- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
- Literature Navigator
- Thesis Dialogue Blueprint
- Writing Wizard's Template
- Research Proposal Compass
- Why students love us
- Why professors love us
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon


A Step-by-Step Guide on How a Thesis is Written

Top BBA Final Year Project Topics in Marketing: A Comprehensive List

Navigating Thesis Writing Anxiety: Tips for a Smooth Process

Overcoming Dissertation Test Anxiety: Strategies for Success

Friends and Thesis Writing: Striking the Right Balance for Your Thesis

Mastering the Art of Communication: Effective Strategies for Voice Your Research in Interviews
Navigating ethical dilemmas: the morality of conducting interviews.
Data Anomalies: Strategies for Analyzing and Interpreting Outlier Data
Optimal thesis proposal length: how many pages should you aim for.

Crafting a thesis proposal is a critical step in the journey of academic research, serving as the blueprint for your study and a pitch to your academic committee. The length of the proposal can significantly impact its effectiveness, making it essential to strike the right balance between comprehensiveness and conciseness. This article delves into the factors that determine the optimal length of a thesis proposal and provides guidance on structuring and refining your proposal to meet academic standards.
Key Takeaways
- The ideal length of a thesis proposal varies based on institutional guidelines, complexity of the study, and the intended audience, typically ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 words.
- A well-structured thesis proposal includes essential elements such as the title page, abstract, introduction, methodology, literature review, and implications.
- Common pitfalls in proposal writing include an overly ambitious scope, neglecting academic conventions, and providing insufficient detail and justification.
- Effective proposal development strategies encompass diligent time management, iterative feedback and revisions, and leveraging academic support resources.
- Finalizing the thesis proposal requires strict adherence to submission guidelines, meticulous proofreading and formatting, and preparation for committee feedback.
Determining the Appropriate Length for Your Thesis Proposal
Understanding institutional requirements.
Before you embark on the meticulous process of crafting your thesis proposal, it is imperative to acquaint yourself with the specific requirements of your institution. Each university or funding agency may prescribe a distinct set of guidelines , including the expected length of your proposal. These stipulations are not arbitrary; they are designed to ensure that your proposal comprehensively addresses the necessary components while remaining succinct enough to be digestible.
To ascertain the precise expectations, you should:
- Consult your department's handbook or website for official guidelines.
- Reach out to your advisor or the graduate coordinator for clarification.
- Review successful proposals from previous students in your field, if available.
Remember, the length of your proposal may also be influenced by the complexity of your study. For instance, projects with intricate methodologies or multiple phases might necessitate a more detailed exposition. Conversely, if your audience is from the business or non-profit sector, a more streamlined approach could be more appropriate. Striking the right balance between depth and brevity is crucial, and understanding the institutional requirements is the first step in achieving this equilibrium.
Balancing Depth with Brevity
When crafting your thesis proposal, you must strike a delicate balance between providing enough detail to outline your research and maintaining conciseness. Your proposal should be comprehensive yet succinct , ensuring that each page serves a purpose towards justifying your research. A common guideline suggests that an executive summary, akin to a thesis proposal, should not exceed 10% of the length of the full document. However, this is not a one-size-fits-all rule.
Consider the following points to achieve the right balance:
- Clearly define the scope of your research to avoid unnecessary elaboration.
- Prioritize the inclusion of key information that demonstrates the feasibility and significance of your study.
- Use bullet points to present essential details in a digestible format, especially when outlining your methodology or summarizing the literature review.
Ultimately, the length of your thesis proposal will be influenced by the complexity of your topic and the expectations of your academic institution. It is imperative to adhere to any specific guidelines provided by your department while ensuring that your proposal is as concise as possible without compromising on the necessary depth.
Factors Influencing Proposal Length
The length of your thesis proposal can be influenced by a variety of factors, each playing a crucial role in determining the optimal number of pages. Complexity of the research topic is a significant determinant; projects with intricate methodologies or numerous phases often necessitate longer proposals to adequately detail the procedures and scope. Conversely, proposals for more straightforward research can be more concise.
Institutional guidelines are another key consideration. Academic institutions and funding agencies may have specific length requirements for proposals. It's essential to consult these guidelines early in the planning process to ensure compliance. For instance, while some institutions may expect detailed proposals that span several pages, others might prefer a more succinct approach, with proposals typically ranging from 1500 to 3000 words .
Lastly, the intended audience of your proposal should influence its length. Proposals aimed at academic audiences may require more comprehensive explanations to demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject matter. In contrast, business or non-profit proposals might benefit from a streamlined presentation that focuses on the core objectives and outcomes. Below is a list of factors to consider when determining the length of your thesis proposal:
- Complexity of the research topic
- Institutional guidelines
- Intended audience
- Depth of literature review
- Detail required in methodology section
By carefully considering these elements, you can tailor your proposal to effectively convey your research plan while adhering to any necessary constraints.
Structural Elements of a Thesis Proposal
Title page and abstract.
The title page of your thesis proposal is the gateway to your research, presenting the essential details at a glance. It should be crafted to capture attention, much like a book cover, and include your research title, name, contact details, department or organization, and the date of submission. The design should be clean, with ample white space to enhance readability and focus on the critical points.
Following the title page, the abstract serves as a succinct summary of your project. It outlines your research question, the rationale behind the study, and the methods you plan to employ. The abstract page immediately follows the title page and provides a snapshot for readers to grasp the essence of your proposal without delving into the full document. It's crucial to ensure that the abstract is clear, concise, and effectively communicates the significance of your research.
Here are the key elements to include on your title page:
- Title of your research
- Contact Details
- Name of the department or organization
- Date of submission
Introduction and Objectives
The Introduction of your thesis proposal is where you capture the essence of your research question and the objectives you aim to achieve. It is your opportunity to articulate the significance of your study and its potential contribution to the field. Begin by presenting your academic background, highlighting any relevant research experience or publications that underscore your preparedness for the proposed study.
Clearly state the purpose of your research and the specific objectives you intend to accomplish. This should include both your short-term goals, such as completing the research, and your long-term aspirations, like how this work will advance your academic or professional trajectory. Ensure that your objectives are SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Here's a concise list to guide you:
- Specific: Define what you want to accomplish with precision.
- Measurable: Determine how you will evaluate success.
- Achievable: Set goals that are within your capabilities and resources.
- Relevant: Align your objectives with broader academic or industry interests.
- Time-bound: Establish a realistic timeline for achieving your goals.
In doing so, you will present a compelling case for why your research is not only necessary but also well-conceived and feasible.
Methodology and Literature Review
In crafting your thesis proposal, the Methodology and Literature Review sections are pivotal. The Methodology outlines the approach you will take to conduct your research, detailing the techniques and tools you will use. It is essential to justify your choices and explain how they align with your research objectives. Ensure your methods are robust and replicable , providing a clear path to your study's intended outcomes.
The Literature Review serves to anchor your research in the existing body of knowledge. Here, you will summarize and synthesize the scholarly works that inform your study, highlighting the relevance and significance of your work. This section should not only reflect your understanding of the topic but also identify gaps in the current research that your thesis aims to fill. To effectively organize your Literature Review, consider the following points:
- The historical context of your research topic
- Key studies and their findings
- Theoretical frameworks that underpin your study
- Methodological similarities and differences with previous work
By meticulously combining these elements, your proposal will demonstrate a comprehensive grasp of your research landscape and a clear direction for your inquiry.
Implications and Contributions
In crafting your thesis proposal, it is crucial to articulate the implications and contributions your research will make to the field. Clearly outline how your work will advance your field of study and why this new knowledge is essential. Your proposal should demonstrate the significance of your research and its potential to fill knowledge gaps or challenge existing beliefs.
Consider the following points when detailing the implications and contributions of your research:
- The relevance of your study to current academic debates or societal issues.
- How your research may inform policy decisions or practical applications.
- The potential for your work to set a foundation for future studies.
By addressing these aspects, you ensure that your proposal not only proposes a research question but also provides a compelling rationale for why the question is worth investigating.
Common Pitfalls in Thesis Proposal Writing
Overly ambitious scope.
When crafting your thesis proposal, it's crucial to define a clear and manageable scope. An overly ambitious scope can not only lead to thesis anxiety but also compromise the feasibility of your research. Start with a strong project concept and ensure that your research questions are well-defined to avoid easy rejection. Here are some qualitative points to consider:
- Ensure your project concept is specific and your research problems are clearly articulated.
- Balance the complexity of your methodology with the expectations of your audience.
- Allocate your resources wisely, including time, funding, and academic support.
By setting realistic boundaries for your study, you can create a proposal that is both ambitious and achievable, thus mitigating the risk of overwhelming yourself and your committee.
Neglecting Academic Conventions
Adhering to academic conventions is a cornerstone of scholarly writing, yet it is often overlooked in thesis proposals. Failure to properly cite sources or follow stylistic guidelines can undermine the credibility of your work . It is essential to familiarize yourself with the citation style that is preferred by your institution or field of study, whether it be APA, MLA, or another format.
In addition to citations, academic conventions encompass a range of elements from the structure of your argument to the precision of your language. Here are some key points to consider:
- Ensure that your proposal is free of grammatical errors and typos, as these can detract from the professionalism of your document.
- Use terminology that is appropriate for your audience and field, avoiding overly complex jargon that may obscure your points.
- Structure your proposal in a logical manner, with a clear introduction, methodology, and conclusion.
By paying close attention to these details, you can present a proposal that not only conveys your research intentions effectively but also respects the scholarly traditions of your discipline.
Insufficient Detail and Justification
A common pitfall in thesis proposal writing is providing insufficient detail and justification for your research. This can lead to a proposal that appears underdeveloped and unconvincing to your review committee. To avoid this, ensure that each section of your proposal clearly articulates the rationale for your study, the significance of your research question, and the robustness of your methodology.
Develop a comprehensive literature review that demonstrates your understanding of the field and identifies the gap your research aims to fill. This should be accompanied by a clear explanation of your research methods, including why they are appropriate and how they will address the research questions or hypotheses. Below is a list of elements to include for a well-justified proposal:
- A clear statement of the research problem
- The objectives and significance of your study
- A thorough literature review
- A detailed methodology section
- Anticipated results and their potential impact
Remember, the goal is to present a proposal that is both thorough and concise, providing enough detail to showcase the depth of your research while remaining focused and relevant.
Strategies for Effective Proposal Development
Time management and planning.
Effective time management is crucial in developing a thesis proposal that is both comprehensive and concise. Begin by creating a timeline with important milestones, such as completing your literature review and finalizing your analysis. This not only demonstrates your ability to manage time effectively but also ensures that you account for possible delays, allowing you to adapt your schedule as needed.
To aid in this process, consider utilizing visual tools like a Gantt chart or a spreadsheet. These can help you organize tasks, assign deadlines, and track your project's progress. For instance, a Gantt chart template from a platform like Visme can be customized to fit your specific timeline needs. Ensure that each task is given a realistic deadline , reflecting both the scope of your project and the time you can commit.
In addition to setting deadlines, itemize and categorize your project into smaller steps. This breakdown can assist in identifying potential bottlenecks and allocating resources effectively. For example, group expenses into categories such as personnel and equipment, which can be particularly useful when planning the budget for your research.
Seeking Feedback and Revisions
As you develop your thesis proposal, it's crucial to actively seek feedback and engage in revisions. This iterative process not only refines your ideas but also ensures that your proposal aligns with academic standards and expectations. Engage with your advisors and peers , presenting your draft and being open to constructive criticism. This dialogue can reveal insights and perspectives that you may have overlooked.
Consider the following steps to effectively incorporate feedback:
- Compile comments and suggestions from multiple sources.
- Prioritize revisions based on the significance of the feedback.
- Revise your proposal systematically, addressing both major concerns and minor edits.
Remember, the goal is to strengthen your proposal's clarity, coherence, and feasibility . Revisions are not a sign of weakness but a testament to your commitment to excellence. By embracing this process, you ensure that your thesis proposal is robust and ready for formal evaluation.
Utilizing Academic Support Resources
Leveraging academic support resources is a critical strategy in developing an effective thesis proposal. Universities often provide a wealth of resources tailored to assist you in the writing process. These can range from writing guides and citation tools to personalized feedback from writing centers. Identify and utilize these resources early in your proposal development to enhance the quality and coherence of your work.
For instance, many institutions offer access to research guides, which can help you navigate through the complexities of literature reviews and methodology sections. Here's a list of common resources you might find useful:
- Writing centers or labs
- Online writing guides and tutorials
- Research and citation software
- Workshops on academic writing and research skills
- One-on-one consultations with faculty or writing specialists
Remember, these resources are designed to support you; take advantage of them to refine your proposal and align it with academic standards. By doing so, you not only improve your proposal but also develop skills that will benefit your overall research project.
Finalizing and Submitting Your Thesis Proposal
Adhering to submission guidelines.
As you finalize your thesis proposal, it is crucial to adhere to the specific submission guidelines provided by your institution or funding body. These guidelines often include detailed instructions on formatting, document structure, and the submission process itself. Ensure that your proposal meets all the specified requirements to avoid unnecessary delays or rejection.
Pay close attention to the formatting rules, which may dictate font size, line spacing, margin widths, and the inclusion of necessary sections such as the title page, abstract, and references. Additionally, the submission guidelines might outline the process for electronic submission, including file types and naming conventions. Here is a concise checklist to guide you:
- Verify the required proposal length and structure.
- Check for specific formatting details (font, spacing, margins).
- Confirm the inclusion of all mandatory sections.
- Adhere to the file type and naming conventions for electronic submissions.
- Review the deadline and plan your submission accordingly.
By meticulously following these steps, you can ensure that your proposal is not only academically sound but also professionally presented . This attention to detail reflects your commitment to the academic process and increases the likelihood of a favorable reception from the review committee.
Proofreading and Formatting
After meticulously developing your thesis proposal, it's crucial to ensure that it is free of errors and adheres to the expected academic standards. Proofreading is not merely a final check but an integral part of the writing process. It's your opportunity to refine your work and present it in the best possible light. A well-proofread proposal reflects professionalism and demonstrates your attention to detail.
Formatting your proposal according to institutional guidelines is equally important. It includes consistent use of fonts, headings, margins, and citation styles. Here's a concise checklist to help you with the proofreading and formatting process:
- Review grammar and spelling for accuracy.
- Ensure that all figures and tables are correctly labeled and referenced.
- Verify that citations and references comply with the chosen style guide.
- Check the alignment and spacing of text and paragraphs.
- Confirm that the pagination is correct throughout the document.
By following these steps, you can present a polished and scholarly proposal that is ready for submission.
Anticipating Committee Feedback
After meticulously preparing your thesis proposal, it's essential to anticipate the feedback from your committee. This step is not about predicting every question but rather preparing for the discursive environment you will encounter. Committee members may provide insights that challenge your assumptions or suggest alternative methodologies. Engage with their feedback constructively , considering it an opportunity to refine your proposal and strengthen your research design.
To effectively anticipate feedback, consider the following:
- Reflect on potential questions regarding your methodology and the feasibility of your study.
- Prepare to discuss the significance of your research and its contribution to the field.
- Think about how you will address possible concerns about the scope and limitations of your study.
Remember, the goal is to demonstrate your preparedness and ability to think critically about your research. By anticipating and responding to committee feedback, you show your commitment to scholarly rigor and the success of your project.
As you approach the pivotal moment of finalizing and submitting your thesis proposal, remember that guidance and support are just a click away. Our comprehensive resources and expert advice are designed to streamline the process, ensuring your proposal meets the highest standards. Don't hesitate to visit our website for invaluable tips and personalized assistance. Take the next step in your academic journey with confidence!
In conclusion, the optimal length of a thesis proposal is not a one-size-fits-all answer but rather a balance between thoroughness and conciseness. It should be long enough to cover all necessary aspects of the proposed research, including the methodology, significance, and literature review, while remaining succinct enough to maintain the reader's engagement. Typically, proposals range from 1,000 to 5,000 words, but this can vary based on institutional guidelines, the complexity of the study, and the expectations of the audience. Aspiring scholars should aim for clarity and precision, ensuring their proposal is comprehensive yet focused, without straying into unnecessary detail. Ultimately, the quality of the content is paramount, and the proposal should reflect a deep understanding of the research topic and a clear plan for investigation. By adhering to these principles, students can craft a proposal that not only meets academic standards but also serves as a strong foundation for their research journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical length range for a thesis proposal.
Thesis proposals can vary in length, but they typically range from 15 to 30 pages. However, the exact length depends on your institution's guidelines and the complexity of your research.
How do I determine the right length for my thesis proposal?
Consult your institution's requirements, consider the scope of your research, and ensure you have enough space to clearly articulate your research objectives, methodology, and literature review.
Can a thesis proposal be too long?
Yes, a proposal that is excessively long can be burdensome for reviewers and may suggest an overly ambitious project scope. It's important to be concise and to the point.
Should I include a detailed literature review in my thesis proposal?
Include a literature review that is sufficient to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and to justify your research question, but avoid excessive detail that can be saved for the actual thesis.
What are the key structural elements that I should include in my thesis proposal?
Your proposal should typically include a title page, abstract, introduction, objectives, methodology, literature review, and a section on implications and contributions.
How can I ensure my thesis proposal is well-received by the committee?
Follow your institution's guidelines, write clearly and concisely, provide a strong rationale for your research, and thoroughly proofread your document before submission.

