology
I am saddened to hear of Rob Gordon’s passing. I first met him while I was a visiting professor of criminology at SFU in the early 1980s. He asked me to supervise a reading course in the Sociology of Law for his Ph.D. program. I happily did and realized that a student with his intelligence, wit, great social skills and ambition would do very well in his subsequent career. He hit the ball out of the park in his career as a scholar, leader and someone concerned about connecting academics with real-world change and social justice. Over the decades I have had the good fortune to get together with him and it was always a delight. He will be sorely missed by many.
Chuck Reasons, professor emeritus, Law and Justice, Central Washington University
Rob and I met when we were 16 years old and joined the Metropolitan Police cadets in London, UK, an educational and apprentice program for policing. We trained together and, at 19 years old, we became constables on the streets of London. He was stationed in North London, and I was in the centre of town. We met frequently to chat about our lives as young constables dealing with the rigours of London in the 60s.
After a few years, I decided to move to Vancouver and joined the Vancouver Police Department. Robert departed the UK to join the Hong Kong Police. Discretion, and self-preservation, being the better part of valour, he moved on to Australia and joined the Melbourne Police. Our discussions of policing now broadened to an international perspective.
Our lives continued a parallel course. Rob left the police and attended Monash University in Melbourne and I moved on to UBC, Cambridge, and Sheffield Universities.
On one of our international chats, he spoke of the desire to move. I described the many attractions of Vancouver and the then-somewhat-new Simon Fraser University with its Criminology Department. He applied and was accepted.
Rob and I spent many hours hiking in the North Shore mountains. Our frequent stops were because of laughter rather than the gruelling terrain. They were fun times.
These were the early days of police research and governance of police. Our more cerebral moments were spent on discussion of how policing could be enhanced; how the police could be made part of the weft and weave of the community, to support public safety.
I would like to think that these early discussions as young constables in London and, decades later, as we hiked, laid the foundation for Rob’s stellar academic career. His collegial approach and his observations and insights on policing issues will be missed.
Keith Taylor

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Sociology Research
- Academic Staff
- Affiliated Staff
- Postdoctoral and Research Staff
- Postgraduate Students
- Emeritus Academics
- Administrative Staff
- Research Projects
- Research Groups
- Research Ethics
- Applying for Research
- Visiting Scholars ↗
- Department ↗
Tom Kissock
Tom Kissock is a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge. He holds a BA from the Metropolitan Film School and an MSc in Globalisation and Latin American Development from University College London. He has over a decade of international experience working in terrestrial and online broadcasting that has influenced his research into video activism, NGOs, and live human rights documentation in Latin America focusing specifically on indigenous groups in the Brazilian Amazon.
Research Interests
Video as Evidence, Narrowcasting, Digital Activism, Sociology of Human Rights, and Indigenous Media
Publications
Book Chapter Kissock-Mamede, T. (2023). Indigenous Livestreaming in Brazil: A Methodological Case for Reflective Distant Witnessing. In T. Masenya (Ed.), Digital Preservation and Documentation of Global Indigenous Knowledge Systems (pp. 262-281). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-7024-4.ch014
Media Articles
Kissock-Mamede, T. and Gatehouse, T. (2022) Brazil: Mariana disaster victims get their day in court , Latin American Bureau . Available at: https://lab.org.uk/brazil-mariana-disaster-victims-uk-court/
Kissock, T. (2022) ‘Brazil: mining destruction in the Amazon’, Latin American Bureau , March. Available at: https://lab.org.uk/destructive-mining-practices-brazil-amazon-new-report/
Kissock, T (2021). "Why the English-speaking world should take notice of Brazil’s #3JForaBolsonaro Movement" LatAm Dialogue. Available at: https://www.latamdialogue.org/post/why-the-english-speaking-world-should-take-notice-of-brazil-s-3jforabolsonaro-movement
PhD Supervisor
Dr Ella McPherson
The Unique Burial of a Child of Early Scythian Time at the Cemetery of Saryg-Bulun (Tuva)
<< Previous page
Pages: 379-406
In 1988, the Tuvan Archaeological Expedition (led by M. E. Kilunovskaya and V. A. Semenov) discovered a unique burial of the early Iron Age at Saryg-Bulun in Central Tuva. There are two burial mounds of the Aldy-Bel culture dated by 7th century BC. Within the barrows, which adjoined one another, forming a figure-of-eight, there were discovered 7 burials, from which a representative collection of artifacts was recovered. Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather headdress painted with red pigment and a coat, sewn from jerboa fur. The coat was belted with a leather belt with bronze ornaments and buckles. Besides that, a leather quiver with arrows with the shafts decorated with painted ornaments, fully preserved battle pick and a bow were buried in the coffin. Unexpectedly, the full-genomic analysis, showed that the individual was female. This fact opens a new aspect in the study of the social history of the Scythian society and perhaps brings us back to the myth of the Amazons, discussed by Herodotus. Of course, this discovery is unique in its preservation for the Scythian culture of Tuva and requires careful study and conservation.
Keywords: Tuva, Early Iron Age, early Scythian period, Aldy-Bel culture, barrow, burial in the coffin, mummy, full genome sequencing, aDNA
Information about authors: Marina Kilunovskaya (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Vladimir Semenov (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Candidate of Historical Sciences. Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Varvara Busova (Moscow, Russian Federation). (Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation). Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Dvortsovaya Emb., 18, Saint Petersburg, 191186, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Kharis Mustafin (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Technical Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Irina Alborova (Moscow, Russian Federation). Candidate of Biological Sciences. Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected] Alina Matzvai (Moscow, Russian Federation). Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Institutsky Lane, 9, Dolgoprudny, 141701, Moscow Oblast, Russian Federation E-mail: [email protected]
Shopping Cart Items: 0 Cart Total: 0,00 € place your order
Price pdf version
student - 2,75 € individual - 3,00 € institutional - 7,00 €

Copyright В© 1999-2022. Stratum Publishing House
- Yekaterinburg
- Novosibirsk
- Vladivostok
- Tours to Russia
- Practicalities
- Russia in Lists
Rusmania • Deep into Russia
Out of the Centre
Savvino-storozhevsky monastery and museum.

Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar Alexis, who chose the monastery as his family church and often went on pilgrimage there and made lots of donations to it. Most of the monastery’s buildings date from this time. The monastery is heavily fortified with thick walls and six towers, the most impressive of which is the Krasny Tower which also serves as the eastern entrance. The monastery was closed in 1918 and only reopened in 1995. In 1998 Patriarch Alexius II took part in a service to return the relics of St Sabbas to the monastery. Today the monastery has the status of a stauropegic monastery, which is second in status to a lavra. In addition to being a working monastery, it also holds the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum.
Belfry and Neighbouring Churches
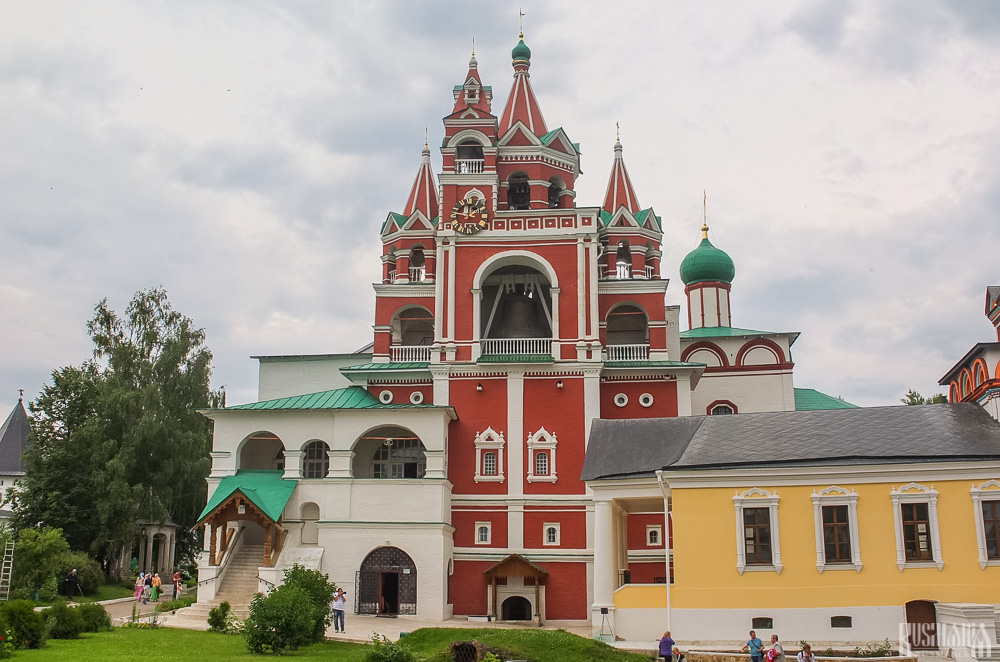

