Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Academic writing
- Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples

Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples
Published on May 29, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2023.
Transition words and phrases (also called linking words, connecting words, or transitional words) are used to link together different ideas in your text. They help the reader to follow your arguments by expressing the relationships between different sentences or parts of a sentence.
The proposed solution to the problem did not work. Therefore , we attempted a second solution. However , this solution was also unsuccessful.
For clear writing, it’s essential to understand the meaning of transition words and use them correctly.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When and how to use transition words, types and examples of transition words, common mistakes with transition words, other interesting articles.
Transition words commonly appear at the start of a new sentence or clause (followed by a comma ), serving to express how this clause relates to the previous one.
Transition words can also appear in the middle of a clause. It’s important to place them correctly to convey the meaning you intend.
Example text with and without transition words
The text below describes all the events it needs to, but it does not use any transition words to connect them. Because of this, it’s not clear exactly how these different events are related or what point the author is making by telling us about them.
If we add some transition words at appropriate moments, the text reads more smoothly and the relationship among the events described becomes clearer.
Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. Consequently , France and the United Kingdom declared war on Germany. The Soviet Union initially worked with Germany in order to partition Poland. However , Germany invaded the Soviet Union in 1941.
Don’t overuse transition words
While transition words are essential to clear writing, it’s possible to use too many of them. Consider the following example, in which the overuse of linking words slows down the text and makes it feel repetitive.
In this case the best way to fix the problem is to simplify the text so that fewer linking words are needed.
The key to using transition words effectively is striking the right balance. It is difficult to follow the logic of a text with no transition words, but a text where every sentence begins with a transition word can feel over-explained.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
There are four main types of transition word: additive, adversative, causal, and sequential. Within each category, words are divided into several more specific functions.
Remember that transition words with similar meanings are not necessarily interchangeable. It’s important to understand the meaning of all the transition words you use. If unsure, consult a dictionary to find the precise definition.
Additive transition words
Additive transition words introduce new information or examples. They can be used to expand upon, compare with, or clarify the preceding text.
Adversative transition words
Adversative transition words always signal a contrast of some kind. They can be used to introduce information that disagrees or contrasts with the preceding text.
Causal transition words
Causal transition words are used to describe cause and effect. They can be used to express purpose, consequence, and condition.
Sequential transition words
Sequential transition words indicate a sequence, whether it’s the order in which events occurred chronologically or the order you’re presenting them in your text. They can be used for signposting in academic texts.
Transition words are often used incorrectly. Make sure you understand the proper usage of transition words and phrases, and remember that words with similar meanings don’t necessarily work the same way grammatically.
Misused transition words can make your writing unclear or illogical. Your audience will be easily lost if you misrepresent the connections between your sentences and ideas.
Confused use of therefore
“Therefore” and similar cause-and-effect words are used to state that something is the result of, or follows logically from, the previous. Make sure not to use these words in a way that implies illogical connections.
- We asked participants to rate their satisfaction with their work from 1 to 10. Therefore , the average satisfaction among participants was 7.5.
The use of “therefore” in this example is illogical: it suggests that the result of 7.5 follows logically from the question being asked, when in fact many other results were possible. To fix this, we simply remove the word “therefore.”
- We asked participants to rate their satisfaction with their work from 1 to 10. The average satisfaction among participants was 7.5.
Starting a sentence with also , and , or so
While the words “also,” “and,” and “so” are used in academic writing, they are considered too informal when used at the start of a sentence.
- Also , a second round of testing was carried out.
To fix this issue, we can either move the transition word to a different point in the sentence or use a more formal alternative.
- A second round of testing was also carried out.
- Additionally , a second round of testing was carried out.
Transition words creating sentence fragments
Words like “although” and “because” are called subordinating conjunctions . This means that they introduce clauses which cannot stand on their own. A clause introduced by one of these words should always follow or be followed by another clause in the same sentence.
The second sentence in this example is a fragment, because it consists only of the “although” clause.
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed. Although other researchers disagree.
We can fix this in two different ways. One option is to combine the two sentences into one using a comma. The other option is to use a different transition word that does not create this problem, like “however.”
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed, although other researchers disagree.
- Smith (2015) argues that the period should be reassessed. However , other researchers disagree.
And vs. as well as
Students often use the phrase “ as well as ” in place of “and,” but its usage is slightly different. Using “and” suggests that the things you’re listing are of equal importance, while “as well as” introduces additional information that is less important.
- Chapter 1 discusses some background information on Woolf, as well as presenting my analysis of To the Lighthouse .
In this example, the analysis is more important than the background information. To fix this mistake, we can use “and,” or we can change the order of the sentence so that the most important information comes first. Note that we add a comma before “as well as” but not before “and.”
- Chapter 1 discusses some background information on Woolf and presents my analysis of To the Lighthouse .
- Chapter 1 presents my analysis of To the Lighthouse , as well as discussing some background information on Woolf.
Note that in fixed phrases like “both x and y ,” you must use “and,” not “as well as.”
- Both my results as well as my interpretations are presented below.
- Both my results and my interpretations are presented below.
Use of and/or
The combination of transition words “and/or” should generally be avoided in academic writing. It makes your text look messy and is usually unnecessary to your meaning.
First consider whether you really do mean “and/or” and not just “and” or “or.” If you are certain that you need both, it’s best to separate them to make your meaning as clear as possible.
- Participants were asked whether they used the bus and/or the train.
- Participants were asked whether they used the bus, the train, or both.
Archaic transition words
Words like “hereby,” “therewith,” and most others formed by the combination of “here,” “there,” or “where” with a preposition are typically avoided in modern academic writing. Using them makes your writing feel old-fashioned and strained and can sometimes obscure your meaning.
- Poverty is best understood as a disease. Hereby , we not only see that it is hereditary, but acknowledge its devastating effects on a person’s health.
These words should usually be replaced with a more explicit phrasing expressing how the current statement relates to the preceding one.
- Poverty is best understood as a disease. Understanding it as such , we not only see that it is hereditary, but also acknowledge its devastating effects on a person’s health.
Using a paraphrasing tool for clear writing
With the use of certain tools, you can make your writing clear. One of these tools is a paraphrasing tool . One thing the tool does is help your sentences make more sense. It has different modes where it checks how your text can be improved. For example, automatically adding transition words where needed.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or writing rules make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Academic Writing
- Avoiding repetition
- Effective headings
- Passive voice
- Taboo words
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 23). Transition Words & Phrases | List & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-writing/transition-words/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, using conjunctions | definition, rules & examples, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, what is your plagiarism score.
A guide to writing history essays
This guide has been prepared for students at all undergraduate university levels. Some points are specifically aimed at 100-level students, and may seem basic to those in upper levels. Similarly, some of the advice is aimed at upper-level students, and new arrivals should not be put off by it.
The key point is that learning to write good essays is a long process. We hope that students will refer to this guide frequently, whatever their level of study.
Why do history students write essays?
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written.
An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument. In a history essay, this will inevitably involve a degree of narrative (storytelling), but this should be kept to the minimum necessary to support the argument – do your best to avoid the trap of substituting narrative for analytical argument. Instead, focus on the key elements of your argument, making sure they are well supported by evidence. As a historian, this evidence will come from your sources, whether primary and secondary.
The following guide is designed to help you research and write your essays, and you will almost certainly earn better grades if you can follow this advice. You should also look at the essay-marking criteria set out in your course guide, as this will give you a more specific idea of what the person marking your work is looking for.
Where to start
First, take time to understand the question. Underline the key words and consider very carefully what you need to do to provide a persuasive answer. For example, if the question asks you to compare and contrast two or more things, you need to do more than define these things – what are the similarities and differences between them? If a question asks you to 'assess' or 'explore', it is calling for you to weigh up an issue by considering the evidence put forward by scholars, then present your argument on the matter in hand.
A history essay must be based on research. If the topic is covered by lectures, you might begin with lecture and tutorial notes and readings. However, the lecturer does not want you simply to echo or reproduce the lecture content or point of view, nor use their lectures as sources in your footnotes. They want you to develop your own argument. To do this you will need to look closely at secondary sources, such as academic books and journal articles, to find out what other scholars have written about the topic. Often your lecturer will have suggested some key texts, and these are usually listed near the essay questions in your course guide. But you should not rely solely on these suggestions.
Tip : Start the research with more general works to get an overview of your topic, then move on to look at more specialised work.
Crafting a strong essay
Before you begin writing, make an essay plan. Identify the two-to-four key points you want to make. Organize your ideas into an argument which flows logically and coherently. Work out which examples you will use to make the strongest case. You may need to use an initial paragraph (or two) to bring in some context or to define key terms and events, or provide brief identifying detail about key people – but avoid simply telling the story.
An essay is really a series of paragraphs that advance an argument and build towards your conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on one central idea. Introduce this idea at the start of the paragraph with a 'topic sentence', then expand on it with evidence or examples from your research. Some paragraphs should finish with a concluding sentence that reiterates a main point or links your argument back to the essay question.
A good length for a paragraph is 150-200 words. When you want to move to a new idea or angle, start a new paragraph. While each paragraph deals with its own idea, paragraphs should flow logically, and work together as a greater whole. Try using linking phrases at the start of your paragraphs, such as 'An additional factor that explains', 'Further', or 'Similarly'.
We discourage using subheadings for a history essay (unless they are over 5000 words in length). Instead, throughout your essay use 'signposts'. This means clearly explaining what your essay will cover, how an example demonstrates your point, or reiterating what a particular section has added to your overall argument.
Remember that a history essay isn't necessarily about getting the 'right' answer – it's about putting forward a strong case that is well supported by evidence from academic sources. You don't have to cover everything – focus on your key points.
In your introduction or opening paragraph you could indicate that while there are a number of other explanations or factors that apply to your topic, you have chosen to focus on the selected ones (and say why). This demonstrates to your marker that while your argument will focus on selected elements, you do understand the bigger picture.
The classic sections of an essay
Introduction.
- Establishes what your argument will be, and outlines how the essay will develop it