- Rebels Blog
- Blog Articles
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 11 November 2022.
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it’s about, how you’ll conduct it, and why it’s worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student.
A dissertation proposal should generally include:
- An introduction to your topic and aims
- A literature review of the current state of knowledge
- An outline of your proposed methodology
- A discussion of the possible implications of the research
- A bibliography of relevant sources
Dissertation proposals vary a lot in terms of length and structure, so make sure to follow any guidelines given to you by your institution, and check with your supervisor when you’re unsure.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: coming up with an idea, step 2: presenting your idea in the introduction, step 3: exploring related research in the literature review, step 4: describing your methodology, step 5: outlining the potential implications of your research, step 6: creating a reference list or bibliography.
Before writing your proposal, it’s important to come up with a strong idea for your dissertation.
Find an area of your field that interests you and do some preliminary reading in that area. What are the key concerns of other researchers? What do they suggest as areas for further research, and what strikes you personally as an interesting gap in the field?
Once you have an idea, consider how to narrow it down and the best way to frame it. Don’t be too ambitious or too vague – a dissertation topic needs to be specific enough to be feasible. Move from a broad field of interest to a specific niche:
- Russian literature 19th century Russian literature The novels of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky
- Social media Mental health effects of social media Influence of social media on young adults suffering from anxiety
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Like most academic texts, a dissertation proposal begins with an introduction . This is where you introduce the topic of your research, provide some background, and most importantly, present your aim , objectives and research question(s) .
Try to dive straight into your chosen topic: What’s at stake in your research? Why is it interesting? Don’t spend too long on generalisations or grand statements:
- Social media is the most important technological trend of the 21st century. It has changed the world and influences our lives every day.
- Psychologists generally agree that the ubiquity of social media in the lives of young adults today has a profound impact on their mental health. However, the exact nature of this impact needs further investigation.
Once your area of research is clear, you can present more background and context. What does the reader need to know to understand your proposed questions? What’s the current state of research on this topic, and what will your dissertation contribute to the field?
If you’re including a literature review, you don’t need to go into too much detail at this point, but give the reader a general sense of the debates that you’re intervening in.
This leads you into the most important part of the introduction: your aim, objectives and research question(s) . These should be clearly identifiable and stand out from the text – for example, you could present them using bullet points or bold font.
Make sure that your research questions are specific and workable – something you can reasonably answer within the scope of your dissertation. Avoid being too broad or having too many different questions. Remember that your goal in a dissertation proposal is to convince the reader that your research is valuable and feasible:
- Does social media harm mental health?
- What is the impact of daily social media use on 18– to 25–year–olds suffering from general anxiety disorder?
Now that your topic is clear, it’s time to explore existing research covering similar ideas. This is important because it shows you what is missing from other research in the field and ensures that you’re not asking a question someone else has already answered.
You’ve probably already done some preliminary reading, but now that your topic is more clearly defined, you need to thoroughly analyse and evaluate the most relevant sources in your literature review .
Here you should summarise the findings of other researchers and comment on gaps and problems in their studies. There may be a lot of research to cover, so make effective use of paraphrasing to write concisely:
- Smith and Prakash state that ‘our results indicate a 25% decrease in the incidence of mechanical failure after the new formula was applied’.
- Smith and Prakash’s formula reduced mechanical failures by 25%.
The point is to identify findings and theories that will influence your own research, but also to highlight gaps and limitations in previous research which your dissertation can address:
- Subsequent research has failed to replicate this result, however, suggesting a flaw in Smith and Prakash’s methods. It is likely that the failure resulted from…
Next, you’ll describe your proposed methodology : the specific things you hope to do, the structure of your research and the methods that you will use to gather and analyse data.
You should get quite specific in this section – you need to convince your supervisor that you’ve thought through your approach to the research and can realistically carry it out. This section will look quite different, and vary in length, depending on your field of study.
You may be engaged in more empirical research, focusing on data collection and discovering new information, or more theoretical research, attempting to develop a new conceptual model or add nuance to an existing one.
Dissertation research often involves both, but the content of your methodology section will vary according to how important each approach is to your dissertation.
Empirical research
Empirical research involves collecting new data and analysing it in order to answer your research questions. It can be quantitative (focused on numbers), qualitative (focused on words and meanings), or a combination of both.
With empirical research, it’s important to describe in detail how you plan to collect your data:
- Will you use surveys ? A lab experiment ? Interviews?
- What variables will you measure?
- How will you select a representative sample ?
- If other people will participate in your research, what measures will you take to ensure they are treated ethically?
- What tools (conceptual and physical) will you use, and why?
It’s appropriate to cite other research here. When you need to justify your choice of a particular research method or tool, for example, you can cite a text describing the advantages and appropriate usage of that method.
Don’t overdo this, though; you don’t need to reiterate the whole theoretical literature, just what’s relevant to the choices you have made.
Moreover, your research will necessarily involve analysing the data after you have collected it. Though you don’t know yet what the data will look like, it’s important to know what you’re looking for and indicate what methods (e.g. statistical tests , thematic analysis ) you will use.
Theoretical research
You can also do theoretical research that doesn’t involve original data collection. In this case, your methodology section will focus more on the theory you plan to work with in your dissertation: relevant conceptual models and the approach you intend to take.
For example, a literary analysis dissertation rarely involves collecting new data, but it’s still necessary to explain the theoretical approach that will be taken to the text(s) under discussion, as well as which parts of the text(s) you will focus on:
- This dissertation will utilise Foucault’s theory of panopticism to explore the theme of surveillance in Orwell’s 1984 and Kafka’s The Trial…
Here, you may refer to the same theorists you have already discussed in the literature review. In this case, the emphasis is placed on how you plan to use their contributions in your own research.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You’ll usually conclude your dissertation proposal with a section discussing what you expect your research to achieve.
You obviously can’t be too sure: you don’t know yet what your results and conclusions will be. Instead, you should describe the projected implications and contribution to knowledge of your dissertation.
First, consider the potential implications of your research. Will you:
- Develop or test a theory?
- Provide new information to governments or businesses?
- Challenge a commonly held belief?
- Suggest an improvement to a specific process?
Describe the intended result of your research and the theoretical or practical impact it will have:
Finally, it’s sensible to conclude by briefly restating the contribution to knowledge you hope to make: the specific question(s) you hope to answer and the gap the answer(s) will fill in existing knowledge:
Like any academic text, it’s important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal.
Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing – commonly used styles include Harvard , Vancouver , APA , or MHRA . If your department does not have specific requirements, choose a style and apply it consistently.
A reference list includes only the sources that you cited in your proposal. A bibliography is slightly different: it can include every source you consulted in preparing the proposal, even if you didn’t mention it in the text. In the case of a dissertation proposal, a bibliography may also list relevant sources that you haven’t yet read, but that you intend to use during the research itself.
Check with your supervisor what type of bibliography or reference list you should include.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 11). How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/proposal/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- How it works

How to Write a Dissertation Proposal with Structure & Steps
Published by Anastasia Lois at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
“A dissertation proposal is a stepping stone towards writing the final dissertation paper. It’s a unique document that informs the reader of the aim & objectives of dissertation research and its course of action.”
The main purpose of a proposal paper is to showcase to your supervisor or dissertation committee members that your dissertation research will add value to existing knowledge in your area of study.
Although the exact structure of a dissertation proposal may vary depending on your academic level, academic subject, and size of the paper, the contents remain pretty much the same.
However, it will still make sense to consult with your supervisor about the proposal formatting and structuring guidelines before working on your dissertation proposal paper.
You may lose out on scoring some important marks if your proposal paper does not follow your department’s specific rules. Here are some tips for you on how to structure a dissertation proposal paper.
Tips on Completing a Dissertation Proposal in Due Time
Consult your supervisor or department to find out how much time you have to complete your dissertation proposal . Each graduate program is different, so you must adhere to the specific rules to avoid unwelcome surprises.
Depending on the degree program you are enrolled in, you may have to start working on your chosen topic right away, or you might need to deal with some assignments and exams first.
You can learn about the rules and timelines concerning your dissertation project on the university’s online portal. If you are still unsure, it will be best to speak with your department’s admin clerk, the program head, or supervisor.
Look for Proposal Structural Requirements in the Guidelines
Most academic institutions will provide precise rules for structuring your dissertation proposal in terms of the document’s content and how to arrange it. If you have not figured out these requirements, you must speak with your supervisor to find out what they recommend. Typical contents and structure of a dissertation proposal include the following;
- Statement of the Problem
- Background/Rationale
- Introduction (Justifying your Research)
- Research Questions or Hypothesis (Research aim and objectives)
- Literature Review
- Proposed Methodology
- Opportunities and Limitations
Project Schedule
Have an unhelpful dissertation project supervisor? Here is some advice to help you deal with an uncompromising dissertation advisor.
How Long is a Dissertation Proposal?
The length of your dissertation proposal will depend on your degree program and your research topic. PhD-level dissertation proposals are much longer in terms of word count than Bachelors’s and Master’s level proposals.
- Bachelor’s level dissertation proposals are about 5-6 pages long.
- Masters and Ph.D. level proposals’ length varies from 15-25 pages depending on the academic subject and degree program’s specifications.
- If the word count or page length expectation is not mentioned in the dissertation handbook or the guidelines on the university’s website, you should check with your supervisor or program coordinator for a clear understanding of this particular requirement.
The proposals we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources

Dissertation Proposal Formatting
Formatting your dissertation proposal will also depend on your program’s specific guidelines and your research area. Find the exact guidelines for formatting cover sheets and title pages, referencing style, notes, bibliography, margin sizes, page numbers, and fonts. Again if you are unsure about anything, it is recommended to consult with your project advisor.
Find out About the Approval Criteria
The process of writing your dissertation proposal paper and getting acceptance from the committee of members of your supervisor is tricky.
Consult your department’s academic assistant, supervisor, or program chair to learn about all the process stages. Here are a couple of points you will need to be aware of:
- You might be required to have your chosen research topic approved by your academic supervisor or department chair.
- Submit your proposal and have it formally signed and approved so you can continue with your research.
You may find the dissertation proposal writing process perplexing and challenging if this is the first time you are preparing such a document. All the essential elements of a dissertation proposal paper need to be present before submitting it for approval.
Any feedback received from the tutor or the supervising committee should be taken very seriously and incorporated into your planning for dissertation research. Do not start working on your final dissertation paper until your supervisor has accepted the proposal.
To help you organise your dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have detailed guidelines for structuring a dissertation proposal. Irrespective of the degree program you are developing your dissertation proposal for, you will find these guidelines equally important.
Our expert academics can produce a flawless dissertation proposal on your chosen topic. They can also suggest free topics in your area of study if you haven’t selected a topic. Order free topics here or get a quote for our proposal writing service here.
Select a Topic
Selecting an appropriate topic is the key to having your research work recognised in your field of study. Make sure your chosen topic is relevant, interesting, and manageable.
Ideally, you would want to research a topic that previous researchers have not explored so you can contribute to knowledge on the academic subject.
But even if your topic has been well-researched previously, you can make your study stand out by tweaking the research design and research questions to add a new dimension to your research.
How to Choose a Suitable Research Topic
Here are some guidelines on how to choose a suitable research topic.
List all the topics that you find interesting and relevant to your area of study. PhD and MaMasters’sevel students are already well aware of their academic interests.
Bachelor students can consider unanswered questions that emerged from their past academic assignments and drove them to conduct a detailed investigation to find answers.
Follow this process, and you’ll be able to choose the most appropriate topic for your research. Not only will this make your dissertation unique, but it also increases the chances of your proposal being accepted in the first attempt.
- Think about all your past academic achievements and associations, such as any research notes you might have written for your classes, any unsettled questions from your previous academic assignments that left you wondering, and the material you learned in classes taught by professors.
- For example , you learned about how natural gas is supplied to households in the UK in one of your coursework assignments and now eagerly wish to know exactly how natural gas is processed at an industrial scale.
ORDER YOUR PROPOSAL NOW
Conduct initial research on your chosen topic(s). This will include reading authentic text material on the topic(s) to familiarise yourself with each potential topic. Doing so will help you figure out whether there really is a need to investigate your selected topics further.
Visit your university’s library or online academic databases such as ProQuest, EBSCO, QuickBase to find articles, journals, books, peer-reviewed articles, and thesis/dissertation papers (by other students) written on your possible research topic .
Ignore all academic sources that you find methodologically flawed or obsolete. Visit our online research topics library to choose a topic relevant to your interests .
Consult your academic supervisor and show them your list of potential topics. Their advice will be crucial for deciding whether the topic you are interested in is appropriate and meets your degree program requirements.
It is recommended to set up an appointment with your supervisor to see them in person to discuss your potential topics, even though you can do the same in email too.
- If the topics you are interested in are too broad or lack focus, your supervisor will be able to guide you towards academic sources that could help narrow down your research.
- Having several topics in your list of potential topics will mean that you will have something to fall back onto if they don’t approve your first choice.
Narrow the Focus of your Research – Once a topic has been mutually agreed upon between you and your academic supervisor, it is time to narrow down the focus. Hence, your research explores an aspect of the topic that has not been investigated before.
Spend as much time as possible examining different aspects of the topic to establish a research aim that would truly add value to the existing knowledge.
- For example, you were initially interested in studying the different natural gas process techniques in the UK on an industrial scale. But you noticed that the existing literature doesn’t count for one advanced gas processing method that helps the industry save millions of pounds every year. Hence, you decide to make that the focus of your research.
- Your topic could be too broad as you start your research, but as you dig deep into your research, the topic will continue to narrow and evolve. TIP – It is better to work on a topic that is too broad rather than on something there is not enough text material to work with.
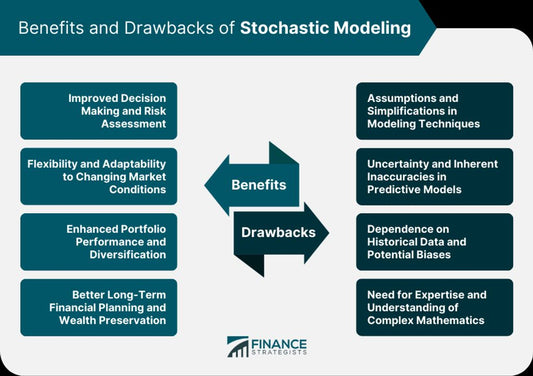
Structure of a Dissertation Proposal
The key elements of a great dissertation proposal are explained in detail under this section ‘structure of a dissertation proposal’. Once you’ve finalised your topic, you need to switch to writing your dissertation proposal paper quickly. As previously mentioned, your proposal paper’s exact structure may vary depending on your university/college requirements.
A good dissertation proposal title will give the reader an insight into the aim/idea of your study. Describe the purpose and/or contents of your dissertation proposal paper in the fewest possible words.
A concise and focused title will help you gain the attention of the readers. However, you might need to adjust your title several times as you write the paper because your comprehensive research might continue to add new dimensions to your study.
- Your title must be as categorical as possible. For example, instead of “Natural Gas Processing Techniques in the UK”, use a more specific title like “Investigating various industrial natural gas processing technologies employed in the UK” so the reader can understand exactly what your research is about.
Write a brief executive summary or an abstract of your proposal if you have been asked to do so in the structural guidelines. Generally, the abstract is included in the final dissertation paper with a length of around 300-400 words.
If you have to write an abstract for your proposal, here are the key points that it must cover;
- The background to your research.
- Research questions that you wish to address.
- Your proposed methods of research, which will either test the hypothesis or address the research problem.
- The significance of your research as to how it will add value to the scientific or academic community.
Get Help With Your Assignment!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try.

Introduction
This is your first chance to make a strong impression on the reader. Not only your introduction section should be engaging, contextually, but it is also supposed to provide a background to the topic and explain the thesis problem .
Here is what the first paragraph of the introduction section should include:
- Explain your research idea and present a clear understanding as to why you’ve chosen this topic.
- Present a summary of the scope of your research study, taking into account the existing literature.
- Briefly describe the issues and specific problems your research aims to address!
In the next paragraphs, summarise the statement of the problem . Explain what gap in the existing knowledge your research will fill and how your work will prove significant in your area of study.
For example, the focus of your research could be the stage of carbon monoxide removal from natural gas. Still, other similar studies do not sufficiently explore this aspect of natural gas processing technology.
Here is a comprehensive article on “ How to Write Introduction for Dissertation Paper .”
Aim & Objectives
This is the most critical section of the proposal paper . List the research questions or the research objectives your study will address. When writing this particular section, it will make sense to think of the following questions:
- Are there any specific findings that you are expecting?
- What aspects of the topic have you decided not to investigate and why?
- How will your research contribute to the existing knowledge in your field?
Literature Review
The literature review section is your chance to state the key established research trends, hypotheses , and theories on the subject. Demonstrate to the reader that your research is a unique contribution to your field because it explores the topic from a new angle.
In a dissertation proposal, you won’t be expected to provide an extensive list of all previous research studies on the topic. Still, all the key theories reported by other scholars should be briefly referred to.
Take into consideration the following when writing the literature review section:
- The gaps identified in the previous research studies on the topic which your own research aims to fill. State the limitations of previous studies, whether lacking sufficient evidence, invalid, or too broad.
- The key established research trends, theories, and hypotheses as reported by other researchers.
- Any specific arguments and/or methodologies that previous scholars used when investigating your topic.
Our expert dissertation proposal editors can improve the quality of your proposal paper to the First Class standard. Complete this short and simple order form here so we can get feedback from our writers.
Methodology
A focused and well-defined methodology in a proposal paper can help you explain to your readers how you plan to conduct your research and why your chosen research design can provide reliable answers to your research questions.
The choice of research design and analytical approach will depend on several factors, including but not limited to your area of study and research constraints.
Depending on your topic and the existing literature, you will need to decide whether your dissertation will be purely descriptive or use primary (quantitative/qualitative data) as part of the research design.
Any research limitations and ethical issues that you expect to deal with should be clearly stated. For example, you might not be able to use a large sample size of respondents due to financial constraints. Small sample size can undermine your research significance.
How to Write a First Class Dissertation Proposal or Research Proposal.
“If you’re unable to pull off a first-class proposal, we’re here to help. We at ResearchProspect make sure that our writers prepare a flawless dissertation proposal for you. Our highly qualified team of writers will also help you choose a relevant topic for your subject area. Get in touch with us today, and let us take care of all your dissertation worries! Learn more about our dissertation proposal writing service.
Some Masters and PhD level degree programs require students to include a project timeline or timetable to give readers an idea of how and when they plan to complete different stages of the project.
Project timeline can be a great planning tool, mainly if your research includes experiments, statistical analysis , designing, and primary data collection. However, it may have to be modified slightly as you progress into your research.
By no means is it a fixed program for carrying out your work. When developing the project timeline in your proposal, always consider the time needed for practical aspects of the research, such as travelling, experiments, and fieldwork.
Referencing and In-Text Citations
Underrated, but referencing is one of the most crucial aspects of preparing a proposal. You can think of your proposal as the first impression of your dissertation.
You would want everything to be perfect and in place, wouldn’t you? Thus, always make sure that your dissertation consists of all the necessary elements.
You will have to cite information and data that you include in your dissertation. So make sure that the references that you include are credible and authentic.
You can use well-known academic journals, official websites, past researches, and concepts presented by renowned authors and writers in the respective field.
The same rule applies to in-text citations. Make sure that you cite references accurately according to the required referencing style as mentioned in the guidelines.
References should back statistics, facts, and figures at all times. It is highly recommended to back every 100-200 words written with at least one academic reference. The quantity of references does not matter; however, the quality does.
These are the basic elements of a dissertation proposal. Taking care of all these sections will help you when you are confused about structuring a dissertation proposal. In addition to these steps, look for different dissertation proposal examples on your research topic. A sample dissertation proposal paper can provide a clear understanding of how to go about the “pro”osal stage” of”the dissertation project.
“If you’re unable to pull off a first-class proposal, we’re here to help. We at ResearchProspect make sure that our writers prepare a flawless dissertation proposal for you. Our highly qualified team of writers will also help you choose a relevant topic for your subject area. Get in touch with us today, and let us take care of all your dissertation worries! Learn more about our dissertation proposal writing service .”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dissertation proposal in research.
A dissertation proposal in research outlines the planned study. It includes research objectives, methods, scope, and significance. It’s a blueprint that demonstrates the feasibility and value of the research, helping gain approval before proceeding with the full dissertation.
How do you write a dissertation proposal?
A dissertation proposal outlines your research topic, objectives, methodology, and potential significance. Start with a clear title, state your research question, detail the methods you will use to answer it, and highlight the contribution it will make to the field. Ensure it is well-researched, concise, and compelling to gain approval.
How long is a dissertation proposal?
A dissertation proposal’s length varies by field and institution. Typically, it ranges from 10 to 20 pages, but can be longer for complex topics. It includes an introduction, research question, literature review, methodology, and potential significance. Always consult department guidelines or advisors to ensure appropriate length and content.
What are the types of dissertation proposals?
Dissertation proposal types largely depend on the research’s nature and methodology. Common types include empirical (collecting data from the real world), non-empirical (theory or literature-based), and narrative (case studies). Each type dictates a different approach to data collection, analysis, and presentation, tailored to the subject and field of study.
You May Also Like
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Find how to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose an interesting topic and begin your research.
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

