161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples
🏆 best research title examples about online class, 💡 most interesting online learning topics to write about, 📚 good online education topics for presentation, 🌐 catchy titled for online learning essay, 💻 online class research titles, ❓ research topics about online classes.
- Online Classes Vs. Traditional Classes Essay The essay shall endeavor to examine the differences between online classes and the traditional classes, with a preference for the later.
- Benefits of Online Learning This knowledge and skill one gains from online help the person to intermingle with others in a better way, progress their profession, or develop their business successfully.
- Traditional vs. Distance Learning Systems On the other hand, in online learning, the students partake learning individually, and in some cases, students doing the same course in the same college do not even get to know each other.
- The Importance of Online Learning For this purpose, it is possible to conduct classes in real-time, when they can ask and receive the opinion of others.
- Comparison of Stress Level Among Traditional Learning and Online Learning College Students The distance learners have been perceived to be enjoying a suitable environment of learning as opposed to the traditional classroom learners who experience high levels of stress.
- Online Learning and Classroom Learning Combining the two concepts then, we can define e-learning “as a learning environment that exists solely in the form of digital content that is stored, accessed and exchanged through networked computer and information systems” The […]
- Distance Learning: Advantages and Limitations All three articles cover the topic of distance learning in the context of the coronavirus and everyday practice. Speaking of the advantages of distance learning, the author suggests that remote learning may not be ideal […]
- How to Succeed in Online Classes The time you attend the class has to coincide with the time of day when your brain is also most receptive to the information it receives.
- Zoom for Online Learning Updates During the pandemic, the zoom was and is still the most downloaded App in the USA and globally compared to others.
- Virtual Learning: Yes and No Argumentation The argument stems from the quality of the education that can be received via the internet and what the drawbacks are once there is no physical contact between students and the professors.
- Personal Reflections for the MBA Distance Learning I was able to concentrate on various subjects, complete assignments, and liaise with different instructors throughout the learning process. The approach made the learning process desirable and capable of supporting my aims.
- The Impact of Distance Learning on the Mental State The argument of the supporters of the first perspective is based on the fact that online education reduces the ability of students to concentrate and deteriorates overall motivation.
- Administrative Progressivism in Relation to Online Learning The main idea of the discussion is to consider online learning from the perspective of administrative progressivism with identifying the advantages and disadvantages of using the mentioned approach along with the chosen method of study.
- Online Learning in Vocational Education and Training There are different variations in the process of learning on the basis of the types of combination and integration with the other technologies used for the teaching and learning process.
- Learning Objectives Implementation With the advent of the internet, online courses have sprouted resulting in the debate on the two options, traditional class setting, and the online class.
- Distance Learning and Its Evolution Definitions of distance education are varied and diverse, but the main concept of distance learning can be summarized from the situation wherein the student and the educator are separated by distance and time and the […]
- Changes in Learning and Motivation With the Advent of Online Learning Institutions of learning have introduced online learning through improvement of infrastructure, incorporation of new technologies in learning, recruitment of professionals who are conversant with new technologies, and revision of curriculums in order to accommodate new […]
- Distance Education vs Traditional Institutions Though both foreign and traditional education institutions provide knowledge and skills to students in order to enable them become competent in their profession, the institutions vary in the quality of degree courses they provide to […]
- The Roles of Families in Virtual Learning By analyzing the various roles that families play in virtual learning, the authors demonstrate that family involvement and support are critical to the success of their children The authors begin by discussing the impact of […]
- Distance Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic The radical transition from the traditional system of obtaining knowledge to virtual education actualizes research related to the analysis of the specifics and dysfunctions of distance learning.
- The Need for Online Learning at St. Francis Elementary School This has led to the need to design an online learning platform suitable for interactive and critical learning experiences by the tutors and their learners.
- Online Learning Perception and Effectiveness While the solution allowed students to access information and continue their studies, there was apprehension in regard to the efficacy of online learning and the outcomes such shifts have on students’ academic performances.
- Distance Learning of Forest Management Considering that the goal of the research was to analyze the results and implications of a practical approach to the forest management course engagement and e-learning development, most information was derived from the expert team […]
- A Distance Learning Program: Strategies for Successful Starting or Expanding An institution has to identify the most appropriate communication tools and media to be used by students and teachers in a distance learning program.
- Starting and Expanding Distance Learning Program Therefore, decision-makers must grapple with the problem of distant learning planning, as institutions are caught between the desire to serve students online and the requirement to maintain traditional student services.
- Factors for Teachers’ Motivation in Distance Learning Efficient communication with the administration of an institution is a crucial factor that affects the motivation of teachers in distance learning.
- Strengths and Weaknesses of Online Learning Amidst that confusion, it would be important to take a deep look into the subject and see the disadvantages and the advantages of online learning.
- Pros and Cons of Distance Education On the one hand, modernization of education allows it to expand the usual boundaries of transmitting and receiving information in the educational process while retaining all the integral components.
- Rhetorical Analysis of the Distance Education The essay can be addressed both to the children and parents for whom the issues of health and psychology are important.
- Distance Learning Experiences of In-Service Music Teachers From Puerto Rico The study explores the experiences of in-service music teachers in distance learning. This paper examines the motivations of in-service teachers in distance learning.
- Design Thinking for Online Learning Project In this paper, attention will be paid to the problem of a lack of engagement with online learning and a reflection on design thinking as its solution.
- Maximizing the Effectiveness of Online Learning Flipped learning allows the teacher to provide the greatest amount of time for direct interaction with students, which is especially important in the framework of online learning.
- New Online Learning Platform: Market Analysis The goal of online education is to enhance the knowledge of people who want to pursue a particular career for a fee that is lesser when compared to offline studies in Universities.
- Software Engineering Online Learning Center However, it is not easy to tell what the website is promoting just by the look of the homepage and thus, visitors with less time might not be interested to click to the sub-sections and […]
- Distance Education Problem Overview Generally, distance education can be evaluated as a binary prospect: on one hand, it presents a row of advantages for the people who are busy with their work and family duties, and on the other […]
- Negotiation: Distance Learning and Social Change The conflict that arises, in this case, is that the Pirates are demanding ransom money from the owners of the tanker in order to release it and its crew. The essay has given a detailed […]
- Online Learning in Jordan Universities: Effectiveness and Obstruction For the quality learning process, e-learning has been developed to use different approaches to ease the process of learning. E-learning is a novel idea in most of the Arab world and it has come with […]
- Online Learning Institutions and Courses This account allows you to access the online learning institutions library. Which are the most reliable online learning institutions?
- Professional Development Methods: Distance Education Technologies Professional development at universities has included methods to assist faculty in improving course design and educational methods, as well as in becoming familiar with and applying educational technologies, such as distance education tools. These centers […]
- Why Distance Education Can Fulfill the Purpose of a True Education? The only reason I can see for professors to frown upon distance education is that it has removed their infallibility in the eyes of the students.
- Distance Learning Fulfilling Education Purpose Distance learning mode of education, which is a kind of education that takes place when the teachers and the students are separated by space and time, does not entirely serve the purpose of education. The […]
- Distributed and Distance Learning Systems It is a system that can be of great impact to the researchers this is because one is able to get information that will help him or her get a cue for that group that […]
- Social Constructivism in Cooperative and Distance Learning As opposed to the behaviorist view of learning which gives more importance to the imitation aspects of the learner in the learning process, this constructivist theory gives greater room for the active interaction of the […]
- Online Learning and Learning Behaviours In such a way, the main reason for the creation of this project is the increased popularity of online learning and the need for the in-depth investigation of this phenomenon because of its increased demand.
- Nurses and Virtual Learning Environments: Understanding Limits in Nursing Education Despite the expected benefits and improvements in nursing education due to the use of virtual learning environments, this practice may create a number of challenges for students and teachers.
- Online Learning Design Specifications The rapid rise of technologies and the evolution of communication means resulted in the appearance of new approaches to the learning process.
- Innovative Social Networking in Online High School The preparedness of the school is also critical towards the success of this innovative technology. The school should also examine the benefits and bottlenecks of the new technology.
- Online Class and Its Outcome Measurement The focus of the paper will be on the aspect of public evaluation while considering what was involved while evaluating the impact on the class. Therefore, these are some of the outcome measures that can […]
- Online Classes for High School Students I wish to submit to you that the need for extra input in terms of study has caused many parents to enroll their children in online study classes to supplement the knowledge they get from […]
- Online Learning Environments The questions will be posted to the group by the instructor. The learners are likely to face a number of challenges in the course of the module.
- Evaluating Online Learning Tools The learners can be referred to reliable wikis and blogs to integrate the ideas learnt from the class. In this manner, the desires of people to learn are not limited by distance and time.
- Online Learning Principles and Objectives In this way, the students will not only argue the purposes and significance of the course to their life, but also create an interactive session among the students and their instructor. As the instructor, I […]
- Online Learning Space Creating Process On the other hand, a community of practice has been known to mean a crowd of people who are in the same career or share the same interest.
- Distance Learning and Virtual High School This implies that district schools in lines with virtual High school are of much importance to both the educators and students.
- Distance Education: Best Practices and Approaches The study with the use of a case-based learning system undertaken by Cifuentes, Mercer, Alverez, and Bettati in 2010 demonstrated that students could remotely participate in the learning process without the need to be physically […]
- The Importance of Virtual Learning Communities The learning communities enable the instructors and the students to volunteer their questions. The virtual learning communities enable online degree programs to give students autonomy over the learning process.
- Online Learning and Innovations in Pedagogy On the other hand, computer-based learning can be understood as a learning environment in which computers are used to mediate between learners and content without necessarily being online.
- Efficient Interaction in Distance Learning Classroom The problem is that the number of enrolments in the online form of education is augmenting, even as the knowledge regarding the factors that influence the effectiveness of distance education continues to be scarce.
- Virtual Learning Environments: Effective Use Tutors often face the challenge of effective delivery of lessons in the classroom given the diverse categories of students. Learning objects basically refer to blocks of content that can be interlinked to produce a course.
- Using Wikis to Encourage Online Classes Collaborative Work The problem is that the entire process seems to ignore the relevance of enabling students to interact and share their ideas in the learning environment.
- Technology Acceptance Model of Online Learning The findings of the study demonstrate the effectiveness of external variables related to online learning environments in predicting the ability of users to adopt online learning community.
- Formulating an Online Learning Course Reviewing is done from the student side where a person analyzes the content and readability of the information contained in the online learning program.
- Tone Impact in Distance Education Thus, in this paper, the tone will refer to the tone the instructor implies in the text material and the tone of conversations between the instructors and the students.
- Ethical Issues in Online Learning The online assessment methods should consider the ethical issues arising from the learning process. The assessment methods should be able to prevent all forms of dishonesty during the learning process.
- Virtual Learning Environment: Concord Consortium The problem is that this capitalization can be perceived as sign of rudeness, and it can make reluctant to take part in the discussion. Provided that a teacher can promote the involvement of students, they […]
- High School of Virtual Learning Environment The aim will be to see incorporation of the system, the opportunities, and the challenges faced while using Virtual Learning Environment.
- Transition From Traditional Education to Online Learning The speed of information transfer at any time and anywhere through the internet makes online learning relatively cheap compared to the traditional education system.
- Distance Learning OL and Interactive Video in Higher Education The two-way communication systems as well as the need to interact ‘physically’ between and among the participants are what propelled the adoption of this mode of learning.
- Distance Learning Foundational Concepts Another problem that arises as a result of distance learning is the lack of face to face or one on one contact between teachers or instructors and their students.
- Convenience and Flexibility of the Online Classes The advantage of online courses for full or part-time employed individuals is that you can plan how you take your courses. Online classes also introduce students to a variety of web-based tools and techniques that […]
- Concept of Distance Learning in Modern Education System The accessibility of the distance learning courses mainly depend on the awareness of the instructor to the accessibility issues and how the instructor can best handle the course with consideration of accessibility.
- Creating Student Engagement in Online Learning Environment To contribute to creating and stimulating student engagement in online learning environments, it is important to focus on such factors as the increase of students’ motivation, focus on independent and inquiry-based learning, the active role […]
- Online Learning Is a Superior Form of Education This paper will argue that online learning is a superior form of education since it helps students and learning institutes to overcome limitations imposed by the traditional learning environment.
- Contrasting an Online Class to a Traditional Class In most cases, the traditional class syllabus is usually a bit wider hence offering the trainee much more as opposed to online classes where there is lack of provisions for diversification of the subject.
- Comparison of Online Learning and Traditional Learning
- Historical and Socio Cultural Analysis of Online Learning
- Analysis of Using Online Video Lecture on Learning Outcome: The Mediating Role of Student Interaction and Student Engagement
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning in an Online Class
- Analysis of the Cyber School as an Institution With Online Methods of Learning
- Benefits & Issues of Online Learning
- Swot Analyis for Online Learning
- Comparing the Effectiveness of Classroom and Online Learning
- How Does Prior Knowledge Impact Students Online Learning Behaviors?
- How Learning Online Works?
- How Technology Can Improve Online Learning?
- Is Face For Face Learning Better Then Online Learning?
- Online Classes: A Successful Learning Environment
- Online Learning For Students With Disabilities
- Pros And Disadvantages of Online Education
- Should Online Learning Be Encouraged?
- Knowledge Gradient Algorithm for a General Class of Online Learning Problems
- Three Online Learning Strategies
- Virtual Learning Environment and Online Education
- What Factors Promote Sustained Online Discussions and Collaborative Learning in a Web-Based Course?
- Adult Learning in an Online Environment
- Analysis on Early Design for Online Learning
- Assessment of Conflict Resolution Strategies Within an Online Learning Team
- Compare and Contrast Online Learning vs Traditional Classroom Learning
- Examining the Factors that Influence how Instructors Provide Feedback in Online Learning Environments
- False Concepts Surrounding The Online Learning Environment
- Generalized Feature Embedding for Supervised, Unsupervised, and Online Learning Tasks
- Implementing Comprehensive Interventions to Support Student Success in Online Learning
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) and Online Education
- Managing Online Learning In Collabrative Group
- Managing the Online Learning Revolution in an MBA course: Quality Assurance through Strategic Development
- Online Education Is a Type of Distance Learning
- Online Learning: High School Students For College
- Online Learning: Stochastic Approximation
- Planning Strategies And Time Management Essential in Online Learning
- Development of Online Technology and the Advantages of E-Learning
- Effectiveness of Online Learning
- Reasons Why Older Students Have a Difficult Time Adjusting to Online Classes
- How Does Online Classes Work
- Why Online Learning Is Not Common Among Primary School Students
- Reasons for Taking Online Classes
- Online Classes Are More Flexible Than Conventional Education
- Online Classes Are Less Effective Than Regular Classroom Classes
- The Four Coursera Online Classes
- The Pros and Cons of Online Classes
- The Advocacy for Online Classes According to Todd Gilman
- Online Classes and Face With Face Classes
- Are Online Classes Beneficial To Students
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional and Online Classes
- Online Classes Are Becoming A Trend for College Campuses
- Online Classes Should Not Reduce Students’ Options and Opportunities
- Why Are More Students Taking Online Classes
- Online Classes vs. Traditional Classroom Learning
- The Demand for Online Classes
- Online Courses and the Impact of Weaker Interpersonal Connections in Online Classes
- The Similarities Between Online Classes and Traditional Classes
- Comparision Between Traditional Classes and Online Classes
- Online Classes Are Becoming More and More Relevant Now
- Online Classes and Oral Presentation Challenges
- The Primary Difference Between Classroom and Online Classes
- What Is the Newest Innovation in Online Learning?
- What Are Some Good Websites for Online Learning?
- Will Online Learning Will Replace Face to Face Teaching?
- Do Students Appreciate Online Learning?
- What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Online Learning?
- Which Is the Best Online Learning Platform?
- Which Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification Support Online Learning?
- How Much Does It Cost to Set up an Online Learning Management System?
- How Is Online Learning More Convenient Over the Traditional Classroom?
- Is Online Learning Becoming More Interactive With the Passage of Time?
- What Is the Relation Between Reinforcement Learning and Online Learning?
- What Are the Issues Related to Online Learning and Teaching?
- Why Do Students Struggle With Online Learning?
- What Problems and Issues Are Seen in Online Learning Communities?
- What Are the Disadvantages of Online Learning?
- What Opportunities Does Online Learning Give?
- What Are the Benefits and Challenges of Online Learning?
- What Is the Difference Between Distance Learning and Online Learning?
- Where Do Online Learning Sites Keep Videos?
- Why Do Many People Find Online Learning Really Hard?
- Is It Possible to Do Online Learning With LSTM?
- Why Do Online Learning Sites Use So Much Handwriting?
- How Effective Is Online Learning in Higher Education?
- Is SMC University a Credible Online Learning Institution?
- What Is Online Learning and Its Types?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/
"161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
- Bilingual Education Essay Ideas
- Brain-Based Learning Essay Titles
- Computers Essay Ideas
- Performance Indicators Essay Topics
- Learning Styles Essay Topics
- Online Community Essay Topics
- Cheating Questions
- Plagiarism Research Ideas

94 Online Learning Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on online learning, 👍 good online learning research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting online learning research titles, 💡 simple online learning essay ideas, ❓ research questions for online learning.
- Reasons Why Face-To-Face Education Is Better Than Online Learning
- Pros and Cons of Online Learning
- Online Learning vs. In-Person Learning
- Distance Learning: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Distance Learning vs. The Traditional Classroom
- Online Learning Technologies
- Why More and More Students Are Taking Online Classes?
- Online Learning During the Pandemic When it comes to the notion of education, the process of online learning has become salvation to the problem of education access and efficiency.
- Distance Learning and Social Change Distance learning can be defined as a form of education where learners can learn wherever they are through the use of technology.
- Online Learning and Students’ Mental Health Mental health is an aspect that attracts significant attention from researchers interested in investigating the connection between the lack of social interactions.
- Traditional vs. Virtual Learning Environment With the development of the ICT system, the traditional learning environments are in the process of developing new virtual spaces designed for learning.
- Online Classes: Computer Literacy and Knowledge The aim of the paper is to prove that educational establishments should change their policies to introduce online classes.
- Technology, Distance Education, and Its Quality This paper examines major issues associated with technology and distance learning and how they impact on the quality of education offered to learners.
- Information Technology Enabled Online Learning This paper investigates on the aspect of Information Technology – enabled online learning and the relevant technologies that are utilized.
- Learning Methods: Online Learning Online learning takes place without the physical presence of the instructor. It is a structured learning which involves online teaching in absence of the instructor.
- Learner Isolation in Distance Education Research demonstrates that distance education is the “magic bullet” in addressing nursing shortage issues and ensuring that nurses have the opportunity to advance their skills.
- Education Theory for Online Learning Teaching online entails the development of instructions for students and delivering them through technological gadgets.
- Benefits, Challenges, and Opportunities of Distance Learning This paper will explore the question of the extent distance learning can be used as an effective tool for promoting equal educational opportunities.
- Hidden Curriculum in Online Classes The hidden curriculum both for online and face-to-face classes specifies the necessity to obey rules, standards, and laws, listen to people who have more knowledge and experience.
- Theories, Tools, and Principles of Online Learning Modern technology has changed education designs. Using a range of new communications and network tools it is easy to design an online education platform.
- Past and Current Trends in Distance Education Distance learning has been evolving as time goes by and this means that there are certain trends that need to be looked at.
- Online Learning as an Integral Component of the Education System The essay will examine how online learning has become an integral component of the education system and the benefits it offers compared to the physical classroom model.
- The Benefits of Taking Online Classes The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted the majority of public and private sectors, including the education system.
- Analysis of Cultural Disconnect in Virtual Learning Environments There has been a cultural disconnect in learning environments in education. Language is the most significant contributor to cultural disconnect within the educational centers.
- The Social Interaction in an Online Learning Community The modern online education needs adjustments related to the facilitation of independent learning, student collaboration, and minimization of the role of the teacher.
- Zines Distance Learning Education and Before You Go Magazine The review of zines Distance Learning Education and Before managed to underline their significance for the modern population in terms of their functions and characteristics.
- Online Learning and Education Course Reflections The course on online learning and the application of information technologies has demonstrated to me that educators should help students reduce extraneous processing.
- Adobe Connect GoToMeeting in Distance Learning The study has focused on the impacts of implementing Adobe Connect Gotomeeting in distance learning as a collaboration tool and its impact on instructions and learning.