- A good formula to follow is to lay out about 3 key reasons that support the answer you plan to give (these points will provide a road-map for your essay and will become the ideas behind each paragraph)
- If you are focusing on selected aspects of a topic or particular sources and case studies, you should state that in your introduction
- Define any key terms that are essential to your argument
- Keep your introduction relatively concise – aim for about 10% of the word count
- Consists of a series of paragraphs that systematically develop the argument outlined in your introduction
- Each paragraph should focus on one central idea, building towards your conclusion
- Paragraphs should flow logically. Tie them together with 'bridge' sentences – e.g. you might use a word or words from the end of the previous paragraph and build it into the opening sentence of the next, to form a bridge
- Also be sure to link each paragraph to the question/topic/argument in some way (e.g. use a key word from the question or your introductory points) so the reader does not lose the thread of your argument
- Ties up the main points of your discussion
- Should link back to the essay question, and clearly summarise your answer to that question
- May draw out or reflect on any greater themes or observations, but you should avoid introducing new material
- If you have suggested several explanations, evaluate which one is strongest
Using scholarly sources: books, journal articles, chapters from edited volumes
Try to read critically: do not take what you read as the only truth, and try to weigh up the arguments presented by scholars. Read several books, chapters, or articles, so that you understand the historical debates about your topic before deciding which viewpoint you support. The best sources for your history essays are those written by experts, and may include books, journal articles, and chapters in edited volumes. The marking criteria in your course guide may state a minimum number of academic sources you should consult when writing your essay. A good essay considers a range of evidence, so aim to use more than this minimum number of sources.
Tip : Pick one of the books or journal articles suggested in your course guide and look at the author's first few footnotes – these will direct you to other prominent sources on this topic.
Don't overlook journal articles as a source. They contain the most in-depth research on a particular topic. Often the first pages will summarise the prior research into this topic, so articles can be a good way to familiarise yourself with what else has 'been done'.
Edited volumes can also be a useful source. These are books on a particular theme, topic or question, with each chapter written by a different expert.
One way to assess the reliability of a source is to check the footnotes or endnotes. When the author makes a claim, is this supported by primary or secondary sources? If there are very few footnotes, then this may not be a credible scholarly source. Also check the date of publication, and prioritise more recent scholarship. Aim to use a variety of sources, but focus most of your attention on academic books and journal articles.
Paraphrasing and quotations
A good essay is about your ability to interpret and analyse sources, and to establish your own informed opinion with a persuasive argument that uses sources as supporting evidence. You should express most of your ideas and arguments in your own words. Cutting and pasting together the words of other scholars, or simply changing a few words in quotations taken from the work of others, will prevent you from getting a good grade, and may be regarded as academic dishonesty (see more below).
Direct quotations can be useful tools if they provide authority and colour. For maximum effect though, use direct quotations sparingly – where possible, paraphrase most material into your own words. Save direct quotations for phrases that are interesting, contentious, or especially well-phrased.
A good writing practice is to introduce and follow up every direct quotation you use with one or two sentences of your own words, clearly explaining the relevance of the quote, and putting it in context with the rest of your paragraph. Tell the reader who you are quoting, why this quote is here, and what it demonstrates. Avoid simply plonking a quotation into the middle of your own prose. This can be quite off-putting for a reader.
- Only include punctuation in your quote if it was in the original text. Otherwise, punctuation should come after the quotation marks. If you cut out words from a quotation, put in three dots (an ellipsis [ . . .]) to indicate where material has been cut
- If your quote is longer than 50 words, it should be indented and does not need quotation marks. This is called a block quote (use these sparingly: remember you have a limited word count and it is your analysis that is most significant)
- Quotations should not be italicised
Referencing, plagiarism and Turnitin
When writing essays or assignments, it is very important to acknowledge the sources you have used. You risk the charge of academic dishonesty (or plagiarism) if you copy or paraphrase words written by another person without providing a proper acknowledgment (a 'reference'). In your essay, whenever you refer to ideas from elsewhere, statistics, direct quotations, or information from primary source material, you must give details of where this information has come from in footnotes and a bibliography.
Your assignment may be checked through Turnitin, a type of plagiarism-detecting software which checks assignments for evidence of copied material. If you have used a wide variety of primary and secondary sources, you may receive a high Turnitin percentage score. This is nothing to be alarmed about if you have referenced those sources. Any matches with other written material that are not referenced may be interpreted as plagiarism – for which there are penalties. You can find full information about all of this in the History Programme's Quick Guide Referencing Guide contained in all course booklets.
Final suggestions
Remember that the easier it is to read your essay, the more likely you are to get full credit for your ideas and work. If the person marking your work has difficulty reading it, either because of poor writing or poor presentation, they will find it harder to grasp your points. Try reading your work aloud, or to a friend/flatmate. This should expose any issues with flow or structure, which you can then rectify.
Make sure that major and controversial points in your argument are clearly stated and well- supported by evidence and footnotes. Aspire to understand – rather than judge – the past. A historian's job is to think about people, patterns, and events in the context of the time, though you can also reflect on changing perceptions of these over time.
Things to remember
- Write history essays in the past tense
- Generally, avoid sub-headings in your essays
- Avoid using the word 'bias' or 'biased' too freely when discussing your research materials. Almost any text could be said to be 'biased'. Your task is to attempt to explain why an author might argue or interpret the past as they do, and what the potential limitations of their conclusions might be
- Use the passive voice judiciously. Active sentences are better!
- Be cautious about using websites as sources of information. The internet has its uses, particularly for primary sources, but the best sources are academic books and articles. You may use websites maintained by legitimate academic and government authorities, such as those with domain suffixes like .gov .govt .ac or .edu
- Keep an eye on word count – aim to be within 10% of the required length. If your essay is substantially over the limit, revisit your argument and overall structure, and see if you are trying to fit in too much information. If it falls considerably short, look into adding another paragraph or two
- Leave time for a final edit and spell-check, go through your footnotes and bibliography to check that your references are correctly formatted, and don't forget to back up your work as you go!
Other useful strategies and sources
- Student Learning Development , which offers peer support and one-on-one writing advice (located near the central library)
- Harvard College's guide to writing history essays (PDF)
- Harvard College's advice on essay structure
- Victoria University's comprehensive essay writing guide (PDF)
History Essay Format & Thesis Statement
- 1 Thesis Statement
- 2 The History Essay Format
- 3 Quotes, Footnotes and Bibliography
- 4 Plagiarism
- 5 Formatting Requirements
- 6 Basic Essay Conventions
- 7 Use of Capital Letters
- 8 Miscellaneous Characteristics
- 9 References
Thesis Statement [ edit | edit source ]
A thesis statement is generally a single sentence (The last sentence of Intro) within the introductory paragraph of the history (or thesis) essay, which makes a claim or tells the reader exactly what to expect from the rest of the text. It may be the writer's interpretation of what the author or teacher is saying or implying about the topic. It may also be a hypothesis statement (educated guess) which the writer intends to develop and prove in the course of the essay.
The thesis statement, which is in some cases underlined, is the heart of a history or thesis essay and is the most vital part of the introduction. The assignment may not ask for a thesis statement because it may be assumed that the writer will include one. If the history assignment asks for the student to take a position, to show the cause and effect, to interpret or to compare and contrast, then the student should develop and include a good thesis statement.
Following the introductory paragraph and its statement, the body of the essay presents the reader with organized evidence directly relating to the thesis and must support it.
It's a summarized writing about what you're talking about and why who what where when or how.
Characteristics of a great thesis statement
- Is a strong statement or fact which ends with a period, not a question.
- Is not a cliché [1] such as “fit as a fiddle”, “time after time”, “a chain is only as strong as its weakest link”, “all in due time” or “what goes around comes around”.
- Is not a dictionary definition.
- Is not a generalization.
- Is not vague, narrow or broad.
- States an analytic argument or claim, not a personal opinion or emotion.
- Uses clear and meaningful words.
- Don't overuse a topic.
- Try to use many different information.
- Don't say something boring like "today im going to tell you yada yada yada"
- Start with a hook then back it up with informations
The History Essay Format [ edit | edit source ]
Essay is an old French word which means to “attempt”. An essay is the testing of an idea or hypothesis (theory). A history essay (sometimes referred to as a thesis essay ) will describe an argument or claim about one or more historical events and will support that claim with evidence, arguments and references. The text must make it clear to the reader why the argument or claim is as such.
Introduction
Unlike a persuasive essay where the writer captures the reader's attention with a leading question, quotation or story related to the topic, the introduction in a history essay announces a clear thesis statement and explains what to expect in the coming paragraphs. The Introduction includes the key facts that are going to be presented in each paragraph.
The following phrases are considered to be poor and are normally avoided in the introduction: “ I will talk about ”, “ You will discover that ”, “ In this essay ”, “ You will learn ” or other such statements.
Body (Supporting Paragraphs)
The paragraphs which make up the body of a history essay offers historical evidence to support the thesis statement. Typically, in a high school history essay, there will be as many supporting paragraphs as there are events or topics. The history teacher or assignment outline may ask for a specific number of paragraphs. Evidence such as dates, names, events and terms are provided to support the key thesis.
The topic sentence tells the reader exactly what the paragraph is about. Typically, the following phrases are never part of a topic sentence: “ I will talk about ”, “ I will write about ” or “ You will see ”. Instead, clear statements which reflect the content of the paragraph are written.
The last sentence of a supporting paragraph can either be a closing or linking sentence. A closing sentence summarizes the key elements that were presented. A linking sentence efficiently links the current paragraph to the next. Linking can also be done by using a transitional word or phrase at the beginning of the next paragraph.
In the closing paragraph, the claim or argument from the introduction is restated differently. The best evidence and facts are summarized without the use of any new information. This paragraph mainly reviews what has already been written. Writers don't use exactly the same words as in their introduction since this shows laziness. This is the author's last chance to present the reader with the facts which support their thesis statement.
Quotes, Footnotes and Bibliography [ edit | edit source ]
Quotations in a history essay are used in moderation and to address particulars of a given historical event. Students who tend to use too many quotes normally lose marks for doing so. The author of a history essay normally will read the text from a selected source, understand it, close the source (book for web site for example) and then condense it using their own words. Simply paraphrasing someone else’s work is still considered to be plagiarism. History essays may contain many short quotes.
Quotations of three or fewer lines are placed between double quotation marks. For longer quotes, the left and right margins are indented by an additional 0.5” or 1 cm, the text is single-spaced and no quotation marks are used. Footnotes are used to cite the source.
Single quotation marks are used for quotations within a quotation. Three ellipsis points (...) are used when leaving part of the quotation out. Ellipsis cannot be used at the start of a quotation.
Footnotes are used to cite quotation sources or to provide additional tidbits of information such as short comments.
Internet sources are treated in the same way printed sources are. Footnotes or endnotes are used in a history essay to document all quotations. Footnotes normally provide the author's name, the title of the work, the full title of the site (if the work is part of a larger site), the date of publication, and the full URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the document being quoted. The date on which the web site was consulted is normally included in a footnote since websites are often short-lived. [2]

