Mathematics
Share this page.
This program is designed for students looking to conduct original mathematical research with the aim of becoming a research mathematician . Students will be located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, one of the most active centers of mathematics in the world. Other universities in the area include Boston College, Boston University, Brandeis University, MIT, and Northeastern University.
Students will have access to a wide range of resources including the Center of Mathematical Sciences and Applications, which brings together researchers from an extensive variety of disciplines and institutions and hosts conferences, seminars, and workshops.
Most graduates of the program have been very successful at securing postdoctoral fellowships in academia. A number of recent graduates have won prestigious fellowships including the Clay Fellowship, the Simons Fellowship, and NSF Graduate Research Fellowship. Others now have jobs in industry.
Additional information on the graduate program is available from the Department of Mathematics and requirements for the degree are detailed in Policies .

Admissions Requirements
Please review admissions requirements and other information before applying. You can find degree program-specific admissions requirements below and access additional guidance on applying from the Department of Mathematics .
Statement of Purpose
The statement of purpose should convince the admissions committee that the applicant is able to communicate effectively and with a deep understanding of mathematics. It is not intended to be a biographical sketch or a reflection on one’s decision to enter the field.
Standardized Tests
GRE General: Not Accepted GRE Subject: Required
Theses & Dissertations
Theses & Dissertations for Mathematics
See list of Mathematics faculty
APPLICATION DEADLINE
Questions about the program.
Overview of the PhD Program
For specific information on the Applied Mathematics PhD program, see the navigation links to the right.
What follows on this page is an overview of all Ph.D. programs at the School; additional information and guidance can be found on the Graduate Policies pages.
General Ph.D. Requirements
- 10 semester-long graduate courses, including at least 8 disciplinary. At least 5 of the 10 should be graduate-level SEAS "technical" courses (or FAS graduate-level technical courses taught by SEAS faculty), not including seminar/reading/project courses. Undergraduate-level courses cannot be used. For details on course requirements, see the school's overall PhD course requirements and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Program Plan (i.e., the set of courses to be used towards the degree) approval by the Committee on Higher Degrees (CHD).
- Minimum full-time academic residency of two years .
- Serve as a Teaching Fellow (TF) in one semester of the second year.
- Oral Qualifying Examination Preparation in the major field is evaluated in an oral examination by a qualifying committee. The examination has the dual purpose of verifying the adequacy of the student's preparation for undertaking research in a chosen field and of assessing the student's ability to synthesize knowledge already acquired. For details on arranging your Qualifying Exam, see the exam policies and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Committee Meetings : PhD students' research committees meet according to the guidelines in each area's "Committee Meetings" listing. For details see the "G3+ Committee Meetings" section of the Policies of the CHD and the individual program pages linked therein.
- Final Oral Examination (Defense) This public examination devoted to the field of the dissertation is conducted by the student's research committee. It includes, but is not restricted to, a defense of the dissertation itself. For details of arranging your final oral exam see the Ph.D. Timeline page.
- Dissertation Upon successful completion of the qualifying examination, a committee chaired by the research supervisor is constituted to oversee the dissertation research. The dissertation must, in the judgment of the research committee, meet the standards of significant and original research.
Optional additions to the Ph.D. program
Harvard PhD students may choose to pursue these additional aspects:
- a Secondary Field (which is similar to a "minor" subject area). SEAS offers PhD Secondary Field programs in Data Science and in Computational Science and Engineering . GSAS lists secondary fields offered by other programs.
- a Master of Science (S.M.) degree conferred en route to the Ph.D in one of several of SEAS's subject areas. For details see here .
- a Teaching Certificate awarded by the Derek Bok Center for Teaching and Learning .
SEAS PhD students may apply to participate in the Health Sciences and Technology graduate program with Harvard Medical School and MIT. Please check with the HST program for details on eligibility (e.g., only students in their G1 year may apply) and the application process.