Located near the main entrance is the monastery's belfry which is perhaps the calling card of the monastery due to its uniqueness. It was built in the 1650s and the St Sergius of Radonezh’s Church was opened on the middle tier in the mid-17th century, although it was originally dedicated to the Trinity. The belfry's 35-tonne Great Bladgovestny Bell fell in 1941 and was only restored and returned in 2003. Attached to the belfry is a large refectory and the Transfiguration Church, both of which were built on the orders of Tsar Alexis in the 1650s.
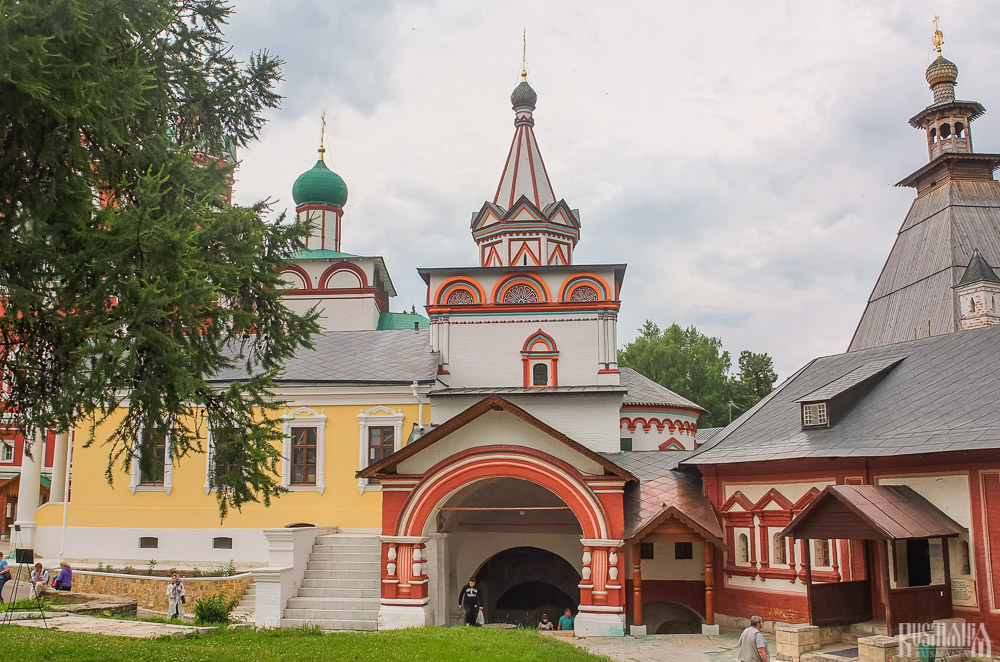

To the left of the belfry is another, smaller, refectory which is attached to the Trinity Gate-Church, which was also constructed in the 1650s on the orders of Tsar Alexis who made it his own family church. The church is elaborately decorated with colourful trims and underneath the archway is a beautiful 19th century fresco.
Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral
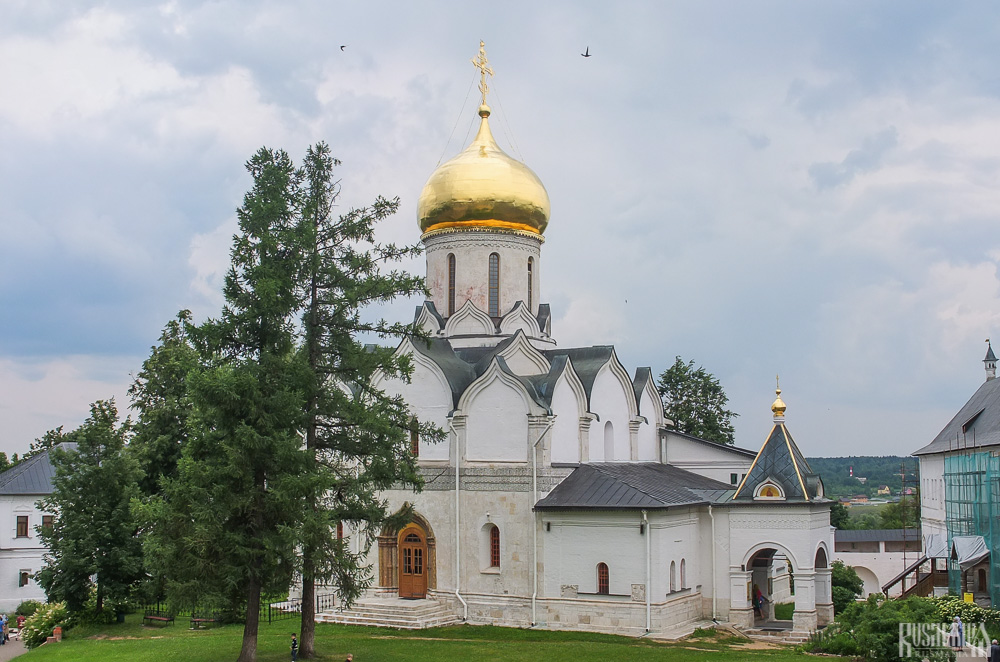

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is the oldest building in the monastery and among the oldest buildings in the Moscow Region. It was built between 1404 and 1405 during the lifetime of St Sabbas and using the funds of Prince Yury of Zvenigorod. The white-stone cathedral is a standard four-pillar design with a single golden dome. After the death of St Sabbas he was interred in the cathedral and a new altar dedicated to him was added.
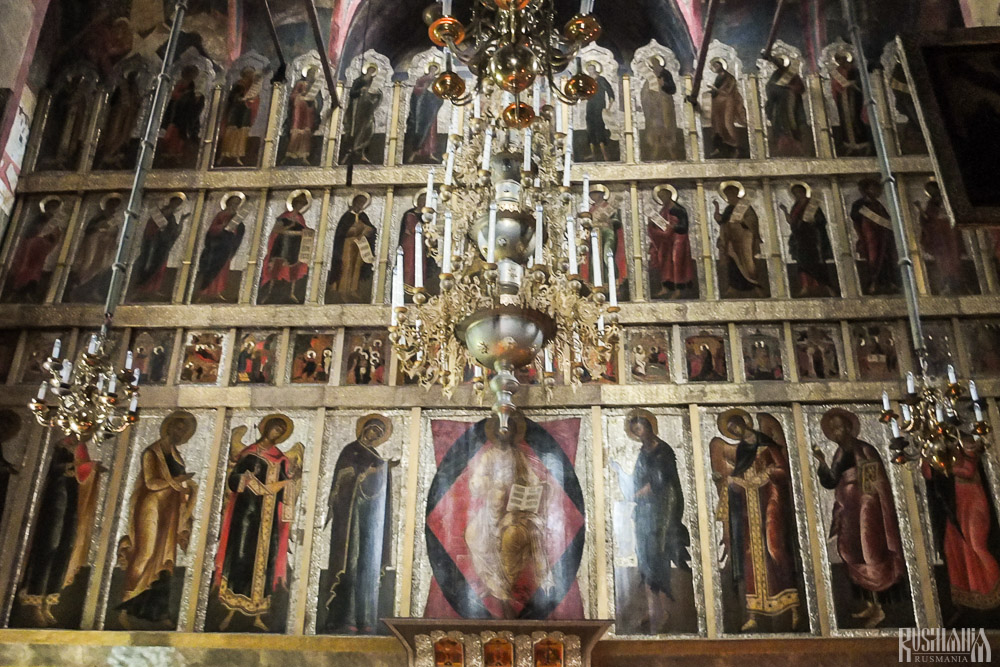