Bibliography
Unless otherwise specified by the history teacher or assignment outline, a bibliography should always be included on a separate page which lists the sources used in preparing the essay.
The list is always sorted alphabetically according to the authors’ last name. The second and subsequent line of each entry of a bibliography is indented by about 1 inch, 2.5 cm or 10 spaces.
A bibliography is normally formatted according to the “Chicago Manual of Style” or “The MLA Style Manual”.
Plagiarism [ edit | edit source ]
History and thesis essay writers are very careful to avoid plagiarism since it is considered to be a form of cheating in which part or all of someone else’s work is passed as one’s own. Useful guidelines to help avoid plagiarism can be found in the University of Ottawa document "Beware of Plagiarism". [3]
Formatting Requirements [ edit | edit source ]
- Letter-sized 8.5”x11” or A4 plain white paper
- Double-spaced text
- 1.5” (3 cm) left and right margins, 1” (2.5 cm) top and bottom margins
- Regular 12-point font such as Arial, Century Gothic, Helvetica, Times New Roman and Verdana
- A cover page with the course name, course number, group number, essay title, the teacher’s name, the author's name, the due date and optionally, the name of the author's school, its location and logo
- Page numbers (with the exception of the cover page)
- No underlined text with the exeception of the thesis statement
- No italicized text with the exception of foreign words
- No bolded characters
- No headings
- No bullets, numbered lists or point form
- No use of the these words: “Firstly”, “Secondly”, “Thirdly”, etc.
- Paragraph indentation of approximately 0.5 inch, 1 cm or 5 spaces
- Formatting according to the “Chicago Manual of Style” [4] or the “MLA Style”. [5]
Basic Essay Conventions [ edit | edit source ]
- Dates: a full date is formatted as August 20, 2009 or August 20th, 2009. The comma and the “th” separate the day from the year.
- Dates: a span of years within the same century is written as 1939-45 (not 1939-1945).
- Dates: no apostrophe is used for 1600s, 1700s, etc.
- Diction: a formal tone (sophisticated language) is used to address an academic audience.
- Numbers: for essays written in countries where the metric system is used (e.g., Europe, Canada), no commas are used to separate groups of three digits (thousands). For example, ten thousand is written as 10 000 as opposed to 10,000.
- Numbers: numbers less than and equal to 100 are spelled out (e.g., fifteen).
- Numbers: round numbers are spelled out (e.g., 10 thousand, 5 million).
- Numbers: for successive numbers, digits are used (e.g., 11 women and 96 men).
- Percentages: the word “percent” is used instead of its symbol % unless listing successive figures. When listing many figures, the % symbol is also used.
- Pronouns: the pronoun “I” is not used since the writer does not need to refer to him/herself unless writing about “taking a position” or making a “citizenship” statement.
- Pronouns: the pronoun “you” is not used since the writer does not need to address the reader directly.
- Tone: in a history or thesis essay, the writer does not nag, preach or give advice.
Use of Capital Letters [ edit | edit source ]
A history or thesis essay will make use of capital letters where necessary.
- Brand names, trademarks or product names
- First word of a direct quotation
- First word of a sentence
- Name or title of a book, disc, movie or other literary works
- Names of distinctive historical periods (e.g., Middle Ages)
- Names of festivals and holidays
- Names of languages (e.g., English, French)
- Names of school subjects, disciplines or specialties are not capitalized unless they happen to be the names of languages
- Names of the days of the week and of the months of the year (e.g., Monday, January)
- Pronoun I (e.g., “Yesterday, I was very happy.”)
- Proper names (e.g., John Smith, Jacques Cartier)
- Religious terms (e.g., God, Sikhs)
- Roman numerals (e.g., XIV)
- Words that create a connection with a specific place (e.g., French is capitalized when it is used in the context of having to do with France)
- Words that identify nationalities, ethnic groups or social groups (e.g., Americans, Canadians, Loyalists)
Miscellaneous Characteristics [ edit | edit source ]
- A word processor such as Microsoft Word [6] or a free downloadable processor such as Open Office [7] could be used to format and spell-check the text.
- An essay plan or a graphic organizer could be used to collect important facts before attempting to write the essay.
- Correct use of punctuation; periods, commas, semicolons and colons are used to break down or separate sentences.
- Paragraphs are not lengthy in nature.
- Street or Internet messaging jargon such as “a lot”, “:)”, “lol” or “bc” is not used.
- Text that remains consistent with the thesis statement.
- The essay has been verified by a peer and/or with the word processor's spell-check tool.
- The same verb tense is used throughout the essay.
References [ edit | edit source ]
- ↑ A cliché is an expression or saying which has been overused to the point of losing its original meaning; something repeated so often that has become stale or commonplace; "ready-made phrases".
- ↑ “History and Classics: Essay Writing Guide” (on-line). Edmonton, Alberta: Faculty of Arts, University of Alberta. uofaweb.ualbert.ca (January 2009).
- ↑ Uottawa.ca
- ↑ More information on the “Chicago Manual of Style” can be found at chicagomanualofstyle.org
- ↑ More information on the “MLA Style Manual” and “Guide to Scholarly Publishing” can be found on the Modern Language Association web site at mla.org Guides can be ordered online.
- ↑ Office.microsoft.com
- ↑ Openoffice.org
- Pages moved from Wikipedia
Navigation menu
How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.
What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?
Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?
Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
AllAssignmentHelp.com
Linking Words To Use In An Essay

Table of Contents
Concerned that your essay isn’t logical or has enough structure? You can include linking words, or transition words to make it stronger.
An essay is a crucial type of academic paper. It needs to have a clear flow so that the readability is perfect. Precisely stated, the sentences you create should naturally flow into one another. However, using linking words helps ensure that the sentences in your essay make sense. The words serve as the perfect linkers and overpasses to break up sentence segmentation. Additionally, these words can be used to present a conclusion, provide details, summarise, highlight a point, arrange material, compare and contrast ideas, and give illustrations. You might not be aware of these words and how to use them in your essay writing. Don’t worry. We are here to help you! This blog of All Assignment Help will let you know all about linking words and how you can use them in your essay writing to make it more effective and readable.
What are Linking Words?
Linking words are those words that showcase a connection between sentences. They help in forming the uniformity in the essay. Often referred to as transition words, these words serve to establish a connection between paragraphs or other essay sections. Linking words serves as a means of connecting the ideas or thoughts expressed in essays.
Moreover, the use of linking words makes your writing look more logical. Thus, you should use proper linking words to reduce the reading efforts of the readers. Your essay shouldn’t cause readers mental strain to understand it. Therefore, it is essential to make things simple for them.
Essays commonly use linking words in the following places:
- The beginning of a paragraph
- Beginning of a statement that expands on an argument or presents something new
- At the start of a concluding statement
However, you need to use the right to link it from one another sentences or paragraphs. For example, when you are writing an argumentative essay , you need to make sure the flow of linking words is correct and logical so that the argument you are presenting sounds accurate.
Read Here: Words You May Find Confusing
The Reasons Behind Using Linking Words in Essays
Essay sentences that link is a crucial component of academic writing. To put it another way, you cannot write a paper without using them. Otherwise, readers will not understand what you have written. Linking words in the essay are used to:
- Link concepts in your writing
- Organize your ideas and arguments so that readers can follow along and grasp what you are trying to communicate.
- Lead readers from one concept to the next while highlighting their connections.
- Draw readers in and encourage them to continue reading the following sentence or paragraph
- Provide more details
- Strengthen or disprove an argument
- Show the outcome, draw a conclusion, and illustrate how this or that point is affected
Every phrase and paragraph in an essay must lead the reader to the next one using essay maker and connecting words. The purpose of these transitional words is to help readers move from one idea or point to the next.
Three Main Types of Linking Words
There are three main types of linking words i.e. coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions. Let’s discuss these three more briefly.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are utilized to join two or more equally important items. Another name for them is FANBOYS, which is a shorthand for For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, and So.
For example, she is putting a lot of effort into her studies to gain admission to a reputable university.
Subordinating Conjunctions
A subordinate clause is joined to a main clause by a subordinating conjunction. However, the supporting clause cannot stand alone as a sentence and is of lesser significance than the main clause.
For example, she stayed home from work because she felt sick.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are utilized in pairs to connect two things of equal value. They are used to illustrate the connection between two concepts.
For example, not only did she finish her work, but she also helped her colleagues.
You can learn about the types of linking words by taking an online course. You can also hire someone to take your online class for you to get professional assistance which will help you in acing your online course with great credits.
Useful Linking Words for Essay Writing
It is not an easy task to compose a compelling essay. If you want to make your essay more appealing and expressive, focus on research, presentation, and persuasion. However, if you don’t have a knack for writing, then you will fail miserably in forming a logical essay with judicial use of linking words.
There are various categories of linking words one can use while writing an essay. Here, you will share the main categories and word lists to be used while framing an essay.