In Applied Mathematics
- First-Year Exploration
- Areas of Application
- AM & Economics
- How to Declare
- Who are my Advisors?
- Secondary Field
- Senior Thesis
- Research for Course Credit (AM 91R & AM 99R)
- AB/SM Information
- Peer Concentration Advisors (PCA) Program
- Student Organizations
- How to Apply
- PhD Timeline
- PhD Model Program (Course Guidelines)
- Oral Qualifying Examination
- Committee Meetings
- Committee on Higher Degrees
- Research Interest Comparison
- Collaborations
- Cross-Harvard Engagement
- Clubs & Organizations
- Centers & Initiatives
- Alumni Stories
Ph.D. Program
Degree requirements.
In outline, to earn the PhD in either Mathematics or Applied Mathematics, the candidate must meet the following requirements.
- Take at least 4 courses, 2 or more of which are graduate courses offered by the Department of Mathematics
- Pass the six-hour written Preliminary Examination covering calculus, real analysis, complex analysis, linear algebra, and abstract algebra; students must pass the prelim before the start of their second year in the program (within three semesters of starting the program)
- Pass a three-hour, oral Qualifying Examination emphasizing, but not exclusively restricted to, the area of specialization. The Qualifying Examination must be attempted within two years of entering the program
- Complete a seminar, giving a talk of at least one-hour duration
- Write a dissertation embodying the results of original research and acceptable to a properly constituted dissertation committee
- Meet the University residence requirement of two years or four semesters
Detailed Regulations
The detailed regulations of the Ph.D. program are the following:
Course Requirements
During the first year of the Ph.D. program, the student must enroll in at least 4 courses. At least 2 of these must be graduate courses offered by the Department of Mathematics. Exceptions can be granted by the Vice-Chair for Graduate Studies.
Preliminary Examination
The Preliminary Examination consists of 6 hours (total) of written work given over a two-day period (3 hours/day). Exam questions are given in calculus, real analysis, complex analysis, linear algebra, and abstract algebra. The Preliminary Examination is offered twice a year during the first week of the fall and spring semesters.
Qualifying Examination
To arrange the Qualifying Examination, a student must first settle on an area of concentration, and a prospective Dissertation Advisor (Dissertation Chair), someone who agrees to supervise the dissertation if the examination is passed. With the aid of the prospective advisor, the student forms an examination committee of 4 members. All committee members can be faculty in the Mathematics Department and the chair must be in the Mathematics Department. The QE chair and Dissertation Chair cannot be the same person; therefore, t he Math member least likely to serve as the dissertation advisor should be selected as chair of the qualifying exam committee . The syllabus of the examination is to be worked out jointly by the committee and the student, but before final approval, it is to be circulated to all faculty members of the appropriate research sections. The Qualifying Examination must cover material falling in at least 3 subject areas and these must be listed on the application to take the examination. Moreover, the material covered must fall within more than one section of the department. Sample syllabi can be reviewed online or in 910 Evans Hall. The student must attempt the Qualifying Examination within twenty-five months of entering the PhD program. If a student does not pass on the first attempt, then, on the recommendation of the student's examining committee, and subject to the approval of the Graduate Division, the student may repeat the examination once. The examining committee must be the same, and the re-examination must be held within thirty months of the student's entrance into the PhD program. For a student to pass the Qualifying Examination, at least one identified member of the subject area group must be willing to accept the candidate as a dissertation student.
Department of Mathematics
Mathematics phd program.
The Ph.D. program in the Department of Mathematics provides students with in-depth knowledge and rigorous training in all the subject areas of mathematics. A core feature is the first-year program, which helps bring students to the forefront of modern mathematics. Students work closely with faculty and each other and participate fully in both research and student-run seminars.
Questions? Email [email protected]
- The firm deadline for applications for Autumn 2025, is December 5, 2024.
- The (general and advanced) GRE tests are no longer accepted. Please do not submit these scores.
PhD Program
More information and a full list of requirements for the PhD program in Mathematics can be found in the University Bulletin .