Under the reign of Tsar Alexis the cathedral was decorated with frescoes by Stepan Ryazanets, some of which remain today. Tsar Alexis also presented the cathedral with a five-tier iconostasis, the top row of icons have been preserved.
Tsaritsa's Chambers
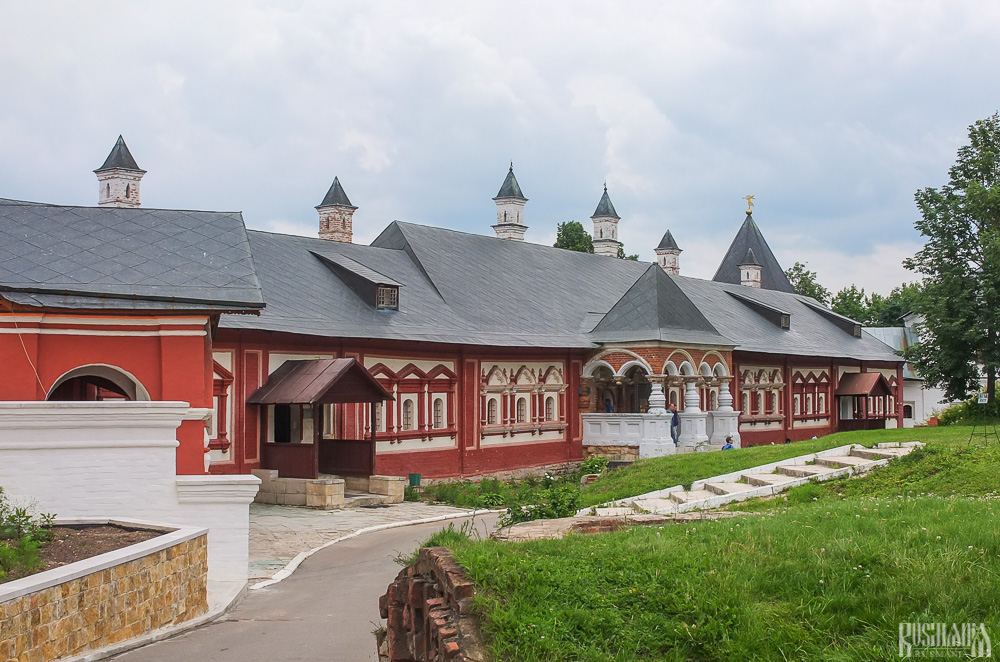

The Nativity of Virgin Mary Cathedral is located between the Tsaritsa's Chambers of the left and the Palace of Tsar Alexis on the right. The Tsaritsa's Chambers were built in the mid-17th century for the wife of Tsar Alexey - Tsaritsa Maria Ilinichna Miloskavskaya. The design of the building is influenced by the ancient Russian architectural style. Is prettier than the Tsar's chambers opposite, being red in colour with elaborately decorated window frames and entrance.
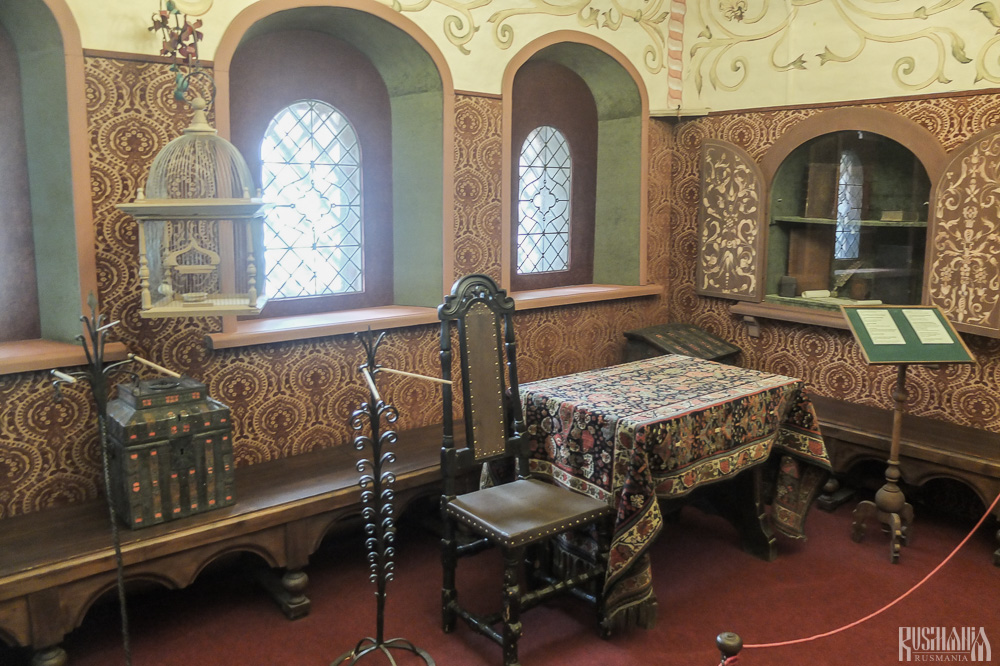

At present the Tsaritsa's Chambers houses the Zvenigorod Historical, Architectural and Art Museum. Among its displays is an accurate recreation of the interior of a noble lady's chambers including furniture, decorations and a decorated tiled oven, and an exhibition on the history of Zvenigorod and the monastery.
Palace of Tsar Alexis
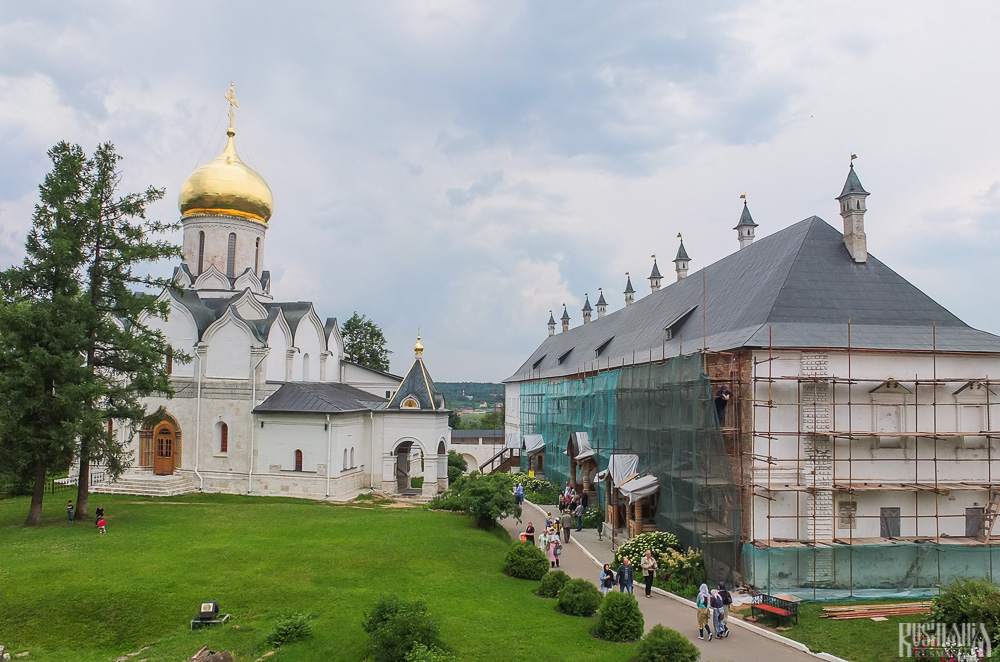