Linking Words List for Agreement/Addition/Similarity
Using linking words can help the reader understand further remarks or concepts in a statement. They might also convey agreement or similarities. These words are also known as additive transition words, which are often utilized in narrative and explanatory essay writings. The words used to link in such context are:
- In the first place
- As a matter of fact
- In like manner
- In addition
- Not only, but also
- In the same manner
- First, second, third
- Not to mention
- In the light of
- Furthermore
- Comparatively
- At the same time
- Together with
- Identically
List Of Linking Words for Sequence/Order
Any kind of essay needs to have flow. Your essay will lose its brilliance if there is a lack of consistency or logical flow of ideas. Here is a linking word list that helps by showing a sequence order in the essay.
- First/ Second/ Third or Firstly/ secondly/ Thirdly
- Primary/ Secondary
- At this point of time
- Concurrently
- First of all
- Following this
- The next step
- In the beginning
- It all started when
- Once upon a time
- To begin with/ To start with
Linking Word List for Opposition/Limitation/Contradiction
However, certain linking words provide additional information, these transitional words and phrases convey opposing concepts in writing. These are:
- Although this may be true
- In contrast
- Different from
- On the other hand
- On the contrary
- Nonetheless
- Even so/though
- Nevertheless
List Of Words for The Conclusion
An essay with a strong conclusion is considered to be excellent. Unfortunately, most students conclude their essays with nearly the same words, but you have the opportunity to do so here. Look at the linking words list for an excellent conclusion:
- To conclude
- In conclusion
- On the whole
- Summarising
- By and large
- All things considered
- In the long run
- For the most part
- By the large
- Consequently
- As a result
Linking Word List to Give Place/Location/Geographical Area
They can be used alone or in combination with words from other categories. They are almost often used together with other terms from the aforementioned groups. They are used to define, limit, or restrict space like the time ones. However, students often face difficulties when using linking words to write about a place and location, which ultimately leads them to buy online essay writing help from professionals. Here is your list of words that you can use to give a location or place.
- in the background
- in the center of
- adjacent to
- opposite to
- to the left/right
- on this site
List of Linking Words for Examples/Support/Emphasis
Transition words that provide examples or strengthen an idea might be used in your essay writing. Here is a list of words that can be used to improvise such contexts:
- In other words
- To put it differently
- For one thing
- In particular
- As an illustration
- In this case
- For example
- For instance
- For this reason
- To put it another way
- To demonstrate
- That is to say
- With attention to
- By all means
- To emphasize
Words for Reason/Reference
You can use these linking words to explain connections between concepts and give explanations for what has started or happened.
- for the purpose of
- seeing that
- with this in mind
- as applied to
- the fact that
- granted that
- in order to
- with this purpose
- considering
- in connection to
- with regards to
- provided that
Linking Words for Time/Chronology/Sequence
Another function of linking words in literature is to illustrate chronology or sequence. These expressions give time a meaning that is included in the time category. These are the types of words that appear in the introduction of an essay when a writer outlines the structure of the work.
- Sooner or later
- Up to the present time
- To begin with
- Straightaway
- In the meantime
- In a moment
- Without delay
Linking Words for Outcomes/Impacts/Repercussions
These particular words are used to demonstrate how one item affected another, to illustrate the outcomes of an action, or to demonstrate how something affected something else. A short list of transitions that work well for this specific category is shown below.
- consequently
- for this reason
- in that case
- as a result
Also Read: Your Guide Towards Writing An Outstanding Short Essay!
Final Thoughts!
The importance of linking words in essay writing cannot be overstated. These words are crucial for connecting concepts and making your essay read as a cohesive whole. Your essay will flow more naturally the more well-organized your thoughts are. Additionally, your writing will have a logical framework and an engaging read when you make use of linking words correctly.
However, to learn more about these words, you can choose to sign up for an online English class. An online English class will help you boost your knowledge about linking words and how you can use them in your writing. Furthermore, whenever you find yourself struggling with your English class and want to pay someone to take my online English class for me, you can hire an online class helper who will be there to take your worries aside.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 243,115 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source

Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?
Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

Transition Words
As a "part of speech" transition words are used to link words, phrases or sentences. They help the reader to progress from one idea (expressed by the author) to the next idea. Thus, they help to build up coherent relationships within the text.
Transitional Words
This structured list of commonly used English transition words — approximately 200, can be considered as quasi complete. It can be used (by students and teachers alike) to find the right expression. English transition words are essential, since they not only connect ideas, but also can introduce a certain shift, contrast or opposition, emphasis or agreement, purpose, result or conclusion, etc. in the line of argument. The transition words and phrases have been assigned only once to somewhat artificial categories, although some words belong to more than one category.
There is some overlapping with prepositions and postpositions, but for the purpose of usage and completeness of this concise guide, I did not differentiate.
Linking & Connecting Words — Part 1/2
Agreement / Addition / Similarity
Opposition / limitation / contradiction, examples / support / emphasis, cause / condition / purpose, effect / consequence / result, conclusion / summary / restatement, time / chronology / sequence, space / location / place.
The transition words like also, in addition, and, likewise , add information , reinforce ideas , and express agreement with preceding material.
in the first place
not only ... but also
as a matter of fact
in like manner
in addition
coupled with
in the same fashion / way
first, second, third
in the light of
not to mention
to say nothing of
equally important
by the same token
identically
together with
comparatively
correspondingly
furthermore
additionally
Transition phrases like but , rather and or , express that there is evidence to the contrary or point out alternatives , and thus introduce a change the line of reasoning ( contrast ).
although this may be true
in contrast
different from
of course ..., but
on the other hand
on the contrary
at the same time
in spite of
even so / though
be that as it may
(and) still
even though
nevertheless
nonetheless
notwithstanding
These transitional phrases present specific conditions or intentions .
in the event that
granted (that)
as / so long as
on (the) condition (that)
for the purpose of
with this intention
with this in mind
in the hope that
to the end that
for fear that
in order to
seeing / being that
provided that
only / even if
inasmuch as
These transitional devices (like especially ) are used to introduce examples as support , to indicate importance or as an illustration so that an idea is cued to the reader.
in other words
to put it differently
for one thing
as an illustration
in this case
for this reason
to put it another way
that is to say
with attention to
by all means
important to realize
another key point
first thing to remember
most compelling evidence
must be remembered
point often overlooked
to point out
on the positive side
on the negative side
specifically
surprisingly
significantly
particularly
in particular
for example
for instance
to demonstrate
to emphasize
to enumerate
Some of these transition words ( thus, then, accordingly, consequently, therefore, henceforth ) are time words that are used to show that after a particular time there was a consequence or an effect .
Note that for and because are placed before the cause/reason. The other devices are placed before the consequences or effects.
as a result
under those circumstances
in that case
because the
consequently
accordingly
These transition words and phrases conclude , summarize and / or restate ideas, or indicate a final general statement . Also some words (like therefore ) from the Effect / Consequence category can be used to summarize.
as can be seen
generally speaking
in the final analysis
all things considered
as shown above
in the long run
given these points
as has been noted
for the most part
in conclusion
to summarize
by and large
on the whole
in any event
in either case
These transitional words (like finally ) have the function of limiting, restricting, and defining time . They can be used either alone or as part of adverbial expressions .
at the present time
from time to time
sooner or later
up to the present time
to begin with
in due time
in the meantime
in a moment
without delay
all of a sudden
at this instant
first, second
immediately
straightaway
by the time
occasionally
Many transition words in the time category ( consequently; first, second, third; further; hence; henceforth; since; then, when; and whenever ) have other uses.
Except for the numbers ( first, second, third ) and further they add a meaning of time in expressing conditions, qualifications, or reasons. The numbers are also used to add information or list examples . Further is also used to indicate added space as well as added time.
These transition words are often used as part of adverbial expressions and have the function to restrict, limit or qualify space . Quite a few of these are also found in the Time category and can be used to describe spatial order or spatial reference.
in the middle
to the left/right
in front of
on this side
in the distance
here and there
in the foreground
in the background
in the center of
adjacent to
opposite to
List of Transition Words

Transition Words are also sometimes called (or put in the category of) Connecting Words. Please feel free to download them via this link to the category page: Linking Words & Connecting Words as a PDF. It contains all the transition words listed on this site. The image to the left gives you an impression how it looks like.
Usage of Transition Words in Essays
Transition words and phrases are vital devices for essays , papers or other literary compositions. They improve the connections and transitions between sentences and paragraphs. They thus give the text a logical organization and structure (see also: a List of Synonyms ).
All English transition words and phrases (sometimes also called 'conjunctive adverbs') do the same work as coordinating conjunctions : they connect two words, phrases or clauses together and thus the text is easier to read and the coherence is improved.
Usage: transition words are used with a special rule for punctuation : a semicolon or a period is used after the first 'sentence', and a comma is almost always used to set off the transition word from the second 'sentence'.
Example 1: People use 43 muscles when they frown; however, they use only 28 muscles when they smile.
Example 2: however, transition words can also be placed at the beginning of a new paragraph or sentence - not only to indicate a step forward in the reasoning, but also to relate the new material to the preceding thoughts..
Use a semicolon to connect sentences, only if the group of words on either side of the semicolon is a complete sentence each (both must have a subject and a verb, and could thus stand alone as a complete thought).
Further helpful readings about expressions, writing and grammar: Compilation of Writing Tips How to write good ¦ Correct Spelling Study by an English University
Are you using WORD for writing professional texts and essays? There are many easy Windows Shortcuts available which work (almost) system-wide (e.g. in every programm you use).