Elite Editing
You write it. We right it.™

How to Write a Thesis Proposal
If you want to build a house, step one is not wandering over to the next vacant lot with a hammer, some nails, and a pile of boards. Your first step is probably finding an appealing place to build your house—an empty plot of land where the roads are good and where you can pretty easily connect the gas, electricity, and water. Step two is drawing up a blueprint for what you plan to build.
If a thesis is a house, then a thesis proposal is your blueprint. It’s you figuring out how your thesis will fit into the space you’ve found, how you’ll build it, and whether it will stand up to the harsh winds of your thesis adviser’s opinions and the tremors of a difficult defense. A thesis proposal allows you to clearly define—and even more crucially, limit—the focus and scope of your research. Producing an excellent thesis blueprint means that you won’t accidentally find you’re trying to build a skyscraper when you should be aiming at a bungalow—and that you have all the supplies and equipment you need.
But how do you create a research proposal? How do you know what it should include? The style and length of your thesis proposal will vary a bit depending on your school’s requirements and the type of thesis you will eventually produce, but the fundamentals will always be the same, and those are what we’re going to cover here. So let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal.
Choosing a Topic
The first step (a step that you must take before figuring out how to write a thesis proposal or even a thesis proposal outline) is choosing a topic for your thesis. The point of embarking on this kind of project is that you’ll first find and then fill a gap in the established, preexisting research in your field. You’re looking for a manageable topic—something focused enough that you can cover it within your word limit but broad enough that you actually have something to write about.
Undergraduate theses are often less revolutionary and more about surveying or analyzing the existing research on a particular topic. This is appropriate because these projects are shorter in length—and you have much less time (typically months rather than years) to work on them. An undergraduate thesis can run anywhere from ten to thirty pages. A master’s thesis is typically forty to eighty pages and might present some original research, or it might be a significant reinterpretation of preexisting research.
A doctoral thesis is (naturally) the longest of these three, and the research it presents should be more groundbreaking and challenging to complete. That investment of time and mental energy is what’s going to earn you the right to demand that everyone call you “Doctor.”
Tips for Choosing a Thesis Topic
- Consider your interests. What makes you sit up and your brain feel fizzy? You’re about to spend a lot of time working on this topic. It had better be something that fascinates you.
- Explore open-ended questions. How or why questions offer you more scope and flexibility than what or who questions.
- Consider the time. How long will your project take to complete? Make sure you have enough time to get from here to there.
- Research any funding you’ll need. Will you need to travel or establish an experimental protocol? If so, can you get the funding for these projects? How do these affect your projected timeline? Save the long-view research for your later career, and find something you can finish.
- If it’s a controversial topic, choose wisely. Be realistic about whether you’re likely to encounter stiff resistance during your defense. Something that goes against all existing research will demand greater rigor and effort from you than something that challenges only a part of what is currently considered established knowledge.
- Make it publishable. Are all possible outcomes to your research interesting and academically publishable? Or is there a potential dead end that you can avoid by shifting your focus now?
- Think long term. How will the project affect (and improve) your marketability for the future? There is life after your thesis, after all. Where do you want to be, and how can your work now help get you there?
Structuring Your Thesis Proposal
A thesis proposal usually includes some or all of the following elements:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Literature review or annotated bibliography
- Approach/methods
- Preliminary results and discussion
- Work plan and schedule
- Research implications
The thesis proposal outline above shows one potential way to order the parts, but (and this is important) you won’t work on those elements in that order. For example, that table of contents? It’s probably the last thing you’ll work on. Similarly, you can’t write the abstract until you’ve written everything else.

Let’s look at how to write a thesis proposal in greater detail.
Title Page and Creating a Title
The title of your project is likely to be a brief statement of your research topic, approach, and intent. It will be far easier to write a title once you’ve written a thesis statement (see below) because it is likely to restate or incorporate your thesis statement.
Violence and Redemption in Modern Afghani Literature: A Marxist Analysis of Power Structures in The Kite Runner and The Wasted Vigil
Living the Fantasy: Addiction and Social Identity in World of Warcraft
Your title page will include this title, your name, your department and institution, your adviser, your adviser’s institution, and the date you’re submitting the proposal.
Writing an Abstract
An abstract is a short summary of your full proposal, usually about a page in length. It hits the highlights of the proposal as a whole, including your title, your thesis statement, a quick summary of your plan of research, and a statement about why this project matters.
Table of Contents
If you’re writing your table of contents, you’re minutes away from a celebratory “Woo-hoo!” because you’re almost finished. A table of contents will list all the headings and subheadings of your proposal with lovely indentations and the correct page numbers. If you’re using MS Word, and you’ve been formatting your headings in the appropriate styles, you can automatically generate a table of contents that will make everything look very pretty indeed.
Writing the Thesis Statement
It’s not a simple question: How do you write a good thesis statement? Your thesis statement may well be the hardest sentence (or two—three at the most) you ever have to write. Despairing tears or frustrated anger are not out of the question. However, once you formulate that thesis statement, you will be off and running because now you have a beautifully clear and specific goal to head for.
A thesis statement should clearly define the scope and intent of your project. It might be a hypothesis or a question, or it might be a firm statement. The hours of work that will become your thesis will then prove (or possibly disprove, though hopefully in a deeply productive way) your thesis statement, so it should be something provable—something that can in some way be measured.
Let’s look at some examples of how to write a good thesis statement.
Not so good:
Taking a year off between high school and college is a good idea.
A “good idea” is vague and indefensible. Good by whose standards? How can you prove that?
Students who take a year off between high school and college are more academically successful than their peers.
This is better because it limits the scope of the project to academics, but it’s still rather vague and unwieldy. It also doesn’t suggest what metrics will be used to judge “academically successful.”
Better still:
Students who take a year off between high school and college are significantly more likely than their peers to graduate within four years with a B average or better.
This thesis statement works because it is concrete and measurable. The data you collect will either clearly prove the statement or disprove it.
How does the internet affect social behavior?
Wow, that’s a huge question. Also, there is nothing to prove, measure, or evaluate. It’s a topic rather than a thesis. It might be what you’re generally interested in, but you have yet to find the aspect of this topic that you can effectively research.
The internet has changed how American teens approach gender.
At least this is a statement, but it’s still too vague. “Changed” how? And what does “approach” mean?
The social media profiles of American teens thirteen to eighteen years old reflect this demographic’s increasing comfort with fluid sexual and gender identities.
This thesis statement could probably still be improved, but it is getting toward something measurable and provable.
Writing a Thesis Proposal Introduction
Your introduction will do just that—introduce your readers to your topic and thesis. Don’t mistake this for an introductory paragraph, however. This is where you’ll summarize your project in the hopes of intriguing and engaging the committee that will either approve your thesis project or send you back to the drawing board. Your writing should be as clear, straightforward, and free from jargon as possible. You’ll contextualize your project within the broader scope of the topic, perhaps exploring the papers, research, or work that led to your formulation of your thesis. You’ll explain why your project excites you. You’ll illustrate your competence to embark on this project. Basically, you’ll sell your proposal.
Literature Review or Annotated Bibliography
You might be able to quickly cover the most relevant literature in your proposal introduction, but if there are many articles or books relevant to your research, your thesis proposal might include an annotated bibliography or a literature review (which is slightly more informal and conversational in approach). Here is where you’d not only list the most influential and crucial texts that underpin your research but also explain why they matter—that is, how they fit into your project. This is a way to show that gap in the research that you will be filling with your thesis project.
Explain Your Proposed Methods or Approach
Most thesis projects demand original research of some kind, and for degrees in the sciences (including the social sciences), that research may very well take the form of an experiment or raw data collection. Here is where you should describe your proposed methodology. What materials will you use? How will you collect your data? How will you analyze the data once it’s collected? Are you taking a qualitative or quantitative approach? Why? Will you need outside funding (for travel or other costs), and how do you propose to acquire that funding? Do you need space and equipment to conduct your research?
Provide Preliminary Results
It may be that you have already been testing the viability of your thesis project with some preliminary research (which is not a bad idea). If so, here is where you should provide the results of that research and your tentative interpretation of those results. Clearly show how this work fits into your larger project—and how it proves that you’re heading down a productive road of inquiry.
Design a Work Plan
Even if your particular program or professor doesn’t require you to include a work plan in your thesis proposal, you should still make one. There’s nothing more likely than a schedule—with deadlines!—to keep you on track and get your thesis done on time.
This section should
- lay out your plan,
- list the various stages of your project,
- set deadlines for the completion of each stage, and
- detail any work you’ve already completed.
In addition, your work plan should take into account any challenges (personal, practical, or institutional) that may affect the completion of the study.
Discuss Research Implications
Here, you are striving to answer this question: Why does this project matter in this place and at this time? It’s actually a wonderful exercise in focusing your own thoughts and evaluating the worth of your proposed project. Are you remedying a misunderstanding that might affect how to treat a particular medical condition? Are you exploring the dynamics of a culture that is (socially or politically) especially relevant at the moment? Are you providing new insight into a classic work of literature or music that will reinvigorate teachers and academics? Your research might have implications for the entire world or it might be of interest only to other specialists in your subject, but that really doesn’t matter. The point is to figure out and clearly state how your research will enhance the sum total of knowledge.
Notes and Bibliography
All statements in this thesis proposal need to be supported with data, whether that data is derived from your own research or gleaned from a third party. Using whatever citation style is most appropriate to your field, you should give credit to all your sources, primary or secondary. Note that this is separate from your literature review in that you’re only going to cite the sources you’ve used in your proposal.
Thesis Proposal Defense / Thesis Proposal Presentation
Your college or university may require you to appear in person at a thesis proposal defense or to make a thesis proposal presentation. In both cases, however, you’ll be presenting your proposal to your thesis committee (and possibly others) and then potentially answering their questions about your project. While this might seem alarming, this event is actually an excellent opportunity to pick your committee’s brain about possible obstacles or objections you will need to overcome while working on your project. Better to know right now that they’d rather you took a quantitative approach than do all the work and then discover their preference. It will also help focus you since knowing something is one level of understanding it—but explaining it to someone else can take your understanding to a much deeper level.
You should now have a much deeper understanding of how to write a thesis proposal. A clear, thorough, well-thought-out thesis proposal allows you to see the entire shape of your project before you invest huge amounts of time and energy into research that might end up leading nowhere. Your thesis proposal sets the stage for the success of your project as a whole, and it should reflect and predict the quality you intend to produce in your final thesis. That’s why your thesis proposal presentation also matters. In addition, remember that proofreading counts. It’s extremely important to carefully review your finished proposal for spelling, grammar, and structural errors.
With your thesis proposal completed and approved, you’re well on your way to embarking on what might be the most important project of your life to date. We wish you all the best with your studies, and if you decide you want an editor to cast an expert eye over any part—large or small—of your project, we here at Elite are happy to help!
Want more? Check out this post on credible online sources and how to find them.
Other Resources You Might Like

Crafting Timeless Content

Mastering the Art of Persuasive White Papers

Writing Effective Press Releases in a Digital Age
Get elite updates straight to your inbox..
- Content Writing
- Marketing and Sales Enablement
- Program Management
- AI Implementation
Who We Help
- Thought Leaders
- Cybersecurity
- Health Care
- Full-Time Careers
- Freelance Opportunities
- Press and Awards
- Success Stories
- About Elite
In the News
- Elite Creative Makes the Inc. 5000 for the Third Year in a Row

- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

- Current Students Hub

Doctoral handbook
You are here
- Dissertation Proposal
On this page:
Proposal Overview and Format
Proposal committee, proposal hearing or meeting.
- Printing Credit for Use in School of Education Labs
Students are urged to begin thinking about a dissertation topic early in their degree program. Concentrated work on a dissertation proposal normally begins after successful completion of the Second-Year Review, which often includes a “mini” proposal, an extended literature review, or a theoretical essay, plus advancement to doctoral candidacy. In defining a dissertation topic, the student collaborates with their faculty advisor or dissertation advisor (if one is selected) in the choice of a topic for the dissertation.
The dissertation proposal is a comprehensive statement on the extent and nature of the student’s dissertation research interests. Students submit a draft of the proposal to their dissertation advisor between the end of the seventh and middle of the ninth quarters. The student must provide a written copy of the proposal to the faculty committee no later than two weeks prior to the date of the proposal hearing. Committee members could require an earlier deadline (e.g., four weeks before the hearing).
The major components of the proposal are as follows, with some variations across Areas and disciplines:
- A detailed statement of the problem that is to be studied and the context within which it is to be seen. This should include a justification of the importance of the problem on both theoretical and educational grounds.
- A thorough review of the literature pertinent to the research problem. This review should provide proof that the relevant literature in the field has been thoroughly researched. Good research is cumulative; it builds on the thoughts, findings, and mistakes of others.
- its general explanatory interest
- the overall theoretical framework within which this interest is to be pursued
- the model or hypotheses to be tested or the research questions to be answered
- a discussion of the conceptual and operational properties of the variables
- an overview of strategies for collecting appropriate evidence (sampling, instrumentation, data collection, data reduction, data analysis)
- a discussion of how the evidence is to be interpreted (This aspect of the proposal will be somewhat different in fields such as history and philosophy of education.)
- If applicable, students should complete a request for approval of research with human subjects, using the Human Subjects Review Form ( http://humansubjects.stanford.edu/ ). Except for pilot work, the University requires the approval of the Administrative Panel on Human Subjects in Behavioral Science Research before any data can be collected from human subjects.
Registration (i.e., enrollment) is required for any quarter during which a degree requirement is completed, including the dissertation proposal. Refer to the Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion section for more details.
As students progress through the program, their interests may change. There is no commitment on the part of the student’s advisor to automatically serve as the dissertation chair. Based on the student’s interests and the dissertation topic, many students approach other GSE professors to serve as the dissertation advisor, if appropriate.
A dissertation proposal committee is comprised of three academic council faculty members, one of whom will serve as the major dissertation advisor. Whether or not the student’s general program advisor serves on the dissertation proposal committee and later the reading committee will depend on the relevance of that faculty member’s expertise to the topic of the dissertation, and their availability. There is no requirement that a program advisor serve, although very often they do. Members of the dissertation proposal committee may be drawn from other area committees within the GSE, from other departments in the University, or from emeriti faculty. At least one person serving on the proposal committee must be from the student’s area committee (CTE, DAPS, SHIPS). All three members must be on the Academic Council; if the student desires the expertise of a non-Academic Council member, it may be possible to petition. After the hearing, a memorandum listing the changes to be made will be written and submitted with the signed proposal cover sheet and a copy of the proposal itself to the Doctoral Programs Officer.
Review and approval of the dissertation proposal occurs normally during the third year. The proposal hearing seeks to review the quality and feasibility of the proposal. The Second-Year Review and the Proposal Hearing are separate milestones and may not occur as part of the same hearing or meeting.
The student and the dissertation advisor are responsible for scheduling a formal meeting or hearing to review the proposal; the student and proposal committee convene for this evaluative period. Normally, all must be present at the meeting either in person or via conference phone call.
At the end of this meeting, the dissertation proposal committee members should sign the Cover Sheet for Dissertation Proposal and indicate their approval or rejection of the proposal. This signed form should be submitted to the Doctoral Programs Officer. If the student is required to make revisions, an addendum is required with the written approval of each member of the committee stating that the proposal has been revised to their satisfaction.
After submitting the Proposal Hearing material to the Doctoral Programs Officer, the student should make arrangements with three faculty members to serve on their Dissertation Reading Committee. The Doctoral Dissertation Reading Committee form should be completed and given to the Doctoral Programs Officer to enter in the University student records system. Note: The proposal hearing committee and the reading committee do not have to be the same three faculty members. Normally, the proposal hearing precedes the designation of a Dissertation Reading Committee, and faculty on either committee may differ (except for the primary dissertation advisor). However, some students may advance to Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status before completing their dissertation proposal hearing if they have established a dissertation reading committee. In these cases, it is acceptable for the student to form a reading committee prior to the dissertation proposal hearing. The reading committee then serves as the proposal committee.
The proposal and reading committee forms and related instructions are on the GSE website, under current students>forms.
Printing Credit for Use in GSE Labs
Upon completion of their doctoral dissertation proposal, GSE students are eligible for a $300 printing credit redeemable in any of the GSE computer labs where students are normally charged for print jobs. Only one $300 credit per student will be issued, but it is usable throughout the remainder of her or his doctoral program until the balance is exhausted. The print credit can be used only at the printers in Cubberley basement and CERAS, and cannot be used toward copying.
After submitting the signed dissertation proposal cover sheet to the Doctoral Programs Officer indicating approval (see above), students can submit a HELP SU ticket online at helpsu.stanford.edu to request the credit. When submitting the help ticket, the following should be selected from the drop-down menus for HELP SU:
Request Category : Computer, Handhelds (PDAs), Printers, Servers Request Type : Printer Operating System : (whatever system is used by the student, e.g., Windows XP.)
The help ticket will be routed to the GSE's IT Group for processing; they will in turn notify the student via email when the credit is available.
- Printer-friendly version
Handbook Contents
- Timetable for the Doctoral Degree
- Degree Requirements
- Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion
- The Graduate Study Program
- Student Virtual and Teleconference Participation in Hearings
- First Year (3rd Quarter) Review
- Second Year (6th Quarter) Review
- Committee Composition for First- and Second-Year Reviews
- Advancement to Candidacy
- Academic Program Revision
- Dissertation Content
- Dissertation Reading Committee
- University Oral Examination
- Submitting the Dissertation
- Registration and Student Statuses
- Graduate Financial Support
- GSE Courses
- Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education (CTE)
- Developmental and Psychological Sciences (DAPS)
- Learning Sciences and Technology Design (LSTD)
- Race, Inequality, and Language in Education (RILE)
- Social Sciences, Humanities, and Interdisciplinary Policy Studies in Education (SHIPS)
- Contact Information
- Stanford University Honor Code
- Stanford University Fundamental Standard
- Doctoral Programs Degree Progress Checklist
- GSE Open Access Policies
PhD students, please contact