The Palace of Tsar Alexis was built in the 1650s and is now one of the best surviving examples of non-religious architecture of that era. It was built especially for Tsar Alexis who often visited the monastery on religious pilgrimages. Its most striking feature is its pretty row of nine chimney spouts which resemble towers.

Plan your next trip to Russia
Ready-to-book tours.
Your holiday in Russia starts here. Choose and book your tour to Russia.
REQUEST A CUSTOMISED TRIP
Looking for something unique? Create the trip of your dreams with the help of our experts.
To please Putin, universities purge liberals and embrace patriots
Russian university leaders are imbuing the country’s education system with patriotism to favor Putin, quashing Western influences and dissent.

Two weeks before the start of his 25th year as Russia’s supreme political leader, Vladimir Putin made a sweeping proclamation: “Wars are won by teachers.”
The remark, which Putin repeated twice during his year-end news conference in December, shed light on a campaign he is waging that has received little attention outside wartime Russia: to imbue the country’s education system with patriotism, purge universities of Western influences, and quash any dissent among professors and students on campuses that are often hotbeds of political activism.
At St. Petersburg State University, this meant dismantling a prestigious humanities program called the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Sciences. For more than a decade, until May 2022, the faculty — or college — was led by Alexei Kudrin, a liberal economist and former finance minister who had been a close associate of Putin’s since the early 1990s, when they were deputy mayors together in St. Petersburg.
“We had many classes on U.S. history, American political life, democracy and political thought, as well as courses on Russian history and political science, history of U.S.-Russian relations, and even a course titled ‘The ABCs of War: Causes, Effects, Consequences,’” said a student at the faculty, also known as Smolny College. “They are all gone now,” the student said, speaking on the condition of anonymity for fear of retribution.
About this series

In a radical reshaping of Russia’s education system, curriculums are being redrawn to stress patriotism and textbooks rewritten to belittle Ukraine, glorify Russia and whitewash the totalitarian Soviet past. These changes — the most sweeping to schooling in Russia since the 1930s — are a core part of Putin’s effort to harness the war in Ukraine to remaster his country as a regressive, militarized state.
Since the February 2022 invasion of Ukraine, leaders of Russian universities, which are overwhelmingly funded by the state, have zealously adopted the Kremlin’s intolerance of any dissent or self-organization, according to an extensive examination by The Washington Post of events on campuses across Russia, including interviews with students and professors both still in the country and in exile.
Professors who spoke out against the war, or allowed safe spaces for students to question it, have been fired. Students who picketed or posted on social media for peace were expelled.
Meanwhile, those who volunteer to fight in Ukraine have been celebrated in line with Putin’s promises that war heroes and their descendants will become the new Russian elite, with enhanced social benefits, including special preference for children seeking to enter top academic programs. Normally, such programs require near-perfect grades and high scores on competitive exams — uniform standards that applicants from all societal backgrounds have relied on for decades.
And the most fundamental precept of academic life — the freedom to think independently, to challenge conventional assumptions and pursue new, bold ideas — has been eroded by edicts that classrooms become echo chambers of the authoritarian nativism and historical distortions that Putin uses to justify his war and his will.
As a result, a system of higher learning that once was a beacon for students across the developing world is now shutting itself off from peer academies in the West, severing one of the few ties that had survived years of political turbulence. Freedom of thought is being trampled, if not eradicated. Eminent scholars have fled for positions abroad, while others said in interviews that they are planning to do so.
At the Russian State University for the Humanities in Moscow, officials last July created the Ivan Ilyin Higher Political School, which is now being led by Alexander Dugin, a fervent pro-Putin and Orthodox Christian ideologue who was tasked with “revising domestic scientific and educational paradigms and bringing them into line with our traditional Russian spiritual and moral values.”
“There has been a catastrophic degradation in Western humanitarian history,” Dugin said at a January seminar on transforming Russian humanities education. “This is evidenced by gender problems, postmodernism and ultraliberalism. We can study the West, but not as the ultimate universal truth. We need to focus on our own Russian development model.”
How we reported ‘Russia, Remastered’
Last month, students pushed an online petition to protest the naming of the school after Ilyin, a philosopher who defended Hitler and Mussolini in World War II and advocated for the return of czarist autocracy in Russia. In a statement to Tass, the state-controlled news service, the university denounced the petition as “part of the information war of the West and its supporters against Russia” and asserted, without providing evidence, that the group behind it had no connection to students at the school.
Programs specializing in the liberal arts and sciences are primary targets because they are viewed as breeding grounds for dissent. Major universities have cut the hours spent studying Western governments, human rights and international law, and even the English language.
“We were destroyed,” said Denis Skopin, a philosophy professor at Smolny College who was fired for criticizing the war. “Because the last thing people who run universities need are unreliable actors who do the ‘wrong’ thing, think in a different way, and teach their students to do the same.”

The demise of
Smolny College

The demise of Smolny College

St. Petersburg State University, commonly known as SPbU, has long been one of Russia’s premier academies of higher learning. It is the alma mater of both Putin, who graduated with a degree in law in 1975, and former president Dmitry Medvedev, who received his law degree 12 years later and now routinely threatens nuclear strikes on the West as deputy chairman of Russia’s national security council.
In many ways, the university has become the leader in reprisals against students and staff not loyal to the Kremlin, with one newspaper dubbing it the “repressions champion” of Russian education. Its halls have become a microcosm of modern Russia in which conservatives in power are pushing out the few remaining Western-oriented liberals.
Like other aspects of Putin’s remastering of Russia — such as patriotic mandates in the arts and the redrawing of the role of women to focus on childbearing — the shift in education started well before the invasion of Ukraine. In 2021, Russia ended a more than 20-year-old exchange program between Smolny College and Bard College in New York state by designating the private American liberal arts school an “undesirable” organization.
Jonathan Becker, Bard’s vice president for academic affairs and a professor of political studies, said the demise of Smolny was emblematic of a wider shift in Russia as well as a new intolerance of the West.
“A huge number of faculty have been let go, several departments closed, core liberal arts programs which focus on critical thinking have been eliminated,” Becker said. “All of that has happened, and it’s not just happened at Smolny — it has happened elsewhere. But we were doubly problematic because we both represent critical thinking and partnership with the West. And neither of those are acceptable in present-day Russia.”
In October 2022, in a scene captured on video and posted on social media, dozens of students gathered in a courtyard to bid a tearful goodbye to Skopin, Smolny’s cherished philosophy professor who was fired for an “immoral act” — protesting Putin’s announcement of a partial military mobilization to replenish his depleted forces in Ukraine.
The month before, according to court records and interviews, Skopin was arrested at an antiwar rally. He ended up sharing a jail cell with another professor, Artem Kalmykov, a young mathematician who had recently finished his PhD at the University of Zurich.
That fall, the university launched an overhaul that all but shut Smolny College and replaced the curriculum with a thoroughly revamped arts and humanities program.
The dismantling of Smolny marked the resolution of a years-long feud between Kudrin, the liberal-economist dean, and Nikolai Kropachev, the university rector, whom tutors and students described as a volatile character with a passion for building ties in the highest echelons of the government.