How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
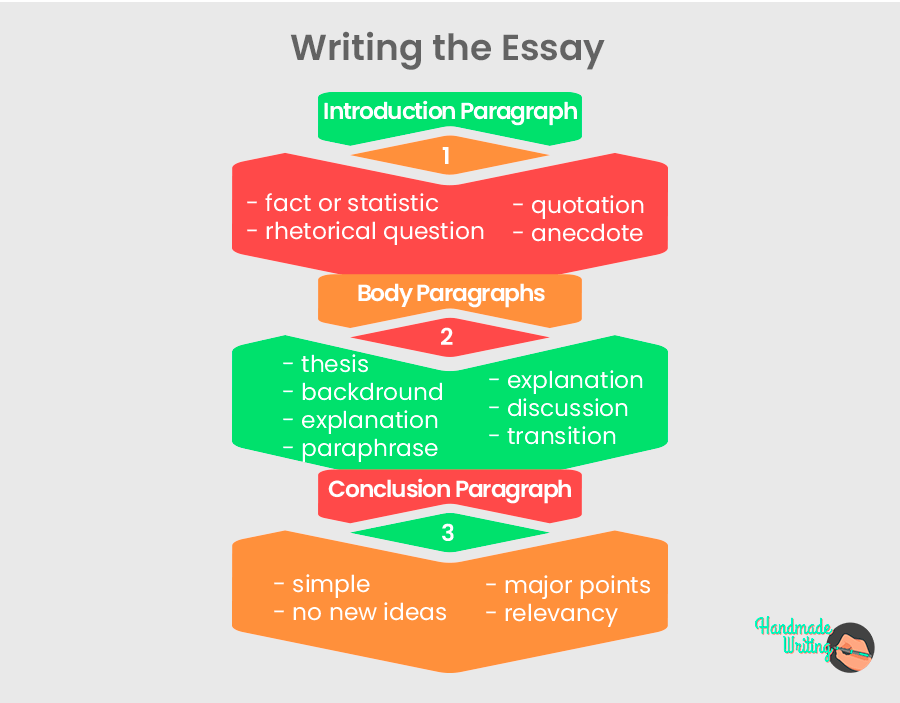
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

- TEFL Internship
- TEFL Masters
- Find a TEFL Course
- Special Offers
- Course Providers
- Teach English Abroad
- Find a TEFL Job
- About DoTEFL
- Our Mission
- How DoTEFL Works
Forgotten Password

- Linking Words & Connector Words: Ultimate List With Examples
- Learn English
- James Prior
- No Comments
- Updated February 23, 2024

Linking words and connector words are essential tools for effective communication and writing. They play a crucial role in connecting ideas, enhancing coherence, and guiding the flow of information. Whether you’re writing an essay, giving a presentation, or engaging in a conversation, using appropriate linking words can greatly improve the clarity and effectiveness of your message.
In this ultimate list of linking words, we have compiled a comprehensive collection of linking words along with examples to help you understand their usage and apply them in various contexts. From words that highlight contrast and similarity to those that indicate cause and effect or order of importance, this list covers a wide range of linking words to suit different purposes.
Ready to link your words? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What are linking words?
Linking words, also known as connector words or transition words, are words or phrases that connect ideas or parts of a text, providing coherence and smoothness to the overall flow of information. They serve as bridges between sentences, paragraphs, or even larger sections of a document, helping to establish relationships, indicate contrasts, add information, show cause and effect, provide examples, and more.
Here are some common categories of linking words with examples:
Linking words for addition
Addition: Words that show the addition of information or ideas.
These linking words and phrases can help you add information, reinforce ideas, or provide further examples in your writing or conversation. Use them appropriately to expand on your points and enhance the overall coherence and richness of your communication.
- She is fluent in English, and additionally, she speaks French and Spanish.
- The report highlights the benefits of renewable energy; furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of conservation.
- The new system not only improves efficiency but moreover, it reduces costs.
- In addition to his regular job, he volunteers at a local charity.
- She not only excels in academics but also actively participates in extracurricular activities.
- The team consists of experienced professionals as well as enthusiastic newcomers.
- The company values teamwork; likewise, it fosters individual growth and development.
- Besides working full-time, he manages to pursue his hobbies and spend time with famil
- The website offers free shipping; what’s more, customers can enjoy a 30-day money-back guarantee.
- On top of their regular duties, employees are encouraged to take part in professional development opportunities.
- Developing strong interpersonal skills is equally important as acquiring technical knowledge.
- The event attracted a large audience, not to mention the media coverage it received.
- Along with the new software update, customers will also receive enhanced customer support.
- The company achieved its sales targets for the year; what is more, it surpassed them by 20%.
- The team completed the project ahead of schedule; besides that, they received positive feedback from the client.
- The company’s commitment to quality, coupled with its competitive pricing, sets it apart from its competitors.
Linking words for contrast
Contrast: Words that highlight differences or contrasting ideas.
These linking words and phrases can help you express contrasting ideas and show the differences between two or more concepts or situations. Remember to use them appropriately based on the context and your intended meaning.
- She studied hard; however, she didn’t pass the exam.
- John loves traveling; on the other hand, his sister prefers staying at home.
- The weather was terrible; nevertheless, they decided to go for a walk.
- He had a sprained ankle; nonetheless, he played in the soccer match.
- Despite the rain, they went to the beach.
- In spite of the traffic, they arrived on time.
- Although it was late, they continued with their work.
- Even though she was tired, she went to the gym.
- I enjoy reading, while my brother prefers watching movies.
- Sarah loves cooking, whereas her husband prefers eating out.
- Unlike his friends, Mark is not a fan of horror movies.
- She hates winter; conversely, I love it.
- She expected him to be upset; on the contrary, he was happy.
- They planned to go to the cinema, but instead, they stayed home and watched a movie.
- The cat is small and playful, in contrast to the dog, which is big and lazy.
- He enjoys sports; conversely, his sister prefers art.
- On one hand, the book is interesting; on the other hand, it’s quite lengthy.
- They could go by car, or alternatively, they could take the train.
- The movie received mixed reviews; nevertheless, it became a box office hit.
- She didn’t pass the test, but in any case, she learned a lot from studying.
Linking words for similarity
Similarity: Words that highlight similarities or shared ideas.
These linking words and phrases can help you express similarities between two or more ideas, situations, or individuals. Use them appropriately based on the context to highlight shared characteristics or experiences.
- Sarah enjoys reading; likewise, her brother is an avid reader.
- John and Emily both love hiking; similarly, they enjoy spending time in nature.
- Just as Sarah likes swimming, in the same way, her best friend enjoys diving.
- Jack has a passion for photography, similarly to his sister who is also an enthusiast.
- Just like her mother, Jane has a talent for playing the piano.
- The two artists approach their work in a similar vein, both using vibrant colors and bold brushstrokes.
- Mark loves cooking, and by the same token, he also enjoys experimenting with new recipes.
- As the workload increased, the stress levels of the employees correspondingly rose.
- Both Sarah and Emily are equally skilled in playing the guitar.
- The designer creates unique clothing pieces, and in a similar fashion, the jewelry maker crafts one-of-a-kind accessories.
- Just as the sun rises in the morning, the moon appears in the evening.
- The teacher explains complex concepts in a simple and understandable way, in the same manner as her colleague.
- He enjoys hiking and camping, and his friends, likewise, too, share his enthusiasm for outdoor activities.
- Just as a bird builds its nest with care and precision, in the same way, an architect plans and constructs a building.
- The two books explore themes of love and loss, along similar lines, inviting readers to contemplate the human experience.
- As with all great artists, Picasso’s work continues to inspire and influence generations.
- Exercise is essential for physical health, and just as importantly, it is crucial for mental well-being.
- Much like a puzzle, life consists of various pieces that fit together to form a bigger picture.
Linking words for cause and effect
Cause and Effect: Words that demonstrate cause and effect relationships.
These linking words and phrases can help you express the cause-and-effect relationship between events or actions. Use them appropriately based on the context to convey the reason and result of a particular situation or occurrence.
- He failed the exam because he didn’t study.
- They arrived early since they left home on time.
- As a result of heavy rainfall, the streets were flooded.
- The event was canceled due to bad weather conditions.
- The store was closed, therefore, they had to find another place to shop.
- He missed the train, consequently, he arrived late to the meeting.
- Owing to a power outage, the concert was postponed.
- She didn’t have enough sleep, thus, she felt tired throughout the day.
- He couldn’t attend the party, for this reason, he sent his apologies.
- The storm caused damage to the houses, resulting in the need for repairs.
- The baby was hungry, so she started crying.
- Lack of exercise and poor diet often leads to weight gain.
- They missed the train because of heavy traffic.
- The roads were icy, this is why there were many accidents.
- They spent all their money, as a consequence, they couldn’t afford the trip.
- He quit smoking, and since then, he feels healthier.
- The company introduced a new product, and in turn, its sales increased.
- She studied hard so that she could pass the exam.
Linking words for time and sequence
Time and sequence: Words that indicate time or sequence of events or actions.
These linking words and phrases can help you express the chronological order and sequence of events or actions. Use them appropriately to guide your audience through the progression of ideas or to outline the steps in a process or narrative.
- Firstly, let’s discuss the main causes of climate change.
- Secondly, we need to consider the potential solutions to the problem.
- Next, we will move on to the implementation phase of the project.
- We need to complete the research phase first. Then, we can start analyzing the data.
- After that, we can proceed with the construction of the building.
- The company experienced financial difficulties. Subsequently, they had to lay off several employees.
- The team was working on the project. Meanwhile, the marketing department was preparing the promotional materials.
- The two processes are happening simultaneously, ensuring efficient production.
- The report will be ready in a week. In the meantime, please proceed with the other tasks.
- During the meeting, we will discuss the budget and timeline.
- While he was studying, his friends were playing video games.
- Please wait here until your name is called.
- We need to complete the paperwork before the deadline.
- She attended the conference, and afterward, she shared her insights with the team.
- Finally, we reached an agreement after a long negotiation process.
- In the end, they decided to cancel the project due to budget constraints.
- The presentation was engaging, and at the same time, informative.
- Initially, he struggled with the new software, but with practice, he became proficient.
- At first, the project seemed overwhelming, but with proper planning, it became manageable.
Linking words for order of importance
Order of Importance: Words that highlight the hierarchy or ranking of ideas based on their significance.
These linking words and phrases can help you establish the order of importance when presenting ideas or arguments. Use them to emphasize the significance of certain points, highlight key considerations, or guide the reader’s attention to the most critical aspects.
- Most importantly, we need to prioritize the safety of our employees.
- Above all, we must prioritize the needs of our customers.
- The company’s success primarily depends on effective leadership and strategic planning.
- First and foremost, we need to address the urgent issue of inflation.
- The new policy chiefly focuses on reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Notably, the project resulted in significant cost savings for the organization.
- Above anything else, maintaining a high standard of quality is our top priority.
- It is essential to note that effective communication is the foundation of strong relationships.
- It is worth mentioning that the company’s ethical practices have earned it a positive reputation.
Linking words for exemplification
Example: Words that provide examples or illustrate a point.
These linking words and phrases can help you introduce examples and provide further clarification or evidence to support your statements. Use them to enhance your explanations and illustrate your points effectively.
Here’s a list of linking words and phrases that are commonly used to illustrate an example, along with examples:
- There are many fruits you can choose from, for example, apples, oranges, and bananas.
- Many countries have implemented environmental policies; for instance, Sweden has significantly reduced its carbon emissions.
- I enjoy outdoor activities such as hiking, cycling, and swimming.
- The party was attended by several guests, including friends, family, and colleagues.
- He has many hobbies, like painting, playing the guitar, and photography.
- The company provides various employee benefits, as an illustration, health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
- Let me give you an example to illustrate my point.
- There are several endangered species in the area, namely the African elephant, the Bengal tiger, and the giant panda.
- The city offers various attractions, in particular, museums, parks, and historical landmarks.
- The project requires specific skills, specifically programming and data analysis.
- By way of example, let’s consider the case of a successful startup that disrupted the market.
- To give an example, let’s say you want to improve your fitness; you can try activities like jogging, swimming, or joining a gym.
- The experiment was conducted to demonstrate the effects of temperature on plant growth.
- As a case in point, many countries have implemented renewable energy initiatives to combat pollution.
- I will use a specific scenario to exemplify how the new policy can be implemented effectively.
- The job requires strong communication skills , in essence, the ability to express ideas clearly and persuasively.
- The city has invested in renewable energy projects to reduce its carbon footprint. One example of this is the installation of solar panels on public buildings.
- To be specific, the company offers three main product lines: electronics, appliances, and furniture.
- The data collected serves as proof that the new marketing strategy is effective.
- In a similar manner, many companies have embraced remote work as a response to the pandemic.
Linking words for focusing
These linking words and phrases can help you direct attention or emphasize a specific aspect of your discussion or argument. Use them appropriately to highlight the main points or focus areas, ensuring clarity and precision in your communication.
Here’s a list of linking words and phrases that are commonly used to express focusing or directing attention, along with examples:
- Specifically, we need to address the issue of employee turnover in our department.
- The marketing team has made significant progress, particularly in digital advertising.
- In particular, we need to improve our customer service to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Notably, the company achieved a record-breaking sales figure in the last quarter.
- This task requires attention to detail, especially when dealing with sensitive data.
- Specifically speaking, the new software update addresses the security vulnerabilities.
- Above all, we must prioritize the safety of our employees.
- The company’s success mainly relies on customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- The primary goal of our project is to reduce waste and promote sustainability.
- Essentially, our focus should be on optimizing operational efficiency.
- Individually, each team member plays a crucial role in achieving our objectives.
- Precisely, we need to adhere to the project timeline to meet the deadline.
- Specifically, with regards to customer feedback, we have received positive reviews.
- The new product line has a sleek design, not to mention its advanced features.
- It is worth noting that the market trends are shifting towards online shopping.
- Above everything else, we need to prioritize the quality of our products.
- In essence, our primary objective is to provide exceptional customer service.
- To be more precise, we should focus on improving our supply chain management.
- In specific terms, the sales team needs to focus on building client relationships.
- More importantly, we need to address the concerns raised by our customers.
Linking words for conclusion
Conclusion: Words that summarize or conclude a text.
These linking words and phrases can help you signal the conclusion of your argument, presentation, or essay. Use them to summarize key points, restate your main argument, or provide a final thought or recommendation.
- In conclusion, it is evident that deforestation poses a significant threat to our planet.
- To sum up, the project was a great success, exceeding all expectations.
- Ultimately, the decision lies in your hands.
- All in all, it was a memorable vacation filled with adventure and relaxation.
- Lastly, I would like to thank everyone for their hard work and dedication.
- In summary, the findings of the study suggest a strong correlation between exercise and mental well-being.
- To conclude, the evidence supports the hypothesis that regular exercise improves cardiovascular health.
- The data collected consistently points to the same conclusion; therefore, we can confidently assert our findings.
- In essence, the research demonstrates that social media has a profound impact on interpersonal relationships.
- The campaign received widespread support, and as a result, donations increased significantly.
- In a nutshell, the project aims to promote sustainability through renewable energy initiatives.
- The experiments consistently yielded similar results; thus, we can draw a definitive conclusion.
- The evidence strongly suggests a link between smoking and lung cancer; hence, it is crucial to raise awareness about the risks.
- In light of these findings, it is necessary to reconsider the current educational policies.
- The company faced financial challenges, and consequently, had to downsize its workforce.
- In conclusion, it can be stated that effective communication is the key to successful teamwork.
- Taking all factors into account, it is clear that globalization has both positive and negative consequences.
- The lack of investment resulted in decreased productivity, as a consequence, the company experienced a decline in profits.
- The study findings reveal a correlation between stress levels and sleep quality; thus, it can be inferred that managing stress positively affects sleep.
- Given these points, it is evident that the project should be prioritized for its long-term benefits.
If you’d like more examples, check out this list of other ways to say in conclusion .
Conclusion: Ready to link your words?
These are just some examples of linking words, and there are numerous other linking words and phrases available for different purposes and contexts. Using them appropriately can greatly enhance the clarity and coherence of your writing or speech. So, if you want to become more fluent in English, it’s time to start thinking about linking words!
- Recent Posts
- What Can You Do with a TEFL Certificate? - April 5, 2024
- 19 Best Learning Management System Examples for 2024 - April 4, 2024
- How to Study While Working: 11 Tips for Working & Studying - March 29, 2024
More from DoTEFL