- Distance Learning for Addressing Nurse Shortage Distance education could be embraced to teach more individuals and address the current predicament of the nursing shortage.
- Continuing Education and Online Learning Effectiveness
- Difference Between Classroom Learning and Online Learning
- Online Learning Spanish Lesson on Reflexive Verbs and Pronouns
- Convergent and Divergent Thinking of Online Learning
- Online Learning and Traditional Learning: An Outlook Into the Past and the Future of Education
- Tips for Successful Online Learning
- Online Learning and Forecast Combination in Unbalanced Panels
- Effective Online Learning Content Delivery
- Global Opportunities for Education via Online Learning
- Kalman Filtering and Online Learning Algorithms for Portfolio Selection
- Overcoming Asynchronous Online Learning Limitations
- Generalized Feature Embedding for Supervised, Unsupervised, and Online Learning Tasks
- Online Learning for Students With Disabilities
- Study Curriculum and Instruction With an Emphasis on Online Learning
- The Knowledge Gradient Algorithm for a General Class of Online Learning Problems
- Examining the Factors That Influence How Instructors Provide Feedback in Online Learning Environments
- Students’ Achievement Emotions and Online Learning in Teacher Education
- Success Factors for Self-Paced Online Learning in Business
- Improving Online Learning: Student Perceptions of Useful and Challenging Characteristics
- Online Learning: Anywhere Anytime Education for Specialist Nursing
- Increasing Student Engagement With Online Learning Platforms
- Writing and Online Learning Tools
- Oracle-Based Robust Optimization via Online Learning
- Online Learning Event for Adult Learners
- Online Learning, Research, and Services
- The Value and Effectiveness of Online Learning
- False Concepts Surrounding the Online Learning Environment
- E-Learning, Its Effects, Advantages, Disadvantages and Why People Use It
- How Important Is Technology in Online Education? Benefits, Challenges, and Impact on Students
- The Benefits of Online Training in Schooling
- 10 Minute School – One of the Largest and Best Online Education Platforms
- Role of Digital Library in Support to Teaching and Learning: A Study
- Benefits and Challenges for the Online Learner
- Students’ Online Learning Challenges During the Pandemic
- The Effects of an Online Learning Environment
- Students’ Motivations and Barriers to Online Education
- The Different Roles Within an Online Learning Environment
- The Trends Towards Online Learning
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of Online Learning
- Planning Strategies and Time Management Essential in Online Learning
- Can Online Learning Bend the Higher Education Cost Curve?
- How Can Technology Improve Online Learning?
- What Are the Biggest Challenges Facing Online Learning Today?
- Is Online Learning Accessible to All?
- Why Is Online Learning a Very Effective Way for Students to Study?
- What Is the Impact of Online Learning on Students?
- Is Online Learning as Effective as In-Person Learning?
- What Are the Key Factors for Making Online Learning Effective in Education?
- How Can the CoI Framework Support Positive Online Learning?
- What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Online Learning?
- How Is Effective Online Learning in This Time of Pandemic?
- Is Online Learning More Effective Than Classroom?
- What Is the Environment of Online Learning?
- How Does Online Learning Affect Students’ Academic Performance?
- What Are the Best Practices for Online Teaching and Learning?
- Why Is Online Learning More Accessible?
- How Is Academic Performance Measured in Online Learning?
- Is Online Learning Effective in Educating Students?
- What Is the Impact of Online Learning on the Quality of Education?
- Why Is Online Learning Harder for Students?
- How Can We Make Online Learning More Effective?
- What Are the Negative Impacts of Online Learning?
- Is Online Learning the Future of Education?
- How Do Students Feel About Online Learning?
- What Makes a Good Online Learning Environment?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, May 10). 94 Online Learning Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/online-learning-essay-topics/
"94 Online Learning Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 10 May 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/online-learning-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '94 Online Learning Essay Topics'. 10 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "94 Online Learning Essay Topics." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/online-learning-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "94 Online Learning Essay Topics." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/online-learning-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "94 Online Learning Essay Topics." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/online-learning-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Online Learning were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on December 26, 2023 .
Advertisement
The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study
- Published: 06 September 2021
- Volume 27 , pages 429–450, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Hakan Ulum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1398-6935 1
79k Accesses
26 Citations
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students’ academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this study will provide a source to assist future studies with comparing the effect of online education on academic achievement before and after the pandemic. This meta-analysis study consists of 27 studies in total. The meta-analysis involves the studies conducted in the USA, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia. The studies included in the meta-analysis are experimental studies, and the total sample size is 1772. In the study, the funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test were utilized to determine the publication bias, which has been found to be quite low. Besides, Hedge’s g statistic was employed to measure the effect size for the difference between the means performed in accordance with the random effects model. The results of the study show that the effect size of online education on academic achievement is on a medium level. The heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Information and communication technologies have become a powerful force in transforming the educational settings around the world. The pandemic has been an important factor in transferring traditional physical classrooms settings through adopting information and communication technologies and has also accelerated the transformation. The literature supports that learning environments connected to information and communication technologies highly satisfy students. Therefore, we need to keep interest in technology-based learning environments. Clearly, technology has had a huge impact on young people's online lives. This digital revolution can synergize the educational ambitions and interests of digitally addicted students. In essence, COVID-19 has provided us with an opportunity to embrace online learning as education systems have to keep up with the rapid emergence of new technologies.
Information and communication technologies that have an effect on all spheres of life are also actively included in the education field. With the recent developments, using technology in education has become inevitable due to personal and social reasons (Usta, 2011a ). Online education may be given as an example of using information and communication technologies as a consequence of the technological developments. Also, it is crystal clear that online learning is a popular way of obtaining instruction (Demiralay et al., 2016 ; Pillay et al., 2007 ), which is defined by Horton ( 2000 ) as a way of education that is performed through a web browser or an online application without requiring an extra software or a learning source. Furthermore, online learning is described as a way of utilizing the internet to obtain the related learning sources during the learning process, to interact with the content, the teacher, and other learners, as well as to get support throughout the learning process (Ally, 2004 ). Online learning has such benefits as learning independently at any time and place (Vrasidas & MsIsaac, 2000 ), granting facility (Poole, 2000 ), flexibility (Chizmar & Walbert, 1999 ), self-regulation skills (Usta, 2011b ), learning with collaboration, and opportunity to plan self-learning process.
Even though online education practices have not been comprehensive as it is now, internet and computers have been used in education as alternative learning tools in correlation with the advances in technology. The first distance education attempt in the world was initiated by the ‘Steno Courses’ announcement published in Boston newspaper in 1728. Furthermore, in the nineteenth century, Sweden University started the “Correspondence Composition Courses” for women, and University Correspondence College was afterwards founded for the correspondence courses in 1843 (Arat & Bakan, 2011 ). Recently, distance education has been performed through computers, assisted by the facilities of the internet technologies, and soon, it has evolved into a mobile education practice that is emanating from progress in the speed of internet connection, and the development of mobile devices.
With the emergence of pandemic (Covid-19), face to face education has almost been put to a halt, and online education has gained significant importance. The Microsoft management team declared to have 750 users involved in the online education activities on the 10 th March, just before the pandemic; however, on March 24, they informed that the number of users increased significantly, reaching the number of 138,698 users (OECD, 2020 ). This event supports the view that it is better to commonly use online education rather than using it as a traditional alternative educational tool when students do not have the opportunity to have a face to face education (Geostat, 2019 ). The period of Covid-19 pandemic has emerged as a sudden state of having limited opportunities. Face to face education has stopped in this period for a long time. The global spread of Covid-19 affected more than 850 million students all around the world, and it caused the suspension of face to face education. Different countries have proposed several solutions in order to maintain the education process during the pandemic. Schools have had to change their curriculum, and many countries supported the online education practices soon after the pandemic. In other words, traditional education gave its way to online education practices. At least 96 countries have been motivated to access online libraries, TV broadcasts, instructions, sources, video lectures, and online channels (UNESCO, 2020 ). In such a painful period, educational institutions went through online education practices by the help of huge companies such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Skype, FaceTime, and Slack. Thus, online education has been discussed in the education agenda more intensively than ever before.
Although online education approaches were not used as comprehensively as it has been used recently, it was utilized as an alternative learning approach in education for a long time in parallel with the development of technology, internet and computers. The academic achievement of the students is often aimed to be promoted by employing online education approaches. In this regard, academicians in various countries have conducted many studies on the evaluation of online education approaches and published the related results. However, the accumulation of scientific data on online education approaches creates difficulties in keeping, organizing and synthesizing the findings. In this research area, studies are being conducted at an increasing rate making it difficult for scientists to be aware of all the research outside of their expertise. Another problem encountered in the related study area is that online education studies are repetitive. Studies often utilize slightly different methods, measures, and/or examples to avoid duplication. This erroneous approach makes it difficult to distinguish between significant differences in the related results. In other words, if there are significant differences in the results of the studies, it may be difficult to express what variety explains the differences in these results. One obvious solution to these problems is to systematically review the results of various studies and uncover the sources. One method of performing such systematic syntheses is the application of meta-analysis which is a methodological and statistical approach to draw conclusions from the literature. At this point, how effective online education applications are in increasing the academic success is an important detail. Has online education, which is likely to be encountered frequently in the continuing pandemic period, been successful in the last ten years? If successful, how much was the impact? Did different variables have an impact on this effect? Academics across the globe have carried out studies on the evaluation of online education platforms and publishing the related results (Chiao et al., 2018 ). It is quite important to evaluate the results of the studies that have been published up until now, and that will be published in the future. Has the online education been successful? If it has been, how big is the impact? Do the different variables affect this impact? What should we consider in the next coming online education practices? These questions have all motivated us to carry out this study. We have conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis study that tries to provide a discussion platform on how to develop efficient online programs for educators and policy makers by reviewing the related studies on online education, presenting the effect size, and revealing the effect of diverse variables on the general impact.
There have been many critical discussions and comprehensive studies on the differences between online and face to face learning; however, the focus of this paper is different in the sense that it clarifies the magnitude of the effect of online education and teaching process, and it represents what factors should be controlled to help increase the effect size. Indeed, the purpose here is to provide conscious decisions in the implementation of the online education process.
The general impact of online education on the academic achievement will be discovered in the study. Therefore, this will provide an opportunity to get a general overview of the online education which has been practiced and discussed intensively in the pandemic period. Moreover, the general impact of online education on academic achievement will be analyzed, considering different variables. In other words, the current study will allow to totally evaluate the study results from the related literature, and to analyze the results considering several cultures, lectures, and class levels. Considering all the related points, this study seeks to answer the following research questions:
What is the effect size of online education on academic achievement?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the country?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the class level?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the lecture?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the online education approaches?
This study aims at determining the effect size of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, on students’ academic achievement in different courses by using a meta-analysis method. Meta-analysis is a synthesis method that enables gathering of several study results accurately and efficiently, and getting the total results in the end (Tsagris & Fragkos, 2018 ).
2.1 Selecting and coding the data (studies)
The required literature for the meta-analysis study was reviewed in July, 2020, and the follow-up review was conducted in September, 2020. The purpose of the follow-up review was to include the studies which were published in the conduction period of this study, and which met the related inclusion criteria. However, no study was encountered to be included in the follow-up review.
In order to access the studies in the meta-analysis, the databases of Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS were reviewed by utilizing the keywords ‘online learning and online education’. Not every database has a search engine that grants access to the studies by writing the keywords, and this obstacle was considered to be an important problem to be overcome. Therefore, a platform that has a special design was utilized by the researcher. With this purpose, through the open access system of Cukurova University Library, detailed reviews were practiced using EBSCO Information Services (EBSCO) that allow reviewing the whole collection of research through a sole searching box. Since the fundamental variables of this study are online education and online learning, the literature was systematically reviewed in the related databases (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) by referring to the keywords. Within this scope, 225 articles were accessed, and the studies were included in the coding key list formed by the researcher. The name of the researchers, the year, the database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS), the sample group and size, the lectures that the academic achievement was tested in, the country that the study was conducted in, and the class levels were all included in this coding key.
The following criteria were identified to include 225 research studies which were coded based on the theoretical basis of the meta-analysis study: (1) The studies should be published in the refereed journals between the years 2020 and 2021, (2) The studies should be experimental studies that try to determine the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement, (3) The values of the stated variables or the required statistics to calculate these values should be stated in the results of the studies, and (4) The sample group of the study should be at a primary education level. These criteria were also used as the exclusion criteria in the sense that the studies that do not meet the required criteria were not included in the present study.
After the inclusion criteria were determined, a systematic review process was conducted, following the year criterion of the study by means of EBSCO. Within this scope, 290,365 studies that analyze the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement were accordingly accessed. The database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) was also used as a filter by analyzing the inclusion criteria. Hence, the number of the studies that were analyzed was 58,616. Afterwards, the keyword ‘primary education’ was used as the filter and the number of studies included in the study decreased to 3152. Lastly, the literature was reviewed by using the keyword ‘academic achievement’ and 225 studies were accessed. All the information of 225 articles was included in the coding key.
It is necessary for the coders to review the related studies accurately and control the validity, safety, and accuracy of the studies (Stewart & Kamins, 2001 ). Within this scope, the studies that were determined based on the variables used in this study were first reviewed by three researchers from primary education field, then the accessed studies were combined and processed in the coding key by the researcher. All these studies that were processed in the coding key were analyzed in accordance with the inclusion criteria by all the researchers in the meetings, and it was decided that 27 studies met the inclusion criteria (Atici & Polat, 2010 ; Carreon, 2018 ; Ceylan & Elitok Kesici, 2017 ; Chae & Shin, 2016 ; Chiang et al. 2014 ; Ercan, 2014 ; Ercan et al., 2016 ; Gwo-Jen et al., 2018 ; Hayes & Stewart, 2016 ; Hwang et al., 2012 ; Kert et al., 2017 ; Lai & Chen, 2010 ; Lai et al., 2015 ; Meyers et al., 2015 ; Ravenel et al., 2014 ; Sung et al., 2016 ; Wang & Chen, 2013 ; Yu, 2019 ; Yu & Chen, 2014 ; Yu & Pan, 2014 ; Yu et al., 2010 ; Zhong et al., 2017 ). The data from the studies meeting the inclusion criteria were independently processed in the second coding key by three researchers, and consensus meetings were arranged for further discussion. After the meetings, researchers came to an agreement that the data were coded accurately and precisely. Having identified the effect sizes and heterogeneity of the study, moderator variables that will show the differences between the effect sizes were determined. The data related to the determined moderator variables were added to the coding key by three researchers, and a new consensus meeting was arranged. After the meeting, researchers came to an agreement that moderator variables were coded accurately and precisely.
2.2 Study group
27 studies are included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies that are included in the analysis is 1772. The characteristics of the studies included are given in Table 1 .
2.3 Publication bias
Publication bias is the low capability of published studies on a research subject to represent all completed studies on the same subject (Card, 2011 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Similarly, publication bias is the state of having a relationship between the probability of the publication of a study on a subject, and the effect size and significance that it produces. Within this scope, publication bias may occur when the researchers do not want to publish the study as a result of failing to obtain the expected results, or not being approved by the scientific journals, and consequently not being included in the study synthesis (Makowski et al., 2019 ). The high possibility of publication bias in a meta-analysis study negatively affects (Pecoraro, 2018 ) the accuracy of the combined effect size, causing the average effect size to be reported differently than it should be (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). For this reason, the possibility of publication bias in the included studies was tested before determining the effect sizes of the relationships between the stated variables. The possibility of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
2.4 Selecting the model
After determining the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study, the statistical model used to calculate the effect sizes was selected. The main approaches used in the effect size calculations according to the differentiation level of inter-study variance are fixed and random effects models (Pigott, 2012 ). Fixed effects model refers to the homogeneity of the characteristics of combined studies apart from the sample sizes, while random effects model refers to the parameter diversity between the studies (Cumming, 2012 ). While calculating the average effect size in the random effects model (Deeks et al., 2008 ) that is based on the assumption that effect predictions of different studies are only the result of a similar distribution, it is necessary to consider several situations such as the effect size apart from the sample error of combined studies, characteristics of the participants, duration, scope, and pattern of the study (Littell et al., 2008 ). While deciding the model in the meta-analysis study, the assumptions on the sample characteristics of the studies included in the analysis and the inferences that the researcher aims to make should be taken into consideration. The fact that the sample characteristics of the studies conducted in the field of social sciences are affected by various parameters shows that using random effects model is more appropriate in this sense. Besides, it is stated that the inferences made with the random effects model are beyond the studies included in the meta-analysis (Field, 2003 ; Field & Gillett, 2010 ). Therefore, using random effects model also contributes to the generalization of research data. The specified criteria for the statistical model selection show that according to the nature of the meta-analysis study, the model should be selected just before the analysis (Borenstein et al., 2007 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Within this framework, it was decided to make use of the random effects model, considering that the students who are the samples of the studies included in the meta-analysis are from different countries and cultures, the sample characteristics of the studies differ, and the patterns and scopes of the studies vary as well.
2.5 Heterogeneity
Meta-analysis facilitates analyzing the research subject with different parameters by showing the level of diversity between the included studies. Within this frame, whether there is a heterogeneous distribution between the studies included in the study or not has been evaluated in the present study. The heterogeneity of the studies combined in this meta-analysis study has been determined through Q and I 2 tests. Q test evaluates the random distribution probability of the differences between the observed results (Deeks et al., 2008 ). Q value exceeding 2 value calculated according to the degree of freedom and significance, indicates the heterogeneity of the combined effect sizes (Card, 2011 ). I 2 test, which is the complementary of the Q test, shows the heterogeneity amount of the effect sizes (Cleophas & Zwinderman, 2017 ). I 2 value being higher than 75% is explained as high level of heterogeneity.
In case of encountering heterogeneity in the studies included in the meta-analysis, the reasons of heterogeneity can be analyzed by referring to the study characteristics. The study characteristics which may be related to the heterogeneity between the included studies can be interpreted through subgroup analysis or meta-regression analysis (Deeks et al., 2008 ). While determining the moderator variables, the sufficiency of the number of variables, the relationship between the moderators, and the condition to explain the differences between the results of the studies have all been considered in the present study. Within this scope, it was predicted in this meta-analysis study that the heterogeneity can be explained with the country, class level, and lecture moderator variables of the study in terms of the effect of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, and it has an impact on the students’ academic achievement in different lectures. Some subgroups were evaluated and categorized together, considering that the number of effect sizes of the sub-dimensions of the specified variables is not sufficient to perform moderator analysis (e.g. the countries where the studies were conducted).
2.6 Interpreting the effect sizes
Effect size is a factor that shows how much the independent variable affects the dependent variable positively or negatively in each included study in the meta-analysis (Dinçer, 2014 ). While interpreting the effect sizes obtained from the meta-analysis, the classifications of Cohen et al. ( 2007 ) have been utilized. The case of differentiating the specified relationships of the situation of the country, class level, and school subject variables of the study has been identified through the Q test, degree of freedom, and p significance value Fig. 1 and 2 .
3 Findings and results
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement. Before determining the effect sizes in the study, the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
When the funnel plots are examined, it is seen that the studies included in the analysis are distributed symmetrically on both sides of the combined effect size axis, and they are generally collected in the middle and lower sections. The probability of publication bias is low according to the plots. However, since the results of the funnel scatter plots may cause subjective interpretations, they have been supported by additional analyses (Littell et al., 2008 ). Therefore, in order to provide an extra proof for the probability of publication bias, it has been analyzed through Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test (Table 2 ).
Table 2 consists of the results of the rates of publication bias probability before counting the effect size of online education on academic achievement. According to the table, Orwin Safe N analysis results show that it is not necessary to add new studies to the meta-analysis in order for Hedges g to reach a value outside the range of ± 0.01. The Duval and Tweedie test shows that excluding the studies that negatively affect the symmetry of the funnel scatter plots for each meta-analysis or adding their exact symmetrical equivalents does not significantly differentiate the calculated effect size. The insignificance of the Egger tests results reveals that there is no publication bias in the meta-analysis study. The results of the analysis indicate the high internal validity of the effect sizes and the adequacy of representing the studies conducted on the relevant subject.