During their first year in the program, students typically engage in coursework and seminars which prepare them for the Qualifying Examinations . Currently, these two exams test the student’s breadth of knowledge in algebra and real analysis.
Starting in Autumn 2023, students will choose 2 out of 4 qualifying exam topics:
- real analysis
- geometry and topology
- applied mathematics
Course Requirements for students starting prior to Autumn 2023
To qualify for candidacy, the student must have successfully completed 27 units of Math graduate courses numbered between 200 and 297.
Within the 27 units, students must satisfactorily complete a course sequence. This can be fulfilled in one of the following ways:
- Math 215A, B, & C: Algebraic Topology, Differential Topology, and Differential Geometry
- Math 216A, B, & C: Introduction to Algebraic Geometry
- Math 230A, B, & C: Theory of Probability
- 3 quarter course sequence in a single subject approved in advance by the Director of Graduate Studies.
Course Requirements for students starting in Autumn 2023 and later
To qualify for candidacy, the student must have successfully completed 27 units of Math graduate courses numbered between 200 and 297. The course sequence requirement is discontinued for students starting in Autumn 2023 and later.
By the end of Spring Quarter of their second year in the program, students must have a dissertation advisor and apply for Candidacy.
During their third year, students will take their Area Examination , which must be completed by the end of Winter Quarter. This exam assesses the student’s breadth of knowledge in their particular area of research. The Area Examination is also used as an opportunity for the student to present their committee with a summary of research conducted to date as well as a detailed plan for the remaining research.
Years 4&5
Typically during the latter part of the fourth or early part of the fifth year of study, students are expected to finish their dissertation research. At this time, students defend their dissertation as they sit for their University Oral Examination. Following the dissertation defense, students take a short time to make final revisions to their actual papers and submit the dissertation to their reading committee for final approval.
Throughout the PhD Program
All students continue through each year of the program serving some form of Assistantship: Course, Teaching or Research, unless they have funding from outside the department.
Our graduate students are very active as both leaders and participants in seminars and colloquia in their chosen areas of interest.

Letters of recommendation
Personal statement or "statement of purpose", other stuff, funding expectations, more resources, ccny math department specific:, outside resources:, sample phd applications.

Ph.D. Program Overview
Description.
The graduate program in the field of mathematics at Cornell leads to the Ph.D. degree, which takes most students five to six years of graduate study to complete. One feature that makes the program at Cornell particularly attractive is the broad range of interests of the faculty . The department has outstanding groups in the areas of algebra, algebraic geometry, analysis, applied mathematics, combinatorics, dynamical systems, geometry, logic, Lie groups, number theory, probability, and topology. The field also maintains close ties with distinguished graduate programs in the fields of applied mathematics , computer science , operations research , and statistics .
Core Courses
A normal course load for a beginning graduate student is three courses per term.
There are no qualifying exams, but the program requires that all students pass four courses to be selected from the six core courses. First-year students are allowed to place out of some (possibly, all) of the core courses. In order to place out of a course, students should contact the faculty member who is teaching the course during the current academic year, and that faculty member will make a decision. The minimum passing grade for the core courses is B-; no grade is assigned for placing out of a core course.
At least two core courses should be taken (or placed out) by the end of the first year. At least four core courses should be taken (or placed out) by the end of the second year (cumulative). These time requirements can be waived for students with health problems or other significant non-academic problems. They can be also waived for students who take time-consuming courses in another area (for example, CS) and who have strong support from a faculty; requests from such students should be made before the beginning of the spring semester.
The core courses are distributed among three main areas: analysis, algebra and topology/geometry. A student must pass at least one course from each group. All entering graduate students are encouraged to eventually take all six core courses with the option of an S/U grade for two of them.
The six core courses are:
MATH 6110, Real Analysis
MATH 6120, Complex Analysis
MATH 6310, Algebra 1
MATH 6320, Algebra 2
MATH 6510, Introductory Algebraic Topology
MATH 6520, Differentiable Manifolds.