MA POLS and MA/PP students, please contact

EDS, ICE/IEPA, Individually Designed, LDT, MA/JD, MA/MBA students, please contact

Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Graduate School
How to Write a Master's Thesis Proposal
How to write a master’s thesis proposal is one of the most-asked questions by graduate students. A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis. Your proposal should serve as a foundational blueprint on which you will later build your entire project. To have the perfect thesis proposal, you need to have original ideas, solid information, and proper presentation. While it is a good idea to take assistance from thesis writing services , you still need to personally understand the elements that contribute to a master’s thesis proposal worthy of approval. In this blog, we will discuss the process of writing your master’s thesis proposal and give you tips for making your proposal strong. Stay tuned!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 8 min read
How to decide the goals for your master's thesis.
If you are pursuing a master’s or a PhD , you will be undertaking a major research paper or a thesis. Thus, writing a thesis proposal becomes inevitable. Your major objective for pursuing a master’s degree is to improve your knowledge in your field of study. When you start your degree, you delve deeper into different concepts in your discipline and try to search for answers to all kinds of questions. If you come across a question that no one can answer, you can select that question as your research thesis topic.
A master's thesis proposal will have multiple sections depending on your decided layout. These sections will continuously support your argument and try to convince the reader of your core argument. The structure will also help you arrange the various parts of the paper to have a greater impact on the readers. A paper should always begin with you giving a brief summary of the topic and how you have come across it. The introduction is particularly important because it will give the readers a brief idea about the topic of discussion and win their interest in the matter.
After the summary has been given, slowly you need to progress into the body of the thesis proposal which would explain your argument, research methodology, literary texts that have a relation to the topic, and the conclusion of your study. It would be similar to an essay or a literary review consisting of 3 or 4 parts. The bibliography will be placed at the end of the paper so that people can cross-check your sources.
Let's take a look at the sections most master's thesis proposals should cover. Please note that each university has its own guidelines for how to structure and what to include in a master’s thesis proposal. The outline we provide below is general, so please make sure to follow the exact guidelines provided by your school:
Restate your primary argument and give us a glimpse of what you will include in the main master\u2019s thesis. Leave the reader wanting more. Your research proposal should talk about what research chapters you are trying to undertake in your final thesis. You can also mention the proposed time in which you will complete these chapters. ","label":"Conclusion and proposed chapters","title":"Conclusion and proposed chapters"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
A thesis proposal needs to be convincing enough to get approval. If the information is not enough to satisfy the evaluation committee, it would require revision. Hence, you need to select and follow the right methodology to make your argument convincing. When a research proposal is presented, the reader will determine the validity of your argument by judging the strength of your evidence and conclusions. Therefore, even writige:ng a proposal will require extensive research on your part. You should start writing your thesis proposal by working through the following steps.
Interested in a summary of the points covered below? Check out this infographic:
Exploring your topic in detail
You need to delve deeper into your chosen topic to see if your idea is original. In the process of this exploration, you will find tons of materials that will be supportive of your argument. When choosing your research topic and the problem you want to explore, you should always consider your primary research interest (yes, the one which you had mentioned in your research interest statement during grad school applications) for a better master’s thesis. You have a high probability of performing better in an area that you have always liked as compared to any other research area or topic.
Reviewing the literature
You have to include all the sources from where you have formed your argument and mention them in the thesis proposal. If you neglect to mention important source texts, the reader may consider it to be plagiarism. Furthermore, you want to keep track of all your research because it will be easier to provide references if you know the exact source of each piece of information.

Finding opposing arguments for your study
You should also mention any texts that would counter your argument and try to disprove their claims in the thesis. Make sure to use evidence if you try to disprove the counterarguments you face.
Emphasizing the importance of your research
At the end of the thesis proposal, you need to convince the reader why your proposal is important to your chosen field of study, which would ultimately help you in getting your topic approved. Thus, it is essential to outline the importance of your research thoroughly.
Drafting your proposal
After doing proper research, you should go ahead and draft your proposal. Remember you will not get it right in just one draft, it will take at least 50 attempts to come up with a satisfactory proposal. You should proofread your draft several times and even have a fellow student review it for you before sending it further to your research supervisor.
Getting your proposal evaluated by your supervisor
After you have written sufficient drafts, you need to get your proposal evaluated by your research supervisor. This is necessary to meet the graduate research requirements. It will ensure the clarity and correctness of your proposal. For your supervisor to evaluate your proposal, you should complete the research methodology part along with sufficient proposed work.
Since your supervisor will play a crucial role in your master's research thesis, you must choose a supervisor who can be your ultimate guide in writing your master's thesis. They will be your partner and support system during your study and will help you in eliminating obstacles to achieving your goal.
Choosing the ideal supervisor is a pretty daunting task. Here’s how you can go about the process:
You should approach your professor with an open mind and discuss the potential goals of your research. You should hear what they think and then if you both mutually agree, you can choose them as your supervisor for your master\u2019s thesis. "}]">
Length of a Master’s Thesis Proposal
The length of a master’s thesis proposal differs from university to university and depends on the discipline of research as well. Usually, you have to include all the above-mentioned sections, and the length is around 8 pages and can go up to 12-15 pages for subjects such as the liberal arts. Universities might also define the number of words in the guidelines for your master’s thesis proposal and you have to adhere to that word limit.
Are you debating between pursuing a Masters or a PhD? This video has details that can help you decide which is best for you:
How to Format a Research Thesis Proposal Correctly?
Now that you know how to write a thesis proposal, you must make it presentable. Although your school might give your specific instructions, you can keep in mind some of the general advice:
- You can use some basic font like Times New Roman and keep the font size to 10 or 12 points.
- The left margin should be 1.5 inches and all other margins should be 1 inch each.
- You should follow double-spacing for your content.
- The first line of paragraphs should be indented 0.5 inches and the paragraphs should be left or center aligned.
Tips to Write a Strong Master's Thesis Proposal
When you are writing your master’s thesis proposal, you should keep these tips in mind to write an excellent master’s thesis proposal with all the correct elements to get approval from the evaluating committee:
Select your research objectives wisely
You should be clear on what you wish to learn from your research. Your learning objectives should stem from your research interests. If you are unsure, refer to your grad school career goals statement to review what you wanted out of grad school in the first place. Then, choose your objectives around it.
Write a clear title
The title of your research proposal should be concise and written in a language that can be understood easily by others. The title should be able to give the reader an idea of your intended research and should be interesting.
Jot down your thoughts, arguments, and evidence
You should always start with a rough outline of your arguments because you will not miss any point in this way. Brainstorm what you want to include in the proposal and then expand those points to complete your proposal. You can decide the major headings with the help of the guidelines provided to you.
Focus on the feasibility and importance
You should consider whether your research is feasible with the available resources. Additionally, your proposal should clearly convey the significance of your research in your field.
Use simple language
Since the evaluation committee can have researchers from different subject areas, it is best to write your proposal in a simple language that is understandable by all.
Stick to the guidelines
Your university will be providing the guidelines for writing your research proposal. You should adhere to those guidelines strictly since your proposal will be primarily evaluated on the basis of those.
Have an impactful opening section
It is a no-brainer that the opening statement of your proposal should be powerful enough to grasp the attention of the readers and get them interested in your research topic. You should be able to convey your interest and enthusiasm in the introductory section.
Peer review prior to submission
Apart from working with your research supervisor, it is essential that you ask some classmates and friends to review your proposal. The comments and suggestions that they give will be valuable in helping you to make the language of your proposal clearer.
You have worked hard to get into grad school and even harder on searching your research topic. Thus, you must be careful while building your thesis proposal so that you have maximum chances of acceptance.
If you're curious how your graduate school education will differ from your undergraduate education, take a look at this video so you know what to expect:
Writing the perfect research proposal might be challenging, but keeping to the basics might make your task easier. In a nutshell, you need to be thorough in your study question. You should conduct sufficient research to gather all relevant materials required to support your argument. After collecting all data, make sure to present it systematically to give a clearer understanding and convince the evaluators to approve your proposal. Lastly, remember to submit your proposal well within the deadline set by your university. Your performance at grad school is essential, especially if you need a graduate degree to gain admission to med school and your thesis contributes to that performance. Thus, start with a suitable research problem, draft a strong proposal, and then begin with your thesis after your proposal is approved.
In your master’s thesis proposal, you should include your research topic and the problem statement being addressed in your research, along with a proposed solution. The proposal should explain the importance and limitations of your research.
The length of a master’s thesis proposal is outlined by the university in the instructions for preparing your master’s thesis proposal.
The time taken to write a master’s thesis proposal depends upon the study which you are undertaking and your discipline of research. It will take a minimum time of three months. The ideal time can be around six months.
You should begin your master’s thesis proposal by writing an introduction to your research topic. You should state your topic clearly and provide some background. Keep notes and rough drafts of your proposal so you can always refer to them when you write the first real draft.
The basic sections that your master’s thesis proposal should cover are the problem statement, research methodology, proposed activities, importance, and the limitations of your research.
A master’s thesis proposal which clearly defines the problem in a straightforward and explains the research methodology in simple words is considered a good thesis proposal.
You can use any classic font for your master’s thesis proposal such as Times New Roman. If you are recommended a specific font in the proposal guidelines by your institution, it would be advisable to stick to that.
The ideal font size for your master’s thesis proposal will be 10 or 12 points.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How To Write A Dissertation Proposal: Learn With Guides And Tips

Don’t know how to write a dissertation proposal? Don’t worry about it! In this blog post, you will learn everything there is to know about the dissertation proposal. We will show you what it is and why it is important to write one correctly. We will discuss the dissertation proposal format in great detail and show you a dissertation proposal outline that works great for most topics. In addition, you will get an example of dissertation proposal for free.
To help you write a great proposal, we have also included a step by step guide on how to write a proposal for dissertation. Finally, we have compiled a list of tips, tricks and advice that should help you do an even better job. Are you ready to start writing a dissertation proposal? Read on!
Table of Contents
What is a dissertation proposal, why is the dissertation proposal important, a simple dissertation proposal outline, how to write dissertation proposal: a step by step guide, tips, tricks and advice, a free dissertation proposal sample.
So, what is a dissertation proposal? Why is it important? Why would you want to write one? A dissertation proposal is a document that outlines the proposed research project that a student intends to undertake as part of their doctoral program. The purpose of the proposal is to convince the student’s academic committee that the proposed research is worthwhile, feasible and original. The proposal typically includes:
An introduction Literature review Research methodology Research aims and objectives Expected outcomes A timeline for completion
The proposal should also address any potential ethical considerations or limitations of the study, and should provide a justification for the significance of the research. Once the proposal is accepted, the student can begin working on their dissertation, which will be a more extensive and detailed version of the proposal.
Before we show you how to write a proposal for a dissertation, we want to make sure you understand just how important this paper is. A proposal is important because it:
Provides a framework for the research project. The proposal outlines the structure of the research project, including the research questions, methodology, and expected outcomes. Demonstrates the student’s readiness for the research. The proposal requires the student to undertake a rigorous review of the literature and develop a research plan. Helps to identify potential issues. The proposal provides an opportunity to identify any potential issues or limitations with the research project before it even begins. Facilitates feedback and discussion. The proposal is typically reviewed and critiqued by the student’s academic committee.
If you’re looking for an example proposal dissertation, you’re in luck. The thesis proposal format is not overly difficult, but you should definitely take a look at our outline to get a feel of how you should structure your paper:
I. Introduction Introduce the topic of the dissertation and provide background information. Write a clear research question or statement of the problem that the study aims to address. Explain the significance of your research and discuss the contribution it will make to the field of study. II. Literature Review Review and critically evaluate relevant literature in the field of study. Identify gaps or inconsistencies in the literature; gaps that the research project will address. Demonstrate how the proposed research fits into and advances the existing body of knowledge. III. Methodology Describe the research design and methodology that will be used to collect and analyze data. Justify the choice of methodology and explain how it aims to answer the research question. Address potential limitations and ethical considerations related to the methodology. IV. Research Aims and Objectives Clearly state the research aims and objectives that the study will address. Explain how these aims and objectives are linked to the research question and contribute to advancing the body of knowledge on the matter. V. Expected Outcomes Talk about the expected outcomes of your research. Explain how these outcomes will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address the research question. VI. Timeline for Completion Provide a detailed timeline for completing the research project. Clearly present key milestones and deadlines, including the expected completion date for the dissertation. VII. Conclusion Summarize the main ideas in your proposal. Reinforce the significance of the research project. Indicate the potential implications of your findings.
If you want to learn how to write dissertation proposal quickly, the best way to do it is to follow a reliable step by step guide. The good news is that our experts have written one such guide for you. Here is exactly what you need to do to write dissertation proposal papers the right way:
Choose a topic. Start by choosing a topic that interests you and that is relevant to your field of study. The topic should be specific enough to allow you to conduct focused research and broad enough to allow for adequate exploration. Research existing literature. Conduct a review of all of the existing literature on the topic you’ve chosen. This will help you identify any gaps in knowledge that you can address in your research. Define your research questions. Based on the literature review, develop specific research questions that you will address in your dissertation. Your research questions should be clear and concise. Remember that you will need to answer these questions. Develop the research methodology. Choose a research methodology that is appropriate for your research questions. You can use qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. Be sure to justify your choice of methodology so that the committee doesn’t ask for clarifications. Write the introduction. Start your proposal with an introduction that provides an overview of your research topic, research questions and methodology. You should include the thesis in the introduction. Write the literature review. Next, write a literature review that summarizes existing research on your topic. Identify any gaps in knowledge that you will address in your research. Present your methodology. Describe your research methodology in detail, including your data collection methods and data analysis techniques. Another researcher should be able to replicate your experiments and get the same results after reading your methodology. Define your expected results. Based on your research questions and methodology, define the expected results of your research. Be very specific about what you aim to demonstrate with your paper. Develop a timeline for writing a proposal for dissertation. Create a timeline that outlines the different stages of your research, from data collection to analysis and writing. Also, don’t forget to include the date on which you expect the paper to be completed. Write the conclusion. End your proposal with a conclusion that summarizes your research topic, research questions, methodology, and expected results. Show your readers why your research is important. Edit and proofread your work. Before submitting your proposal, be sure to edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is free of errors and presents your research clearly. You want your proposal to be perfect in every way.
It is usually a good idea to have your friends and family take a look at the proposal and give you some feedback. You’d be surprised by how many things can be improved this way. Even better, you could get in touch with our expert editors and proofreaders and have them revise your work. This is a sure way to ensure that your proposal is top notch.