Traveling or Travelling? Which is the Correct Spelling?
- Updated February 5, 2024
Insure vs Ensure vs Assure: Difference, Meanings & Examples
- Updated October 19, 2023

Do TEFL Certificates Expire? What You Need to Know
- Updated January 29, 2024

21 Synonyms for Communication Skills to Use on Your Resume
- Updated February 14, 2024

What is an EFL Teacher & What Does EFL Teaching Involve?
- Updated March 7, 2024

25 Fun Games to Play on Zoom With Your Students
- Updated May 12, 2023
- The global TEFL course directory.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
The Ultimate List of Linking Words for Your Essay

Let’s face it: You can’t write an essay (or any other writing piece) without linking words.
Also known as connecting words or transition words, they serve to make your writing flow and help those reading your work follow the flow of your thoughts, ideas , and arguments .
This post is your guide to linking words and their role in writing. Not only will you learn the types of these words, examples, and reasons to use them, but you’ll also get a massive list of transition words and phrases as well as linking words PDF to download and use whenever necessary.
Table of Contents:
What are Linking Words?
Why use transition words in essays, linking words examples, addition/agreement/similarity, contrast/contradiction/limitation/opposition, comparison/concession/condition, clarification, cause/effect/result, emphasis/example, generalization, illustration, location/place/space, reason/reference, time/sequence, summary/conclusion/restatement.
- The Ultimate List of Linking Words: Download
Linking words are lexical items (words and phrases) we use to connect ideas in writing and get a reader to the next sentence or paragraph.
They aren’t about essay writing only:
Whether you write a fiction book, marketing content , academic works, autobiography , or poems, you’ll need to connect ideas. That’s what transition words do:
They link your thoughts and arguments into a chain to show how they relate to each other. Also known as transition words, these phrases often start a sentence or a paragraph. However, you’ll also use them in the middle of sentences to bring ideas together.
The most common places for linking words in essays are:
- the start of a paragraph
- the start of a sentence introducing a new idea or extending an argument
- the beginning of a concluding statement
Essay linking words is an integral part of academic writing. Put it simply, you can’t write a paper without using them; otherwise, your writing won’t make any sense for readers.
Transition words for essay serve to:
- connect ideas in writing
- create a flow of thoughts and arguments for readers to understand what you want to say
- guide readers from one idea to another, demonstrating how they relate to each other
- hook readers and encourage them to read the next sentence or paragraph
- add more information
- support or contrast a point
- show the result, conclude, demonstrate an effect of this or that point
Using essay maker and connecting words, each sentence and paragraph must pass readers on to the next one. These connecting words serve as an instrument to guide readers from one thought or point to the next.
Linking words examples are many, and it’s clear why: every piece of writing contains tons of connecting and transition words. Let’s take an essay sample from Bid4Papers writers to see the example of linking words in academic writing:

This one was an essay introduction .
Now, why not take a step further and look for essay linking words in essay conclusions ?