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement after testing the publication bias. In line with the first purpose of the study, the forest graph regarding the effect size of online education on academic achievement is shown in Fig. 3 , and the statistics regarding the effect size are given in Table 3 .
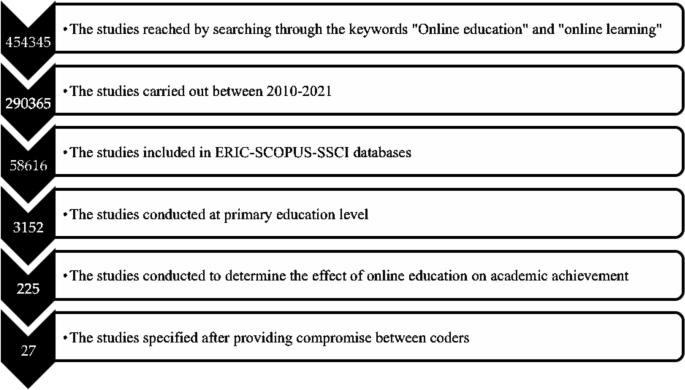
The flow chart of the scanning and selection process of the studies
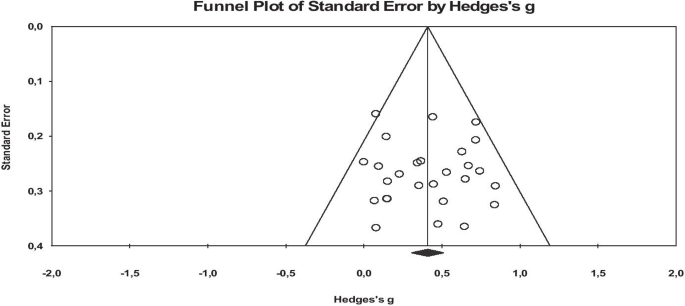
Funnel plot graphics representing the effect size of the effects of online education on academic success
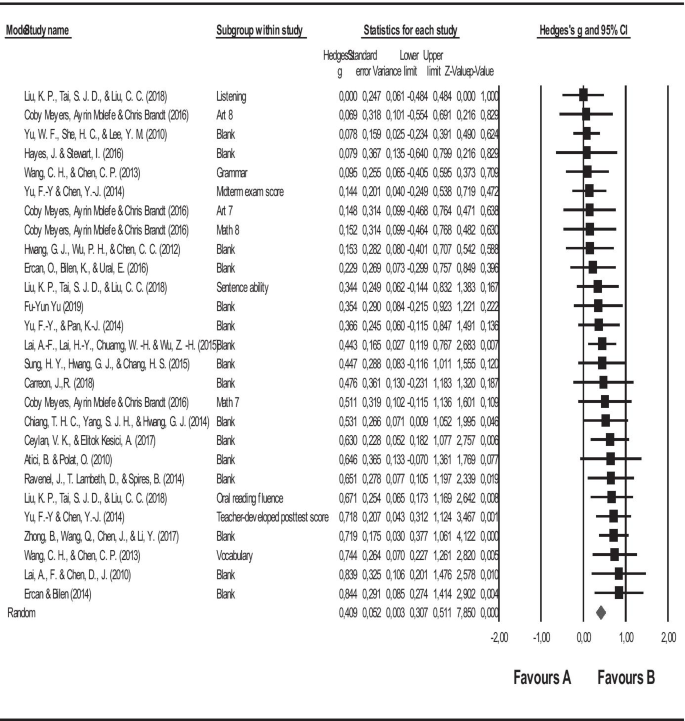
Forest graph related to the effect size of online education on academic success
The square symbols in the forest graph in Fig. 3 represent the effect sizes, while the horizontal lines show the intervals in 95% confidence of the effect sizes, and the diamond symbol shows the overall effect size. When the forest graph is analyzed, it is seen that the lower and upper limits of the combined effect sizes are generally close to each other, and the study loads are similar. This similarity in terms of study loads indicates the similarity of the contribution of the combined studies to the overall effect size.
Figure 3 clearly represents that the study of Liu and others (Liu et al., 2018 ) has the lowest, and the study of Ercan and Bilen ( 2014 ) has the highest effect sizes. The forest graph shows that all the combined studies and the overall effect are positive. Furthermore, it is simply understood from the forest graph in Fig. 3 and the effect size statistics in Table 3 that the results of the meta-analysis study conducted with 27 studies and analyzing the effect of online education on academic achievement illustrate that this relationship is on average level (= 0.409).
After the analysis of the effect size in the study, whether the studies included in the analysis are distributed heterogeneously or not has also been analyzed. The heterogeneity of the combined studies was determined through the Q and I 2 tests. As a result of the heterogeneity test, Q statistical value was calculated as 29.576. With 26 degrees of freedom at 95% significance level in the chi-square table, the critical value is accepted as 38.885. The Q statistical value (29.576) counted in this study is lower than the critical value of 38.885. The I 2 value, which is the complementary of the Q statistics, is 12.100%. This value indicates that the accurate heterogeneity or the total variability that can be attributed to variability between the studies is 12%. Besides, p value is higher than (0.285) p = 0.05. All these values [Q (26) = 29.579, p = 0.285; I2 = 12.100] indicate that there is a homogeneous distribution between the effect sizes, and fixed effects model should be used to interpret these effect sizes. However, some researchers argue that even if the heterogeneity is low, it should be evaluated based on the random effects model (Borenstein et al., 2007 ). Therefore, this study gives information about both models. The heterogeneity of the combined studies has been attempted to be explained with the characteristics of the studies included in the analysis. In this context, the final purpose of the study is to determine the effect of the country, academic level, and year variables on the findings. Accordingly, the statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the countries where the studies were conducted are given in Table 4 .
As seen in Table 4 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ significantly according to the countries where the studies were conducted in. Q test results indicate the heterogeneity of the relationships between the variables in terms of countries where the studies were conducted in. According to the table, the effect of online education on academic achievement was reported as the highest in other countries, and the lowest in the US. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 5 .
As seen in Table 5 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the class level. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in the 4 th class. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 6 .
As seen in Table 6 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the school subjects included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in ICT subject.
The obtained effect size in the study was formed as a result of the findings attained from primary studies conducted in 7 different countries. In addition, these studies are the ones on different approaches to online education (online learning environments, social networks, blended learning, etc.). In this respect, the results may raise some questions about the validity and generalizability of the results of the study. However, the moderator analyzes, whether for the country variable or for the approaches covered by online education, did not create significant differences in terms of the effect sizes. If significant differences were to occur in terms of effect sizes, we could say that the comparisons we will make by comparing countries under the umbrella of online education would raise doubts in terms of generalizability. Moreover, no study has been found in the literature that is not based on a special approach or does not contain a specific technique conducted under the name of online education alone. For instance, one of the commonly used definitions is blended education which is defined as an educational model in which online education is combined with traditional education method (Colis & Moonen, 2001 ). Similarly, Rasmussen ( 2003 ) defines blended learning as “a distance education method that combines technology (high technology such as television, internet, or low technology such as voice e-mail, conferences) with traditional education and training.” Further, Kerres and Witt (2003) define blended learning as “combining face-to-face learning with technology-assisted learning.” As it is clearly observed, online education, which has a wider scope, includes many approaches.
As seen in Table 7 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to online education approaches included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in Web Based Problem Solving Approach.
4 Conclusions and discussion
Considering the developments during the pandemics, it is thought that the diversity in online education applications as an interdisciplinary pragmatist field will increase, and the learning content and processes will be enriched with the integration of new technologies into online education processes. Another prediction is that more flexible and accessible learning opportunities will be created in online education processes, and in this way, lifelong learning processes will be strengthened. As a result, it is predicted that in the near future, online education and even digital learning with a newer name will turn into the main ground of education instead of being an alternative or having a support function in face-to-face learning. The lessons learned from the early period online learning experience, which was passed with rapid adaptation due to the Covid19 epidemic, will serve to develop this method all over the world, and in the near future, online learning will become the main learning structure through increasing its functionality with the contribution of new technologies and systems. If we look at it from this point of view, there is a necessity to strengthen online education.
In this study, the effect of online learning on academic achievement is at a moderate level. To increase this effect, the implementation of online learning requires support from teachers to prepare learning materials, to design learning appropriately, and to utilize various digital-based media such as websites, software technology and various other tools to support the effectiveness of online learning (Rolisca & Achadiyah, 2014 ). According to research conducted by Rahayu et al. ( 2017 ), it has been proven that the use of various types of software increases the effectiveness and quality of online learning. Implementation of online learning can affect students' ability to adapt to technological developments in that it makes students use various learning resources on the internet to access various types of information, and enables them to get used to performing inquiry learning and active learning (Hart et al., 2019 ; Prestiadi et al., 2019 ). In addition, there may be many reasons for the low level of effect in this study. The moderator variables examined in this study could be a guide in increasing the level of practical effect. However, the effect size did not differ significantly for all moderator variables. Different moderator analyzes can be evaluated in order to increase the level of impact of online education on academic success. If confounding variables that significantly change the effect level are detected, it can be spoken more precisely in order to increase this level. In addition to the technical and financial problems, the level of impact will increase if a few other difficulties are eliminated such as students, lack of interaction with the instructor, response time, and lack of traditional classroom socialization.
In addition, COVID-19 pandemic related social distancing has posed extreme difficulties for all stakeholders to get online as they have to work in time constraints and resource constraints. Adopting the online learning environment is not just a technical issue, it is a pedagogical and instructive challenge as well. Therefore, extensive preparation of teaching materials, curriculum, and assessment is vital in online education. Technology is the delivery tool and requires close cross-collaboration between teaching, content and technology teams (CoSN, 2020 ).
Online education applications have been used for many years. However, it has come to the fore more during the pandemic process. This result of necessity has brought with it the discussion of using online education instead of traditional education methods in the future. However, with this research, it has been revealed that online education applications are moderately effective. The use of online education instead of face-to-face education applications can only be possible with an increase in the level of success. This may have been possible with the experience and knowledge gained during the pandemic process. Therefore, the meta-analysis of experimental studies conducted in the coming years will guide us. In this context, experimental studies using online education applications should be analyzed well. It would be useful to identify variables that can change the level of impacts with different moderators. Moderator analyzes are valuable in meta-analysis studies (for example, the role of moderators in Karl Pearson's typhoid vaccine studies). In this context, each analysis study sheds light on future studies. In meta-analyses to be made about online education, it would be beneficial to go beyond the moderators determined in this study. Thus, the contribution of similar studies to the field will increase more.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of online education on academic achievement. In line with this purpose, the studies that analyze the effect of online education approaches on academic achievement have been included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies included in the meta-analysis is 1772. While the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in the US, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia, the studies carried out in Europe could not be reached. The reason may be attributed to that there may be more use of quantitative research methods from a positivist perspective in the countries with an American academic tradition. As a result of the study, it was found out that the effect size of online education on academic achievement (g = 0.409) was moderate. In the studies included in the present research, we found that online education approaches were more effective than traditional ones. However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016 ; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020 ; Wei & Chou, 2020 ). Online education has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of online learning compared to face-to-face learning in the classroom is the flexibility of learning time in online learning, the learning time does not include a single program, and it can be shaped according to circumstances (Lai et al., 2019 ). The next advantage is the ease of collecting assignments for students, as these can be done without having to talk to the teacher. Despite this, online education has several weaknesses, such as students having difficulty in understanding the material, teachers' inability to control students, and students’ still having difficulty interacting with teachers in case of internet network cuts (Swan, 2007 ). According to Astuti et al ( 2019 ), face-to-face education method is still considered better by students than e-learning because it is easier to understand the material and easier to interact with teachers. The results of the study illustrated that the effect size (g = 0.409) of online education on academic achievement is of medium level. Therefore, the results of the moderator analysis showed that the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ in terms of country, lecture, class level, and online education approaches variables. After analyzing the literature, several meta-analyses on online education were published (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Machtmes & Asher, 2000 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ). Typically, these meta-analyzes also include the studies of older generation technologies such as audio, video, or satellite transmission. One of the most comprehensive studies on online education was conducted by Bernard et al. ( 2004 ). In this study, 699 independent effect sizes of 232 studies published from 1985 to 2001 were analyzed, and face-to-face education was compared to online education, with respect to success criteria and attitudes of various learners from young children to adults. In this meta-analysis, an overall effect size close to zero was found for the students' achievement (g + = 0.01).
In another meta-analysis study carried out by Zhao et al. ( 2005 ), 98 effect sizes were examined, including 51 studies on online education conducted between 1996 and 2002. According to the study of Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), this meta-analysis focuses on the activities done in online education lectures. As a result of the research, an overall effect size close to zero was found for online education utilizing more than one generation technology for students at different levels. However, the salient point of the meta-analysis study of Zhao et al. is that it takes the average of different types of results used in a study to calculate an overall effect size. This practice is problematic because the factors that develop one type of learner outcome (e.g. learner rehabilitation), particularly course characteristics and practices, may be quite different from those that develop another type of outcome (e.g. learner's achievement), and it may even cause damage to the latter outcome. While mixing the studies with different types of results, this implementation may obscure the relationship between practices and learning.
Some meta-analytical studies have focused on the effectiveness of the new generation distance learning courses accessed through the internet for specific student populations. For instance, Sitzmann and others (Sitzmann et al., 2006 ) reviewed 96 studies published from 1996 to 2005, comparing web-based education of job-related knowledge or skills with face-to-face one. The researchers found that web-based education in general was slightly more effective than face-to-face education, but it is insufficient in terms of applicability ("knowing how to apply"). In addition, Sitzmann et al. ( 2006 ) revealed that Internet-based education has a positive effect on theoretical knowledge in quasi-experimental studies; however, it positively affects face-to-face education in experimental studies performed by random assignment. This moderator analysis emphasizes the need to pay attention to the factors of designs of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The designs of the studies included in this meta-analysis study were ignored. This can be presented as a suggestion to the new studies that will be conducted.
Another meta-analysis study was conducted by Cavanaugh et al. ( 2004 ), in which they focused on online education. In this study on internet-based distance education programs for students under 12 years of age, the researchers combined 116 results from 14 studies published between 1999 and 2004 to calculate an overall effect that was not statistically different from zero. The moderator analysis carried out in this study showed that there was no significant factor affecting the students' success. This meta-analysis used multiple results of the same study, ignoring the fact that different results of the same student would not be independent from each other.
In conclusion, some meta-analytical studies analyzed the consequences of online education for a wide range of students (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ), and the effect sizes were generally low in these studies. Furthermore, none of the large-scale meta-analyzes considered the moderators, database quality standards or class levels in the selection of the studies, while some of them just referred to the country and lecture moderators. Advances in internet-based learning tools, the pandemic process, and increasing popularity in different learning contexts have required a precise meta-analysis of students' learning outcomes through online learning. Previous meta-analysis studies were typically based on the studies, involving narrow range of confounding variables. In the present study, common but significant moderators such as class level and lectures during the pandemic process were discussed. For instance, the problems have been experienced especially in terms of eligibility of class levels in online education platforms during the pandemic process. It was found that there is a need to study and make suggestions on whether online education can meet the needs of teachers and students.
Besides, the main forms of online education in the past were to watch the open lectures of famous universities and educational videos of institutions. In addition, online education is mainly a classroom-based teaching implemented by teachers in their own schools during the pandemic period, which is an extension of the original school education. This meta-analysis study will stand as a source to compare the effect size of the online education forms of the past decade with what is done today, and what will be done in the future.
Lastly, the heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
*Studies included in meta-analysis
Ahmad, S., Sumardi, K., & Purnawan, P. (2016). Komparasi Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Antara Pembelajaran Menggunakan Sistem Pembelajaran Online Terpadu Dengan Pembelajaran Klasikal Pada Mata Kuliah Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education, 2 (2), 286–292.
Article Google Scholar
Ally, M. (2004). Foundations of educational theory for online learning. Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2 , 15–44. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://eddl.tru.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/01_Anderson_2008-Theory_and_Practice_of_Online_Learning.pdf
Arat, T., & Bakan, Ö. (2011). Uzaktan eğitim ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi , 14 (1–2), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.29249/selcuksbmyd.540741
Astuti, C. C., Sari, H. M. K., & Azizah, N. L. (2019). Perbandingan Efektifitas Proses Pembelajaran Menggunakan Metode E-Learning dan Konvensional. Proceedings of the ICECRS, 2 (1), 35–40.
*Atici, B., & Polat, O. C. (2010). Influence of the online learning environments and tools on the student achievement and opinions. Educational Research and Reviews, 5 (8), 455–464. Retrieved on the 11th of October, 2020 from https://academicjournals.org/journal/ERR/article-full-text-pdf/4C8DD044180.pdf
Bernard, R. M., Abrami, P. C., Lou, Y., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Wozney, L., et al. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta- analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 3 (74), 379–439. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074003379
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis . Wiley.
Book Google Scholar
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L., & Rothstein, H. (2007). Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects . UK: Wiley.
Card, N. A. (2011). Applied meta-analysis for social science research: Methodology in the social sciences . Guilford.
Google Scholar
*Carreon, J. R. (2018 ). Facebook as integrated blended learning tool in technology and livelihood education exploratory. Retrieved on the 1st of October, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1197714.pdf
Cavanaugh, C., Gillan, K. J., Kromrey, J., Hess, M., & Blomeyer, R. (2004). The effects of distance education on K-12 student outcomes: A meta-analysis. Learning Point Associates/North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) . Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED489533.pdf
*Ceylan, V. K., & Elitok Kesici, A. (2017). Effect of blended learning to academic achievement. Journal of Human Sciences, 14 (1), 308. https://doi.org/10.14687/jhs.v14i1.4141
*Chae, S. E., & Shin, J. H. (2016). Tutoring styles that encourage learner satisfaction, academic engagement, and achievement in an online environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1371–1385. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2015.1009472
*Chiang, T. H. C., Yang, S. J. H., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). An augmented reality-based mobile learning system to improve students’ learning achievements and motivations in natural science inquiry activities. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (4), 352–365. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gwo_Jen_Hwang/publication/287529242_An_Augmented_Reality-based_Mobile_Learning_System_to_Improve_Students'_Learning_Achievements_and_Motivations_in_Natural_Science_Inquiry_Activities/links/57198c4808ae30c3f9f2c4ac.pdf
Chiao, H. M., Chen, Y. L., & Huang, W. H. (2018). Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 23 (29–38), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.05.002
Chizmar, J. F., & Walbert, M. S. (1999). Web-based learning environments guided by principles of good teaching practice. Journal of Economic Education, 30 (3), 248–264. https://doi.org/10.2307/1183061
Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2017). Modern meta-analysis: Review and update of methodologies . Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55895-0
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Observation. Research Methods in Education, 6 , 396–412. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabil_Ashraf2/post/How_to_get_surface_potential_Vs_Voltage_curve_from_CV_and_GV_measurements_of_MOS_capacitor/attachment/5ac6033cb53d2f63c3c405b4/AS%3A612011817844736%401522926396219/download/Very+important_C-V+characterization+Lehigh+University+thesis.pdf
Colis, B., & Moonen, J. (2001). Flexible Learning in a Digital World: Experiences and Expectations. Open & Distance Learning Series . Stylus Publishing.
CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. Retrieved on the 3rd of September, 2021 from https://www.cosn.org/sites/default/files/COVID-19%20Member%20Exclusive_0.pdf
Cumming, G. (2012). Understanding new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. New York, USA: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203807002
Deeks, J. J., Higgins, J. P. T., & Altman, D. G. (2008). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses . In J. P. T. Higgins & S. Green (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 243–296). Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.ch9
Demiralay, R., Bayır, E. A., & Gelibolu, M. F. (2016). Öğrencilerin bireysel yenilikçilik özellikleri ile çevrimiçi öğrenmeye hazır bulunuşlukları ilişkisinin incelenmesi. Eğitim ve Öğretim Araştırmaları Dergisi, 5 (1), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.23891/efdyyu.2017.10
Dinçer, S. (2014). Eğitim bilimlerinde uygulamalı meta-analiz. Pegem Atıf İndeksi, 2014(1), 1–133. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegem.001
*Durak, G., Cankaya, S., Yunkul, E., & Ozturk, G. (2017). The effects of a social learning network on students’ performances and attitudes. European Journal of Education Studies, 3 (3), 312–333. 10.5281/zenodo.292951
*Ercan, O. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes . European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Ercan, O., & Bilen, K. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes. European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23.