It’s hard to describe the insane level of anxiety the students felt at the start of the invasion, and I’d say 99 percent of them were against it.”
Denis Skopin
Former philosophy professor at Smolny College

It’s hard to describe the insane level of anxiety the students felt at the start of the invasion, and I’d say
99 percent of them were against it.”

It’s hard to describe the insane level
of anxiety the students felt at the start
of the invasion, and I’d say 99 percent
of them were against it.”

It’s hard to describe the insane level of anxiety
the students felt at the start of the invasion,
and I’d say 99 percent of them were against it.”
In February, Sergei Naryshkin, the head of Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service, sent a heartfelt birthday message to Kropachev, thanking him for his “civic and political activity” and for “comprehensive assistance in replenishing personnel.”
One student described how Kropachev once interrupted a meeting with students and hinted that he needed to take a call from Putin, in what the student viewed as a boast of his direct access to the Russian leader. Both St. Petersburg State University and Moscow State University were assigned a special status in 2009, under which their rectors are appointed personally by the president.
Skopin, who earned his PhD in France, and his cellmate, Kalmykov, were perfect examples of the type of academic that Russia aspired to attract from the early 2000s to the mid-2010s — enticed after studying abroad to bring knowledge home amid booming investment in higher education. But by 2022, the system seemed to have no need for them.
Video of the gathering in the courtyard shows students erupting in sustained applause, and one student coming forward to hug Skopin.
“It’s hard to describe the insane level of anxiety the students felt at the start of the invasion, and I’d say 99 percent of them were against it,” Skopin said.
After his dismissal, some students tried to fight the administration’s plan to dismantle the Smolny program.
“At one point we found ourselves in a situation where out of 30 original faculty staff, we had just three tutors left,” said Polina Ulanovskaya, a sociology student and activist who led the student union. “And the quality of education definitely suffered, especially all of the politics-related classes.”
Ulanovskaya said that on the political science track, only two professors have stayed, and many classes were eliminated, including a human rights course. There are now just two courses offered in English, down from 21.
With every new professor, Ulanovskaya said, she felt a need to test the waters. Would the word “gender” trigger them? Could she say something opposition-leaning? What would be a red flag?
Ulanovskaya opted out of writing a thesis on her main research topic — Russian social movements, politicization of workers and historic-preservation activists — out of fear that it would be blacklisted. Instead, she wrote about Uruguay.
“The main problem at the faculty now is that there is no freedom and especially no sense of security,” she said. “I guess there is no such thing anywhere in Russia now ... you can’t trust anyone in any university.”
A few weeks after The Post interviewed Ulanovskaya last fall, she was expelled, formally for failing an exam, but she and Skopin said they believe it was retaliation for her activism.
Another student, Yelizaveta Antonova, was supposed to get her bachelor’s degree in journalism just days after legendary Novaya Gazeta newspaper reporter Yelena Milashina was brutally beaten in Chechnya, the small Muslim-majority republic in southern Russia under the dictatorial rule of Ramzan Kadyrov.
Antonova, who interned at Novaya Gazeta and looked up to Milashina, felt she could not accept her diploma without showing support for her colleague. She and a roommate printed a photo of Milashina, depicting the reporter’s shaved head and bandaged hands, to stage a demonstration at their graduation ceremony — much to the dismay of other classmates, who sought to block the protest.
“They essentially prevented us from going on stage,” Antonova said. “So we did it outside of the law school, and we felt it was extra symbolic because Putin and Medvedev studied in these halls.”
They held up the poster for about half an hour, until another student threatened them by saying riot police were on the way to arrest them. Antonova believes the protest cost her a spot in graduate school, where she hoped to continue her research comparing Russia’s media landscape before and after the invasion.
Eight months after the graduation ceremony, authorities launched a case against Antonova and her roommate for staging an unauthorized demonstration — an administrative offense that is punishable by a fine and puts people on law enforcement’s radar. Antonova left the country to continue her studies abroad.

Ideological divides

The history college at St. Petersburg State has long been a battleground for various ideologies, with cliques ranging from conservatives and Kremlin loyalists to unyielding opposition-minded liberals, according to interviews with students and professors.
The February 2022 invasion of Ukraine caused a deeper split. Some students and professors openly praised Putin’s “special military operation,” as the Kremlin called the war, while others joined rallies against it.
“The war gave them carte blanche,” said Michael Martin, 22, a former star at the college — to which he was automatically admitted after winning two nationwide academic competitions and where he earned straight A’s.
Martin was a leader of the student council, which on the day of the invasion issued an antiwar manifesto quickly drafted in a cafe.
Another history student, Fedor Solomonov, took the opposite view and praised the special military operation on social media. When Solomonov was called up as part of the mobilization, he declined to take a student deferral and went to fight. He died on the front on April 1, 2023.
Soon after Solomonov’s death, screenshots from internal chats where students often debated history and politics were leaked and went viral on pro-war Telegram channels. In some, Martin and other classmates expressed antiwar sentiments, while another showed a message — allegedly written by an assistant professor, Mikhail Belousov — vaguely describing events in Ukraine as “Rashism,” a wordplay combining “Russia” and “fascism.”
In an aggressive online campaign, pro-war activists demanded that Belousov, who denied writing the message, be fired and that the antiwar students, whom they labeled “a pro-Ukrainian organized crime group,” be expelled.
“A cell of anti-Russian students led by a Russophobe associate professor is operating at the history faculty,” read posts on Readovka, a radical outlet with 2.5 million followers. “They are rabid liberals who hate their country.” Belousov was dismissed and seven students, including Martin, were accused of desecrating Solomonov’s memory and expelled.
Belousov has gone underground and could not be reached for comment.
“They essentially tried to make me do the Sieg Heil,” Martin said, recalling the expulsion hearing, where he said the committee repeatedly asked leading questions trying to get him to say the war was justified. The committee also asked him repeatedly about Solomonov.
“I said he was for the war and I was against it — we could argue about that,” Martin said. “I didn’t find anything funny or interesting in this — I’m truly sorry for what happened to him, but at the same time, I don’t think that he did something good or great by going to war.”
Martin said that as the war raged on, the university began “glorifying death” and praising alumni who had joined the military.
This narrative also warped the curriculum.
A few weeks into the invasion, the school introduced a class on modern Ukrainian history, with a course description asserting that Ukrainian statehood is based “on a certain mythology.”

They essentially tried to make me do the Sieg Heil.”
Michael Martin
Former student at St. Petersburg State University

Belousov, the former assistant professor, criticized a course titled “The Great Patriotic War: No Statute of Limitations,” taught by an instructor with a degree in library science. The key message of the course is that the Soviet Union had no role in the start of World War II — a denial of Russia’s joint invasion of Poland with Nazi Germany in 1939.
According to a government document reviewed by The Post, Russia’s Higher Education Ministry plans to introduce this course at other universities to ensure the “civic-patriotic and spiritual-moral education of youth,” specifically future lawyers, teachers and historians, and to “correct false ideas.”
“These are obviously propaganda courses that are aimed at turning historians into court apologists,” Martin said.
Martin was expelled days before he was supposed to defend his thesis. He quickly left the country after warnings that he and his classmates could be charged with discrediting the army, a crime punishable by up to 15 years in prison. A criminal case was initiated against Belousov on charges of rehabilitating Nazism.
“This is all very reminiscent of the Stalinist 1930s purges,” Martin said. “The limit of tolerated protest now is to sit silently and say nothing. There is despair at the faculty and a feeling that they have crushed everything.”