Types and List of Linking Words to Use in Essays
Below you’ll find the ultimate list of transition words for essays by categories. Choose the role you need a word to play (reason, contrast, emphasis, restatement, etc.) and consider the corresponding table of transitions.
If you need the whole transition words list in one place, jump to the next category of this post to find the downloadable linking words pdf.
And now, for connecting words categories:
These words serve to add info to what you’ve previously stated, demonstrate the commonality between arguments, and support your thoughts.
Linking words for contrast is your instrument to show how things are different and provide counterarguments. They work best in persuasive and critical essays.
These lexical items will help you if you need to provide conditions to your statements, show how things are different/similar, or accept a point with reservation.
These words will help you with personal or narrative essays: They are linking words in opinion writing that indicates you’re going to explore ideas in more detail.
Expository essays will win with these words too.
Cause and effect connecting words do what their name says exactly: demonstrating a cause of some point and providing the result of what has been done or started.
These words are for putting forward your point more forcefully, providing examples.
Perfect transition words for hypothesis essays , generalization lexical items serve to make a general statement you’ll then specify and prove in detail.
These words and phrases are for you to provide examples in essays.
Use these words to provide order and reference or clarify spatial relationships between your points or ideas.
These transitional words will help you demonstrate relationships between ideas and provide reasons for what and why has started or occurred.
Use these words in your essay when you need to indicate the time and order of what you say.
Restatement words will help you express an alternative to what you previously stated. They work for all essay types, including rhetorical precis and dialectic essays .
Use summary and conclusion transitional phrases to sum up your points and come up with the final paragraph of your writing.
The Ultimate List of Connecting Words: Download
And now, for the most interesting and practical part:
Below you can find the linking words worksheet that gathers all the most commonly used transitional words in essays. Feel free to download this linking words PDF and refer to it every time you write an essay and experience writer’s block:
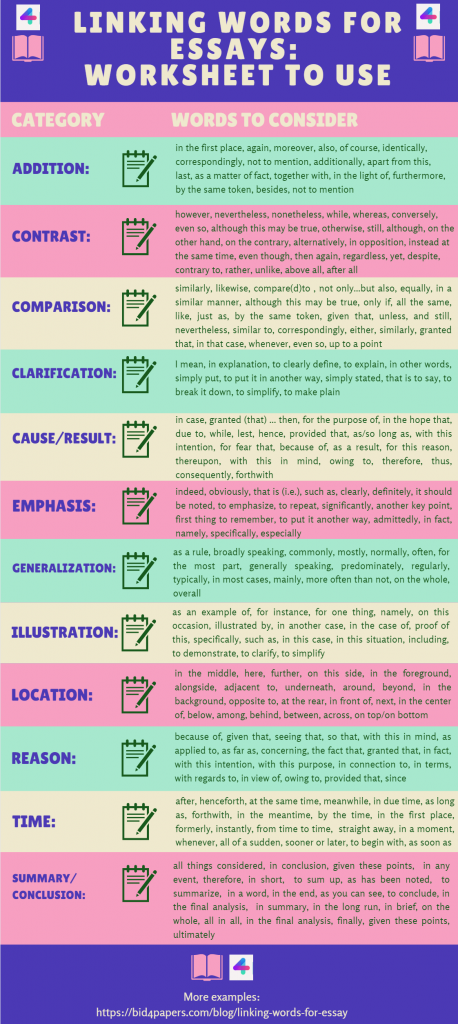
Do you need more guides and worksheets like this to assist you with academic writing? Please share your ideas in the comments, and our writers will be happy to help!
Related posts
- What Is the Difference between Primary and Secondary Sources
- Common Types of Plagiarism with Examples
- Exemplification Essay – Ideas and Tips
Our Writing Guides
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Linking Words for Essay Writing: Useful Paragraph Phrases

Importance of Linking Words in Essay Writing
An essay is an important piece of writing when a student is seeking college admission. It needs to have a clear flow so that the readability is perfect. Rightly so, the sentences you construct need to flow and lead to each other seamlessly.
Linking or transition words come in handy to make your essay have comprehensible sentences. The words act as the ideal connectors and bridges that eliminate sentence isolation.

Factually, both writing and speaking need linking words that will help the audience form a clear relationship between ideas. Listeners and readers are able to comprehend responses when the right linking words are in place.
What are Linking Words in Essay Writing?
Linking words are the uniformity basis of an essay. When these words are in an essay, they showcase a connection between sentences. As usual, a typical essay consists of different sections and paragraphs.
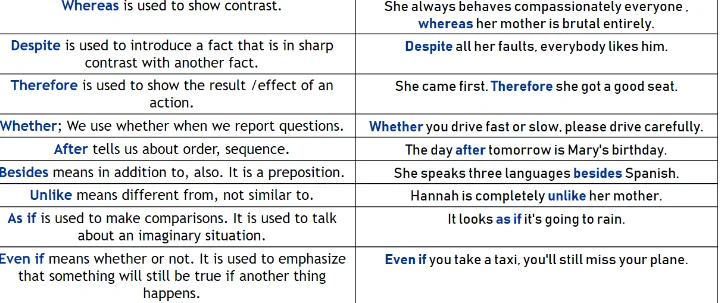
If there are no transition words, the sentences will appear incoherent and messy. The use of linking words clearly show the relationship existing between all sections and paragraphs in an essay.
When writing your essay, make use of linking words as a bridge between the concepts you are writing and ideas in your essay. The readers will enjoy a cohesive piece of essay with texts that are flowing smoothly.
The assessment team has a lot of essays to read and you can make their work easy by using your linking words appropriately. If this is not the case, your professor will have to go through a lot of stress in trying to understand your essay.
Basically, if you want to impress your readers and consequently improve your scores, practice the best linking words skills.
Reasons for Using Linking Words in Essay Writing
Only proper usage of linking words will help you come up with a compelling essay. After toiling to conduct research for your essay, improper structure of sentences will make your efforts go to waste.
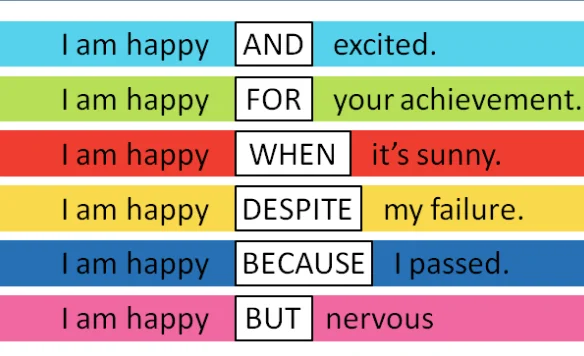
Good students endeavor and strive to create an appealing and expressive essay. A thorough use of the right linking words will make your presentation and persuasion of ideas flow perfectly.
Linking words are very crucial in any type of essay . If you do not want your texts to appear clucky, transition words ought to be in place.
Here are more reasons why you need linking words in your essay:
1. Flow of order and sequence
An essay needs flow of texts, ideas and thoughts otherwise it will lose its quality. Therefore, writers need to make huge efforts and use the right linking words that will bring a sequence of order in the essay.
Such words include next, then, firstly, secondly, afterwards, finally and afterwards. Other transition words to use include concurrently, at the same time, earlier, first of all, following this and for now.
A good sequence order in your essay is also enhanced when you use words such as lastly, in the end, in the beginning or once upon a time.
2. Showcasing comparison
There are essays that will require the writer to show comparison. Linking words play an important role in contrast and argumentative essays .
If you need to bring out comparison clearly, consider the use of words such as similarly, equally, comparable, in the same time and likewise.
Apart from same as, other words or phrases to use include just like, just as and comparably.
3. Contrasting

Transition words are the best when you want to bring out contrast in a sentence. In most of the cases, place then at the beginning or in the middle of your sentence to create the right contrast.
However, despite this, yet, whereas and alternatively are some of the words you can use.
4. Illustration of examples
There are places in your essay where you will have to give examples. Obviously, most essays will need illustration of evidence with the use of linking words.
Giving examples without these words will make your text to sound blunt.
Linking words such as for instance, in the case of, and for instance will make it easy to introduce your examples.
5. Including additions
You will also need to use linking words when putting additions in your essays. These words will ensure that you have added a txt with the correct meaning to your essay.
Furthermore, also, secondly, in addition and moreover are some of the linking words to use.
6. Introduction of cause and effects
Cause and effects in an essay can help the writer draw a sensible conclusion. In essence, it helps to bring about good connection of the essay when a conclusion is being added. Therefore, the relationship between cause and effect is better shown using the right linking words.
Owing to, thus, since, as a result of and because are some of the transition words you can use. Other words to use include stems from, leads to, results from, for this reason etc.
7. For conclusion purposes
Starting an impressive essay can only be better if the conclusion is attractive. It is good to bring about the conclusion using appropriate linking words that are not common.
You can conclude your essay using words such as finally, in conclusion, summarizing, in summary and briefly.
As a writer, you need to bear in mind that adjusting and positioning these words is a must if you are to impress your readers.
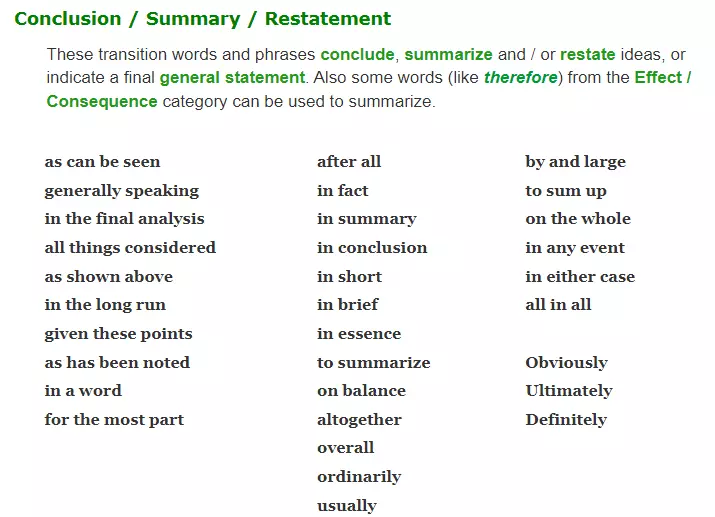
Dos of Using Linking Words
- Adjust and position your linking words properly otherwise the reader will not be impressed.
- Do mix up the linking words you use. Using one word several times can be very annoying to the reader. Since the transition phrases are many, mix them up in your essay to avoid repetition.
- Be accurate in using these words when connecting your ideas in an essay. Know the difference between these phrases to understand the meaning correctly.
- You can use these words when you want to accentuate a point. In other words, use them to stress something important in your writing.
30 Examples of Linking Words for Essay Writing
- On the flipside
- On the contrary
- By and large
- As a consequence of
- In conclusion
- Following this
- At this point of time
- In the same way
- As an example
- In other words
- To put it differently
- Under the circumstances
- That is to say
- With this intention
- Subsequently
- In order to
- Of less importance
- What’s more
- Furthermore
- Alternatively
- In spite of
- To illustrate
- To demonstrate
- In the middle of
- For the avoidance of doubt
Wrapping Up on Linking words on Essay Writing
You can’t overlook the significance of linking words in essay writing. Transition words are important in bringing ideas together so that they appear as a whole in your essay.
All in all, an essay that flows well must incorporate the right transition words to link arguments and actions. The readers will be able to connect an event that took place because of a consequence of a different action.
Essays need to have a flow of ideas with each one building on the other. Yet still, organization of thoughts in essay writing is valuable and this is where linking words play a critical role.
To sum it up, the more your thoughts are in good organization, the smoother your essay will flow. When you use linking words appropriately, your piece will have a logical structure that is appealing to the reader.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Writing a College Admission Essay
Is College Essay Mandatory: Universities It’s not an Option