*Ercan, O., Bilen, K., & Ural, E. (2016). “Earth, sun and moon”: Computer assisted instruction in secondary school science - Achievement and attitudes. Issues in Educational Research, 26 (2), 206–224. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Field, A. P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics, 2 (2), 105–124. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328031us0202_02
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63 (3), 665–694. https://doi.org/10.1348/00071010x502733
Geostat. (2019). ‘Share of households with internet access’, National statistics office of Georgia . Retrieved on the 2nd September 2020 from https://www.geostat.ge/en/modules/categories/106/information-and-communication-technologies-usage-in-households
*Gwo-Jen, H., Nien-Ting, T., & Xiao-Ming, W. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society., 21 (1), 25–36. Retrieved on the 2nd of October, 2020 https://ae-uploads.uoregon.edu/ISTE/ISTE2019/PROGRAM_SESSION_MODEL/HANDOUTS/112172923/CreatingInteractiveeBooksthroughLearningbyDesignArticle2018.pdf
Hamdani, A. R., & Priatna, A. (2020). Efektifitas implementasi pembelajaran daring (full online) dimasa pandemi Covid-19 pada jenjang Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten Subang. Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD STKIP Subang, 6 (1), 1–9.
Hart, C. M., Berger, D., Jacob, B., Loeb, S., & Hill, M. (2019). Online learning, offline outcomes: Online course taking and high school student performance. Aera Open, 5(1).
*Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86 (3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114
Horton, W. K. (2000). Designing web-based training: How to teach anyone anything anywhere anytime (Vol. 1). Wiley Publishing.
*Hwang, G. J., Wu, P. H., & Chen, C. C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers and Education, 59 (4), 1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
*Kert, S. B., Köşkeroğlu Büyükimdat, M., Uzun, A., & Çayiroğlu, B. (2017). Comparing active game-playing scores and academic performances of elementary school students. Education 3–13, 45 (5), 532–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2016.1140800
*Lai, A. F., & Chen, D. J. (2010). Web-based two-tier diagnostic test and remedial learning experiment. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 8 (1), 31–53. https://doi.org/10.4018/jdet.2010010103
*Lai, A. F., Lai, H. Y., Chuang W. H., & Wu, Z.H. (2015). Developing a mobile learning management system for outdoors nature science activities based on 5e learning cycle. Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Learning, ICEL. Proceedings of the International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS) International Conference on e-Learning (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, July 21–24, 2015). Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562095.pdf
Lai, C. H., Lin, H. W., Lin, R. M., & Tho, P. D. (2019). Effect of peer interaction among online learning community on learning engagement and achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET), 17 (1), 66–77.
Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta-analysis . Oxford University.
*Liu, K. P., Tai, S. J. D., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Enhancing language learning through creation: the effect of digital storytelling on student learning motivation and performance in a school English course. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (4), 913–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9592-z
Machtmes, K., & Asher, J. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of telecourses in distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 14 (1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923640009527043
Makowski, D., Piraux, F., & Brun, F. (2019). From experimental network to meta-analysis: Methods and applications with R for agronomic and environmental sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024_1696-1
* Meyers, C., Molefe, A., & Brandt, C. (2015). The Impact of the" Enhancing Missouri's Instructional Networked Teaching Strategies"(eMINTS) Program on Student Achievement, 21st-Century Skills, and Academic Engagement--Second-Year Results . Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness. Retrieved on the 14 th November, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562508.pdf
OECD. (2020). ‘A framework to guide an education response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020 ’. https://doi.org/10.26524/royal.37.6
Pecoraro, V. (2018). Appraising evidence . In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 99–114). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_9
Pigott, T. (2012). Advances in meta-analysis . Springer.
Pillay, H. , Irving, K., & Tones, M. (2007). Validation of the diagnostic tool for assessing Tertiary students’ readiness for online learning. Higher Education Research & Development, 26 (2), 217–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701310821
Prestiadi, D., Zulkarnain, W., & Sumarsono, R. B. (2019). Visionary leadership in total quality management: efforts to improve the quality of education in the industrial revolution 4.0. In the 4th International Conference on Education and Management (COEMA 2019). Atlantis Press
Poole, D. M. (2000). Student participation in a discussion-oriented online course: a case study. Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 33 (2), 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/08886504.2000.10782307
Rahayu, F. S., Budiyanto, D., & Palyama, D. (2017). Analisis penerimaan e-learning menggunakan technology acceptance model (Tam)(Studi Kasus: Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta). Jurnal Terapan Teknologi Informasi, 1 (2), 87–98.
Rasmussen, R. C. (2003). The quantity and quality of human interaction in a synchronous blended learning environment . Brigham Young University Press.
*Ravenel, J., T. Lambeth, D., & Spires, B. (2014). Effects of computer-based programs on mathematical achievement scores for fourth-grade students. i-manager’s Journal on School Educational Technology, 10 (1), 8–21. https://doi.org/10.26634/jsch.10.1.2830
Rolisca, R. U. C., & Achadiyah, B. N. (2014). Pengembangan media evaluasi pembelajaran dalam bentuk online berbasis e-learning menggunakan software wondershare quiz creator dalam mata pelajaran akuntansi SMA Brawijaya Smart School (BSS). Jurnal Pendidikan Akuntansi Indonesia, 12(2).
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effective- ness of Web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis . Personnel Psychology, 59 (3), 623–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2006.00049.x
Stewart, D. W., & Kamins, M. A. (2001). Developing a coding scheme and coding study reports. In M. W. Lipsey & D. B. Wilson (Eds.), Practical metaanalysis: Applied social research methods series (Vol. 49, pp. 73–90). Sage.
Swan, K. (2007). Research on online learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 11 (1), 55–59.
*Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., & Chang, Y. C. (2016). Development of a mobile learning system based on a collaborative problem-posing strategy. Interactive Learning Environments, 24 (3), 456–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2013.867889
Tsagris, M., & Fragkos, K. C. (2018). Meta-analyses of clinical trials versus diagnostic test accuracy studies. In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 31–42). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_4
UNESCO. (2020, Match 13). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved on the 14 th November 2020 from https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/ coronavirus-school-closures
Usta, E. (2011a). The effect of web-based learning environments on attitudes of students regarding computer and internet. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28 (262–269), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.051
Usta, E. (2011b). The examination of online self-regulated learning skills in web-based learning environments in terms of different variables. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 10 (3), 278–286. Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ944994.pdf
Vrasidas, C. & MsIsaac, M. S. (2000). Principles of pedagogy and evaluation for web-based learning. Educational Media International, 37 (2), 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/095239800410405
*Wang, C. H., & Chen, C. P. (2013). Effects of facebook tutoring on learning english as a second language. Proceedings of the International Conference e-Learning 2013, (2009), 135–142. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562299.pdf
Wei, H. C., & Chou, C. (2020). Online learning performance and satisfaction: Do perceptions and readiness matter? Distance Education, 41 (1), 48–69.
*Yu, F. Y. (2019). The learning potential of online student-constructed tests with citing peer-generated questions. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (2), 226–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1458040
*Yu, F. Y., & Chen, Y. J. (2014). Effects of student-generated questions as the source of online drill-and-practice activities on learning . British Journal of Educational Technology, 45 (2), 316–329. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12036
*Yu, F. Y., & Pan, K. J. (2014). The effects of student question-generation with online prompts on learning. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (3), 267–279. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.565.643&rep=rep1&type=pdf
*Yu, W. F., She, H. C., & Lee, Y. M. (2010). The effects of web-based/non-web-based problem-solving instruction and high/low achievement on students’ problem-solving ability and biology achievement. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 47 (2), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703291003718927
Zhao, Y., Lei, J., Yan, B, Lai, C., & Tan, S. (2005). A practical analysis of research on the effectiveness of distance education. Teachers College Record, 107 (8). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2005.00544.x
*Zhong, B., Wang, Q., Chen, J., & Li, Y. (2017). Investigating the period of switching roles in pair programming in a primary school. Educational Technology and Society, 20 (3), 220–233. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://repository.nie.edu.sg/bitstream/10497/18946/1/ETS-20-3-220.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Primary Education, Ministry of Turkish National Education, Mersin, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hakan Ulum .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ulum, H. The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study. Educ Inf Technol 27 , 429–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Download citation
Received : 06 December 2020
Accepted : 30 August 2021
Published : 06 September 2021
Issue Date : January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online education
- Student achievement
- Academic success
- Meta-analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 02 October 2020
Development of a new model on utilizing online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction
- Hassan Abuhassna ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5774-3652 1 ,
- Waleed Mugahed Al-Rahmi 1 ,
- Noraffandy Yahya 1 ,
- Megat Aman Zahiri Megat Zakaria 1 ,
- Azlina Bt. Mohd Kosnin 1 &
- Mohamad Darwish 2
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 17 , Article number: 38 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
178k Accesses
112 Citations
7 Altmetric
Metrics details
This research aims to explore and investigate potential factors influencing students’ academic achievements and satisfaction with using online learning platforms. This study was constructed based on Transactional Distance Theory (TDT) and Bloom’s Taxonomy Theory (BTT). This study was conducted on 243 students using online learning platforms in higher education. This research utilized a quantitative research method. The model of this research illustrates eleven factors on using online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction. The findings showed that the students’ background, experience, collaborations, interactions, and autonomy positively affected students’ satisfaction. Moreover, effects of the students’ application, remembering, understanding, analyzing, and satisfaction was positively aligned with students’ academic achievements. Consequently, the empirical findings present a strong support to the integrative association between TDT and BTT theories in relation to using online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction, which could help decision makers in universities and higher education and colleges to plan, evaluate, and implement online learning platforms in their institutions.
Introduction
Higher education organizations over the previous two decades have offered full courses online as an integral part of their curricula, besides encouraging the completion throughout the online courses. Additionally, the number of students who are not participating in any courses online has continued to drop over the past few years. Similarly, it is perfectly possible to state that learning online is obviously an educational platform (Allen, Seaman, Poulin, & Straut, 2016 ). Courses online are trying to connect social networking components, experts’ content, because online resources are growing on daily basis. Such courses depend on active participation of a significant number of learners who participate independently in accordance with their education objectives, skills, and previous background and experience (McAuley, Stewart, Siemens, & Cormier, 2010 ). Nevertheless, learners differ in their previous background and experience, along with their education techniques, which clearly influence their online courses results besides their achievement (Kauffman, 2015 ). Consequently, despite the online learning evolution, learning online possibly will not be appropriate for each learner (Bouhnik & Carmi, 2013 ). Nevertheless, while online learning application among academic world has grown rapidly, not enough is identified regarding learners’ previous background and experience in learning online. Not so long ago, investigation concentrated on particular characteristics of learners’ experiences along with beliefs, for instance collaboration with their own instructor, online course quality, or studying with a certain learning management system (LMS) (Alexander & Golja, 2007 ; (Lester & King, 2009 ). Generally, limited courses or a single institution were investigated (Coates, James, & Baldwin, 2005 ; Lee, Yoon, & Lee, 2009 ). Few studies examined bigger sample sizes between one or more particular institutes (Alexander & Golja, 2007 ). Additionally, there is a shortage of researches that examine learners’ previous background and experience comparing face-to-face along with learning online elements, e.g., (Bliuc, Goodyear, & Ellis, 2007 ). The development of learners’ previous background and experience, skills, are realized to be the major advantages for administrative level for learning online.
Similarly, learners’ satisfaction and academic achievement towards learning online attracted considerable attention from scholars who employed several theoretical models in order to evaluate learners’ satisfaction and academic achievements (Abuhassna, Megat, Yahaya, Azlina, & Al-rahmi, 2020 ; Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Al-Rahmi, Othman, & Yusuf, 2015a ; Al-Rahmi, Othman, & Yusuf, 2015b ). This present study highlights the effects of online learning platforms on student’s satisfaction, in relation to their background and prior experiences towards online learning platforms to identify learners that are going to be satisfied toward online course. Furthermore, this research explores the effects of transactional distance theory (TDT); student collaboration, student- instructor dialogue or communication, and student autonomy in relation to their satisfaction. Accordingly, this study investigates students’ academic achievements within online platforms, utilizing Bloom theory to measure students’ achievements through four main components, namely, understanding, remembering, applying, and analyzing. This study could have a significant influence on online course design and development. Additionally, this research may influence not only academic online courses but then other educational organizations according to the fact that several organizations offer training courses and solutions online. Both researchers and Instructors will be able to utilize and elaborate in accordance with the preliminary model, which was developed throughout this research, on the effects of online platforms on student’s satisfaction and academic achievements. Advantages of online learning and along with its applications were mentioned in earlier correlated literature (Abuhassna et al., 2020 ;Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Al-Rahmi et al., 2018 ). However, despite the growing usage of online platforms, there is a shortage of employing this technology, which creates an issue in itself (Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Al-Rahmi et al., 2018 ). Consequently, the research problem lies in the point that a model needs to be created to locate the significant evidence based on the data of student’s background, experiences and interactions within online learning environments which influence their academic performance and satisfaction. Thus, this developed model must be as a guidance for instructors and decision makers in the online education industry in terms of using online platforms to improve students learning experience through online platforms. Bearing in mind these conditions, our major problem was: how could we enhance students online learning experience in relation to both their academic achievements and satisfaction?
Research questions
The major research question that are anticipated to be answered is:
how could we enhance students online learning experience in relation to both their academic achievements and satisfaction?
To be able to answer this question, it is required to examine numerous sub-questions which have been stated as follow:
Q1: What is the relationship between students’ background and students’ satisfaction?
Q2: What is the relationship between students’ experience and students’ satisfaction?
Q3: What is the relationship between students’ collaboration and students’ satisfaction?
Q4: What is the relationship between students’ interaction and students’ satisfaction?
Q5: What is the relationship between students’ autonomy and students’ satisfaction?
Q6: What is the relationship between students’ satisfaction and students’ academic achievements?
Q7: What is the relationship between students’ application and students’ academic achievements?
Q8: What is the relationship between students’ remembering and students’ academic achievements?
Q9: What is the relationship between students’ understanding and students’ academic achievements?
Q10: What is the relationship between students’ analyzing and students’ academic achievements?
Research theory and hypotheses development
When designing web-courses within online learning instructions or mechanisms in general, educators are left with several decisions and considerations to face, which accordingly affect how students experience instruction, how they construct and process knowledge, how students could be satisfied through this experiment, and how web-based learning courses could enhance their academic achievements. In this study, we construct our theoretical framework according to Moore transactional distance theory (TDT) to measure student’s satisfaction, in addition to Bloom theory components to measure students’ academic achievements. Though the origins of TDT can be traced to the work of Dewey, it is Michael Moore who is identified as the innovator of this theory that first appeared in 1972. In his study and development of the theory, he acknowledged three main components of TDT that work as the base for much of the research on DL. Also, Bloom’s Taxonomy was established in 1956 under the direction of educational psychologist to measure students’ academic achievement (Bloom, Engelhart, Furst, Hill, & Krathwohl, 1956 ). TDT theory has been selected in this study since Transactional distance’s term indicates the geographical space between the student and instructor. Based on the learning understanding, which happens through learner’s interaction with his environment. This theory considers the role of each of these elements (Student’s autonomy, Dialogue, and class structure) whereas these three elements could help to investigate student’s satisfaction. Moore’s ( 1990 ) notion of ‘Transactional Distance’ adopt the distance that happens in all relations in education. The distance in the theory is mainly specified the dialogue’s amount which happens between the student and the teacher, and the structure’s amount in the course design. Which serves the main goal of this study as to enhance students online learning experience in relation to their satisfaction. Whereas, Bloom Theory has been selected in this study in addition to TDT to enhance students online learning experience in relation to their student’s achievements. In a conclusion both methods were implemented to develop and hypothesis this study hypothesis. See Fig. 1 .
Research Model and Hypotheses
Hypothesis of the study
H1: There is a significant relationship between students’ background and students’ satisfaction.
H2: There is a significant relationship between students’ experience and students’ satisfaction.
H3: There is a significant relationship between students’ collaboration and students’ satisfaction.
H4: There is a significant relationship between students’ interaction and students’ satisfaction.
H5: There is a significant relationship between students’ autonomy and students’ satisfaction.
H6: There is a significant relationship between students’ satisfaction and students’ academic achievements.
H7: There is a significant relationship between students’ application and students’ academic achievements.
H8: There is a significant relationship between students’ remembering and students’ academic achievements.
H9: There is a significant relationship between students’ understanding and students’ academic achievements.
H10: There is a significant relationship between students’ analyzing and students’ academic achievements.
Hypothesis developments and literature review
This Section of the study will discuss the study hypothesis and relates each hypothesis to its related studies from the literature.
Students background toward online platforms
Students’ background regarding online platforms in this study is referred to as their readiness and willingness to use and adapt to different online platforms, providing them with the needed support and assistance. Students’ background towards online learning is a crucial component throughout this process, as prior research revealed that there are implementation issues, for instance; the deficiency of qualified lecturers, infrastructure and facilities, in addition to students’ readiness, besides students’ resistance to accept online learning platforms in addition to the Learning Management System (LMS) platforms, as educational tools (Azhari & Ming, 2015 ). However, student demand continued to increase, spreading to global audiences due to its exceptional functionality, flexibility and eventual accessibility (Azhari & Ming, 2015 ). There have been persistent apprehensions regarding online learning quality compared with traditional learning settings. In their research, (Paechter & Maier, 2010 ; Panyajamorn, Suthathip, Kohda, Chongphaisal, & Supnithi, 2018 ) have discovered that Austrian learners continue to prefer traditional learning environments due to communication goals, along with the interpersonal relations preservation. Moreover, (Lau & Shaikh, 2012 ) have discovered that Malaysian learners’ internet efficiency and computer skills, along with their personal demographics like gender, background, level of the study, as well as their financial income lead to a significant difference in their readiness towards online learning platforms. Abuhassna and Yahaya ( 2018 ) claimed that the current technologies in education play an essential role in providing a full online learning experience which is close enough to a face-to-face class in spite of the physical separation of the students from their educator, along with other students. Platforms of online learning lend themselves towards a less hierarchical methodology in education, fulfilling the learning desires of individuals which do not approach new information in a linear or a systematic manner. Platforms of online learning additionally are the most suitable ways for autonomous students (Abuhassna et al., 2020 ; Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Paechter & Maier, 2010 ; Panyajamorn et al., 2018 ).
Students experience toward online platforms
Students’ experience in the current research indicates that learners must have prior experience in relation to utilizing online learning platform in their education settings. Thus, students experience towards online learning offers several advantages among themselves and their instructors in strengthening students’ learning experiences especially for isolated learners (Jaques & Salmon, 2007 ; Lau & Shaikh, 2012 ; Salmon, 2011 ; Salmon, 2014 ). Regardless of student recognition of the advantages towards supporting their learning throughout utilizing the technology, difficulties may occur through the boundaries about their technical capabilities and prior experiences towards utilizing the software itself from the perspective of its functionality. As demonstrated over learner’s experience and feedback from several online sessions over the years, this may frequently become a frustration source between both learners and their instructors, as this may make typically uncomplicated duties, for instance, watching a video, uploading a document, and other simple tasks to be progressively complicated for them, having no such prior experience. Furthermore, when filling out evaluations, for instance, online group presentations, the relatively limited capability to communicate face-to-face then to rely on a non-verbal signal along with audience’s body language might be a discouraging component. Nonetheless, the significance of being in a position to participate with other colleagues employing online sessions, which are occasionally nonvisual, for instance; teleconference format is a progressively significant skill in the modern workplace, thus affirming the importance of concise, clear, intensive interactions skills (Salmon, 2011 ; Salmon, 2014 ).
Student collaboration among themselves in online platforms
Students’ collaborations in the current study refers to the communication and feedback among themselves in online platforms. To refine and measure transactional distance using a survey tool, (Rabinovich, 2009 ) created a survey instrument to measure transactional distance in a higher education setting. A survey was sent to 235 students enrolled in a synchronous web-based graduate class in business regarding transactional distance and Collaborations (Rabinovich, 2009 ). The synchronous learning environment was described as a place where “live on-campus classes are conveyed simultaneously to both in-class students on campus and remote students on the Web who join via virtual classroom Web collaboration software” (Rabinovich, 2009 ). The virtual classroom software is similar to the characteristics of the two different software described by (Falloon, 2011 ; Mathieson, 2012 ) that it allows for students to interact with the educator and fellow students in real-time (Rabinovich, 2009 ). Moreover, (Kassandrinou, Angelaki, & Mavroidis, 2014 ) reported that the instructor plays a crucial role as interaction and communication helpers, as they are tasked with fostering, reassuring and assisting communication and interaction among students. Face-to-face tutorials have proven to be a vast opportunity for a multitude of students to interchange ideas, argue the content of the course and its related concerns (Vasala & Andreadou, 2010 ).