Before we get to the dissertation proposal example, we want to share some effective tips, tricks and advice that will help you do a better job writing your paper:
Start early. Give yourself plenty of time to write your dissertation proposal. It’s a complex document that requires careful planning, research, and writing, so don’t leave it until the last minute. Get feedback. Before submitting your proposal, share it with your supervisor or another academic who can provide feedback. Be clear and concise. Use clear and concise language to communicate your research topic, questions and methodology. Provide context. Provide context for your research by explaining why it’s important and how it fits into existing research in your field. Justify your methodology. Be sure to explain why you have chosen a particular methodology and how it will help you answer your research questions. Be realistic. Make sure your proposed research is feasible given your time, resources and skills. Avoid proposing research that is too broad or ambitious, as this can make it difficult to complete your dissertation on time. Follow guidelines. Follow the guidelines provided by your university or department for formatting, length, and content. This will help you avoid unnecessary revisions and ensure that your proposal meets the requirements. Keep it organized. Use clear headings, subheadings and sections to organize your proposal. This will make it easier for your readers to follow your argument and find the information they need. Use citations. Use citations to acknowledge the work of other researchers and to support your own arguments. This will demonstrate that you have done your research and are aware of existing literature on your topic.
Are you looking for an excellent dissertation proposal template that you can follow? Our experts are here to help you with your school projects. We have written a great dissertation proposal sample that you can use for free. You can use this example to learn how PhD dissertation proposals are written, but you should avoid copying content from the sample because a plagiarism detector can flag your paper. If you need more than the following example of a dissertation proposal, get in touch with our experts:
Background of the Problem Employee performance is a significant concern of any organization because it determines business performance. According to Fachrunnisa, Adhiatma & Mutamimah (2014), employees achieve the desired level of performance when they are effectively engaged or involved in the management of the organization. However, the impact of organizational culture on both the engagement and performance of employees has not been measured distinctively using empirical evidence, as illustrated by Breevaart, Bakker, Demerouti & Derks (2016). Statement of the Problem Organizations provide their employees with requirements related to expected level of participation in work activities and performance. However, business leaders and managers often forget that they must create a supportive organizational culture that will inspire employee engagement and motivate performance. Purpose of the Study The purpose of the proposed investigation is to determine how organizational culture influences employee engagement and their performance at work. The study aims at providing business leaders and managers with evidence-based insights for establishing organizational cultures that inspire employee engagement and motivate performance. Research Objectives To assess the impact of organizational mission, vision and values on employee engagement in the service sector. To determine how organizational culture influences job performance in the service sector. To establish the relationship between the consistency of organizational culture and employee engagement and job performance in the service sector Research Questions To what extent do the mission, vision and values of organizations in the service sector influence employee engagement? How does organizational culture influence job performance in the service sector? How does the consistency of organizational culture shape employee engagement and job performance in the service sector? Significance of the Study The proposed study is significant to business management practice. It will specifically provide business leaders and managers with practical reasons for establishing supportive organizational cultures that are meant to improve the level of employee engagement and improve their performance at work. Methodology Research Design A descriptive research design will be applied in carrying out the proposed investigation. This design will allow for description of the characteristics of work environments under study in terms of working culture, employee engagement and motivation for performance. Descriptive studies are also useful in establishing relationships existing between research variables (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016). Study Population The population of the proposed study is composed of members of organizations within the service sector. This includes the business leaders, managers and employees of these organizations. Sampling Stratified sampling will be applied in selecting a representative sample from the study population to participate in the research process. The selected sampling technique is useful in categorizing members of a study population into homogenous subgroups, from which participants are randomly selected (Bryman & Bell, 2015). A sample of 120 participants, including business leaders, managers and employees of 10 organizations in the service sector will be selected and engaged in the research process. Data Collection Methods Self-administered questionnaires will be used to gather data for the study. Questionnaires are preferred because they are standardized, efficient and cost-effective data collection tools (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016). The questionnaires will have open and closed ended questions pertaining to the background information of participants, the culture of their organizations, employee engagement strategies and employee performance. Data Analysis Descriptive statistics will be applied in the analysis of research data. Through descriptive statistics, research data will be organized and interpreted in line with the relationship between organizational culture, employee engagement and performance.
Get Quick Help Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Do you need fast online dissertation help? Our experts are ready to spring into action and write you the best possible PhD dissertation proposal. Our writers have extensive experience with such projects as writing a thesis proposal or academic papers, so you will receive a high quality, custom paper written according to your specifications.
All our writers have at least one PhD degree and they are all ENL native English speakers. We can write a proposal for any undergraduate or graduate student in any college or university. In addition, we can help high school, college and uni students with 100% original essays and research papers for any class.
Get the best academic writing services from our team of knowledgeable and highly educated writers, editors and proofreaders.
Find more interesting content related to thesis writing below:
- How To Write A Thesis Introduction Without Effort
- Writing A Top Thesis Outline – Your Comprehensive Guide
- How To Write A Counterclaim For A Successful Result
- Theoretical Framework: Research Writing Guide
- How To Write A Hypothesis – A Guide & Detailed Instructions
- How To Write A Perfect Thesis Proposal
- Writing Thesis Acknowledgement Section Like A Pro
- How To Narrow Down A Research Topic Successfully
- How To Formulate A Research Problem
Below, you can find answers to the most frequently asked questions regarding the dissertation proposal:
Can I make changes to my dissertation proposal after it is approved?
It is possible to make changes to the dissertation proposal after it is approved, but any significant changes may require additional review.
How long should a dissertation proposal be?
The length of a dissertation proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the program. Most proposals are typically between 10 and 20 pages.
Who reviews the dissertation proposal?
The dissertation proposal is typically reviewed by the student’s academic committee.
How long does it take to write a dissertation proposal?
On average, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few months to write a good dissertation proposal. You need professional help if you are about to miss the deadline.
What if my dissertation proposal is not approved?
If the dissertation proposal is not approved, the student will need to revise and resubmit it for review. You can get editing help from an online dissertation writing service , so you have no reason to stress!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Thesis Proposal
Thesis proposals.
Graduate students begin the thesis process by writing a thesis proposal that describes the central elements of the thesis work. Those elements vary depending on the type of thesis (research, artistic, or project) that the student plans to write. Students begin drafting the thesis proposal in the course Thesis Proposal Seminar .
Below, please find detailed information about the following:
- research thesis proposal
- artistic thesis proposal
- project thesis proposal
- formatting your proposal
- getting your proposal approved
- submit your proposal
Research Thesis Proposal
The proposal for a research thesis consists of five sections:
- Thesis Statement Following an optional introduction, the basic function of this section is to articulate a phenomenon that the student proposes to investigate (whether a social event, process, a literary work, an intellectual idea or something else), and the question(s), issue(s) or problem(s) related to that phenomenon that the student plans to address in the thesis. The core of the statement may take the form of a hypothesis that the student will test, of a proposition or argument that the student intends to support, or of a general problem or question the student will explore. The section puts that basic problem statement in a larger context by explaining its historical origins (where did it come from?) and its intellectual, social, and/or artistic context (what conversation, debate, or line of inquiry does it participate in?). It also describes the sub-questions or themes that constitute the general problem. Students will cite appropriate scholarly, professional and other sources for the ideas, questions and background information contained in the section.
- Research Methods In this section, the student will identify (a) the kinds of information that needed to answer the question(s) raised in the Thesis Statement, (b) the methods the student will use to gather that information, and (c) the strategies by which the student will organize and analyze the information in such a way as to reach and support a conclusion, to construct a sound argument. If the central problem has several facets, the student may need an array of different methods for collecting and analyzing information. Students should be as precise as possible in each stage of the methods statement: Is information needed about the stylistic techniques in a novel, about changes in the poverty rates in Kenya since independence, about the ways children think about nature? Will the student pull out the metaphors in a text, find government reports on household income, interview kids about their experiences in the woods? Will the student deploy statistical forms of content analysis, correlate poverty rates with political changes, interpret themes in children’s stories? Students should reflect on the broad methodological approaches that they propose to use, and cite sources from which they derive their methods and tools. A student's central goal is to demonstrate that they know how to go about answering the question(s) that have been raised. Please note that if students intend to conduct research on living people, they will need to get the approval of the University Committee on Activities Involving Human Subjects (UCAIHS). Before they apply for that approval, students will need to take a tutorial and pass a test on the various regulations. Refer to the UCAIHS website for more information.
- Justification and Limitations This section of the proposal should explain the rationale for the thesis and the importance of the topic. Indicate the reasons why this study is important to conduct and whom it will benefit. Identify the limits beyond which the inquiry will not go. For instance, if a student is writing about a historical subject, the student must explain the relevance of the time period selected. Finally, describe the contribution the work will make to the field.
- Conclusion This section should summarize the nature and intention of the student's work. Conclude the discussion and mention any pertinent information which may not have been included above.
- Annotated Bibliography This section consists of a list of books and articles and artworks with accompanying annotations that explain why these readings and other sources are likely to be crucial as the work advances.
back to top
Artistic Thesis Proposal
The artistic thesis consists of an artistic work and supporting essays, and it is important to conceive of each element as contributing to a coherent whole. The proposal itself consists of five sections:
- Concept Statement This section includes a brief introduction that forms the framework for the entire thesis and articulates the questions around which the creative project and supporting essays revolve.
- Description of the Artistic Work and Artistic Aims This section describes the major artistic work that will comprise the submitted artistic thesis. Students may want to refer to particular artistic influences or genres that will inform the work, or describe the aesthetic from which the creative work derives. In this section, students should also: refer to some of the artistic reasons that led to their decision to embark on this particular project; discuss the goals that will guide the development of the work; and provide concrete details about the final form and media of the work (will it be, for example, a collection of short stories, a novel; an evening of dance an exhibition of paintings, a film, or what?). If the artwork involves live performance, this section should state whether it will be a public or private event, where the event will be held, and any other details relevant to bringing the project to completion.
This section should provide the reader with relevant historical or critical information to place the central research question in context, and this section should also discuss the key theories, methods, and sources to be used within the research essay. It should demonstrate that the student knows how to begin answering the question(s) they are posing. What sorts of things will the student need to find out? What research methods will be used? What kinds of sources will be reviewed, and how will information from them be used? Who, if anyone, will be interviewed, and what kinds of questions will the subjects be asked? Students should also reflect, in this section, on the broad analytical approach that will structure their research and identify the school(s) of thought that will inform their investigations.
- Justification and Limitations This section should explain the importance of the student's work in the context of their particular artistic discipline and discuss how all components of the thesis project taken together as a single project will contribute to the scholarly and artistic fields with which it engages. This section should also discuss limitations, personal and practical, relating to the project and the student’s readiness. If the project is a film, for example, how much direct experience has the student already had in that field, and how will the student allocate the time to finish the project by the desired defense date? How much is the project likely to cost, and how does the student expect to obtain funding? What kind of spaces will be needed for rehearsal as well as presentation of the work?
Project Thesis Proposal
The project thesis includes two major components: (a) an activity (program, intervention, campaign, etc.) designed to address (solve, remediate, improve) a problem, issue or opportunity in the student's domain as a professional or activist; and (b) a written document that describes, rationalizes, analyzes, and assesses the activity. It is not strictly a research study, but rather an exercise in reflective practice. Therefore, the proposal takes a form different from that of the research or artistic thesis proposal. Please note, as well, that a project thesis must be not only designed but implemented and evaluated.
- Problem Statement This section of the proposal identifies, describes, and analyzes the problem (issue, need, opportunity) that the student will address in the project. Clearly articulate the nature of the problem: its historical, social and professional context; its dimensions and extent; its impact, and perhaps some previous efforts to address it. Present information that explains the student's understanding of the origins or causes of the problem, to set up the rationale for the choice of a strategy to solve it. At each stage, refer to appropriate scholarly and professional literatures.
- Project Plan Students should spell out their plans for addressing the problem. Students should describe the institutional setting within which the project will take place, as well as the individuals, groups, or organizations with whom they will work. What will the student (and, perhaps, others) do? What resources and strategies will be used? If the student need funds, how will they be raised and disbursed? What schedule will be followed? Be efficient, but concrete and clear in specifying the activities that will make up the project. Identify the professional and theoretical sources of the strategies for the project: What precedents and ideas are the student drawing on? Also, the student should discuss the means by which they will record and report the project activities for the members of the thesis committee. Will the student write a journal, shoot videos, keep material artifacts and documents? Students must be clear about how they intend to document the project. They may also elect to invite the members of their committee to witness the project first-hand.
- Assessment The proposal speaks to three aspects of the assessment process. In all three, students should be concrete and refer to appropriate literatures as sources of their plans. Criteria : First, students should describe and justify the criteria by which they will determine whether the project has succeeded. What are the goals and objectives? What changes does the student want to see in the participants, the organization, the larger world? Methods: What information will be needed to determine whether the goals and objectives have been met? How will that information be collected and organized? Analysis : How will that information be utilized to describe the project’s success or failure? What sorts of lessons does the student hope to draw from the assessment?
- Justification and Limitations This section of the proposal should explain the rationale for the thesis and the importance of the topic. Indicate the reasons why this study is important to conduct and whom it will benefit. Identify the limits beyond which the inquiry will not go. Finally, describe the contribution the work will make to the field.
- Conclusion This section should summarize the nature and intention of the work. Conclude the discussion and mention any pertinent information which may not have been included above.
Format of the Proposal
All thesis proposals should conform to the following specifications:
- Title Page The title should be reasonably succinct, but descriptive enough to convey the nature of the thesis; the title page should include your full name, the date of submission, and your adviser’s name.
- Length The thesis proposal should be approximately 8 pages, excluding the annotated bibliography. Remember that this is a proposal, not the thesis itself; tell us what you propose to do and how, don’t do it.
- Annotated Bibliography This bibliography should contain brief commentaries on no fewer than 10–15 relevant source works.
The Approval Process for the Thesis Proposal
The Thesis Proposal Seminar (TPS) Students write their thesis proposals while enrolled in the Thesis Proposal Seminar (CORE-GG 2401, a 2-credit core requirement offered every spring). Throughout that semester, students work closely with their Adviser and Instructor to draft an acceptable proposal. When the proposal has received approval from both the Thesis Proposal Seminar instructor (Gallatin reviewer) and the adviser, the student is allowed to move on to their thesis research. The three steps of the approval process are outlined below.
- TPS Instructor/Reviewer Approval The Thesis Proposal Seminar instructor serves as the Gallatin reviewer of the thesis proposal. A student must receive a grade of ‘Pass’ in the Thesis Proposal Seminar for the proposal to be considered ‘reviewer approved.’ If the student’s proposal is not finished at the end of the semester, the student will receive a grade of 'Incomplete' in the course and will have until June 15th to submit the proposal before moving on to thesis research.
- Adviser Approval Students work closely with their advisers over the course of the semester to produce a proposal that the adviser can approve. Once the adviser agrees that the proposal is ready, students submit their final proposal via the online Thesis Proposal submission form . The Thesis Proposal submission form allows students to provide Gallatin with additional information about the courses, internships, independent studies, jobs, and other experiences that have prepared the student for their thesis work.
- MA Program Approval Once the M.A. Program verifies adviser approval of the proposal and the student has passed the TPS, the MA Program updates the student record to show that the Thesis Proposal requirement has been satisfied.
The deadline for submitting an adviser approved thesis proposal online is June 15.
How to write a thesis proposal
I. Framework II. Structure of a thesis proposal III. Order in which to write the proposal IV. Tips V. Resources
I. Framework
- An environmental issue is identified.
- Other people's work on the topic is collected and evaluated.
- Data necessary to solving the problem are either collected by the student, or obtained independently.
- Data are analyzed using techniques appropriate to the data set.
- Results of the analysis are reported and are interpreted in light of the initial environmental issue.
The purpose of writing a thesis proposal is to demonstrate that
- the thesis topic addresses a significant environmental problem;
- an organized plan is in place for collecting or obtaining data to help solve the problem;
- methods of data analysis have been identified and are appropriate to the data set.
We are well aware that the best laid out research plans may go awry, and that the best completed theses sometimes bear only little resemblance to the thesis planned during the proposal. Therefore, when evaluating a thesis proposal, we are not trying to assure ourselves that you have clearly described a sure-fire research project with 0% risk of failure. (If there was no risk of failure, it wouldn't be research.)
Instead, what we're interested in seeing is if you have a clear handle on the process and structure of research as it's practiced by our discipline. If you can present a clear and reasonable thesis idea, if you can clearly relate it to other relevant literature, if you can justify its significance, if you can describe a method for investigating it, and if you can decompose it into a sequence of steps that lead toward a reasonable conclusion, then the thesis proposal is a success regardless of whether you modify or even scrap the actual idea down the line and start off in a different direction. What a successful thesis proposal demonstrates is that, regardless of the eventual idea you pursue, you know the steps involved in turning it into a thesis.
II. Structure of a thesis proposal
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Approach/methods
- Preliminary results and discussion
- Work plan including time table
- Implications of research
- List of references
- contains short, descriptive title of the proposed thesis project (should be fairly self-explanatory)
- and author, institution, department, research mentor, mentor's institution & email address, advisor's name, instuitution and email address, and date of delivery
- the abstract is a brief summary of your thesis proposal
- its length should not exceed ~200 words
- present a brief introduction to the issue
- make the key statement of your thesis
- give a summary of how you want to address the issue
- include a possible implication of your work, if successfully completed
- list all headings and subheadings with page numbers
- indent subheadings
- this section sets the context for your proposed project and must capture the reader's interest
- explain the background of your study starting from a broad picture narrowing in on your research question
- review what is known about your research topic as far as it is relevant to your thesis
- cite relevant references
- the introduction should be at a level that makes it easy to understand for readers with a general science background, for example your classmates
- in a couple of sentences, state your thesis
- this statement can take the form of a hypothesis, research question, project statement, or goal statement
- the thesis statement should capture the essence of your intended project and also help to put boundaries around it
- this section contains an overall description of your approach, materials, and procedures
- what methods will be used?
- how will data be collected and analyzed?
- what materials will be used?
- include calculations, technique, procedure, equipment, and calibration graphs
- detail limitations, assumptions, and range of validity
- citations should be limited to data sources and more complete descriptions of procedures
- do not include results and discussion of results here
- present any results you already have obtained
- discuss how they fit in the framework of your thesis
- describe in detail what you plan to do until completion of your senior thesis project
- list the stages of your project in a table format
- indicate deadlines you have set for completing each stage of the project, including any work you have already completed
- discuss any particular challenges that need to be overcome
- use this gantt chart format for your time table
- what new knowledge will the proposed project produce that we do not already know?
- why is it worth knowing, what are the major implications?
- cite all ideas, concepts, text, data that are not your own
- if you make a statement, back it up with your own data or a reference
- all references cited in the text must be listed
- cite single-author references by the surname of the author (followed by date of the publication in parenthesis)
- ... according to Hays (1994)
- ... population growth is one of the greatest environmental concerns facing future generations (Hays, 1994).
- cite double-author references by the surnames of both authors (followed by date of the publication in parenthesis)
- e.g. Simpson and Hays (1994)
- cite more than double-author references by the surname of the first author followed by et al. and then the date of the publication
- e.g. Pfirman, Simpson and Hays would be:
- Pfirman et al. (1994)
- cite newspaper articles using the newspaper name and date, e.g.
- ....this problem was also recently discussed in the press (New York Times, 1/15/00)
- do not use footnotes
- list all references cited in the text in alphabetical order using the following format for different types of material:
- Hunt, S. (1966) Carbohydrate and amino acid composition of the egg capsules of the whelk. Nature , 210, 436-437.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (1997) Commonly asked questions about ozone. http://www.noaa.gov/public-affairs/grounders/ozo1.html, 9/27/97.
- Pfirman, S.L., M. Stute, H.J. Simpson, and J. Hays (1996) Undergraduate research at Barnard and Columbia, Journal of Research , 11, 213-214.
- Pechenik, J.A. (1987) A short guide to writing about biology. Harper Collins Publishers, New York, 194pp.
- Pitelka, D.R., and F.M. Child (1964) Review of ciliary structure and function. In: Biochemistry and Physiology of Protozoa , Vol. 3 (S.H. Hutner, editor), Academic Press, New York, 131-198.
- Sambrotto, R. (1997) lecture notes, Environmental Data Analysis, Barnard College, Oct 2, 1997.
- Stute, M., J.F. Clark, P. Schlosser, W.S. Broecker, and G. Bonani (1995) A high altitude continental paleotemperature record derived from noble gases dissolved in groundwater from the San Juan Basin, New Mexico. Quat. Res. , 43, 209-220.
- New York Times (1/15/00) PCBs in the Hudson still an issue, A2.
- it is acceptable to put the initials of the individual authors behind their last names, e.g. Pfirman, S.L., Stute, M., Simpson, H.J., and Hays, J (1996) Undergraduate research at ......
III. Order in which to write the proposal
- Make an outline of your thesis proposal before you start writing
- Prepare figures and tables
- Figure captions
- Discussion of your data
- Inferences from your data
- Bibliography
- "Pictures say more than a thousand words!" Figures serve to illustrate important aspects of the background material, sample data, and analysis techniques.
- A well chosen and well labeled figure can reduce text length, and improve proposal clarity. Proposals often contain figures from other articles. These can be appropriate, but you should consider modifying them if the modifications will improve your point.
- The whole process of making a drawing is important for two reasons. First, it clarifies your thinking. If you don�t understand the process, you can�t draw it. Second, good drawings are very valuable. Other scientists will understand your paper better if you can make a drawing of your ideas. A co-author of mine has advised me: make figures that other people will want to steal. They will cite your paper because they want to use your figure in their paper.
- Make cartoons using a scientific drawing program. Depending upon the subject of your paper, a cartoon might incorporate the following:
- a picture of the scientific equipment that you are using and an explanation of how it works;
- a drawing of a cycle showing steps, feedback loops, and bifurcations: this can include chemical or mathematical equations;
- a flow chart showing the steps in a process and the possible causes and consequences.
- Incorporate graphs in the text or on separated sheets inserted in the thesis proposal
- Modern computer technology such as scanners and drafting programs are available in the department to help you create or modify pictures.
Grammar/spelling
- Poor grammar and spelling distract from the content of the proposal. The reader focuses on the grammar and spelling problems and misses keys points made in the text. Modern word processing programs have grammar and spell checkers. Use them.
- Read your proposal aloud - then have a friend read it aloud. If your sentences seem too long, make two or three sentences instead of one. Try to write the same way that you speak when you are explaining a concept. Most people speak more clearly than they write.
- You should have read your proposal over at least 5 times before handing it in
- Simple wording is generally better
- If you get comments from others that seem completely irrelevant to you, your paper is not written clearly enough never use a complex word if a simpler word will do
V. Resources/Acknowlegements
The senior seminar website has a very detailed document on " How to write a thesis " which you might want to look at. Most of the tips given there are relevant for your thesis proposal as well. Recommended books on scientific writing Some of the material on this page was adapted from: http://abacus.bates.edu/~ganderso/biology/resources/writing/HTWtoc.html http://www.geo.utep.edu/ see Master's guidelines http://info.hartwick.edu/anthropology/proposal.htm http://csdl.ics.hawaii.edu/FAQ/thesis-proposal.html http://www.butler.edu/honors/PropsTheses.html
Login or sign up to be automatically entered into our next $10,000 scholarship giveaway
Get Started
- College Search
- College Search Map
- Graduate Programs
- Featured Colleges
- Scholarship Search
- Lists & Rankings
- User Resources
Articles & Advice
- All Categories
- Ask the Experts
- Campus Visits
- Catholic Colleges and Universities
- Christian Colleges and Universities
- College Admission
- College Athletics
- College Diversity
- Counselors and Consultants
- Education and Teaching
- Financial Aid
- Graduate School
- Health and Medicine
- International Students
- Internships and Careers
- Majors and Academics
- Performing and Visual Arts
- Public Colleges and Universities
- Science and Engineering
- Student Life
- Transfer Students
- Why CollegeXpress
- $10,000 Scholarship
- CollegeXpress Store
- Corporate Website
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- CA and EU Privacy Policy
Articles & Advice > Graduate School > Articles
Writing a Strong Dissertation Proposal for Grad School
We won't sugarcoat it. Your dissertation is a big deal, but you can conquer it. Here's some advice on writing a dissertation for your master's or doctorate.
by GradSchools.com
Last Updated: Mar 16, 2023
Originally Posted: Jun 20, 2011
Brace yourself: the next sentence is going to sound major. Writing a dissertation is the culminating event of your graduate school career. It's also a source of great anxiety for many students. However, even though writing a graduate dissertation involves several steps, if you take them one at a time, the process may not seem so dreadful. The first step of your dissertation proposal process is—brace yourself again—writing a dissertation proposal. According to the American Heritage® Dictionary, a dissertation proposal is a "lengthy, formal treatise, especially one written by a candidate for the doctoral degree at a university; a thesis." More simply, it is your chance to convince your faculty thesis committee that your research question is one worth pursuing in your dissertation.
Dissertation proposal preparation
As you start to think about your dissertation proposal, begin by thinking about the bigger picture, and pare down from there. Write down all of your ideas even if they don't seem to all fit together. You can go back later and choose what interests you. Keep in mind that your dissertation is meant to fulfill an academic requirement—so it is a learning experience and quite a serious endeavor.
Do your research
Now is the time to do preliminary research to pare down your thoughts and determine whether there is enough information available to explore and test your ideas. However, you don't have to engage in extensive reading and research on every relevant piece of literature you come across. This is simply a time to get enough background and information to ensure that your dissertation will be successful and original.
Talk to your advisor and professors
Discuss your ideas for the proposal with your thesis/dissertation advisor and with the professors you would like to have on your thesis committee. Heed their advice and criticism (and remember that they will eventually be your audience). You will also want to include a timeline in your proposal, as your committee will want to know how long you believe it will take you to meet your specific dissertation goals. As you prepare to write your dissertation proposal, ask yourself if you have the necessary understanding, ability and motivation to complete your dissertation on the subject you have chosen. You also want to be sure that you're familiar with other research in that area. It's important to read other proposals to get a better idea of what is expected, as well as to ensure that your research is focused. Borrow successful proposals from your graduate school friends , or ask a professor to share proposals submitted in the past by other graduate students.
Related: The Importance of Finding Balance as a Graduate Student
Begin writing a dissertation proposal
One way of going about writing your dissertation proposal is to organize it around a set of questions with an appropriate methodology to answer those questions. Your problem statement should define and present an issued framed with specific questions. Your dissertation proposal should explain the importance of the problem, as well as the need for research within the context you have established. Your dissertation proposal should answer the following questions:
- What problem are you going to pursue?
- Why is it a problem?
- Why is it important to address?
- Where are you going to look for answers?
- Why are you going there?
Your dissertation proposal should revolve around a significant problem or issue that is of interest to you, your committee and the research community at large. It should include information about who will benefit from the research and what practical applicability your findings could have. You need to express the intention of your research , and be sure that your questions are concise and in question form. The dissertation proposal should demonstrate that you:
- have defined and delimited an interesting research question;
- can explain the importance of the question to someone not intimately familiar with it;
- can formulate testable hypotheses; and
- have a detailed plan for testing the most promising hypotheses.
Dissertation proposal structure
Dissertation proposals should be written in the present tense and should contain an introduction, conceptual framework, methodology, literature review, a bibliography, and appendices. The introduction should summarize the broad concepts and issues, and present your main research question. Get to the point in your introduction—there is no room for editorializing.
Your conceptual framework
In your conceptual framework, be sure to define the terms you will be using and how they will be used. You must also detail your methodology, explaining what you plan to do and why. It's imperative to indicate how your methodology helps to answer your research questions. You will want to list the materials, evidence, and data that you'll use in order to prove your thesis, as well as what contribution you hope your research will make in the field.
Your literature review
With your literature review, identify the conceptual and methodological strengths and weaknesses of the existing research on your subject. The literature review is your opportunity to locate the gaps in existing research that your work could fill. The bibliography is rather self-explanatory. Your appendices should support and define your research.
Going through several drafts
You would be well-advised to write several drafts of your dissertation proposal before arriving at the final proposal. Most graduate students shy away from making bold claims for their work or potential work, but you need to step forward in your proposal and attempt to answer the big question: "So What?" Do your best to project the potential research outcomes and the importance of those outcomes. In short, how will your thesis contribute to the body of knowledge in your field of study?
Final formatting
Your final dissertation proposal should be titled, and include a title page and table of contents. Include a detailed timeline in your proposal. Most dissertation proposals are no less than 10 pages. However, the average length falls between 15 and 20 pages. Don't panic—if you have a strong hypothesis, identify the importance of your research and the prior research, and employ the proper methodology, you will be on your way to writing a successful dissertation proposal.
Related: Time Management: Your Best Friend in Grad School
Writing your dissertation is a major milestone that you’ll remember for most of your life, but don’t let that psyche you out. You’ve done the work and put in the time because you wanted to qualify yourself to pursue your passions. Your dissertation is a culmination of all that hard work—admittedly with quite a bit more work left to do. But you can do it. And you will do great!
Are you prepared to enter the workforce after grad school? Check out our Quick List of Job Search Tips for Graduate Students if you're still looking for opportunities!
Like what you’re reading?
Join the CollegeXpress community! Create a free account and we’ll notify you about new articles, scholarship deadlines, and more.
Tags: doctorates grad programs grad school grad school academics grad student life graduate students
Join our community of over 5 million students!
CollegeXpress has everything you need to simplify your college search, get connected to schools, and find your perfect fit.