New Russian elite

To lure more Russian men to fight in Ukraine, the government has promised their families various sweeteners, including cheap mortgages, large life insurance payments and education benefits for their children.
In 2022, Putin approved changes to education laws to grant children of soldiers who fought in Ukraine admissions preferences at Russia’s best universities — schools that normally accept only students with near-perfect exam scores and impressive high school records.
Now, at least 10 percent of all fully funded university spots must be allocated to students eligible for the military preference. Those whose fathers were killed or wounded do not need to pass entry exams.
The new law solidified a previous Putin decree that gave special preferences to soldiers and their children. In the 2023-24 academic year, about 8,500 students were enrolled based on these preferences, government officials said. According to an investigation by the Russian-language outlet Important Stories, nearly 900 students were admitted to 13 top universities through war quotas, with most failing to meet the normal exam score threshold.
In areas of Ukraine captured by Russian forces since February 2022, a different takeover of the education system is underway, with Moscow imposing its curriculum and standards just as it did after invading and illegally annexing Crimea in 2014.
For the 2023-24 academic year, according to the Russian prime minister’s office, more than 5 percent of fully state-financed tuition stipends — roughly 37,000 out of 626,000 — were allocated for students at universities in Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson or Zaporizhzhia, the four occupied or partly occupied areas of Ukraine that Putin has claimed to be annexed.
The relatively large allocation of tuition aid in occupied areas shows how financial assistance and education are central to Putin’s effort to seize lands in southeast Ukraine and absorb its population into Russia in violation of international law.
Deans of several leading Russian universities have made highly publicized trips to occupied Ukraine to urge students there to enroll into Russian schools, part of a multipronged effort to bring residents into Moscow’s orbit.
The Moscow-based Higher School of Economics, once considered Russia’s most liberal university, recently established patronage over universities in Luhansk, with Rector Nikita Anisimov often traveling there.

An inward turn

A few weeks after the invasion started, Moscow abandoned the Bologna Process , a pan-European effort to align higher education standards, as Russia’s deans and rectors strove to show they weren’t susceptible to foreign influence.
Higher Education Minister Valery Falkov said Russian universities would undergo significant changes in the next half-decade, overseen by the national program “Priority 2030,” which envisions curriculums that ensure “formation of a patriotic worldview in young people.”
Soon after Russia quit the Bologna Process, Smolny College was targeted for overhaul.
“The decision was an expected but distinct shift from the more liberal model of Russian higher education policy that emerged after the collapse of the Soviet Union,” said Victoria Pardini, a program associate at the Kennan Institute, a Washington think tank focused on Russia.
Another prestigious school, the Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration, canceled its liberal arts program in 2022 after authorities accused it of “destroying national values.”
In mid-October 2023, the Higher Education Ministry ordered universities to avoid open discussion of “negative political, economic and social trends,” according to a publicly disclosed report by British intelligence. “In the longer term, this will likely further the trend of Russian policymaking taking place in an echo-chamber,” the report concluded.
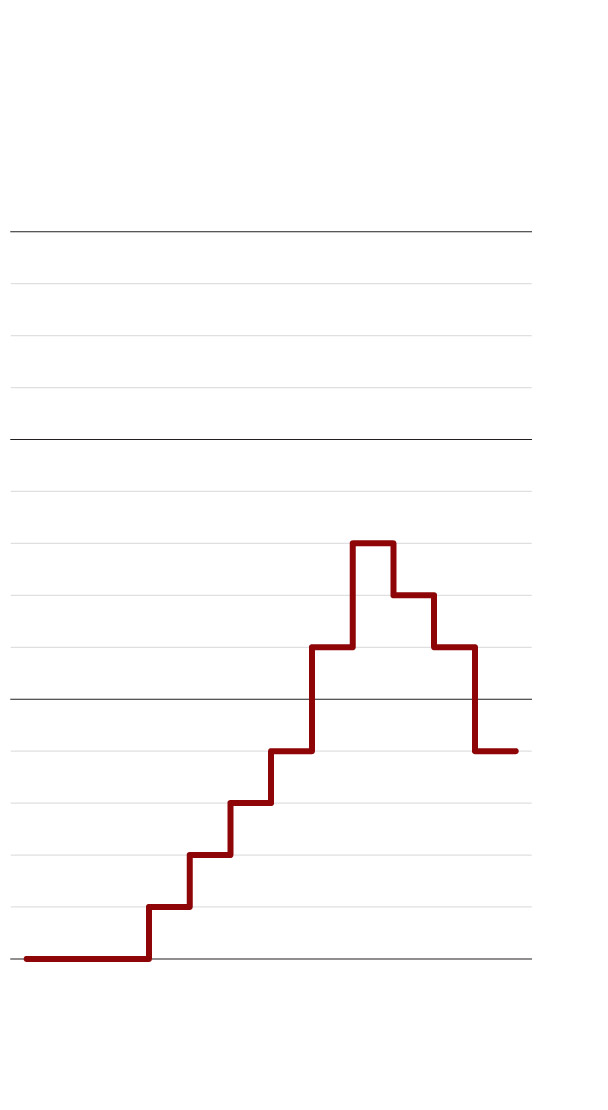
Russia’s position among
countries by number of
scholarly papers published
Source: Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics
of Knowledge
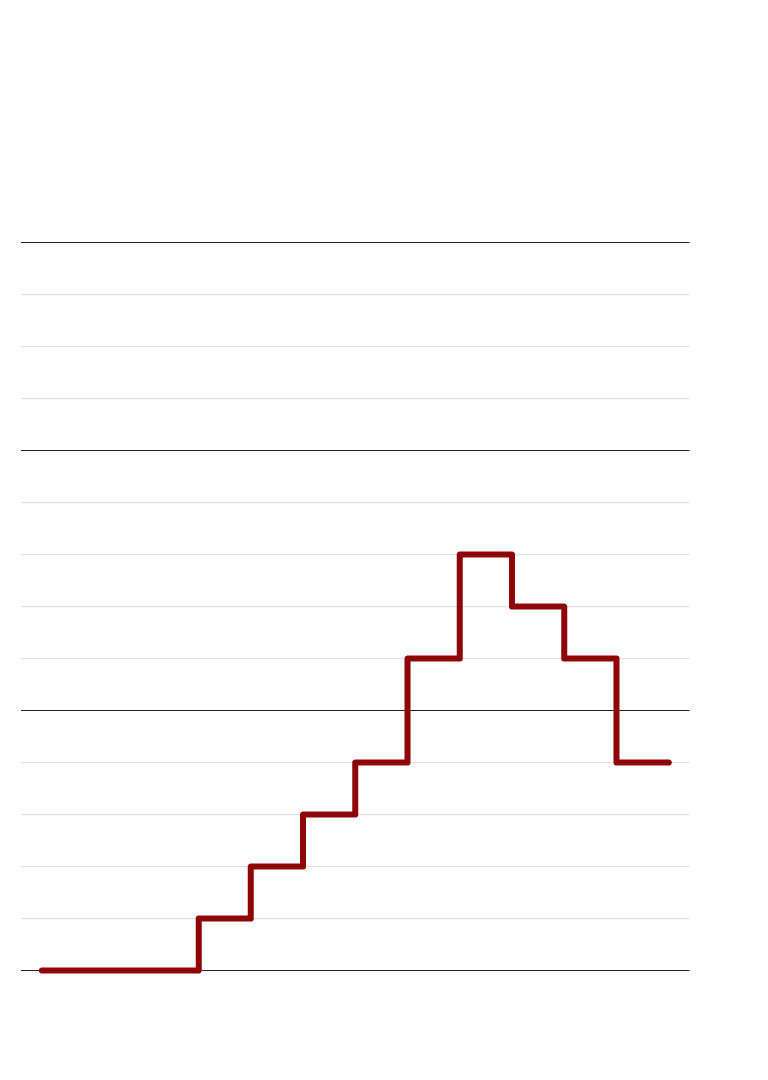
Russia’s position among countries by
number of scholarly papers published
Source: Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge
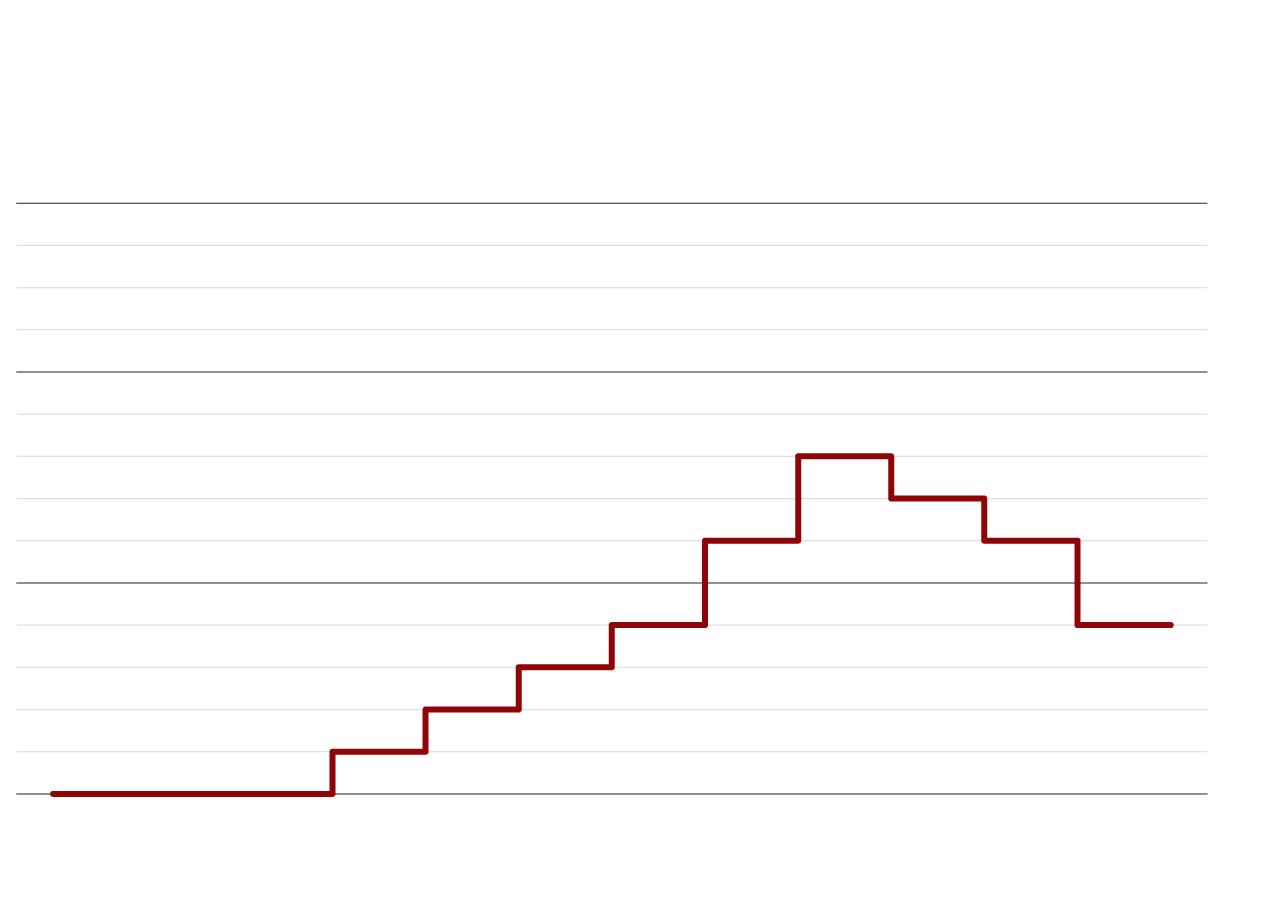
Russia’s position among countries by number of
Many international exchange programs have been canceled — some because Russian students now have difficulty obtaining visas. Still, a heavy brain drain is underway. “All those who could — they left the country,” Skopin said of his students. “Those who can’t are thrashing around as if they are in a cage.”
Martin is among those who got out — he was recently accepted into a prestigious master’s program abroad and plans to continue his research into 19th-century Australian federalism.
Skopin now teaches in Berlin and is a member of Smolny Beyond Borders, an education program that seeks funding to cover the tuition of students who leave Russia because of their political views. As of late 2023, an estimated 700 students were enrolled.


Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Course Directory
MPhil in Sociology (The Sociology of Media and Culture)
Postgraduate Study
- Why Cambridge overview
- Chat with our students
- Cambridge explained overview
- The supervision system
- Student life overview
- In and around Cambridge
- Leisure activities
- Student unions
- Music awards
- Student support overview
- Mental health and wellbeing
- Disabled students
- Accommodation
- Language tuition
- Skills training
- Support for refugees
- Courses overview
- Department directory
- Qualification types
- Funded studentships
- Part-time study
- Research degrees
- Visiting students
- Finance overview
- Fees overview
- What is my fee status?
- Part-time fees
- Application fee
- Living costs
- Funding overview
- Funding search
- How to apply for funding
- University funding overview
- Research Councils (UKRI)
- External funding and loans overview
- Funding searches
- External scholarships
- Charities and the voluntary sector
- Funding for disabled students
- Widening participation in funding
- Colleges overview
- What is a College?
- Choosing a College
- Terms of Residence
- Applying overview
- Before you apply
- Entry requirements
- Application deadlines
- How do I apply? overview
- Application fee overview
- Application fee waiver
- Life Science courses
- Terms and conditions
- Continuing students
- Disabled applicants
- Supporting documents overview
- Academic documents
- Finance documents
- Evidence of competence in English
- AI and postgraduate applications
- Terms and Conditions
- Applicant portal and self-service
- After you apply overview
- Confirmation of admission
- Student registry
- Previous criminal convictions
- Deferring an application
- Updating your personal details
- Appeals and Complaints
- Widening participation
- Postgraduate admissions fraud
- International overview
- Immigration overview
- ATAS overview
- Applying for an ATAS certificate
- Current Cambridge students
- International qualifications
- Competence in English overview
- What tests are accepted?
- International events
- International student views overview
- Akhila’s story
- Alex’s story
- Huijie’s story
- Kelsey’s story
- Nilesh’s story
- Get in touch!
- Events overview
- Upcoming events
- Postgraduate Open Days overview
- Discover Cambridge: Master’s and PhD Study webinars
- Virtual tour
- Research Internships
- How we use participant data
- Postgraduate Newsletter
Primary tabs
- Overview (active tab)
- Requirements
- How To Apply
- Testimonials
Course closed:
Sociology (The Sociology of Media and Culture) is no longer accepting new applications.
The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is a world-class centre for teaching and research in Sociology, with a proud tradition of research grounded in engagement with contemporary real-world issues.
The Department is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2023 . The UK's 2021 Research Excellence Framework ranks our department second overall in the UK, and joint first for the research environment. The QS World University rankings list our department as 6th of 330 sociology departments across the world in 2022.
The MPhil in Sociology of Media and Culture pathway provides students with the opportunity to study the nature and transformation of media and cultural forms at an advanced level. The programme gives students a firm grounding in the theoretical and empirical analysis of media and culture and enables them to study particular media and cultural forms in-depth, examining their transformations over time and their impact on other aspects of social and political life.
There are four elements to the pathway:
1. A core course of six 2-hour sessions in Michaelmas and 2 sessions in Lent (Michaelmas and Lent of the first year for part-time students), covering some of the major theoretical contributions to the study of the media and culture and some key substantive topics. There are also substantive topics which vary from year to year depending on availability of academic staff.
2. All students will receive training in research methods and take a course on research methods which includes sessions on philosophical issues in the social sciences; research design; data collection and analysis in relation to quantitative and qualitative methods; reflection on research ethics and practice; library and computer skills. Students will also have the opportunity to take courses and attend lectures on many other aspects of research method and design and will select these courses in discussion with their supervisor.
3. A series of optional one-hour seminars specific to the Media and Culture Pathway during Lent term.
4. All students will write a dissertation on a topic of their choice that allows for theoretically informed empirical analysis of some aspect of media or culture in contemporary societies. The choice of dissertation topic is made in consultation with your supervisor, who can advise you on the suitability and feasibility of your proposed research and on research design. A dissertation workshop provides the opportunity to present aspects of your dissertation work and to receive constructive feedback from course teachers and fellow students.
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of the programme students should have:
an advanced understanding of current research on selected topics in the sociology of media and culture;
an understanding of the basic principles of social research, the skills necessary to conduct independent research and practical experience in the use of research methods;
an ability to apply modern social theory with respect to empirical topics;
a deeper understanding of their chosen specialist area, including command of the literature and current research; and
the ability to situate their own research within current developments in the field.
Students are encouraged to apply for the department's PhD programme, provided they reach a high level of achievement in all parts of the course. MPhil students who would like apply for the PhD would normally need to have a final mark of at least 70 per cent overall and 70 per cent on the dissertation. Please note that successful completion of the MPhil does not guarantee acceptance onto the PhD programme.
The Postgraduate Virtual Open Day usually takes place at the end of October. It’s a great opportunity to ask questions to admissions staff and academics, explore the Colleges virtually, and to find out more about courses, the application process and funding opportunities. Visit the Postgraduate Open Day page for more details.
See further the Postgraduate Admissions Events pages for other events relating to Postgraduate study, including study fairs, visits and international events.
Details of Open Day events run by the Sociology Department can be found on the Department's Outreach Page .
Key Information
9 months full-time, 21 months part-time, study mode : taught, master of philosophy, department of sociology, course - related enquiries, application - related enquiries, course on department website, dates and deadlines:, michaelmas 2024 (closed).
Some courses can close early. See the Deadlines page for guidance on when to apply.
Funding Deadlines
These deadlines apply to applications for courses starting in Michaelmas 2024, Lent 2025 and Easter 2025.
Similar Courses
- Digital Humanities MPhil
- Digital Humanities PhD
- Film and Screen Studies PhD
- English PhD
- European, Latin American and Comparative Literatures and Cultures by Advanced Study MPhil
Postgraduate Admissions Office
- Admissions Statistics
- Start an Application
- Applicant Self-Service
At a glance
- Bringing a family
- Current Postgraduates
- Cambridge Students' Union (SU)
University Policy and Guidelines
Privacy Policy
Information compliance
Equality and Diversity
Terms of Study
About this site
About our website
Privacy policy
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...