Students’ interactions with the instructor in online platforms
Purposeful interaction or (dialogue) in the current study describes communication that is learner-learner and learner-instructor which is designed to improve the understanding of the student. According to (Shearer, 2010 ) communication should also be constructive in that it builds upon ideas and work from others, as well as assists others in learning. (Moore, 1972 ) affirmed that learners also must realize that, and value the importance of the learning interactions as a vital part of the learning process. In a manner similar to (Benson & Samarawickrema, 2009 ] study of teacher preparatory students, (Falloon, 2011 ) investigated the use of digital tools in a case study at a teacher education program in New Zealand. (Mathieson, 2012 ) also explored the role dialogue plays in digital learning environments. She created a digital survey that examined students’ perception of audio-visual feedback in courses that utilize screen casting digital tools. (Moore, 2007 ) discusses autonomous learners searching for courses that do not stress structure and dialogue in order explain and enhance their learning progression. (Abuhassna et al., 2020 ; Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Al-Rahmi et al., 2015b ; Al-Rahmi, Othman, & Yusuf, 2015d ; Furnborough, 2012 ) concluded that the feeling of cooperation that learners’ share with their fellow students effect their reaction concerning their collaboration with their peers.
Student autonomy in online platforms
Student autonomy in the current study refers to their independence and motivation towards learning. The learner is the motivation of the way toward learning, along with their expectations and requirements, thinking about everyone as a unique individual and hence investigating their own capacities and possibilities. Thus, extraordinary importance is attributed to autonomy in DL environments, since the option of instructive intercession offered in distance education empowers students towards learning autonomy (Massimo, 2014 ). In this respect, the connection between autonomy of student and explicit parts of the learning procedure are in the center of consideration as mentioned. (Madjar, Nave, & Hen, 2013 ) concluded that a learners’ autonomy-supportive environment provides these learners with adoption of a more aims guided learning, leading to more learning achievements. This is why autonomy is desired in the online settings for both individual development and greater achievement in academic environments. The researchers also indicate in their research that while autonomy supports outcomes in goals and aims guiding, educator practices mainly lead to goals which necessary cannot adapt. Thus, supportive-autonomy learning process needs to be designed with affective elements consideration as well. However, (Stroet, Opdenakker, & Minnaert, 2013 ) efficiently surveyed 71 experimental studies on the impacts of autonomy supportive teaching on motivation of learner and discovered a clear positive correlation. Similar to attribution theory, the relationship between learner control and inspiration involves the possibility of learners adjusting their own inspirations, for example, learners may be competent to change self-determined extrinsic motivation to intrinsic motivation. However, (Jacobs, Renandya, & Power, 2016 ) further indicated that learners will not reach the same level of autonomy without reviewing learner’s autonomy insights, reflecting on their learning experiences, sharing these experiences and reflections with other learners, and realizing the elements influencing all these processes, and the process of learning as well.
Student satisfaction in online platforms
Student satisfaction in the current study refers to the fact that there are many factors that play a role in determining the learner’s satisfaction, such as faculty, institution, individual learner element, interaction/communication elements, the course elements, and learning environment. Discussion of the elements also related to the role of the instructor, with the learner’s attitude, social presence, usefulness, and effectiveness of Online Platforms. (Yu, 2015 ) investigated that student satisfaction was positively associated with interaction, self-efficacy and self-regulation without significant gender variations. (Choy & Quek, 2016 ). examined the relationships between the learners’ perceived teaching, social, and cognitive element. In addition, satisfaction, academic performance, and achievement can be measured using a revised form of the survey instrument. (Kirmizi, 2014 ) studied connection between 6 psychosocial scales: personal relevance, educator assistance, student interaction and collaboration, student autonomy, authentic learning, along with active learning. A moderate level of correlation was found between these mentioned variables. Learner satisfaction predictors were educator support, personal relevance and authentic learning, while authentic learning was the only academic success predictor. Findings of (Bordelon, 2013 ) determined and described a positive correlation between both achievement and satisfaction. He demonstrated that the reasons behind these conclusions could be cultural variations in learner’s satisfaction which point out learning accession Zhu ( 2012 ). Scholars in the field of student satisfaction emphasis on the delivery besides the operational side of the student’s experience in the teaching process (Al-Rahmi, Othman, & Yusuf, 2015e ).
Students’ academic achievements in online platforms
Students achievements in this study refers to Bloom’s main four components of achievements, which are remembering, understanding, applying, and analyzing. Finding in a study conducted by (Whitmer, 2013 ) revealed the relationships between student academic achievement and the LMS usage, thus the findings showed a highly systematic association ( p < .0000) in relation to every variable. These variables described 12% and 23% of variations within the final course marks, which indicates that learners who employed the LMS more often obtained higher marks than the others. Thus, the correlation techniques examined these variables separately to ascertain their association with the final mark. Moreover, it is not the technology itself; it is the educational methods in relation to which technology has been utilized that create a change in learners’ achievement. Instruments used are significant in identifying the technology impact, moreover, it is the implementation of those instruments under specific activities and for certain purposes which indicates whether or not they are effective. In contrast, a study conducted by (Barkand, 2017 ) revealed that LMS tools were not considered to have an effect on semester final grades when categorized by school year. In his study, semester final grades were a measure of student achievement, which has subjective elements. To account for the subjective elements in semester final grades, the study also included objective post test scores to evaluate student learning. Additionally, in this study, we refer to Bloom’s Taxonomy established in 1956 under the direction of educational psychologist for measuring students’ academic achievement (Bloom et al., 1956 ). Moreover, in this study, we selected fours domains of Blooms Taxonomy in order to achieve this study objectives, which are; application: which refers to using a concept in new context, for instance; applying what has been learned inside the classroom into different circumstances; remembering, which refers to recalling or retrieving prior learned knowledge; understanding, which refers to realizing the meaning, then clarification of problems instructions; analyzing, which refers to separating concepts or material into parts in such a way that its structure can be distinguished, understood among inferences and facts.
Students’ application
Applying involves “carrying out or using a procedure through executing or implementing” (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001 ). Applying in this study refers to the student’s ability to use online platforms, such as how to log in, how to end session, how to download materials, how to access links and videos. Students can exchange information about a specific topic in online platforms such as Moodle, Google Documents, Wikis and apply knowledge to create and participate in online platforms.
Students’ remembering
Remembering is defined as “retrieving, recognizing, and recalling relevant knowledge from long-term memory” (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001 ). In this study, remembering is referred to the ability to organize and remember online resources to easily find information on the internet. Moreover, students can easily cooperate with their colleagues and educator, contributing to the educational process and justifying their study procedure. Anderson and Krathwohl ( 2001 ) In their review of Bloom’s taxonomy, Anderson and Krathwohl ( 2001 ) recognized greater learning levels as creating, evaluating, and analyzing, with the lower learning levels as applying, understanding, and remembering.
Students’ understanding
Understanding involves “constructing meaning from oral, written, and graphic messages through interpreting, exemplifying, classifying, summarizing, inferring, comparing, and explaining” (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001 ). In this study, understanding is referred to as understanding regarding a subject then putting forward new suggestions about online settings, for instance; understanding how e-learning works, or LMS. For example, students use online platforms to review concepts, courses, and prominent resources are being used inside the classroom environment.
Students’ analyzing
Analyzing includes “breaking material into constituent parts, determining how the parts relate to one another and to an overall structure or purpose through differentiating, organizing, and attributing” (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001 ). Analyzing refers to the student’s ability to connect, discuss, mark-up, then evaluate the information received into one certain workplace or playground. Solomon and Schrum ( 2010 ) claim that educators have started employing online platforms for a range of activities, since they have become more familiar and there are ways for learners to benefit from using them. Generally, the purpose and goal are to publicize the development types, innovation, as well as additional activities that their learners usually do independently. Such instruments have also provided instructors ways to encourage and promote genuine cooperation in their project’s development (Solomon & Schrum, 2010 ).
Research methodology
A quantitative approach was implemented in this study to provide an inclusive insight in relation to students online learning experience and how to enhance both their satisfaction and academic achievements using a questionnaire. Two experts were referred for the evaluation of the questionnaire’s content. Before the collection of the data, permission regarding the current research purpose has been obtained from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM). In relation to the sampling and population, this research was conducted among undergraduate learners who have been online learning users. Learners, who had manually obtained the questionnaires, have been requested to fill in their details, then fill their own assessments regarding online learning platforms and its effects towards their academic achievements. Thus, for data analysis, the data that were attained from questionnaires were then analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Specifically, Structural Equation Modeling (SEM- Amos), which has been employed as a primary data analysis tool. Moreover, utilizing SEM-Amos process involves two main phases: evaluating construct validity, the convergent validity, along with the discriminant validity of the measurements; then analyzing the structural model. These mentioned two phases followed the recommendations of (Bagozzi, Yi, & Nassen, 1998; Hair, Sarstedt, Ringle, & Mena, 2012a , 2012b ).
Sample characteristics and data collection
A total of 283 questionnaires were distributed manually; of these, only 264, which make up 93.3% of the total number, were returned to the authors. Excluding the 26 incomplete questionnaires, 264 were evaluated employing SPSS. A total of 21 questionnaires have been excluded: 14 were incomplete and 7 having outliners. Thus, the overall number of valid questionnaires was 243 following this exclusion. This exclusion step is being supported by Hair et al. ( 2012a , 2012b ) . Moreover, Venkatesh, Thong, & Xu, 2012 who pointed out that this procedure is essential to be implemented as the existence of outliers could be a reason for inaccurate results. Regarding the respondent’s demographic details: 91 (37.4%) were males, and 152 (62.6%) were females. 149 (61.3%) were in the age range of 18 t0 20 years old, 77 (31.7%) were in the age range of 21 to 24 years old, and 17 (7.0%) were in the age range of 25 to 29 years old. Regarding level of study: 63 (25.9%) were from level 1, 72 (29.6%) were from level 2, 50 (20.6%) were from level 3, and 58 (23.9%) were from level 4.
Measurement instruments
The questionnaire in this study has been developed to fit the study hypothesis. Consequently, it was developed based into both theories that have been utilized in this study. The questionnaire has two main sections, first section aims to measure student satisfaction which is based on the TDT theory variables. Second section of the questionnaire has been developed to measure students’ academic achievement based on Bloom theory. According to Bloom theory there are four variables that measure students’ achievements, which are application, remembering, understanding, analyzing. On that basis the questionnaire has been developed to measure both students’ satisfaction and academic achievements . The construct items were adapted to ensure content validity. This questionnaire consisted of two main sections. First part covered the demographic details of the respondents’ including age, gender, educational level. The second part comprises 51 items which were adapted from previous researches as following; student background, five items, student experience, five items adapted from (Akaslan & Law, 2011 ), student collaborations, and, student interactions items adapted from (Bolliger & Inan, 2012 ), student autonomy, five items adapted from (Barnard et al., 2009 ; Pintrich, Smith, Garcia, & McKeachie, 1991 ), student satisfaction, six items adapted from (The blended learning impact evaluation at UCF is conducted by Research Initiative for Teaching Effectiveness, n.d. ). Moreover, effects of the students’ application, four items, students’ remembering, four items, students’ understanding, four items, students’ analyzing, four items, and students’ academic achievements, four items adapted from (Pekrun, Goetz, & Perry, 2005 ). The questionnaire has been distributed to the students after taking the online course.
Result and analysis
Cronbach’s Alpha reliability coefficient result was 0.917 among all research model factors. Thus, the discriminant validity (DV) assessment was carried out through utilizing three criteria, which are: index between variables, which is expected to be less than 0.80 (Bagozzi, Yi, & Nassen, 1988 ); each construct AVE value must be equal to or higher than 0.50; square of (AVE) between every construct should be higher, in value, than the inter construct correlations (IC) associated with the factor [49]. Furthermore, the crematory factor analysis (CFA) findings along with factor loading (FL) should therefore be 0.70 or above although the Cronbach’s Alpha (CA) results are confirmed to be ≥0.70 [50]. Researchers have also added that composite reliability (CR) is supposed to be ≥0.70.
Model analysis
Current research employed AMOS 23 to analyze the data. Both structural equation modeling (SEM) as well as confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) have been employed as the main analysis tools. Uni-dimensionality, reliability, convergent validity along with discriminant validity have been employed to assess the measurement model. (Bagozzi et al., 1988 ; Byrne, 2010 ; Kline, 2011 ) highlighted that goodness-of-fit guidelines, such as the normed chi-square, chi-square/degree of freedom, normed fit index (NFI), relative fit index (RFI), Tucker-Lewis coefficient (TLI) comparative fit index (CFI), incremental fit index (IFI), the parsimonious goodness of fit index (PGFI), thus, the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) besides the root mean-square residual (RMR). All these are tools which could be utilized as the assessment procedures for the model estimation. See Table 1 & Fig. 2 .
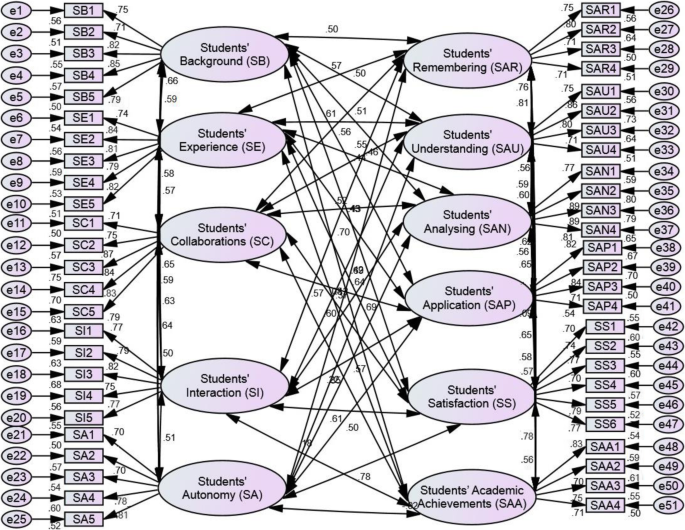
Measurement Model
Measurement model
Such type of validity is commonly employed to specify the size difference between a concept and its indicators and other concepts (Hair et al., 2012a , 2012b ). Through analysis in this context, discriminant validity has proven to be positive over all concepts given that values have been over 0.50 (cut-off value) from p = 0.001 according to Fornell and Larcker ( 1981 ). In line with Hair et al. ( 2012a , 2012b ) . Bagozzi, Yi, & Nassen, (1998), the correlation between items at any two specified constructs must not exceed the square root of the average variance that is shared between them in a single construct. The outcomes values of composite reliability (CR) besides those of Cronbach’s Alpha (CA) remained about 0.70 and over, while the outcomes of the average variance extracted (AVE) remained about 0.50 and higher, indicating that all factor loadings (FL) were significant, thereby fulfilling conventions in the current assessment Bagozzi, Yi, & Nassen, (1998), and Byrne ( 2010 ). Following sections expand on the results of the measurement model. Findings of validity, reliability, average variance extracted (AVE), composite reliability (CR) as well as Cronbach’s Alpha (CA) have all been accepted, which also demonstrated determining the discriminant validity. It is determined that all the values of (CR) vary between 0.812 and 0.917, meaning they are above the cut-off value of 0.70. The (CA) result values also varied between 0.839 and 0.897 exceeding the cut-off value of 0.70. Thus, the (AVE) was similarly higher than 0.50, varying between 0.610 and 0.684. All these findings are positive, thus indicating significant (FLs) and they comply with the conventional assessment guidelines Bagozzi, Yi, & Nassen, (1998), along with Fornell and Larcker ( 1981 ). See Table 2 and Additional file 1 .
Structural model analysis
In the current study, the path modeling analysis has been utilized to examine the impact of students’ academic achievements among higher education institutions through the following factors (students’ background, students’ experience, students’ collaborations, students’ interaction, students’ autonomy, students’ remembering, students’ understanding, students’ analyzing, students’ application, students’ satisfaction), which is based on online learning. The findings are displayed then compared in hypothesis testing discussion. Subsequently, as the second stage, factor analysis (CFA) has being conducted on structural equation modeling (SEM) in order to assess the proposed hypotheses as demonstrated in Fig. 3 .
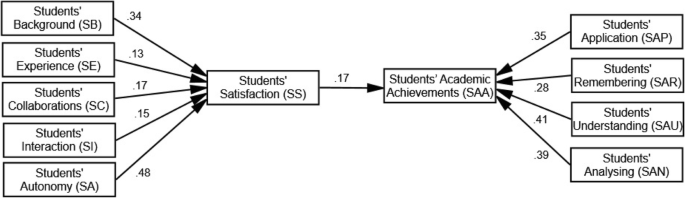
Findings for the Proposed Model Path analysis
As shown in both Figs. 3 and 4 , all hypotheses have been accepted. Moreover, Table 3 below shows that the fundamental statistics of the model was good, which indicates model validity along with the testing results of the hypotheses through demonstrating the values of unstandardized coefficients besides standard errors of the structural model.
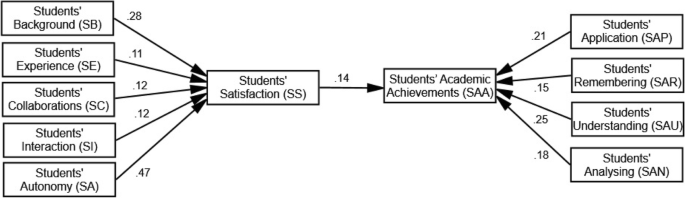
Findings for the Proposed Model T.Values
The first direct five assumptions, students’ background, students’ experience, students’ collaborations, students’ interaction; students’ autonomy with students’ satisfaction, were addressed. In accordance with Fig. 4 and Table 3 , relations between students’ background and students’ satisfaction was (β = .281, t = 5.591, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the first hypothesis (H1) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Following hypothesis illustrated the relationship between students’ experience and students’ satisfaction (β = .111, t = 1.951, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the second hypothesis (H2) proposed a positive and significant relationship. Third hypothesis illustrated the relationship between students’ collaborations and students’ satisfaction (β = .123, t = 2.584, p < 0.001) demonstrating that the third hypothesis (H3) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Additionally, the relationship between students’ background and students’ satisfaction was (β = .116, t = 2.212, p < 0.001), indicating that the fourth hypothesis (H4) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Further to the above-mentioned findings, the relationship between students’ autonomy and students’ satisfaction was (β = .470, t = 7.711, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the fifth hypothesis (H5) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Moreover, in the second section, five assumptions were discussed, which are students’ satisfaction, students’ remembering, students’ understanding, students’ analyzing, students’ application along with students’ academic achievements.
As shown in Fig. 4 and Table 3 , the association between students’ satisfaction and students’ academic achievements was (β = .135, t = 3.473, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the sixth hypothesis (H6) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Following hypothesis indicated the relationship between students’ application and students’ academic achievements (β = .215, t = 6.361, p < 0.001), indicating that the seventh hypothesis (H7) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Thus, the eighth hypothesis indicated the relationship between students’ remembering and students’ academic achievements was (β = .154, t = 4.228, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the eight hypothesis (H8) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Additionally, the correlation between students’ understanding and students’ academic achievements was (β = .252, t = 6.513, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the ninth hypothesis (H9) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Finally, the relationship between students’ analyzing and students’ academic achievements was (β = .179, t = 6.215, p < 0.001), demonstrating that the tenth hypothesis (H10) has suggested a positive and significant relationship. Accordingly, this current model demonstrated student’s compatibility to use online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction. This is in accordance with earlier investigations (Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ; Al-Rahmi et al., 2018 ; Al-rahmi, Othman, & Yusuf, 2015c ; Barkand, 2017 ; Madjar et al., 2013 ; Salmon, 2014 ).