Heaven Johnson
Back to School Scholarship Winner, High School Class of 2023
I’d like to thank everyone on the CollegeXpress team for their generosity. Not only have I been awarded this scholarship, but CollegeXpress makes it easier to apply and gives amazing tips for schools and scholarships. I am extremely grateful as this will help with my schooling and allow me to be able to enter into the field I’ve been dreaming of all my life.
High School Class of 2021
CollegeXpress helped me find Allegheny College with the super-user-friendly search tool for both schools and scholarships. Using CollegeXpress, I was able to search for programs I was interested in studying and find colleges that offered those programs. Also, once you search for the college, CollegeXpress can get you connected!

Emilie Delgado
$2,000 Community Service Scholarship Winner, 2013
CollegeXpress has tremendously helped me in my search for financial aid opportunities as I enter my college career. It is easy to navigate and quickly narrowed down scholarships that I could apply for. Being awarded the scholarship will greatly help me in my finances regarding books and tuition. Thank you for this opportunity. Without CollegeXpress, it would have been more difficult to apply. I would recommend this site to everyone!
High School Class of 2019
My college search began at CollegeXpress. Due to this helpful tool, I was able to gather a lot of information to guide my college planning decisions. Through CollegeXpress, I was also able to apply to several scholarships to help pay for my tuition. I would definitely recommend this website to anyone who wants to explore colleges and get more information from admission experts, counselors, and real students.

Josiah Kegg
I want to sincerely thank you all for this amazing website that's legitimately helped me find so many different scholarship opportunities. I've been stressing out for the longest time about paying for college since I would rather stay out of debt and have been working days trying to find any scholarship opportunity. When I found CollegeXpress, I discovered many easy scholarships that have given me hope for the future. Thank you and God bless!
- The Importance of Finding Balance as a Graduate Student
- Inside My Grad School Experience: Part 2
- Inside My Grad School Experience: Part 1
- The Ultimate Guide to Undergrad vs. Law School
- Insider Advice on How to Be a Successful Graduate Student
Colleges You May Be Interested In
Pace University - Westchester - Pleasantville Campus
Pleasantville, NY
Mayo Clinic College of Medicine & Science
Rochester, MN
The George Washington University
Washington, DC
Malone University
Florida Institute of Technology
Melbourne, FL
Personalize your experience on CollegeXpress.
With this information, we'll display content relevant to your interests. By subscribing, you agree to receive CollegeXpress emails and to make your information available to colleges, scholarship programs, and other companies that have relevant/related offers.
Already have an account?
Log in to be directly connected to
Not a CollegeXpress user?
Don't want to register.
Provide your information below to connect with
The Thesis Process
The thesis is an opportunity to work independently on a research project of your own design and contribute to the scholarly literature in your field. You emerge from the thesis process with a solid understanding of how original research is executed and how to best communicate research results. Many students have gone on to publish their research in academic or professional journals.
To ensure affordability, the per-credit tuition rate for the 8-credit thesis is the same as our regular course tuition. There are no additional fees (regular per-credit graduate tuition x 8 credits).
Below are the steps that you need to follow to fulfill the thesis requirement. Please know that through each step, you will receive guidance and mentorship.
1. Determine Your Thesis Topic and Tentative Question
When you have completed between 24 and 32 credits, you work with your assigned research advisor to narrow down your academic interests to a relevant and manageable thesis topic. Log in to MyDCE , then ALB/ALM Community to schedule an appointment with your assigned research advisor via the Degree Candidate Portal.
Thesis Topic Selection
We’ve put together this guide to help frame your thinking about thesis topic selection.
Every effort is made to support your research interests that are grounded in your ALM course work, but faculty guidance is not available for all possible projects. Therefore, revision or a change of thesis topic may be necessary.
- The point about topic selection is particularly pertinent to scientific research that is dependent upon laboratory space, project funding, and access to private databases. It is also critical for our candidates in ALM, liberal arts fields (English, government, history, international relations, psychology, etc.) who are required to have Harvard faculty direct their thesis projects. Review Harvard’s course catalog online ( my.harvard.edu ) to be sure that there are faculty teaching courses related to your thesis topic. If not, you’ll need to choose an alternative topic.
- Your topic choice must be a new area of research for you. Thesis work represents thoughtful engagement in new academic scholarship. You cannot re-purpose prior research. If you want to draw or expand upon your own previous scholarship for a small portion of your thesis, you need to obtain the explicit permission of your research advisor and cite the work in both the proposal and thesis. Violations of this policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
2. Prepare Prework for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) Course or Tutorial
The next step in the process is to prepare and submit Prework in order to gain registration approval for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) tutorial or course. The Prework process ensures that you have done enough prior reading and thinking about your thesis topic to benefit from the CTP.
The CTP provides an essential onramp to the thesis, mapping critical issues of research design, such as scope, relevance to the field, prior scholarly debate, methodology, and perhaps, metrics for evaluating impact as well as bench-marking. The CTP identifies and works through potential hurdles to successful thesis completion, allowing the thesis project to get off to a good start.
In addition to preparing, submitting, and having your Prework approved, to be eligible for the CTP, you need to be in good standing, have completed a minimum of 32 degree-applicable credits, including the statistics/research methods requirement (if pertinent to your field). You also need to have completed Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (if pertinent to your field). If you were admitted after 9/1/2023 Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (A and B) is required, if admitted before 9/1/2023 this series is encouraged.
Advising Note for Biology, Biotechnology, and Bioengineering and Nanotechnology Candidates : Thesis projects in these fields are designed to support ongoing scientific research happening in Harvard University, other academic institutions, or life science industry labs and usually these are done under the direction of a principal investigator (PI). Hence, you need to have a thesis director approved by your research advisor prior to submitting CTP prework. Your CTP prework is then framed by the lab’s research. Schedule an appointment with your research advisor a few months in advance of the CTP prework deadlines in order to discuss potential research projects and thesis director assignment.
CTP Prework is sent to our central email box: [email protected] between the following firm deadlines:
- April 1 and June 1 for fall CTP
- September 1 and November 1 for spring CTP.
- August 1 and October 1 for the three-week January session (ALM sustainability candidates only)
- International students who need a student visa to attend Harvard Summer School should submit their prework on January 1, so they can register for the CTP on March 1 and submit timely I-20 paperwork. See international students guidelines for more information.
Your research advisor will provide feedback on your prework submission to gain CTP registration approval. If your prework is not approved after 3 submissions, your research advisor cannot approve your CTP registration. If not approved, you’ll need to take additional time for further revisions, and submit new prework during the next CTP prework submission time period for the following term (if your five-year degree completion deadline allows).
3. Register and Successfully Complete the Crafting the Thesis Proposal Tutorial or Course
Once CTP prework is approved, you register for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) course or tutorial as you would any other course. The goal of the CTP is to produce a complete, well-written draft of a proposal containing all of the sections required by your research advisor. Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director. The proposal is normally between 15 to 25 pages in length.
The CTP tutorial is not a course in the traditional sense. You work independently on your proposal with your research advisor by submitting multiple proposal drafts and scheduling individual appointments. You need to make self-directed progress on the proposal without special prompting from the research advisor. You receive a final grade of SAT or UNSAT (failing grade).
The CTP for sustainability is a three-week course in the traditional sense and you receive a letter grade, and it must be B- or higher to receive degree credit for the course.
You are expected to incorporate all of your research advisor’s feedback and be fully committed to producing an academically strong proposal leading to a thesis worthy of a Harvard degree. If you are unable to take advice from your research advisor, follow directions, or produce an acceptable proposal, you will not pass the CTP.
Successful CTP completion also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
Maximum of two attempts . If you don’t pass that CTP, you’ll have — if your five-year, degree-completion date allows — just one more attempt to complete the CTP before being required to withdraw from the program. If you fail the CTP just once and have no more time to complete the degree, your candidacy will automatically expire. Please note that a WD grade counts as an attempt.
If by not passing the CTP you fall into poor academic standing, you will need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before enrolling in the CTP for your second and final time, only if your five-year, degree-completion date allows. If you have no more time on your five-year clock, you will be required to withdraw.
Human Subjects
If your thesis, regardless of field, will involve the use of human subjects (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations), you will need to have your research vetted by the Committee on the Use of Human Subjects (CUHS) of Harvard University. Please review the IRB LIFECYCLE GUIDE located on the CUHS website. Your research advisor will help you prepare a draft copy of the project protocol form that you will need to send to CUHS. The vetting process needs to be started during the CTP tutorial, before a thesis director has been assigned.
4. Thesis Director Assignment and Thesis Registration
We expect you to be registered in thesis soon after CTP completion or within 3 months — no later. You cannot delay. It is critical that once a research project has been approved through the CTP process, the project must commence in a timely fashion to ensure the academic integrity of the thesis process.
Once you (1) successfully complete the CTP and (2) have your proposal officially approved by your research advisor (RA), you move to the thesis director assignment phase. Successful completion of the CTP is not the same as having an officially approved proposal. These are two distinct steps.
If you are a life science student (e.g., biology), your thesis director was identified prior to the CTP, and now you need the thesis director to approve the proposal.
The research advisor places you with a thesis director. Do not approach faculty to ask about directing your thesis. You may suggest names of any potential thesis directors to your research advisor, who will contact them, if they are eligible/available to direct your thesis, after you have an approved thesis proposal.
When a thesis director has been identified or the thesis proposal has been fully vetted by the preassigned life science thesis director, you will receive a letter of authorization from the Assistant Dean of Academic Programs officially approving your thesis work and providing you with instructions on how to register for the eight-credit Master’s Thesis. The letter will also have a tentative graduation date as well as four mandatory thesis submission dates (see Thesis Timetable below).
Continuous Registration Tip: If you want to maintain continued registration from CTP to thesis, you should meet with your RA prior to prework to settle on a workable topic, submit well-documented prework, work diligently throughout the CTP to produce a high-quality proposal that is ready to be matched with a thesis director as soon as the CTP is complete.
Good academic standing. You must be good academic standing to register for the thesis. If not, you’ll need to complete additional courses to bring your GPA up to the 3.0 minimum prior to registration.
Thesis Timetable
The thesis is a 9 to 12 month project that begins after the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP); when your research advisor has approved your proposal and identified a Thesis Director.
The date for the appointment of your Thesis Director determines the graduation cycle that will be automatically assigned to you:
Once registered in the thesis, we will do a 3-month check-in with you and your thesis director to ensure progress is being made. If your thesis director reports little to no progress, the Dean of Academic Programs reserves the right to issue a thesis not complete (TNC) grade (see Thesis Grading below).
As you can see above, you do not submit your thesis all at once at the end, but in four phases: (1) complete draft to TA, (2) final draft to RA for format review and academic integrity check, (3) format approved draft submitted to TA for grading, and (4) upload your 100% complete graded thesis to ETDs.
Due dates for all phases for your assigned graduation cycle cannot be missed. You must submit materials by the date indicated by 5 PM EST (even if the date falls on a weekend). If you are late, you will not be able to graduate during your assigned cycle.
If you need additional time to complete your thesis after the date it is due to the Thesis Director (phase 1), you need to formally request an extension (which needs to be approved by your Director) by emailing that petition to: [email protected] . The maximum allotted time to write your thesis, including any granted extensions of time is 12 months.
Timing Tip: If you want to graduate in May, you should complete the CTP in the fall term two years prior or, if a sustainability student, in the January session one year prior. For example, to graduate in May 2025:
- Complete the CTP in fall 2023 (or in January 2024, if a sustainability student)
- Be assigned a thesis director (TD) in March/April 2024
- Begin the 9-12 month thesis project with TD
- Submit a complete draft of your thesis to your TD by February 1, 2025
- Follow through with all other submission deadlines (April 1, April 15 and May 1 — see table above)
- Graduate in May 2025
5. Conduct Thesis Research
When registered in the thesis, you work diligently and independently, following the advice of your thesis director, in a consistent, regular manner equivalent to full-time academic work to complete the research by your required timeline.
You are required to produce at least 50 pages of text (not including front matter and appendices). Chapter topics (e.g., introduction, background, methods, findings, conclusion) vary by field.
6. Format Review — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
All ALM thesis projects must written in Microsoft Word and follow a specific Harvard University format. A properly formatted thesis is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without it.
Your research advisor will complete the format review prior to submitting your thesis to your director for final grading according to the Thesis Timetable (see above).
You must use our Microsoft Word ALM Thesis Template or Microsoft ALM Thesis Template Creative Writing (just for creative writing degree candidates). It has all the mandatory thesis formatting built in. Besides saving you a considerable amount of time as you write your thesis, the preprogrammed form ensures that your submitted thesis meets the mandatory style guidelines for margins, font, title page, table of contents, and chapter headings. If you use the template, format review should go smoothly, if not, a delayed graduation is highly likely.
Format review also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred directly to the Administrative Board.
7. Mandatory Thesis Archiving — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
Once your thesis is finalized, meaning that the required grade has been earned and all edits have been completed, you must upload your thesis to Harvard University’s electronic thesis and dissertation submission system (ETDs). Uploading your thesis ETDs is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without completing this step.
The thesis project will be sent to several downstream systems:
- Your work will be preserved using Harvard’s digital repository DASH (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard).
- Metadata about your work will be sent to HOLLIS (the Harvard Library catalog).
- Your work will be preserved in Harvard Library’s DRS2 (digital preservation repository).
By submitting work through ETDs @ Harvard you will be signing the Harvard Author Agreement. This license does not constrain your rights to publish your work subsequently. You retain all intellectual property rights.
For more information on Harvard’s open access initiatives, we recommend you view the Director of the Office of Scholarly Communication (OSC), Peter Suber’s brief introduction .
Thesis Grading
You need to earn a grade of B- or higher in the thesis. All standard course letter grades are available to your thesis director. If you fail to complete substantial work on the thesis, you will earn a grade of TNC (thesis not complete). If you have already earned two withdrawal grades, the TNC grade will count as a zero in your cumulative GPA.
If you earn a grade below B-, you will need to petition the Administrative Board for permission to attempt the thesis for a second and final time. The petition process is only available if you are in good academic standing and your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time. Your candidacy will automatically expire if you do not successfully complete the thesis by your required deadline.
If approved for a second attempt, you may be required to develop a new proposal on a different topic by re-enrolling in the CTP and being assigned a different thesis director. Tuition for the second attempt is calculated at the current year’s rate.
If by not passing the thesis you fall into poor academic standing, you’ll need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before re-engaging with the thesis process for the second and final time. This is only an option if your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time.
The Board only reviews cases in which extenuating circumstances prevented the successful completion of the thesis.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.