Writing honors college essay
Honors College Essay: Tips, Prompt Examples and How to Write

Guide to writing narrative essay
How to Write a Narrative Essay: A Stepwise Guide and Length
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Times Insider
Grunge: A Dull Date, the Sound of Seattle, a ‘Time Capsule’
The New York Times has a long and complicated history with the word grunge. Let’s get down and dingy in it.

By Sarah Diamond
In Word Through The Times, we trace how one word or phrase has changed throughout the history of the newspaper.
The New York Times and “grunge” go way back.
“Grunge,” according to the Oxford English Dictionary , was originally “a general term of disparagement for someone or something that is repugnant or odious, unpleasant, or dull.” Per the dictionary, the word was first printed in 1965 — via The Times. In an article, a reporter offered definitions of slang words: “A difficult date is an ‘octopus,’” the reporter wrote, and “a dull one a ‘grunge .’”
“‘ Grunge’ is a back-formation of ‘grungy,’” Jess Zafarris, an etymologist, said. A back-formation is a word that formed when speakers stopped using a suffix or prefix that had been attached to a longer word. Kory Stamper, a lexicographer at Dictionary.com, said the origin of “grungy” was unknown but that it most likely came into being in the mid-20th century from words like dingy, goo and gunge, British slang for a sticky unknown substance.
Soon, the slang word stuck to subversive music. According to Green’s Dictionary of Slang , “grunge” was used in a 1973 New Yorker article to describe the New York Dolls, a rock band. But by the late 1980s, “grunge” defined the sound of a city on the other side of the United States: Seattle . Bands like Nirvana, Pearl Jam, Soundgarden and Mudhoney popularized grunge music, a mash of heavy metal and punk rock. And as the grunge sound reverberated across the country, the aligning subculture grew louder, too.
In November 1992, The Times, eager to cover a hip moment, published a “lexicon of grunge speak.” Megan Jasper, a 25-year-old sales representative at Caroline Records in Seattle, had offered some slang phrases for the article: “Wack slacks,” for example, were old, ripped jeans. “Swingin’ on the flippity-flop” meant hanging out. And “tom-tom club” was code for uncool outsiders. Which, apparently, were some people at The Times: After the article came out, it was revealed in The Baffler that Ms. Jasper had fabricated the words to poke fun at the mainstream media’s coverage of culture. The story behind the prank was explored in a 2017 article by The Ringer.
The embarrassment didn’t stop The Times’s interest in grunge. Appearances of the word in the newspaper peaked in 1993.
That may be because in the early 1990s, grunge itself peaked in popularity. So did grunge fashion, modeled by people like Kurt Cobain, the lead singer of Nirvana. Loose fits, flannel shirts, ripped jeans, Converse sneakers and Dr. Martens defined the disheveled style. Soon, grunge marched down the runways: In 1993, Marc Jacobs was a “grunge enthusiast,” The Times wrote. “Gianni Versace did grunge,” The Times reported from Milan fashion week, in a “luxury” take “on the scruffy look of downtown Seattle music groups.”
By the late 1990s, grunge had lost its cool. But as is often the case, “grunge” eventually came back into style: In February this year, the reporter Callie Holtermann wrote that fans of Olivia Rodrigo were embracing “grunge fashion from the ’90s” at concerts.
“Grunge,” Ms. Stamper said, has “become a time capsule.”
That’s certainly true for Steven Kurutz, a Styles reporter. In 2019, he wrote an article about how “grunge made blue-collar culture cool.” In the ’90s, Mr. Kurutz went to high school in Pennsylvania, 2,600 miles from Seattle, but felt he could see his community in the grunge subculture. “I could not relate, coming from a working-class, rural background, to so much of pop culture,” he said in an interview. “I think that’s why the music meant even more for me as a teenager, because I was seeing guys on MTV who looked like the people I grew up around. And they were cool!”
For Mr. Kurutz, “grunge” is nostalgic. “I just think about Seattle in 1992.”
Sarah Diamond manages production for narrated articles. She previously worked at National Geographic Studios. More about Sarah Diamond

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
50 linking words to use in academic writing. academic writing. linkers. essay writing. thesis. ESL. English. It's very common for students to use long words they don't understand very well in their essays and theses because they have a certain idea of what academic writing should be.
Like. Too. As. As well as. Moreover. Here are some examples of additive linking words in a sentence. The group found that a constructivist approach leads to higher test scores. Moreover, essay examinations show higher levels of learning. The resort has tennis courts.
While transition words are essential to clear writing, it's possible to use too many of them. Consider the following example, in which the overuse of linking words slows down the text and makes it feel repetitive. The first experiment yielded a positive result. However, the second experiment yielded a negative result.
History Essay Guidelines _____ 4 societies. In using one particular form as an example in the following paragraph, we do not suggest that it is the only or necessarily the best model for your essays. A common and effective kind of essay is the kind that attempts to prove the validity of a hypothesis.
While each paragraph deals with its own idea, paragraphs should flow logically, and work together as a greater whole. Try using linking phrases at the start of your paragraphs, such as 'An additional factor that explains', 'Further', or 'Similarly'. We discourage using subheadings for a history essay (unless they are over 5000 words in length).
the History Paper The Challenges of Writing About (a.k.a., Making) History At first glance, writing about history can seem like an overwhelming task. History's subject matter is immense, encompassing all of human affairs in the recorded past — up until the moment, that is, that you started reading this guide.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops ...
A linking sentence efficiently links the current paragraph to the next. Linking can also be done by using a transitional word or phrase at the beginning of the next paragraph. ... The author of a history essay normally will read the text from a selected source, understand it, close the source (book for web site for example) and then condense it ...
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
A system of claiming, settling, ruling and maintaining one or more colonies (see imperialism) communism. A political-economic system with no state, minimal class differences and economic equality. constitutional monarchy. A political system with a monarch whose power is limited and shared with the people. democracy.
Essays commonly use linking words in the following places: The beginning of a paragraph. Beginning of a statement that expands on an argument or presents something new. At the start of a concluding statement. However, you need to use the right to link it from one another sentences or paragraphs.
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
Linking Words & Connecting Words as a PDF. It contains all the transition words listed on this site. The image to the left gives you an impression how it looks like. Usage of Transition Words in Essays. Transition words and phrases are vital devices for essays, papers or other literary compositions. They improve the connections and transitions ...
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
Conclusion: "In conclusion…". "To summarise…". "It is evident that…". "In light of the evidence provided…". "This analysis leads to the conclusion that…". Qualifying ...
These words simply add additional information to your sentence or paragraph to show that two ideas are similar. Here are some examples: It started to rain and I got soaked - 'and' is the linking word that connects the two ideas of the individual being in the rain and getting soaked. It can't be the dog's fault nor the cat's ...
These linking words and phrases can help you express similarities between two or more ideas, situations, or individuals. Use them appropriately based on the context to highlight shared characteristics or experiences. Examples: Likewise: Sarah enjoys reading; likewise, her brother is an avid reader. Similarly:
The most common places for linking words in essays are: the start of a paragraph; the start of a sentence introducing a new idea or extending an argument the beginning of a concluding statement; Why Use Transition Words in Essays. Essay linking words is an integral part of academic writing.
Sentence starters, linking words, transitional phrases To access a large on-line academic writing phrase bank go HERE To download a large PDF academic writing phrase bank go HERE
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
Sharing is caring! Linking words and phrases are used to show relationships between ideas. They can be used to join two or more sentences or clauses. We can use linking words to give a result, add information, summarize, give illustrations, emphasize a point, sequence information, compare or to contrast idea.
Linking words play an important role in contrast and argumentative essays. If you need to bring out comparison clearly, consider the use of words such as similarly, equally, comparable, in the same time and likewise. Apart from same as, other words or phrases to use include just like, just as and comparably. 3.
In an article, a reporter offered definitions of slang words: "A difficult date is an 'octopus,'" the reporter wrote, and "a dull one a 'grunge.'"