Discussion and implications
Developing a new hybrid technology acceptance model through combining TDT and BTT has been the major objective of the current research, which aimed to investigate the guiding factors towards utilizing online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction in higher education institutions. The current research is intensifying a step forward by implementing TDT along with a BTT model. Using the proposed model, the current research examined how students’ background, students’ experience, students’ collaborations, students’ interactions, and students’ autonomy positively affected students’ satisfaction. Moreover, effects of the students’ application, students’ remembering, students’ understanding, students’ analyzing, and students’ satisfaction positively affected students’ academic achievements. The current research found that students’ background, students’ experience, students’ collaborations, students’ interactions, and students’ autonomy were influenced by students’ satisfaction. Also, effects of the students’ application, students’ remembering, students’ understanding, students’ analyzing, and students’ satisfaction positively affected students’ academic achievements. This conclusion is consistent with earlier correlated literature. Thus, this reveals that learners first make sure whether using platforms of online learning were able to meet their study requirements, or that using platforms of online learning are relevant to their study process before considering employing such technology in their study. Learners have been noted to perceive that platforms of online learning is more useful only once they discover that such a technology is actually better than the traditional learning which does not include online learning platforms (Choy & Quek, 2016 ; Illinois Online Network, 2003 ). Using the proposed model, the current research examined how to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction. Thus, the following section will be a comparison between this study results and previous research, as follows.
The first hypotheses of this study demonstrated a positive and significant association between students’ prior background towards online platforms with their satisfaction. As clearly investigated in Osika and Sharp ( 2002 ) study, numerous learners deprived of these main skills enroll in the courses, struggle, and subsequently drop out. In addition, Bocchi, Eastman, and Swift ( 2004 ) investigation claimed that prior knowledge of students’ concerns, demands along with their anticipations is crucial in constructing an efficient instruction. Thus, to clarify, students must have prior knowledge and background before letting them into the online platforms. On the other hand, there are constant concerns about the online learning platforms quality in comparison to a face-to-face learning environment, as students do not have the essential skills required toward using online learning platforms (Illinois Online Network, 2003 ). Moreover, a study by Alalwan et al. ( 2019 ) discovered that Austrian learners still would rather choose face-to-face learning for communication purposes, and the preservation of interpersonal relations. This is due to the fact that learners do not as yet have the background knowledge and skills needed towards using online learning platforms. Additional research by Orton-Johnson ( 2009 ) among UK learners claimed that learners have not accepted online materials, and continue to prefer traditional context materials as the medium for their learning, which also indicates the importance of prior knowledge and background towards online platforms before going through such a technology.
The second hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant association between students’ experience along with students’ satisfaction, which revealed that putting the students in such an experience would provide and support them with the ability to overcome all difficulties that arise through the limits around the technical ability of the online platforms. This is in line with some earlier researches regarding the reasons that lead to people’s technology acceptance behavior. One reason is the notion of “conformity,” which means the degree to which an individual take into consideration that an innovation is consistent with their existing demands, experiences, values and practices (Chau & Hu, 2002 ; Moore & Benbasat, 1991 ; Rogers, 2003 ; Taylor & Todd, 1995 ). Moreover, (Anderson & Reed, 1998 ; Galvin, 2003 ; Lewis, 2004 ) claimed that most students who had prior experience with online education tended to exhibit positive attitudes toward online education, and it affects their attitudes toward online learning platforms.
The third hypotheses of this study demonstrated a positive and significant association among student collaboration with themselves in online platforms, which indicates the key role of collaboration between students in order to make the experiment more realistic and increase their ability to feel more involved and active. This is agreement with Al-rahmi, Othman, and Yusuf ( 2015f ) who claimed that type, quality, and amount of feedback that each student received was correlated to a student’s sense of success or course satisfaction. Moreover, Rabinovich ( 2009 ) found that all types of dialogue were important to transactional distance, which make it easier for the student to adapt to online learning platform. Also, online learning platforms enable learners to share then exchange information among their colleagues Abuhassna et al., 2020 ; Abuhassna & Yahaya, 2018 ).
Students’ interaction with the instructor in online platforms
The fourth hypothesis of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between students’ collaborations and students’ satisfaction, which indicates the significance of the communication between students and their instructor throughout the online platforms experiment. These results agree with (Mathieson, 2012 ) results, which stated that the ability of communication between students and their instructor lowered the sense of separation between learner and educator. Moreover, in line with (Kassandrinou et al., 2014 ), communication guides learners to undergo constructive emotions, for example relief, satisfaction and excitement, which assist them to achieve their educational goals. In addition, (Furnborough, 2012 ) draws conclusion that learners’ feeling of cooperating with their fellow students effects their reaction concerning their collaboration with their peers. Moreover, Kassandrinou et al., 2014 focused on the instructor as crucial part as interaction and communication helpers, as they are thought to constantly foster, reassure and assist communication and interaction amongst students.
Student’s autonomy in online platforms
The fifth hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant relationship between student’s autonomy and online learning platforms, which indicates that students need a sense of dependence towards online platforms, which agrees with Madjar et al. ( 2013 ) who concluded that a learners’ autonomy-supportive environment provides these learners with adoption of more aims, leading to more learning achievements. Moreover, Stroet et al. ( 2013 ) found a clear positive correlation on the impacts of autonomy supportive teaching on motivation of learner. O’Donnell, Chang, and Miller ( 2013 ) also argues that autonomy is the ability of the learners to govern themselves, especially in the process of making decisions and setting their own course and taking responsibility for their own actions.
Student’s satisfaction in online platforms
The sixth hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between student’s satisfaction with online learning platforms, which indicates a level of acceptance by the students to adapt into online learning platforms. This is in agreement with Zhu ( 2012 ) who reported that student’s satisfaction in online platforms is a statement of confidence with the system. Moreover, Kirmizi ( 2014 ) study revealed that the predictors of the learners’ satisfaction were educator’s support, personal relevance and authentic learning, whereas the authentic learning is only the predictor of academic success. Furthermore, the findings of Bordelon ( 2013 ) stated and determined a positive correlation between both satisfaction and achievement. In addition, the results of Mahle ( 2011 ) clarified that student satisfaction occurs when it is realized that the accomplishment has met the learners’ expectations, which is then considered a short-term attitude toward the learning procedure.
Hypotheses seven, eight, nine and ten of this study proposed a positive and significant relationship between student’s academic achievements with online learning platforms, which indicates the key main role of online platform with students’ academic achievements. This agrees with Whitmer ( 2013 ) findings, which revealed that the associations between student usage of the LMS and academic achievement exposed a highly systematic relationship. In contrast, Barkand ( 2017 ) found that there is no significant difference in students’ academic achievements in utilizing online platforms regarding students’ academic achievements, which is due to the fact that academic achievement towards online learning platforms requires a certain set of skills and knowledge as mentioned in the above sections in order to make such technology a success.
The seventh hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between students’ application and students’ academic achievements, which indicates the major key of applying in the learning process as an effected element. This is in line with the Computer Science Teachers’ Association (CSTA) taskforce in the U. S (Computer Science Teachers’ Association (CSTA), 2011 ), where they mentioned that applying elements of computer skills is essential in all state curricula, directing to their value for improving pupils’ higher order thinking in addition to general problem-solving abilities. Moreover, Gouws, Bradshaw, and Wentworth ( 2013 ) created a theoretical framework which drawn education computational thoughts compared to cognitive levels established from Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Purposes. Four thinking skill levels have been utilized to assess the ‘cognitive demands’ initiated by computational concepts for instance abstraction, modelling, developing algorithms, generating automated processes. Through the iPad app, LightBot. thinking skills remained recognizing (which means recognize and recall expertise correlating to the problem); Understanding (interpret, compare besides explain the problem); whereas, applying (make use of computer skills to create a solution) then Assimilating (critically decompose and analyses the problem).
The eighth hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between students’ remembering and students’ academic achievements, which indicates the importance of remembering as a process of retrieving information relating to what needed to be done and/or outcome attributes) over the procedure of learning according to Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. Additionally, Falloon ( 2016 ) claimed that responding to data indicated the use of general thinking skills to clarify and understand steps and stages needed to complete a task (average 29%); recalling or remembering information about a task or available tools (average 13%); and discussing and understanding success criteria (average 3%).
The ninth hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between students’ understanding and students’ academic achievements, which indicates its significance with the academic achievements as a process of criticizing the task or the problem faced by the students into phases or activities to help understanding of how to resolve the problem. The current results agree with Falloon ( 2016 ) who demonstrated the necessity to build understanding over the thinking processes employed by students once they are engaged in their work. In addition, Falloon ( 2016 ) suggested that the purpose and nature of questioning was broader than this, with questioning of self and others being an important strategy in solution development. In many respects, the questioning for those students was not much a perspective, although more a practice, to the degree that assisted them to understand their tasks, analyze intended or developed explanations and to evaluate their outcomes.
The tenth hypotheses of this study proposed a positive and significant correlation between students’ understanding and students’ academic achievements, which reveals the importance of analysis as a process of employing general thinking besides computational knowledge in order to realize the challenges through using online platforms, in addition to predictive thinking to categorize, explore and fix any possible errors throughout the whole process. Falloon ( 2016 ) claimed that analyzing was often a collaborative procedure between pairs receiving and giving counseling from others to assist in solving complications. On the other hand, online learning platforms are highly dependent on connecting and sharing as a basic strategy that needs to be employed over all stages of online learning settings, whether between students and students, or between students and their instructor. Moreover, Falloon ( 2016 ) findings showed that Analyzing (average 17%) was present in various phases of these online students’ work, which is based on what phase they were at together with their tasks, despite the fact that most analysis was associated with students depending on themselves during online process.
Conclusion and future work
In this investigation, both transactional distance theory (TDT) and Bloom’s Taxonomy theory (BTT) have been validated in the educational context, providing further understanding towards the students’ prospective perceptions on using online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievement and satisfaction. The contribution that the current research might have to the field of online learning platforms have been discussed and explained. Additional insights towards students’ satisfactions and students’ academic achievements have also been presented. The current research emphasizes that the incorporation of both TDT and BTT can positively influence the research outcome. The current research has determined that numerous stakeholders, for instance developers, system designers, along with institutional users of online learning platforms reasonably consider student demands and needs, then ensure that the such a system is effectively meeting their requirements and needs. Adoption among users of online learning platforms could be broadly clarified by the eleven factor features which is based on this research model. Thus, the current research suggests more investigation be carried out to examine relationships among the complexity of online learning platforms combined with technology acceptance model (TAM).
Recommendations for stakeholders of online platforms
Based on the study findings, the first recommendation would be for administrators of higher institution. In order to implement online learning, there must be more interest given to the course structure design, whereas it should be based on theories and prior literature. Moreover, instructor and course developer need to be trained and skilled to achieve online learning platforms goals. Workshops and training sessions must be given for both instructors and students to make them more familiar in order to take the most advantages of the learning management system like Moodle and LMS. The software itself is not enough for creating an online learning environment that is suitable for students and instructors. If instructors were not trained and unaware of utilizing the software (e.g. Moodle) in the class, then the quality of education imparted to students will be jeopardized. Training and assessing the class instructor and making modifications to the software could result in a good environment for the instructor and a quality education for the student. Both students’ satisfaction and academic achievements depends on their prior knowledge and experience in relation to online learning. This current research intended to investigate student satisfaction and academic achievements in relation to online learning platforms in on of the higher education in Malaysia. Future research could integrate more in relation to blended learning settings.
Availability of data and materials
All the hardcopy questionnaires, data and statistical analysis are available.
Abuhassna, H., Megat, A., Yahaya, N., Azlina, M., & Al-rahmi, W. M. (2020). Examining Students' satisfaction and learning autonomy through web-based courses. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering , 1 (9), 356–370. https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2020/53912020 .
Article Google Scholar
Abuhassna, H., & Yahaya, N. (2018). Students’ utilization of distance learning through an interventional online module based on Moore transactional distance theory. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education , 14 (7), 3043–3052. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/91606 .
Akaslan, D., & Law, E. L.-C. (2011). Measuring student E-learning readiness: A case about the subject of Electricity in Higher Education Institutions in Turkey. In H. Leung, E. Popescu, Y. Cao, R. W. H. Lau, & W. Nejdl (Eds.), ICWL 2011. LNCS, vol. 7048 , (pp. 209–218). Heidelberg: Springer.
Google Scholar
Alalwan, N., Al-Rahmi, W. M., Alfarraj, O., Alzahrani, A., Yahaya, N., & Al-Rahmi, A. M. (2019). Integrated three theories to develop a model of factors affecting students’ academic performance in higher education. IEEE Access , 7 , 98725–98742.
Alexander, S., & Golja, T. (2007). Using students' experiences to derive quality in an e-learning system: An institution's perspective. Educational Technology & Society , 10 (2), 17–33.
Allen, I. E., Seaman, J., Poulin, R., & Straut, T. T. (2016). Online report card: Tracking online education in the United States. Babson survey research group and the online learning consortium (OLC), Pearson, and WCET state authorization Network .
Al-Rahmi, W., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015b). The role of social media for collaborative learning to improve academic performance of students and researchers in Malaysian higher education. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , 16 (4). http://www.irrodl.org/index.php/irrodl/article/view/2326 . https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v16i4.2326 .
Al-Rahmi, W. M., Alias, N., Othman, M. S., Alzahrani, A. I., Alfarraj, O., Saged, A. A., & Rahman, N. S. A. (2018). Use of e-learning by university students in Malaysian higher educational institutions: A case in Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. IEEE Access , 6 , 14268–14276.
Al-Rahmi, W. M., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015a). The effectiveness of using e-learning in Malaysian higher education: A case study Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences , 6 (5), 625–625.
Al-rahmi, W. M., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015c). Using social media for research: The role of interactivity, collaborative learning, and engagement on the performance of students in Malaysian post-secondary institutes. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences , 6 (5), 536.
Al-Rahmi, W. M., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015d). Exploring the factors that affect student satisfaction through using e-learning in Malaysian higher education institutions. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences , 6 (4), 299.
Al-Rahmi, W. M., Othman, M. S., & Yusuf, L. M. (2015e). Effect of engagement and collaborative learning on satisfaction through the use of social media on Malaysian higher education. Res. J. Appl. Sci., Eng. Technol , 9 (12), 1132–1142.
Anderson, D. K., & Reed, W. M. (1998). The effects of internet instruction, prior computer experience, and learning style on teachers’ internet attitudes and knowledge. Journal of Educational Computing Research , 19 (3), 227–246. https://doi.org/10.2190/8WX1-5Q3J-P3BW-JD61 .
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.) (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives . New York: Longman.
Azhari, F. A., & Ming, L. C. (2015). Review of e-learning practice at the tertiary education level in Malaysia. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research , 49 (4), 248–257.
Bagozzi, R. P., Yi, Y., & Nassen, K. D. (1988). Representation of measurement error in marketing variables: Review of approaches and extension to three-facet designs. Elsevier. Journal of Econometrics , 89 (1–2), 393–421.
Barkand, J. M. (2017). Using educational data mining techniques to analyze the effect of instructors' LMS tool use frequency on student learning and achievement in online secondary courses. Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. Retrieved from https://vpn.utm.my/docview/2007550976?accountid=41678
Barnard, L., Lan, W. Y., To, Y. M, Paton, V. O., & Lai, S. L. (2009). Measuring self-regulation in online and blended learning environments. The Internet and Higher Education , 12 (1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2008.10.005 .
Benson, R., & Samarawickrema, G. (2009). Addressing the context of e-learning: Using transactional distance theory to inform design. Distance Education Journal , 30 (1), 5–21.
Bliuc, A. M., Goodyear, P., & Ellis, R. A. (2007). Research focus and methodological choices in studies into students' experiences of blended learning in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education , 10 , 231–244.
Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, W. H., & Krathwohl, D. R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives, handbook I: The cognitive domain . New York: David McKay Co Inc.
Bocchi, J., Eastman, J. K., & Swift, C. O. (2004). Retaining the online learner: Profile of students in an online MBA program and implications for teaching them. Journal of Education for Business , 79 (4), 245–253.
Bolliger, D. U., & Inan, F. A. (2012). Development and validation of the online student connectedness survey (OSCS). The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning , 13 (3), 41–65. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v13i3.1171 .
Bordelon, K. (2013). Perceptions of achievement and satisfaction as related to interactions in online courses (PhD dissertation) . Northcentral University.
Bouhnik, D., & Carmi, G. (2013). Thinking styles in virtual learning courses , (p. 141e145). Toronto: Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on information society (i-society) Retrieved from: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber¼6619545 .
Byrne, B. M. (2010). Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming , (2nd ed., ). New York: Routledge.
Chau, P. Y. K., & Hu, P. J. (2002). Examining a model of information technology acceptance by individual professionals: An exploratory study. Journal of Management Information System , 18 (4), 191–229.
Choy, J. L. F., & Quek, C. L. (2016). Modelling relationships between students’ academic achievement and community of inquiry in an online learning environment for a blended course. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology , 32 (4), 106–124 https://doi.org/10.14742/ajet.2500 .
Coates, H., James, R., & Baldwin, G. (2005). A critical examination of the effects of learning management systems on university teaching and learning. Tertiary Education and Management , 11 , 19–36.
Computer Science Teachers’ Association (CSTA). (2011) The computational thinking leadership toolkit. [Online] Available from: http://www.csta.acm.org/Curriculum/sub/CompThinking.html [Accessed 13 Jan 2020].
Falloon, G. (2011). Exploring the virtual classroom: What students need to know (and teachers should consider). Journal of online learning and teaching. , 7 (4), 439–451.
Falloon, G. W. (2016). An analysis of young students’ thinking when completing basic coding tasks using scratch Jnr. On the iPad. Journal of Computer-Assisted Learning , 32 , 576–379.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research , 18 (1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312 .
Furnborough, C. (2012). Making the most of others: Autonomous interdependence in adult beginner distance language learners. Distance Education , 33 (1), 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587919.2012.667962 .
Galvin, T. (2003). The (22nd Annual) 2003. Industry report. Training , 40 (9), 19–45.
Gouws, L., Bradshaw, K., & Wentworth, P. (2013). Computational thinking in educational activities. In J. Carter, I. Utting, & A. Clear (Eds.), The proceedings of the 18th conference on innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education , (pp. 10–15). Canterbury: ACM.
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Mena, J. A. (2012a). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science. , 40 (3), 414–433.
Illinois Online Network. 2003. Learning styles and the online environment. Illinois Online Network and the Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois, http://illinois.online.uillinois.edu/IONresources/instructionaldesign/learningstyles.html
Jacobs, G. M., Renandya, W. A., & Power, M. (2016). Learner autonomy. In G. Jacobs, W. A. Renandya, & M. Power (Eds.), Simple, powerful strategies for student centered learning . New York: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25712-9_3 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Jaques, D., & Salmon, G. (2007). Learning in groups: A handbook for face-to-face and online environments . Abingdon: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Kassandrinou, A., Angelaki, C., & Mavroidis, I. (2014). Transactional distance among Open University students. How does it affect the learning Progress? European journal of open. Distance and e-Learning , 16 (1), 78–93.
Kauffman, H. (2015). A review of predictive factors of student success in and satisfaction with online learning. Research in Learning Technology , 23 , 1e13. https://doi.org/10.3402/rlt.v23.26507 .
Kirmizi, O. (2014). A Study on the Predictors of Success and Satisfaction in an Online Higher Education Program in Turkey. International Journal of Education , 6 , 4.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling , (3rd ed., ). New York: The Guilford Press.
MATH Google Scholar
Lau, C. Y., & Shaikh, J. M. (2012). The impacts of personal qualities on online learning readiness at Curtin Sarawak Malaysia (CSM). Educational Research and Reviews , 7 (20), 430–444.
Lee, B. C., Yoon, J. O., & Lee, I. (2009). Learners' acceptance of e-learning in South Korea: Theories and results. Computers & Education , 53 , 1320–1329.
Lester, P. M., & King, C. M. (2009). Analog vs. digital instruction and learning: Teaching within first and second life environments. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 14 , 457–483.
Lewis, N. (2004). Military student participation in distance learning . Doctorate dissertation. Johnson & Wales University. USA.
Madjar, N., Nave, A., & Hen, S. (2013). Are teachers’ psychological control, autonomy support and autonomy suppression associated with students’ goals? Educational Studies , 39 (1), 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/03055698.2012.667871 .