- Future Students
- Parents and Families
Department of English
College of arts and sciences, ph.d. dissertation proposal guidelines.
The following has been adapted for the English Department from the Graduate School’s “Statement on Thesis/Dissertation Proposals.” Guidelines adapted for the Creative Dissertation Proposal Guidelines can be found here .
I. Introduction
A thesis proposal states a problem to be investigated and describes how the research will be performed and reported. Approval signifies that it meets the standards of the University of Rhode Island for the degree desired. Therefore, the preparation and writing of the thesis proposal are of utmost importance. Although the student is expected to seek guidance in the choice of topic and the method of solving the problem involved, responsibility for the proposal lies with the student who will, as far as possible, work independently and demonstrate the ability to plan and outline an acceptable research project. Adherence to the guidelines given below should assure the student that all information necessary for the satisfactory evaluation of the plans for master’s or doctoral research will be included in the proposal.
The thesis proposal should present the required information as concisely and clearly as possible. The ability to describe concisely a research problem and methodology is one of the skills that the proposal process is designed to develop. Therefore, all thesis/dissertation proposals are limited in length to the signature cover-sheet plus 15 or fewer double-spaced, numbered pages in a font size no smaller than 12 point . Proposals longer than this will not be accepted, however, appendices and references are not included in the 15-page limit . Proposals will also be returned for revision if they do not contain the appropriate sections described in the Contents section of this Statement on Thesis/Dissertation Proposals. Sufficient copies of the proposal must be provided to permit distribution to the Graduate School, Institutional Review Board or Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee if required (see Sec. III), department, major professor, thesis or doctoral committee, and the student.
III. Submission
Thesis proposals should be submitted before substantial research has been completed. Typically, it should be submitted before or during the first semester in which the student registers for research credits. In all cases, however, the proposal must be submitted at least one semester before the semester in which the thesis/dissertation itself is to be submitted and defended.
In the English Department, the Dissertation Proposal is submitted for review by the student’s entire dissertation committee once the written and oral comprehensive exams are completed. The student meets with the committee for the purpose of discussing the proposal and the first stages of the dissertation. Then , all copies of the thesis proposal must be signed by the members of the student’s doctoral committee, who thereby approve the proposal for forwarding by the student’s major professor via the Director of Graduate Studies to the Vice Provost for Graduate Studies, Research, and Outreach. The Vice Provost is charged with responsibility for review and approval or rejection of all proposals. Proposals that do not meet the standard of the Graduate School will be returned to the student for revision and resubmission. Approved proposals are returned to the department for distribution, with one copy retained in the student’s file at the Graduate School.
(Sections on “Research Involving Human Subjects” and “Research involving Vertebrate Animals” excluded here, but you may read them by going to the Grad School Webpage and consulting their Statement on the Ph.D. proposal.)
IV. Contents
Thesis Proposals shall contain the following sections, presented in the order shown:
A. Title of the Study
This is the title as the student conceives it at the time the proposal is submitted. It should be no more than 100 characters in length. As the research develops, various rephrasings of the title may prove better suited to the work. In such cases, the most satisfactory one will be used for the dissertation, the final formal report of the investigation. Please note that at that time a title abstract of 40 characters or less must be submitted.
B. Statement of the Problem
This section should be relatively short and sweet — a succinct introduction to your topic, thesis, and the questions that drive your project.
Limit the statement, if possible, to two or three sentences, and note in precise language exactly what is to be investigated. Here is where you introduce your object(s) of study and the principal question or questions you are bringing to it or them. To amplify the Statement of the Problem, it is usually desirable to list:
- The scope or limitations of the problem: e.g., what material will it include and why? Give some thought to the criteria by which you will limit the project, for instance, to a specific time period, geographical locale, genre of literature or film, a particular author or group of authors, a social group, or movement, or school of thought, etc.
- Either one or more hypotheses the research seeks to test or the objectives you expect to attain as a result of the study.
- The major assumptions that underlie both the study as a whole and the methodology you will be following. Note: you will be expanding on this in section D; just give a succinct introduction of the methodology here.
C. The justification for and Significance of the Study
Now you start to get into the substance of your proposal. You may run to a few pages in this section, and amplify on what you introduced in Section B.
This section of the proposal includes:
- A brief statement of the reasons for the selection of the problem: Is there, for instance, a gap in the existing scholarship on this problem? Alternatively, even if this is a topic that has been much discussed, will you be shedding new light on it by examining it in a new context, or bringing to bear a different theoretical framework, or juxtaposing it with other objects with which it has never been considered?
- The relation of the principal literature to the proposal: In the English Department, by “principal literature” we mean both the primary texts or object you plan to treat, as well as the secondary texts that have come to inform your approach to those primary texts. Why these texts? Why now? What is at stake? And what have you got to contribute to our understanding of them?
- An explanation of the study’s importance to the advancement of knowledge and its significance to the student: To show the importance of your study to the advancement of knowledge, you will need to show where that knowledge is now, and how you plan to extend, question, complement, challenge, or revolutionize it (etc).
- The problem selected should be substantial enough to constitute a good example of a report of a scholarly investigation. Completion of a project or several unrelated projects does not satisfy this requirement. At the Ph.D. level, the work should constitute a significant increase in the pool of knowledge.
D. Methodology or Procedures
Again–this is a substantive section of the Proposal. Another few pages.
This section describes the activities necessary to achieve the objectives. Methods should flow naturally from the problems and objectives.
The Graduate School defines methodology in terms of the study population; sampling design and procedures; tools, instruments, and timetables for data collection and testing; definition of terms and concepts. In the English Department, too, you will be expected to present a methodological plan for how your investigation will be carried out, which will necessarily involve a concise statement of the theoretical or critical frameworks most important to your project. Rather than a list of theorists’ or critics’ names, provide specific concepts or well-defined terms from these theorists, and explain how they inform the way you are approaching your problem. Even better, explain how you are intervening in the status quo already established by these existing critics or theorists. You should also give a sense of the kinds of critical activity you plan to carry out: will you do close readings of primary texts? If so, what kind? Will one or more chapters be devoted to a survey of existing scholarship? Will you be conducting archival research, and if so, where, and for what purpose? Does one section of your dissertation rely on your having completed another section first? Is there an interdisciplinary aspect to your project that requires a special methodological approach all its own? A brief, provisional chapter outline is appropriate in this section since it indicates the logic behind how you envision the organization of your material.
E. Resources Required
The last part of the thesis proposal is a statement of the resources needed for the successful completion of the study and an indication of their accessibility to the student proposing to use them. This may be a very brief section, where you summarize the primary and secondary texts necessary to your investigation, with the understanding that the full bibliography will be saved for an appendix. This is also the place to mention travel to archives or to visit any individuals who may be key to your project.
F. Literature Cited in the Proposal
Take note of the following concern of the Graduate School, a concern shared by the English Department:
The most persistent difficulty with thesis proposals is lack of evidence that a search of the literature took place in framing the problem to be studied. The absence of evidence that the scholarly literature in the field has been consulted might be due to one or more of the following reasons:
- That it was omitted because the student was not aware that it was required.
- That the student was unfamiliar with the library as a resource in developing the research proposal.
- That, having searched the literature of the field, the student found that the problem was unique, and therefore, could not be documented. If so, it is important to note where the literature stops and the proposed research starts, itself an intriguing scholarly problem.
- That the thesis problem has been provided “ready-made” as a spin-off from a larger study so that no literature search appeared to be needed. One might question the wisdom of thus isolating the student from the scholarly literature, however valid and important the research topic. (This seems to be directed more at faculty than at students.)
- Since you are limited to only 15 pages for the dissertation proposal, we recommend that you write “See Appendix A” for this section of the proposal, and place your Works Cited in that Appendix. That way you leave more room for the substance of the Proposal. In your “Works Cited,” we recommend that you make sub-divisions where appropriate. For instance, you may want to have a “primary” and a “secondary” list; or a list of “literature,” “film,” and the criticism pertaining to each; or if more than one historical period is covered, you may want to divide your bibliography by period, etc. Make your Works Cited as reflective of the logic of your project as possible.
G. Revised Proposals (not a section of your proposal)
If, as the research proceeds, a significant change in subject or methodology becomes necessary, a revised proposal should be submitted. Sometimes an abbreviated format can be used for such changes. The student or major professor should contact the Graduate School for assistance in such cases.
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal: Structure, Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal: Structure, Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A dissertation proposal offer a brief agenda of a research project that a student intends to conduct in order to obtain a doctoral degree. It requires students to meticulously plan and organize a future study. The purpose of the dissertation proposal is to demonstrate the feasibility and value of the proposed study. It is written to obtain approval from a committee before organizing research.
If you're wondering how to tackle your Ph.D. or Master's thesis proposal, this article lays out the basics of producing a successful one. Continue reading through this article to understand the key steps on how to write your thesis or dissertation proposal, its definition, and its importance. Before penning down your project, we will walk you through its structure and make you aware of what you should know. In addition, we will explain its format as well as provide thesis and dissertation proposals examples, writing tips, and a checklist to help you stay on track. Read on if you are eager to impress committee members with an incredible proposal! Or shop for dissertation proposal help at StudyCrumb to save nerves and time!
What Is a Dissertation Proposal?
A dissertation proposal is a document written to present the main objectives and questions that a researcher will cover in a research project, meaning that this proposal is the foundation of your study. It offers an overview of what you plan to do and how you approach researching a topic and provides a roadmap for composing your thesis. Writing a dissertation proposal aims to explain how your dissertation will investigate a research problem, describe the methods used, as well as justify the research. Another objective of a dissertation or thesis proposal is to demonstrate that your research problem is significant, relevant, and worth exploring. In addition, its purpose is to show how the thesis will be structured and provide a timeline for completion.

Importance of Thesis/ Dissertation Proposals
A strong thesis or dissertation proposal is critical to the success of your study. Writing and correctly presenting it can give you an edge when applying for a thesis project. Below is a list of why proposals for your dissertation are essential:
- Allows researchers to explore and define a study topic of interest.
- Helps you gain approval from supervisors, thesis committees, and boards.
- Assists in clearly defining your research question and planning how to tackle the research.
- Enables you to identify potential sources of information and plan how to use them effectively.
- Serves as a template to guide you through the writing process.
- Aids you in securing funding for your project.
- Useful when planning for the thesis proposal defense.
How Long Should a Dissertation Proposal Be?
Dissertation proposal length varies depending on the level of study. Proposals for Ph.D. dissertations can range from 15-20 pages, sometimes even up to 30 pages. The number of pages depends on every discipline and topic, as well as other requirements stated in provided instructions. Master's thesis proposal is a bit shorter and generally ranges between 4-8 pages. The reason for these differences is that a Ph.D. dissertation proposal requires more in-depth research and has a broader scope than a Master's one. The length also depends on the type of thesis you are writing. For example, scientific research thesis typically has methodological approaches, while humanities Ph.D. proposals use qualitative and quantitative methods, depending on the field of investigation.
Dissertation Proposal Structure
The structure of a dissertation or thesis proposal varies depending on the discipline and how you plan to approach researching that subject. Variation may also result from different research methodologies used. However, you should generally include several standard components when writing a dissertation proposal. These are as follows:
- Introduction Provides an overview of the proposed study and how it fits within your field of investigation.
- Aims and objectives Justify what you hope to achieve and how you plan to do it.
- Literature review Discusses how other researchers have approached the topic under investigation and how your thesis will contribute to the discipline under scrutiny.
- Study Design and Research Methodology Describes how you strategize to conduct your research, what methods you will use, and how the data will be collected and analyzed. Also, include any ethical considerations.
- Implications Evaluate how your dissertation will contribute to the broader field and how it can be helpful for future studies.
- Limitations Examine how your research may not be able to answer some questions and how to address those shortcomings. In other words, how to minimize the effect of identified drawbacks.
- Budget Budget is optional and required only if funding is needed. Here, you need to offer an estimate of how much the investigation will cost and your financing plans.
- References Give a complete list of all sources used throughout the paper.
Following these steps on how to write a proposal for a thesis or dissertation aids you in structuring your proposal, which will help you present a clear and concise outline of how you intend to conduct your research. As a result, it allows you to secure approval and gain support for your project.
Thesis/ Dissertation Proposal Template Outline
A template for a dissertation proposal outline can help create your work. Students can efficiently structure their thesis proposal using this template and ensure it meets the required guidelines. Templates are incredibly useful in streamlining your writing process so that you can concentrate on the proposal's content without stressing over format. In addition, templates should include the main components of a dissertation proposal, with each part delineated and explained clearly. Additionally, formatting should be consistent. The following is an example of a dissertation proposal outline:
- Background/ context of the investigation
- Problem statement
- Purpose of the study
- Research questions
- Significance of the research
- Overview of existing literature
- Gap in literature
- Design of the study
- Data collection and analysis
- Contribution to the field
- Limitations of the research
- Budget (if applicable)
Things to Know Before Writing a Dissertation Proposal
Before writing your dissertation proposal, one must understand the purpose of crafting one. A student must cover these questions in a proposal: what, why, where, who, and how. In other words, it needs to answer questions such as:
- What is the research topic ?
- Why is it important to study this topic?
- Where will the investigation take place?
- Who are the participants involved?
- How will the project be conducted and analyzed?
Answering these inquiries will help you comprehensively write a dissertation or thesis proposal that outlines your paper's purpose, aims, and objectives. Before composing, it is crucial also to consider any ethical concerns or issues that may arise with your work. For example, you should be aware of potential risks as well as ensure that you have the necessary procedures to protect your participants.
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal?
When writing thesis and dissertation proposal, it is crucial to cover the critical elements of how one should approach writing such a document. A thesis proposal is a roadmap for how the researcher plans to conduct their research. A clear structure can only make organizing one's thoughts and ideas easy. Without a clear guideline, your advisor or supervisor might reject your proposal, or you may fail to acquire funding or support. To ensure you compose a satisfying proposal, follow the below step-by-step illustration of how to write a proposal for a dissertation and thesis.