COMMENTS
The PhD in Sociology offers a world-class programme of research study in sociology supervised by experts in their respective fields. The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2024.
The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2023.The UK's 2021 Research Excellence Framework ranks our department second overall in the UK, and joint first for the research environment. And the QS World University rankings list our ...
The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is a world-class centre for teaching and research in Sociology, with a proud tradition of research grounded in engagement with contemporary real-world issues. Our department is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2023.
The PhD in Sociology offers a world-class programme of a research study in sociology supervised by world-renowned experts in their fields. The course aims to provide all students with the skills they need to be professional researchers and academics. There is an organised programme of courses for first-year PhD students, which has three major ...
The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is ranked first for Sociology in the Guardian's Best Universities league table and first for Sociology in the Complete University Guide League Table 2023.The UK's 2021 Research Excellence Framework ranks our department second overall in the UK, and joint first for the research environment. . And the QS World University rankings list ...
Professor Manali Desai received her PhD in Sociology from the University of California, Los Angeles where she trained as a comparative and historical sociologist. ... (2009) States of Trauma: Gender and Violence in South Asia, Zubaan Books and Cambridge University Press, India, pps: 293-313. Key Publications - Journal Articles. Desai, Manali ...
Originally from Brussels, Professor Patrick Baert did his graduate work at the University of Oxford, working on social theory under the supervision of Rom Harré. He subsequently joined the Sociology Department in Cambridge. His recent research in the sociology of intellectuals has been funded by various bodies, including the British Academy, The European Research Council and
sociology; sociology . Topic description and stories. Tales from the edge of modern fertilities ... With our Postgraduate Open Day fast-approaching (3 November), we introduce five PhD students who are already making waves at Cambridge. Read more ... Cambridge University Press & Assessment; Research at Cambridge.
Elektrostal , lit: Electric and Сталь , lit: Steel) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located 58 kilometers east of Moscow. Population: 155,196 ; 146,294 ...
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Sociology Thomas Dietz of Michigan State University was elected into the National Academy in April for his research and contributions to the environmental sciences. Professor Dietz was a Ph.D. student at UC Davis in Ecology, but he was mentored by Professor Jim Cramer with whom he also taught graduate level quantitative methods.
Rob left the police and attended Monash University in Melbourne and I moved on to UBC, Cambridge, and Sheffield Universities. On one of our international chats, he spoke of the desire to move. I described the many attractions of Vancouver and the then-somewhat-new Simon Fraser University with its Criminology Department. He applied and was accepted.
PhD Candidate Sociology, Queens' College. Contact Information: [email protected]. Twitter. Tom Kissock is a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge. He holds a BA from the Metropolitan Film School and an MSc in Globalisation and Latin American Development from University College London. He has over a decade ...
Burial 5 was the most unique, it was found in a coffin made of a larch trunk, with a tightly closed lid. Due to the preservative properties of larch and lack of air access, the coffin contained a well-preserved mummy of a child with an accompanying set of grave goods. The interred individual retained the skin on his face and had a leather ...
Zvenigorod's most famous sight is the Savvino-Storozhevsky Monastery, which was founded in 1398 by the monk Savva from the Troitse-Sergieva Lavra, at the invitation and with the support of Prince Yury Dmitrievich of Zvenigorod. Savva was later canonised as St Sabbas (Savva) of Storozhev. The monastery late flourished under the reign of Tsar ...
At St. Petersburg State University, this meant dismantling a prestigious humanities program called the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Sciences. For more than a decade, until May 2022, the faculty ...
Ms. Deborah Haggard, Beechwood High School, Kentucky, Science (Chemistry and Biology) Nominating Scholar: Joshua Zyzak Mr. Tom Haindfield, Creighton Preparatory School, Nebraska, History Nominating Scholar: Mark M. Bausch Ms. Deborah Hamilton, Dulaney High School, Maryland, AP Language and Composition Nominating Scholar: Mingni L. Dong
The Department of Sociology at the University of Cambridge is a world-class centre for teaching and research in Sociology, with a proud tradition of research grounded in engagement with contemporary real-world issues. ... MPhil students who would like apply for the PhD would normally need to have a final mark of at least 70 per cent overall and ...