Mahle, M. (2011). Effects of interaction on student achievement and motivation in distance education. Quarterly Review of Distance Education , 12 (3), 207–215, 222.
Massimo, P. (2014). Multidimensional analysis applied to the quality of the websites: Some empirical evidences from the Italian public sector. Economics and Sociology , 7 (4), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-789X.2014/7-4/9 .
Mathieson, K. (2012). Exploring student perceptions of audiovisual feedback via screen casting in online courses. American Journal of Distance Education , 26 (3), 143–156.
McAuley, A., Stewart, B., Siemens, G., & Cormier, D. (2010). The MOOC model for digital practice (created through funding received by the University of Prince Edward Island through the social sciences and humanities research Council's “knowledge synthesis Grants on the digital economy”) .
Moore, G. C., & Benbasat, I. (1991). Development of an instrument to measure the perception of adopting an information technology innovation. Information System Research , 2 (3), 192–223.
Moore, M. (1990). Background and overview of contemporary American distance education. In M. Moore (Ed.) Contemporary issues in American distance education.
Moore, M. G. (1972). Learner autonomy: The second dimension of independent learning .
Moore, M. G. (2007). Theory of transactional distance. In M. G. Moore (Ed.), Handbook of distance education . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
O’Donnell, S. L., Chang, K. B., & Miller, K. S. (2013). Relations among autonomy, attribution style, and happiness in college students. College Student Journal .
Orton-Johnson, K. (2009). ‘I’ve stuck to the path I’m afraid’: Exploring student non-use of blended learning. British Journal of Educational Technology , 40 (5), 837–847.
Osika, R. E., & Sharp, D. P. (2002). Minimum technical competencies for distance learning students. Journal of Research on Technology in Education , 34 (3), 318–325.
Paechter, M., & Maier, B. (2010). Online or face-to-face? Students’ experiences and preferences in e-learning. Internet and Higher Education , 13 (4), 292–297.
Panyajamorn, T., Suthathip, S., Kohda, Y., Chongphaisal, P., & Supnithi, T. (2018). Effectiveness of E learning design and affecting variables in Thai public schools. Malaysian Journal of Learning and Instruction , 15 (1), 1–34.
Pekrun, R., Goetz, T., & Perry, P. R. (2005). Academic Emotions Questionnaire (AEQ): User's Manual . Munich: University of Munich, Department of Psychology; University of Manitoba Retrieved February 21, 2017. Available online at: https://de.scribd.com/doc/217451779/2005-AEQ-Manual# (Accessed 17 July 2019.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A. F., Garcia, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1991). A manual for the use of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ) . Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan.
Rabinovich, T. (2009). Transactional distance in a synchronous web-extended classroom learning environment . Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Massachusetts: Boston University.
Rogers, E. M. (2003). Diffusion of innovations , (5th ed., ). New York: Free Press.
Salmon, G. (2011). E-moderating: The key to teaching and learning online , (3rd ed., ). London: Routledge.
Salmon, G. (2014). Learning innovation: A framework for transformation. European Journal of Open, Distance and e-Learning , 17 (1), 219–235.
Shearer, R. L. (2010). Transactional distance and dialogue: An exploratory study to refine the theoretical construct of dialogue in online learning. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A , 71 , 800.
Solomon, G., & Schrum, L. (2010). Web 2.0 how-to for educators .
Stroet, K., Opdenakker, M. C., & Minnaert, A. (2013). Effects of need supportive teaching on early adolescents’ motivation and engagement: A review of the literature. Educational Research Review , 9 , 65–87.
Taylor, S., & Todd, P. A. (1995). Assessing IT usage: The role of prior experience. MIS Quarterly , 19 (2), 561–570.
The blended learning impact evaluation at UCF is conducted by Research Initiative for Teaching Effectiveness. (n.d.) https://digitallearning.ucf.edu/learning-analytics/ . Accessed 25 Feb 2020.
Vasala, P., & Andreadou, D. (2010). Student’s support from tutors and peer students in distance learning. Perceptions of Hellenic Open University “studies in education” postgraduate program graduates. Open Education – The Journal for Open and Distance Education and Educational Technology , 6 (1–2), 123–137 (in Greek with English abstract).
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., & Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Quarterly , 36 (1), 157–178.
Whitmer J.C. (2013). Logging on to improve achievement: Evaluating the relationship between use of the learning management system, student characteristics, and academic achievement in a hybrid large enrollment undergraduate course. Doctorate dissertation, university of California. USA.
Yu, Z. (2015). Indicators of satisfaction in clickers aided EFL class. Frontiers in Psychology , 6 , 587 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00587/full .
Zhu, C. (2012). Student satisfaction, performance, and knowledge construction in online collaborative learning. Educational Technology & Society , 15 (1), 127–136.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Declarations
The study involved both undergraduate and graduate students at unviersiti teknologi Malaysia (UTM), an ethical approve was taken before collecting any data from the participants
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Social Sciences & Humanities, School of Education, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM, 81310, Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Hassan Abuhassna, Waleed Mugahed Al-Rahmi, Noraffandy Yahya, Megat Aman Zahiri Megat Zakaria & Azlina Bt. Mohd Kosnin
Faculty of Engineering, School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM, 81310, Skudai, Johor, Malaysia
Mohamad Darwish
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The corresponding author worked in writing the paper, collecting the data, the second author done all the statistical analysis. Moreover, all authors worked collaboratively to write the literature review and discussion and read and approved the final manuscript.

Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hassan Abuhassna .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
This paper is an original work, as its main objective is to develop a model to enhance students’ satisfaction and academic achievement towards using online platforms. As Universiti teknologi Malaysia (UTM) implementing a fully online courses starting from the second semester of 2020.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1..
General objective of the study
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Abuhassna, H., Al-Rahmi, W.M., Yahya, N. et al. Development of a new model on utilizing online learning platforms to improve students’ academic achievements and satisfaction. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 17 , 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00216-z
Download citation
Received : 10 March 2020
Accepted : 19 May 2020
Published : 02 October 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00216-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online learning platforms
- Students’ achievements
- student’s satisfaction
- Transactional distance theory (TDT)
- Bloom’s taxonomy theory (BTT)

The Savvy Scientist
Experiences of a London PhD student and beyond
Thesis Title: Examples and Suggestions from a PhD Grad

When you’re faced with writing up a thesis, choosing a title can often fall to the bottom of the priority list. After all, it’s only a few words. How hard can it be?!
In the grand scheme of things I agree that picking your thesis title shouldn’t warrant that much thought, however my own choice is one of the few regrets I have from my PhD . I therefore think there is value in spending some time considering the options available.
In this post I’ll guide you through how to write your own thesis title and share real-world examples. Although my focus is on the PhD thesis, I’ve also included plenty of thesis title examples for bachelor’s and master’s research projects too.
Hopefully by the end of the post you’ll feel ready to start crafting your own!
Why your thesis title is at least somewhat important
It sounds obvious but your thesis title is the first, and often only, interaction people will have with your thesis. For instance, hiring managers for jobs that you may wish to apply for in the future. Therefore you want to give a good sense of what your research involved from the title.
Many people will list the title of their thesis on their CV, at least for a while after graduating. All of the example titles I’ve shared below came from my repository of academic CVs . I’d say roughly 30% of all the academics on that page list their thesis title, which includes academics all the way up to full professor.
Your thesis title could therefore feature on your CV for your whole career, so it is probably worth a bit of thought!
My suggestions for choosing a good thesis title
- Make it descriptive of the research so it’s immediately obvious what it is about! Most universities will publish student theses online ( here’s mine! ) and they’re indexed so can be found via Google Scholar etc. Therefore give your thesis a descriptive title so that interested researchers can find it in the future.
- Don’t get lost in the detail . You want a descriptive title but avoid overly lengthy descriptions of experiments. Unless a certain analytical technique etc was central to your research, I’d suggest by default* to avoid having it in your title. Including certain techniques will make your title, and therefore research, look overly dated, which isn’t ideal for potential job applications after you graduate.
- The title should tie together the chapters of your thesis. A well-phrased title can do a good job of summarising the overall story of your thesis. Think about each of your research chapters and ensure that the title makes sense for each of them.
- Be strategic . Certain parts of your work you want to emphasise? Consider making them more prominent in your title. For instance, if you know you want to pivot to a slightly different research area or career path after your PhD, there may be alternative phrasings which describe your work just as well but could be better understood by those in the field you’re moving into. I utilised this a bit in my own title which we’ll come onto shortly.
- Do your own thing. Having just laid out some suggestions, do make sure you’re personally happy with the title. You get a lot of freedom to choose your title, so use it however you fancy. For example, I’ve known people to use puns in their title, so if that’s what you’re into don’t feel overly constrained.
*This doesn’t always hold true and certainly don’t take my advice if 1) listing something in your title could be a strategic move 2) you love the technique so much that you’re desperate to include it!
Thesis title examples
To help give you some ideas, here are some example thesis titles from Bachelors, Masters and PhD graduates. These all came from the academic CVs listed in my repository here .
Bachelor’s thesis title examples
Hysteresis and Avalanches Paul Jager , 2014 – Medical Imaging – DKFZ Head of ML Research Group – direct link to Paul’s machine learning academic CV
The bioenergetics of a marine ciliate, Mesodinium rubrum Holly Moeller , 2008 – Ecology & Marine Biology – UC Santa Barbara Assistant Professor – direct link to Holly’s marine biology academic CV
Functional syntactic analysis of prepositional and causal constructions for a grammatical parser of Russian Ekaterina Kochmar , 2008 – Computer Science – University of Bath Lecturer Assistant Prof – direct link to Ekaterina’s computer science academic CV
Master’s thesis title examples
Creation of an autonomous impulse response measurement system for rooms and transducers with different methods Guy-Bart Stan , 2000 – Bioengineering – Imperial Professor – direct link to Guy-Bart’s bioengineering academic CV
Segmentation of Nerve Bundles and Ganglia in Spine MRI using Particle Filters Adrian Vasile Dalca , 2012 – Machine Learning for healthcare – Harvard Assistant Professor & MIT Research Scientist – direct link to Adrian’s machine learning academic CV
The detection of oil under ice by remote mode conversion of ultrasound Eric Yeatman , 1986 – Electronics – Imperial Professor and Head of Department – direct link to Eric’s electronics academic CV
Ensemble-Based Learning for Morphological Analysis of German Ekaterina Kochmar , 2010 – Computer Science – University of Bath Lecturer Assistant Prof – direct link to Ekaterina’s computer science academic CV
VARiD: A Variation Detection Framework for Color-Space and Letter-Space Platforms Adrian Vasile Dalca , 2010 – Machine Learning for healthcare – Harvard Assistant Professor & MIT Research Scientist – direct link to Adrian’s machine learning academic CV
Identification of a Writer’s Native Language by Error Analysis Ekaterina Kochmar , 2011 – Computer Science – University of Bath Lecturer Assistant Prof – direct link to Ekaterina’s computer science academic CV
On the economic optimality of marine reserves when fishing damages habitat Holly Moeller , 2010 – Ecology & Marine Biology – UC Santa Barbara Assistant Professor – direct link to Holly’s marine biology academic CV
Sensitivity Studies for the Time-Dependent CP Violation Measurement in B 0 → K S K S K S at the Belle II-Experiment Paul Jager , 2016 – Medical Imaging – DKFZ Head of ML Research Group – direct link to Paul’s machine learning academic CV
PhD thesis title examples
Spatio-temporal analysis of three-dimensional real-time ultrasound for quantification of ventricular function Esla Angelini – Medicine – Imperial Senior Data Scientist – direct link to Elsa’s medicine academic CV
The role and maintenance of diversity in a multi-partner mutualism: Trees and Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Holly Moeller , 2015 – Ecology & Marine Biology – UC Santa Barbara Assistant Professor – direct link to Holly’s marine biology academic CV
Bayesian Gaussian processes for sequential prediction, optimisation and quadrature Michael Osborne , 2010 – Machine Learning – Oxford Full Professor – direct link to Michael’s machine learning academic CV
Global analysis and synthesis of oscillations: a dissipativity approach Guy-Bart Stan , 2005 – Bioengineering – Imperial Professor – direct link to Guy-Bart’s bioengineering academic CV
Coarse-grained modelling of DNA and DNA self-assembly Thomas Ouldridge , 2011– Bioengineering – Imperial College London Senior Lecturer / Associate Prof – direct link to Thomas’ bioengineering academic CV
4D tomographic image reconstruction and parametric maps estimation: a model-based strategy for algorithm design using Bayesian inference in Probabilistic Graphical Models (PGM) Michele Scipioni , 2018– Biomedical Engineer – Harvard Postdoctoral Research Fellow – direct link to Michele’s biomedical engineer academic CV
Error Detection in Content Word Combinations Ekaterina Kochmar , 2016 – Computer Science – University of Bath Lecturer Assistant Prof – direct link to Ekaterina’s computer science academic CV
Genetic, Clinical and Population Priors for Brain Images Adrian Vasile Dalca , 2016 – Machine Learning for healthcare – Harvard Assistant Professor & MIT Research Scientist – direct link to Adrian’s machine learning academic CV
Challenges and Opportunities of End-to-End Learning in Medical Image Classification Paul Jager , 2020 – Medical Imaging – DKFZ Head of ML Research Group – direct link to Paul’s machine learning academic CV
K 2 NiF 4 materials as cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells Ainara Aguadero , 2006 – Materials Science – Imperial Reader – direct link to Ainara’s materials science academic CV
Applications of surface plasmons – microscopy and spatial light modulation Eric Yeatman , 1989 – Electronics – Imperial Professor and Head of Department – direct link to Eric’s electronics academic CV
Geometric Algorithms for Objects in Motion Sorelle Friedler , 2010 – Computer science – Haverford College Associate Professor – direct link to Sorelle’s computer science academic CV .
Geometrical models, constraints design, information extraction for pathological and healthy medical image Esla Angelini – Medicine – Imperial Senior Data Scientist – direct link to Elsa’s medicine academic CV
Why I regret my own choice of PhD thesis title
I should say from the outset that I assembled my thesis in quite a short space of time compared to most people. So I didn’t really spend particularly long on any one section, including the title.
However, my main supervisor even spelled out for me that once the title was submitted to the university it would be permanent. In other words: think wisely about your title.
What I started with
Initially I drafted the title as something like: Three dimensional correlative imaging for cartilage regeneration . Which I thought was nice, catchy and descriptive.
I decided to go for “correlative imaging” because, not only did it describe the experiments well, but it also sounded kind of technical and fitting of a potential pivot into AI. I’m pleased with that bit of the title.
What I ended up with
Before submitting the title to the university (required ahead of the viva), I asked my supervisors for their thoughts.
One of my well intentioned supervisors suggested that, given that my project didn’t involve verifying regenerative quality, I probably shouldn’t state cartilage regeneration . Instead, they suggested, I should state what I was experimenting on (the materials) rather than the overall goal of the research (aid cartilage regeneration efforts).
With this advice I dialled back my choice of wording and the thesis title I went with was:
Three dimensional correlative imaging for measurement of strain in cartilage and cartilage replacement materials
Reading it back now I’m reminder about how less I like it than my initial idea!
I put up basically no resistance to the supervisor’s choice, even though the title sounds so much more boring in my opinion. I just didn’t think much of it at the time. Furthermore, most of my PhD was actually in a technique which is four dimensional (looking at a series of 3D scans over time, hence 4D) which would have sounded way more sciency and fitting of a PhD.
What I wish I’d gone with
If I had the choice again, I’d have gone with:
Four-dimensional correlative imaging for cartilage regeneration
Which, would you believe it, is exactly what it states on my CV…
Does the thesis title really matter?
In all honesty, your choice of thesis title isn’t that important. If you come to regret it, as I do, it’s not the end of the world. There are much more important things in life to worry about.
If you decide at a later stage that you don’t like it you can always describe it in a way that you prefer. For instance, in my CV I describe my PhD as I’d have liked the title to be. I make no claim that it’s actually the title so consider it a bit of creative license.
Given that as your career progresses you may not even refer back to your thesis much, it’s really not worth stressing over. However, if you’re yet to finalise your thesis title I do still think it is worth a bit of thought and hopefully this article has provided some insights into how to choose a good thesis title.
My advice for developing a thesis title
- Draft the title early. Drafting it early can help give clarity for the overall message of your research. For instance, while you’re assembling the rest of your thesis you can check that the title encompasses the research chapters you’re included, and likewise that the research experiments you’re including fall within what the title describes. Drafting it early also gives more time you to think it over. As with everything: having a first draft is really important to iterate on.
- Look at some example titles . Such as those featured above!
- If you’re not sure about your title, ask a few other people what they think . But remember that you have the final say!
I hope this post has been useful for those of you are finalising your thesis and need to decide on a thesis title. If you’ve enjoyed this article and would like to hear about future content (and gain access to my free resource library!) you can subscribe for free here:
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Related Posts
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
110+ Exceptional Education Research Topics Ideas

Topics for education research usually comprise school research topics, research problems in education, qualitative research topics in education, and concept paper topics about education to mention a few.
If you’re looking for research titles about education, you’re reading the right post! This article contains 110 of the best education research topics that will come in handy when you need to choose one for your research. From sample research topics in education, to research titles examples for high school students about education – we have it all.
Educational Research Topics
Research title examples for college students, quantitative research titles about education, topics related to education for thesis, research titles about school issues, ph.d. research titles in education, elementary education research topics, research title examples about online class, research titles about modular learning, examples of research questions in education, special education research titles.
The best research titles about education must be done through the detailed process of exploring previous works and improving personal knowledge.
Here are some good research topics in education to consider.
What Are Good Research Topics Related to Education?
- The role of Covid-19 in reinvigorating online learning
- The growth of cognitive abilities through leisure experiences
- The merits of group study in education
- Merits and demerits of traditional learning methods
- The impact of homework on traditional and modern education
- Student underdevelopment as a result of larger class volumes
- Advantages of digital textbooks in learning
- The struggle of older generations in computer education
- The standards of learning in the various academic levels
- Bullying and its effects on educational and mental health
- Exceptional education tutors: Is the need for higher pay justifiable?
The following examples of research titles about education for college students are ideal for a project that will take a long duration to complete. Here are some education topics for research that you can consider for your degree.
- Modern classroom difficulties of students and teachers
- Strategies to reform the learning difficulties within schools
- The rising cost of tuition and its burden on middle-class parents
- The concept of creativity among public schools and how it can be harnessed
- Major difficulties experienced in academic staff training
- Evaluating the learning cultures of college students
- Use of scientific development techniques in student learning
- Research of skill development in high school and college students
- Modern grading methods in underdeveloped institutions
- Dissertations and the difficulties surrounding their completion
- Integration of new gender categories in personalized learning
These research topics about education require a direct quantitative analysis and study of major ideas and arguments. They often contain general statistics and figures to back up regular research. Some of such research topics in education include:
- The relationship between poor education and increased academic fees
- Creating a social link between homeschool and traditional schoolgoers
- The relationship between teacher satisfaction and student performance
- The divide between public and private school performance
- The merits of parental involvement in students’ cognitive growth.
- A study on child welfare and its impact on educational development
- The relationship between academic performance and economic growth
- Urbanization in rural areas and its contribution to institutional growth
- The relationship between students and professors in dissertation writing
- The link between debt accumulation and student loans
- Boarding schools and regular schools: The role these two school types play in cognitive development
Educational-related topics used for a thesis normally require a wide aspect of study and enough educational materials. Here are some education research topics you can use for write my thesis .
- The difficulties of bilingual education in private universities
- Homework and its impact on learning processes in college education
- Dissertation topic selection: Key aspects and research obligations
- Social media research topics and their educational functions
- A detailed educational review of student learning via virtual reality techniques
- Ethnicities in universities and their participation in group activities
- The modern approach to self-studying for college students
- Developing time management skills in modern education
- Guidelines for teacher development in advanced educational institutions
- The need for religious education in boarding schools
- A measure of cognitive development using digital learning methods
A research title about school issues focuses on activities surrounding the school environment and its effects on students, teachers, parents, and education in general. Below are some sample research titles in education, relating to school issues.
- Learning English in bilingual schools
- A study of teachers’ role as parent figures on school grounds
- Addressing the increased use of illegal substances and their effects in schools
- The benefits of after-class activities for foreign students
- Assessing student and teacher relationships
- A study of the best methods to implement safety rules in school
- Major obstacles in meeting school schedules using boarding students as a case study
- The need for counseling in public and private schools: Which is greater?