1. Decide on a Title
Deciding on a title for your dissertation proposal is essential in creating a clear, concise, and attractive document. Your dissertation topic should reflect the main focus of your research. Excellent titles should be easy to understand because it is the first thing people see. An outstanding title also helps grab potential readers' attention and encourages them to read the paper. In addition, students should craft their titles for dissertation and Ph.D. thesis proposals in a way that succinctly portrays the theme of the study. To decide on a good topic, consult information available online and in academic journals so that title is reflective of the current investigation. The following is an example of a title for a thesis proposal:
Impact of Technology on the Education System in America.
2. Write a Dissertation Proposal Introduction
A thesis proposal introduction is an important section of a document that sets the tone for the entire paper, and you should write this part clearly and concisely. Start a dissertation proposal for your research with an introduction that distills the pertinent central question, providing contextualized background information as well as any broader implications. This section is a condensed version of a complete dissertation introduction , which you will need to compose upon topic approval. Affirming the problem statement in your introduction will give more direction to your study objectives, and people will be able to understand the purpose of why you are conducting this exploration. As you craft your introduction, ensure to outline the structure of your paper. Include which sections cover methodology, literature review, research limitations, as well as any other subsections that are relevant. These are critical parts of a dissertation proposal, and outlining them will help keep readers orientated throughout your document and allow them to comprehend the discussion better. Example of dissertation proposal introduction
This dissertation proposal sets out to investigate how technology has changed the education system in America and its impact on student learning outcomes. The research objectives of this study are to examine the development of technology in the American education environment, analyze its impact on learners' studying outcomes as well as evaluate how teachers have adapted their teaching techniques to incorporate technology. This thesis also explores the challenges technology has posed for teachers in America's school system and how to address them. By exploring these issues, this research seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of technology in American education and its subsequent implications. Finally, this thesis will discuss the technological consequences for educational institutions and policymakers.
3. State Your Aims, Objectives, and Purpose
When writing a thesis proposal, your paper's aims, objectives, and purpose are the cornerstones of a successful document. Your aims, objectives, and purpose should be concise and clear. When writing your aims , include the primary goal of your undergraduate or doctoral project as well as what you expect to achieve. Objectives should address the what, why, and how of your study while also explaining all outcomes you anticipate accomplishing. Finally, your purpose should be closely related to your aims and objectives and provide a succinct description of objectives you are trying to undertake. The reason is that aims and objectives are the starting points in crafting a dissertation proposal, as they provide a focus for your investigation. The purpose will help develop the reader's understanding of your work. Examples of dissertation proposals aims and objectives
This thesis proposal aims to study technology implementation in American education and its impact on student learning outcomes. The objectives are to investigate the development and utilization of technology in America's schooling environment, analyze its impact on student studying outcomes, evaluate how teachers have adapted their teaching techniques to incorporate technology as well as explore the challenges it has posed for school instructors. Additionally, the objectives are to examine how these challenges can be addressed, evaluate the implications of technology for educational institutions and policymakers, and provide recommendations for future research on the use and application of technology in American education.
4. Provide a Literature Review
Literature review of a dissertation or Ph.D. thesis proposal is one of the most critical aspects of a project because it serves as the foundation for your research. This part should include an overview and analysis of existing literature related to your topic and conclude how it relates to the current study question. When composing a literature review for your Ph.D. dissertation proposals, you should search for scholarly articles, books, government reports, websites, and other relevant sources to inform your writing. Additionally, you should use a systematic approach in organizing literature and creating your reviews, such as a thematic, theoretical, or methodological approach. Refer to our guide to find a literature review outline example of each of these approaches. Finally, it is crucial to critically analyze available literature and how it connects to your research topic. This could involve examining how existing research has shaped your study question, how it has advanced the field of investigation, and how experts might use it in practice or policy making. Consulting with professionals in your area may be a great way to get additional insights on how to write a thesis and dissertation proposal literature review.
5. Discuss Your Methodology
Writing a proposal for your dissertation or thesis involves developing a methodology section, which outlines a set of techniques and strategies you plan to apply when conducting your study. Dissertation methodology should include:
- Description of your data collection and analysis methods
- Discussion of the research design
- Sampling techniques that are planned to be used
- Explanation of the variables or factors studied
- Outline of how you intend to analyze the data.
Methodology should also provide a rationale for why you have chosen your methods and any ethical considerations that might come with them. Writing a research proposal for a dissertation study will involve discussing how you propose to address any potential limitations of your investigation and how they may affect the validity of its results. Finally, it is essential to outline a timeline for the completion of your project. When describing research methods, it is crucial to be as detailed and specific as possible. You should also demonstrate that you have a well-developed understanding of research methods you strategize to use and the potential implications of their application. When crafting your dissertations proposals, use understandable language as well as avoid technical wording or jargon. Also, you should include a brief description of how the dissemination of results from your study will be so that policymakers or other stakeholders can use them in a meaningful way. Example: Dissertation proposal methodology
For my dissertation, I plan to undertake a qualitative case study of technology's role in American education. Specifically, I will look at implementing technology-based learning environments in three urban school districts. I will use a combination of surveys and interviews with teachers, administrators, parents, and students to gather data. The surveys will focus on attitudes towards technology in the classroom, resource access, and comfort with using technology for studying. The interviews will dig deeper into these topics and allow me to gain more insight into the implementation of technology-based education. Additionally, I plan to observe classrooms and document how technology facilitates knowledge gain. Data will be analyzed using a combination of thematic and content analysis. All findings will be documented in writing and shared publicly through a final report, website, presentations, and other appropriate outlets. All participants will remain anonymous, and the collection of data will be in a secure manner.
6. Mention Implications and Possible Limitations
Considering any potential limitations and implications of the study is an integral part of writing a dissertation or thesis research proposal. When discussing your research's repercussions and possible shortcomings, it is essential to consider how you will handle unforeseen outcomes, errors, or biases that may arise during your investigation. Writers should identify and mention how they'll address the limitations as they prepare a dissertation proposal. This section should include a discussion of how to use results of your study to inform policy decisions or other initiatives. Being honest and realistic in the descriptions of any potential drawbacks that could impact the validity of your results is an advisable way for you to do a thesis or dissertation proposal. Consider any possible ethical considerations that could arise during your research and how to deal with them. Sample of dissertation proposal implications
The implications of this study are twofold. First, it will provide valuable insight into how technology can be utilized most effectively in urban classrooms to improve the quality of education. The results will provide policymakers and other stakeholders with the information necessary to guide decisions regarding technology use in urban schools. Second, this investigation will provide teachers and other educators with a better understanding of the challenges they may face when implementing technology. This will allow educators to better prepare for and respond to these challenges, resulting in more effective implementation of technology-based learning environments. The research will add to the ongoing conversation about the use of technology in education and will contribute to a better understanding of how to use it effectively.
7. List Your References
The last step illustrating how to write a thesis proposal is providing a list of references consulted throughout the writing process. Bibliographies should include scholarly articles, books, and journals, among others, that have informed the research question, literature review, methodology, and other sources mentioned in any part of the proposal. It is crucial to ensure that sources you list are accurate, up-to-date, and appropriate for your dissertation topic proposal. In this section, students should format their references according to the specific style guidelines required by your university. Remember to meet the required total number of citations for your dissertation research proposal as guided. Keep in mind that not all sources are credible for thesis research proposal. You should also provide a copy of any ethics approval forms or permissions granted by your institution to conduct your research.
Dissertation Proposal Format
The dissertation and thesis proposal format will depend on the discipline and field of study. Generally, thesis proposals should follow the exact structure of any scholarly paper on the same subject. Typical dissertation proposal formats include:
- American Psychological Association (APA)
- Modern Language Association (MLA)
- Chicago Manual of Style
The format for writing dissertation proposals may vary according to the style used because each has certain conventions that must be adhered to accordingly. It is important to note that formatting should be consistent throughout your document. Before beginning the writing process, it is imperative to be familiar with all guidelines and requirements of an academic thesis proposal format. View the following guides on the most common styles to make sure you format your proposal properly:
- How to format an APA paper ?
- How to write in MLA format ?
- What is Chicago style format ?
Lastly, back up your work with evidence as well as sources demonstrating potential for success.
Thesis / Dissertation Proposal Examples
When writing your paper, reviewing thesis or dissertation proposal samples is crucial. These samples can provide an understanding of the structure, style, and expected content. They can also provide insight into the research methods and analysis techniques used throughout the thesis or dissertation process. We encourage you to check sample dissertation proposals found online or in public libraries. Many YouTube videos produced to offer clarity and reference are also available. Additionally, thesis proposals may be available through individual academic institutions. Below are samples for you to refer to: Thesis proposal example
Dissertation proposal example 1
Dissertation proposal sample 2
Dissertation Proposal Writing Tips
Writing a proposal for a dissertation requires you to stay focused and organized, as well as produce excellent work in a timely and efficient manner. To ensure the successful completion of your dissertation proposal, here are some valuable tips to keep in mind:
- Research thoroughly It is vital to take the time to research and reference all relevant material while writing your paper.
- Develop a timeline Developing a timeline and plan for completing each task is crucial because it helps keep you on track and ensure you meet all milestones promptly and effectively.
- Be organized Keeping your project well organized will make it easier to read and understand.
- Proofread Before submitting your paper, it is important to proofread and edit for any mistakes to ensure it is high quality and free from any errors.
- Check for free samples Consulting from any professional sample dissertation proposal by other students and experts is crucial before composing yours.
- References Lastly, ensure the credibility and accuracy of your document by referencing all sources used. Provide a bibliography list on the last page or pages of your paper.
Listed above dissertation and thesis proposal writing tips will help you to deliver an outstanding project that is well-planned, accurate as well as high quality.
Dissertation Proposal Checklist
A checklist is necessary to ensure you write a good proposal for a dissertation. This list should include all main topics that are critical to your paper. Here are some essential points to consider when writing a thesis proposal:
- checkbox I formulated an exact statement of purpose.
- checkbox I have presented a clear introduction and background information.
- checkbox I made my research on objectives and questions.
- checkbox I can say that my literature review includes enough information related to my topic.
- checkbox My research methodology includes all the necessary methods I used in my research.
- checkbox I have made all data analysis techniques.
- checkbox I made all calculations for the budget and timeline.
- checkbox My dissertation proposal contains an outline of the expected results.
- checkbox I am sure that I chose the right format for references and bibliography.
- checkbox I have checked the writing style and conventions.
- checkbox My dissertation proposal contains an acknowledgment section.
- checkbox I spent enough time proofreading and editing.
Considering the above items, you can ensure that you include all necessary elements in your research proposal . This will help you write an excellent thesis and get your work funded or accepted by your advisor.
Bottom Line on How to Write a Proposal For a Dissertation or Thesis
This article discussed in depth how to write a dissertation proposal. It has provided you with definition of a dissertation proposal, outlined its importance, length and structure, and how to write it. This blog also discussed the outline of a thesis proposal and listed things you should know before starting to write your own. We provided a step-by-step illustration of how to write and format your work. In addition, we provided thesis and dissertation proposal examples, tips, as well as a checklist of items to consider when crafting your project. Following the guidelines provided in this article should help you write an excellent work that meets your advisor's expectations. Once your topic is approved, make sure to check how to write a dissertation .
If you still struggle with crafting your proposal, our dissertation writing services are your best option. Our academic writers hold PhD degree and deliver top-quality studies within given deadlines.
FAQ About Thesis/ Dissertation Proposals
1. what is a thesis proposal.
A thesis proposal is a document that outlines the topic, defines issues that the paper will address, and explains why the subject is significant. The proposal aims to demonstrate that thesis topic addresses a critical educational problem, outlines a detailed plan for the research, and provides a practical approach for gathering and analyzing data.
2. How long should a thesis proposal be?
Crafting a thesis proposal requires time and dedication, but the length of your project can vary dramatically. While typically 15-20 pages (or up to 30) are needed for most proposals, Master's students may find they only need between 4-8 pages long due to the narrow scope of their research topic. The exact number of pages will mainly depend on which discipline you study as well as the focused nature of your investigation.
3. What is the difference between a dissertation and a proposal?
A dissertation is the main body of work that you produce for your degree, usually based on evidence gathered from research and experiments. On the other hand, a proposal outlines the research you plan to undertake and offers an overview of the topics covered in your thesis.
4. Should I include schedule in a dissertation proposal?
Yes, if you are applying for a grant or funding for the thesis project. In that case, including a schedule in your dissertation proposal outlining the timeline for research, data collection and analysis, and writing is necessary. This will help demonstrate how you plan to complete your project within the required timeframe.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The length of your proposal varies quite a bit depending on your discipline and type of work you're conducting. While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length.
The ideal length of a thesis proposal varies based on institutional guidelines, complexity of the study, and the intended audience, typically ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 words. A well-structured thesis proposal includes essential elements such as the title page, abstract, introduction, methodology, literature review, and implications.
Table of contents. Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
A Thesis Proposal is a document that sets forth what is to be studied as a thesis project, why and in what way. It contains a number of important sections. The purpose of the proposal is to communicate the plan for the work to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies via the First Reader (principal thesis advisor) and a Second Reader.
Gather all the necessary information before you start writing, and stick to formats that highlight the value of your proposal. The usual flow of writing a thesis proposal is as follows. 1. Outline. Start by coming up with a detailed description of the major points you'll be making in your thesis. 2.
2.3 Requirements of a Proposal. In order to achieve its purpose, a thesis proposal must fulfil the following general requirements: • Establish a context for your research and demonstrate the need for it. • Show that your study will meet this need, and how it will meet this need, i.e. the method you will use.
PhD-level dissertation proposals are much longer in terms of word count than Bachelors's and Master's level proposals. Bachelor's level dissertation proposals are about 5-6 pages long. Masters and Ph.D. level proposals' length varies from 15-25 pages depending on the academic subject and degree program's specifications.
The style and length of your thesis proposal will vary a bit depending on your school's requirements and the type of thesis you will eventually produce, but the fundamentals will always be the same, and those are what we're going to cover here. So let's look at how to write a thesis proposal.
Structure your proposal: A well-structured proposal typically includes an introduction, literature review, research question, methodology, and proposed timeline. Be sure to follow your institution's specific guidelines. Improve your writing skills: Clear, concise, and error-free writing is essential for an effective thesis proposal.
The dissertation proposal is a comprehensive statement on the extent and nature of the student's dissertation research interests. Students submit a draft of the proposal to their dissertation advisor between the end of the seventh and middle of the ninth quarters. The student must provide a written copy of the proposal to the faculty ...
Length of a Master's Thesis Proposal. The length of a master's thesis proposal differs from university to university and depends on the discipline of research as well. Usually, you have to include all the above-mentioned sections, and the length is around 8 pages and can go up to 12-15 pages for subjects such as the liberal arts.
The length of a dissertation proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the program. Most proposals are typically between 10 and 20 pages. Who reviews the dissertation proposal? The dissertation proposal is typically reviewed by the student's academic committee. How long does it take to write a dissertation proposal?
Length The thesis proposal should be approximately 8 pages, excluding the annotated bibliography. Remember that this is a proposal, not the thesis itself; tell us what you propose to do and how, don't do it. Annotated Bibliography This bibliography should contain brief commentaries on no fewer than 10-15 relevant source works. back to top
Abstract. the abstract is a brief summary of your thesis proposal. its length should not exceed ~200 words. present a brief introduction to the issue. make the key statement of your thesis. give a summary of how you want to address the issue. include a possible implication of your work, if successfully completed.
An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000-15,000 words. A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words. A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words. However, none of these are strict guidelines - your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided ...
Most dissertation proposals are no less than 10 pages. However, the average length falls between 15 and 20 pages. Don't panic—if you have a strong hypothesis, identify the importance of your research and the prior research, and employ the proper methodology, you will be on your way to writing a successful dissertation proposal.
Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director. The proposal is normally between 15 to 25 pages in length. The CTP tutorial is not a course in the traditional sense. You work independently on your proposal with your research advisor ...
Sections, length, and formatting. Your thesis proposal must include the following sections, each strictly limited to the number of pages specified: Title page (1 page) Specific Aims (1 page) Research Context and Strategy (6 pages, including figures and tables) References. You should observe the following formatting requirements:
Doctoral Dissertation Proposal Guidelines . Writing a thesis proposal is an important and valuable precursor to preparing, researching and writing your doctoral dissertation. Although the nature, style and content of your dissertation proposal will vary ... Overall, your proposal should be 15-20 pages in length (excluding your bibliography ...
Therefore, all thesis/dissertation proposals are limited in length to the signature cover-sheet plus 15 or fewer double-spaced, numbered pages in a font size no smaller than 12 point. Proposals longer than this will not be accepted, however, appendices and references are not included in the 15-page limit. Proposals will also be returned for ...
Crafting a thesis proposal requires time and dedication, but the length of your project can vary dramatically. While typically 15-20 pages (or up to 30) are needed for most proposals, Master's students may find they only need between 4-8 pages long due to the narrow scope of their research topic.
This can be taken from your thesis proposal if your original plan succeeded, or adapted from your proposal based on your findings. Figures. 1-3 separate figures. Included figures should display key data from your thesis needed to support your takeaway conclusions. Each figure must include a caption.