- Academic volunteering in understaffed public schools
- Modern techniques for curbing school violence among college students
- The advantages and disadvantages of teacher unions in schools
As you create your proposed list of research topics in education, consider scientific journals for referencing purposes. Here are some Ph.D. research titles for education.
- The modern methods of academic research writing
- The role of colleges in advanced mental care
- The merits and demerits of Ph.D. studies in Europe and Africa
- Interpersonal relationships between students and professors in advanced institutions
- A review of community colleges: merits and demerits
- Assessing racism in academic ethnic minorities
- The psychological changes of students in higher education
- The questionable standards of student loan provisions
- The merits of personalized teaching techniques in colleges
- The wage gap between private and public university teachers
- Teacher responsibilities in private universities versus public universities
The research topics in elementary education in 2023 are very different from the elementary education research topics from five or ten years ago. This creates interesting grounds for different research titles for elementary education.
Here are some elementary education title research ideas.
- Assessing quick computer literacy among elementary school pupils.
- The role of video games in childhood brain development
- Male vs female role models in early education periods
- The advantages of digital textbooks in elementary schools
- The impact of modern curriculums on elementary education
- Lack of proper school grooming is a cause of violence.
- Should elementary school children be taught about LGBTQ?
- A review of the need for sexual education in elementary schools
- The effects of emotional dependence in early childhood learners.
- The need for constant technology supervision of elementary school students
- Advantages of computer-guided education in elementary schools
Here are some research title examples for students taking online classes.
- The academic difficulties experienced by online students.
- A study of decreased attention in online classes
- The upsides and downsides of online education
- The rising fees of online and traditional education in universities
- A detailed study on the necessity of college internships
- The need to provide college scholarships based on environmental achievements
- How online education terminates university fraternities and sororities.
- The role of academic supervisors in career selection
- Why interactive assignments improved learning capabilities during the pandemic
- Merits of education in online learning environments
- Why online lessons are the least effective for some college students
The modular learning approach focuses primarily on learning outcomes. Here are some examples of research titles about modular learning.
- Modular learning and the role of teachers in its execution
- Teaching techniques of religious institutions
- Potential risks of accelerated learning
- Modular learning on students’ future performances
- The general overview of modular learning amongst students
- The modern Advantages and disadvantages of inclusive classes
- Observing student developments in modular learning
- Music therapy for fostering modular learning techniques
- The creation of a personalized curriculum for students.
- Applications of modular learning both in home-schooling?
- The benefits of modular learning towards creating a more holistic educational system
These research title examples about education answer important questions and they can also be argumentative essay topics .
Here are some titles of research about education questions.
- What impacts do learning approaches provide for students?
- How can schools manage their increasing gender differences?
- What fosters the provision of learning needs?
- What are the best educational recruitment methods?
- How can cognitive development improve education?
- How can you assess the moral growth of institutions?
- What are the primary causes of educational differences in geographical locations?
- How can institutions address increasing mental health needs?
- Why is early intervention essential in students with mental health setbacks?
- What are the characteristics of mental health deterioration among students?
- What techniques are acceptable in regulating the violence of students in institutions
Some of the research title examples about education include:
- How do schools create more personalized learning methods?
- Evaluating mental health setbacks during education
- The impact of modern technology on special education
- The cognitive improvements via specialized learning in dyslexic children
- The psychological link between dyslexia and bullying in high school
- Impact of social isolation in special education classes
- The difficulties in providing specialized learning environments
- A study of orphan students with disabilities and their aptitudes for learning
- How special classes improve the self-esteem of disabled students.
- How to use modern teaching techniques in unique learning environments.
- A study of the application of digital games to autistic learning
Final words about education research topics
We have provided some reliable examples of a research topic about education you can use for write my thesis . You can use these research titles in education to cultivate your ideas, create inspiration, or for online research. Remember always to select a topic that you’re naturally passionate about and do diligent research, and reach out to our professional writing services if you need any help.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Computer Engineering Online Master's Degree
Online learning for graduate students at Wentworth Institute of Technology provides a flexible and accessible educational experience, allowing students to engage with coursework, faculty, and peers from anywhere in the world. This model leverages a digital platform to deliver high-quality collaborative, faculty-led opportunities, accommodating those who need to balance their studies with other professional or personal commitments.
Online Synchronous Learning
Synchronous online learning for graduate students at Wentworth Institute of Technology involves real-time virtual classes where students and professors interact simultaneously, fostering a collaborative and engaging learning environment. This model provides a structured schedule similar to traditional on-campus classes, offering live lectures, discussions, and group work, while still providing the convenience and accessibility of online education.
Ready to Apply? Click Here.
This degree program can be completed part-time or full-time.
At the intersection of technology and innovation, our Master of Science in Computer Engineering will give you the skills and knowledge you need to advance your career in today’s competitive job market. Gain valuable, hands-on experience monitoring, analyzing and redesigning computer systems and components. Get advanced training in computer architecture, embedded design, Internet of Things, and robotics and process automation. Three concentrations to choose from or design a concentration to meet your needs and interests to solve real-world challenges. Full- and part-time options available.
Flexible and Convenient
The Master of Science in Computer Engineering is designed to help you balance, work, school and family.
Accelerated 4+1 Master’s degree
Open to current Wentworth students in the final year of their Bachelor of Science in Computer Engineering or related major, the Accelerated 4+1 Master’s degree enables you to enroll in master’s-level classes while completing your bachelor’s degree. Earn a master’s degree in just 1 year after graduation.
Full-Time Option
Open to candidates with a BS in Computer Engineering or related major, who are not able to transfer the required graduate-level credits into the program. Choose the thesis or non-thesis option and complete your degree in just 3 semesters.
Part-time Option
Open to working professionals with a BS in Computer Engineering or related major, the part-time program can be completed in as little as 2 years, or up to 4 years, depending on the availability of transfer credits the number of classes taken per semester, and the thesis/non-thesis option chosen. Convenient afternoon and evening classes allow you to continue working while you learn and apply what you are studying to work-related situations.
Concentrations
- Computer Architecture
- Embedded Design
- Internet of Things
- Robotics and Process Automation
Students may also work with their advisor to customize a concentration to meet their unique needs and interests.
Self-directed scholarly investigation an important part of both the thesis and non-thesis options. The two-course thesis allows you to choose one of four alternative pathways to
undertake the research and development needed to meet your investigational aspirations and career. The alternative thesis pathways are:
- a science thesis to establish new knowledge using the scientific method
- an engineering thesis to alleviate a deficiency in society or environment
- a partnership thesis to address challenges faced by an external organization
- an entrepreneurial thesis toward a marketable product or service
The thesis option requires 31 credits.
Wentworth Institute of Technology is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education (formerly the Commission on Institutions of Higher Education of the New England Association of Schools and Colleges, Inc.).
The Master of Science in Computer Engineering is offered in two options: thesis and non-thesis. The thesis option requires 31 credits including Thesis I and Thesis II. The non-thesis options requires 34 credits including a two-semester project. All students are required to have at least one concentration.
To be considered for full-time enrollment, students must be enrolled in 3-5 classes per semester. Part-time enrollment requires 1-2 classes per semester.
View more information from the Course Catalog below for program requirements.
The program has a thesis option with 31 required credit hours, and a non-thesis option with 34 required credit hours. Either option has the students undertake an individualized engineering development experience, either as a two-course Thesis, or a one-course Master Project. All students are required to complete a one-credit Professional Perspectives course to increase exposure to recent developments and to aspects of professionalism. All students are required to complete a three-course concentration, either one of the predefined concentrations or an individualized concentration. The course requirements to complete the MSCE degree are shown in this curriculum table. Students must complete the course requirements with a cumulative GPA of at least 3.0, following Wentworth graduate school policies.
Thesis Option
Non-thesis option.
For students with unrelated undergraduate degree, the following foundation courses may be required or recommended. ELEC5510 FOUNDATIONS OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS (3 credits) ELEC5520 FOUNDATIONS IN SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (3 credits) DATA6100 DATA VISUALIZATION (3 credits)
The program offers two structured concentrations and one individualized concentration. A student is required to complete one concentration. To fulfill a concentration, the student is required to:
- Complete three of the courses listed with the concentration.
- Complete a thesis or master project that relates to a field of the concentration.
A student may take more than three of the listed courses for the concentration, and any completed extra courses would be counted as electives. A student may attempt to complete two concentrations. The student would need to complete three unique courses per concentration (no course could be counted as one of the three courses for both concentrations). The thesis or master project would need to be related to a field of both concentrations. The concentrations and associated courses are listed below. ELEC courses at the 5000 level do not have a graduate-level prerequisite. ELEC courses at the 6000 level may have a graduate-level prerequisite.
Careers in Computer Engineering
Graduates from the Computer Engineering program may go on to pursue careers as:
- Software Engineers
- Project Managers
- Data Scientists
- Java Developer
- Cloud Engineering Architect
Job Skills in Computer Engineering
Jobs for Computer Engineers include the following skills:
- Computer Science
- Software Engineering
- Software Development
- Agile Software Development
Salary for Computer Engineers
Graduates with an MS in Computer Engineering earn a median annual salary of $129,000.
Ready to Get Started?
Begin your application today and kickstart your career.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Follow The Liverpool Offside online:
- Follow The Liverpool Offside on Twitter
- Follow The Liverpool Offside on Facebook
Site search
- Liverpool Transfer News & Rumours
- Liverpool Team News
- Liverpool Tactical Review & Longform
- Liverpool Video
- Liverpool Match Coverage
- Full Archive
- TLO Community Guidelines
- Physio Room: Liverpool Injuries
- How to Buy Liverpool Tickets
- Links & Resources
- DraftKings Nation
- Community Guidelines
Filed under:
A Liverpool Fan’s Journey to Accepting the End
It’s all done, but for the final bow.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: A Liverpool Fan’s Journey to Accepting the End
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73349617/2149861809.0.jpg)
A thing I’ll remember about this season is that, even as we’ve come to the close with nothing meaningful left to play for, the grit and the tenacity of this squad made me hold out hope for a very long time at a miracle season. One in which we might have been able to win or, at least, fight to the last moment for every competition that we were in.
In the end, we fell short of that mark. Even allowing for the achievement of winning the League Cup, it feels like a mild disappointment given everything we’d encountered this year. A year that, by all accounts, we’d arrived two-three years early for any kind of inclusion in talk related to claiming cups or titles.
It is, of course, all colored by the announcement that this would be Jurgen Klopp’s last season at the helm of Liverpool Football Club. A tenure that featured a Champions League title and the club’s first league title in over 30 years. Even without noting that, save a Europa League title Klopp has won every major competition for Liverpool, it would have been an iconic stint on the strength of that league trophy alone.
It’s a testament to the man that we managed to still believe after a season as disappointing as last season, a summer transfer window that saw the departure of legendary Reds players and a complete overhaul of our midfield department, transfer shenanigans most notably involving Chelsea players, and questions around the ability of the club to sustain its run with other teams in the Big 6 strengthening - 7 if you want to include Newcastle in that mix now.
But I guess instilling belief shouldn’t be a surprise for a man that managed to do that after the debacle that was the end of the Hicks and Gilette Era and the false dawn of the Brendan Rodgers Show. For people like me, Children of the Hodgepocalypse, it was hard to align with the insistence from more established fans that the state of the club did not match its history. Mostly because I’d only ever experienced the club in turmoil.
Jurgen Klopp came in and changed all of that. Not just in terms of the results, but in once more managing to build that all-important spiritual connection with the City and its fans. I now know what Istanbul might have felt like because I’ve lived through Barcelona. I now know what it’s like to see an expectant Anfield crowd demand an unreal performance because I saw them urging that title-winning club on at every turn. I now know what it means to connect the moment to the history of big moments and, more importantly, desire to do the footballing part the right way.
For all of those reasons, it was hard to accept that we would get to this point without one last moment of magic for the gaffer. And I see how, at this moment and from this vantage point, that it’s easier now to maybe reflect on this being the right time. That Jurgen’s bold declaration that he didn’t have the energy to do this again or at the level he needs to still be true to himself, was another stunning lesson for us to receive - this time in self-awareness.
But I’d argue that the last few weeks have somehow made it harder for me to relent on the hope that maybe Jurgen had second thoughts. That there was maybe just that much more left in the tank. That we could let him leave “the right way.”
Because the biggest reason it is so hard to let go is that Jurgen Klopp was the absolute best fit for Liverpool Football Club’s entire ethos in such a long time. That his unique style and approach were exactly what we needed after a bleak period and entering one of deep uncertainty.
Maybe it’s that latter point that resonates now; there’s no way of knowing how the next period goes. Except that it will be without a human being who managed to not just see the best in the people he encountered and worked with, but on most days, managed to build the foundations to allow them to reach and exceed that mark.
All things must end and there’s wisdom in knowing a new chapter must begin. But I’m in no hurry to flip that page or to meet new characters. Even though I know the conclusion, I want to luxuriate in this reality for just that little bit more. Because I, too, have come to love the feeling of believing in something more. And I know just how precious that seemingly simple thing can be in this world.
I know it’s over, but let me believe just that little bit longer.
More From The Liverpool Offside
- Rumour Mongering: Saudi Pro League Target Alisson and Mohamed Salah
- Official: Pepijn Lijnders Appointed as Red Bull Salzbug Manager
- Rumour Mongering: Diaz Wanted by Barcelona
- Rumour Mongering: Asking Price for Koopmeiners Complicates Juventus Bid
- Elliott: Winning on Sunday For Klopp Is “The Least They Can Do”
- Klopp Talk: “I Am Allowed to See Just the Good Bits of It”
Loading comments...
Sign up for the newsletter sign up for the liverpool offside daily roundup newsletter, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 15, 2024 • 25:48 The Possible Collapse of the U.S. Home Insurance System
- May 14, 2024 • 35:20 Voters Want Change. In Our Poll, They See It in Trump.
- May 13, 2024 • 27:46 How Biden Adopted Trump’s Trade War With China
- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
The Possible Collapse of the U.S. Home Insurance System
A times investigation found climate change may now be a concern for every homeowner in the country..
Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Featuring Christopher Flavelle
Produced by Nina Feldman , Shannon M. Lin and Jessica Cheung
Edited by MJ Davis Lin
With Michael Benoist
Original music by Dan Powell , Marion Lozano and Rowan Niemisto
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
Across the United States, more frequent extreme weather is starting to cause the home insurance market to buckle, even for those who have paid their premiums dutifully year after year.
Christopher Flavelle, a climate reporter, discusses a Times investigation into one of the most consequential effects of the changes.
On today’s episode

Christopher Flavelle , a climate change reporter for The New York Times.

Background reading
As American insurers bleed cash from climate shocks , homeowners lose.
See how the home insurance crunch affects the market in each state .
Here are four takeaways from The Times’s investigation.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
Christopher Flavelle contributed reporting.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Christopher Flavelle is a Times reporter who writes about how the United States is trying to adapt to the effects of climate change. More about Christopher Flavelle
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This page contains a compilation of online education presentation topics, essay ideas 💡 and examples. ... The thesis statement for this study is: "online learning has positive impact on the learners, teachers and the institution offering these courses" Online learning or E learning is a term used to describe various learning ...
The researcher designed this study to examine the impacts of online learning on elementary students' mental and social and emotional well-being amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Also, this study addresses the broader range of extant inequities that may arise due to the shift to online learning (from educator and parent perspectives).
This paper aims to propose a research project targeted to study the impact of online learning on the academic performance of Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University (ERAU) students, as compared to an in-person medium. The research will be conducted over a period of 2 years for 3 modules that are common for students across all courses.
This paper investigates on the aspect of Information Technology - enabled online learning and the relevant technologies that are utilized. Online Classes: Computer Literacy and Knowledge. The aim of the paper is to prove that educational establishments should change their policies to introduce online classes.
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE TEACHING ON HIGHER EDUCATION FACULTY'S PROFESSIONAL IDENTITY AND THE ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY: THE COMING OF AGE OF THE VIRTUAL TEACHER: By EDWIGE SIMON M.A., Université Lille III, 2000 M.A., Indiana University, 2003 M.S., Indiana University, 2005 A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of the
sense of online learning. The altered learning environments created by web-based technologies, not only. eliminate barriers of time, space and arguably l earning styles, providing increased access ...
classroom learning remains largely traditional; the education system, both public and private, follows a national curriculum which promote the practice of standardization in
Teacher shortage, curriculum imbalances (lack of course options) and tight budgets are challenges faced in rural areas that are less prevalent with distance methods of learning (Dachos 2020). In other words, remote learning allows a better chance for equal and high-quality education for students across different areas.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students' academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this ...
gued that effective online instruction is dependent upon 1) w ell-designed course content, motiva t-. ed interaction between the instructor and learners, we ll-prepared and fully-supported ...
Abstract Students' Learning Experiences and Perceptions of Online Course Content and Interactions by Alex A. Nwankwo. MBA, University of Nigeria BS, University of Nigeria. Doctoral Study Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for a Degree of Doctor of Education. Walden University February 2015.
THE DESIGN OF ONLINE LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS. A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in Communication, Culture, and Technology. By. Daniel John Davis, B.A.
This research aims to explore and investigate potential factors influencing students' academic achievements and satisfaction with using online learning platforms. This study was constructed based on Transactional Distance Theory (TDT) and Bloom's Taxonomy Theory (BTT). This study was conducted on 243 students using online learning platforms in higher education. This research utilized a ...
Summarizing students' concerns towards online education, interaction and collaboration, as well as confusing layout/organization, were reported as areas that cause barriers in online and hybrid environments. The use of asynchronous, collaborative tools is recommended for improvement of students' motivation and attitudes towards online learning.
report, co-sponsored by the Online Learning Consortium, a collaborative community focused on the advancement of quality online education, revealed that enrollment in online courses had steadily increased over the past 14 years and as of Fall 2016, 31.6% of students were enrolled in at least one online education course (Seaman et al., 2018).
Master's thesis title examples. Creation of an autonomous impulse response measurement system for rooms and transducers with different methods. Guy-Bart Stan, 2000 - Bioengineering - Imperial Professor - direct link to Guy-Bart's bioengineering academic CV. Segmentation of Nerve Bundles and Ganglia in Spine MRI using Particle Filters.
students took at least one online course in 2010, and 65% of higher education institutions consider online learning to be a critical part of their long-term strategies (Allen & Seaman, 2011). Figure 1: Online Enrollment Trends In addition to use of online courses at traditional institutions, one of the most recent - and popular - phenomena ...
online learning allows students to study in a "safe" environment, without experiencing embarrassment about asking questions. According to Harrison (2018), young children can access pictures and videos, navigate 'Youtube', and interact and participate in games and digital applications that are suited to their age.
Nashville, TN 3720 3 USA. t [email protected]. Abstract. The physical "brick and mortar" classroom is starting to lose its monopoly as the place of. learning. The Internet has made ...
Award: 2018 Charles A. Beard Senior Thesis Prize. Title: "A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man": UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947. University: University College London. Faculty: Geography. Author: Anna Knowles-Smith. Award: 2017 Royal Geographical Society Undergraduate Dissertation Prize. Title: Refugees and ...
Here are some elementary education title research ideas. Assessing quick computer literacy among elementary school pupils. The role of video games in childhood brain development. Male vs female role models in early education periods. The advantages of digital textbooks in elementary schools.
Online learning for graduate students at Wentworth provides a flexible and accessible educational experience, allowing students to engage with coursework, faculty, and peers from anywhere in the world. ... Choose the thesis or non-thesis option and complete your degree in just 3 semesters. Part-time Option. ... Title Credits; Mathematics ...
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
A tenure that featured a Champions League title and the club's first league title in over 30 years. Even without noting that, save a Europa League title Klopp has won every major competition for ...
Today, online learning is a challenging teaching strategy used by higher educational institutions (HEI) and requires ample technological and psychological preparation.
Christopher Flavelle contributed reporting.. The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad ...
The Department of Education's new Title IX regulations provide a good opportunity to think about how your organization might level up. May 15, 2024 at 04:08 PM. 6 minute read. Commentary.
During the years 2019 and 2020, when the online learning approach was deployed in the teaching of the four mechanical engineering courses (Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Heat Transfer, and ...