Students who are not ready to take some of the core courses may take MATH 4130-4140, Introduction to Analysis, and/or MATH 4330-4340, Introduction to Algebra, which are the honors versions of our core undergraduate courses.
"What is...?" Seminar
The "What Is...?" Seminar is a series of talks given by faculty in the graduate field of Mathematics. Speakers are selected by an organizing committee of graduate students. The goal of the seminar is to aid students in finding advisors.
Schedule for the "What Is...?" seminar
Special Committee
The Cornell Graduate School requires that every student selects a special committee (in particular, a thesis adviser, who is the chair or the committee) by the end of the third semester.
The emphasis in the Graduate School at Cornell is on individualized instruction and training for independent investigation. There are very few formal requirements and each student develops a program in conjunction with his or her special committee, which consists of three faculty members, some of which may be chosen from outside the field of mathematics.
Entering students are not assigned special committees. Such students may contact any of the members on the Advising Committee if they have questions or need advice.
Current Advising Committee
Analysis / Probability / Dynamical Systems / Logic: Lionel Levine Geometry / Topology / Combinatorics: Kathryn Mann Probability / Statistics: Philippe Sosoe Applied Mathematics Liaison: Richard Rand
Admission to Candidacy
To be admitted formally to candidacy for the Ph.D. degree, the student must pass the oral admission to candidacy examination or A exam. This must be completed before the beginning of the student's fourth year. Upon passing the A exam, the student will be awarded (at his/her request) an M.S. degree without thesis.
The admission to candidacy examination is given to determine if the student is “ready to begin work on a thesis.” The content and methods of examination are agreed on by the student and his/her special committee before the examination. The student must be prepared to answer questions on the proposed area of research, and to pass the exam, he/she must demonstrate expertise beyond just mastery of basic mathematics covered in the core graduate courses.
To receive an advanced degree a student must fulfill the residence requirements of the Graduate School. One unit of residence is granted for successful completion of one semester of full-time study, as judged by the chair of the special committee. The Ph.D. program requires a minimum of six residence units. This is not a difficult requirement to satisfy since the program generally takes five to six years to complete. A student who has done graduate work at another institution may petition to transfer residence credit but may not receive more than two such credits.
The candidate must write a thesis that represents creative work and contains original results in that area. The research is carried on independently by the candidate under the supervision of the chairperson of the special committee. By the time of the oral admission to candidacy examination, the candidate should have selected as chairperson of the committee the faculty member who will supervise the research. When the thesis is completed, the student presents his/her results at the thesis defense or B Exam. All doctoral students take a Final Examination (the B Exam, which is the oral defense of the dissertation) upon completion of all requirements for the degree, no earlier than one month before completion of the minimum registration requirement.
Masters Degree in the Minor Field
Ph.D. students in the field of mathematics may earn a Special Master's of Science in Computer Science. Interested students must apply to the Graduate School using a form available for this purpose. To be eligible for this degree, the student must have a member representing the minor field on the special committee and pass the A-exam in the major field. The rules and the specific requirements for each master's program are explained on the referenced page.
Cornell will award at most one master's degree to any student. In particular, a student awarded a master's degree in a minor field will not be eligible for a master's degree in the major field.
Graduate Student Funding
Funding commitments made at the time of admission to the Ph.D. program are typically for a period of five years. Support in the sixth year is available by application, as needed. Support in the seventh year is only available by request from an advisor, and dependent on the availability of teaching lines. Following a policy from the Cornell Graduate School, students who require more than seven years to complete their degree shall not be funded as teaching assistants after the 14th semester.
Special Requests
Students who have special requests should first discuss them with their Ph.D. advisor (or with a field member with whom they work, if they don't have an advisor yet). If the advisor (or field faculty) supports the request, then it should be sent to the Director of Graduate Studies.
RIT graduate pursues Ph.D. across time zones
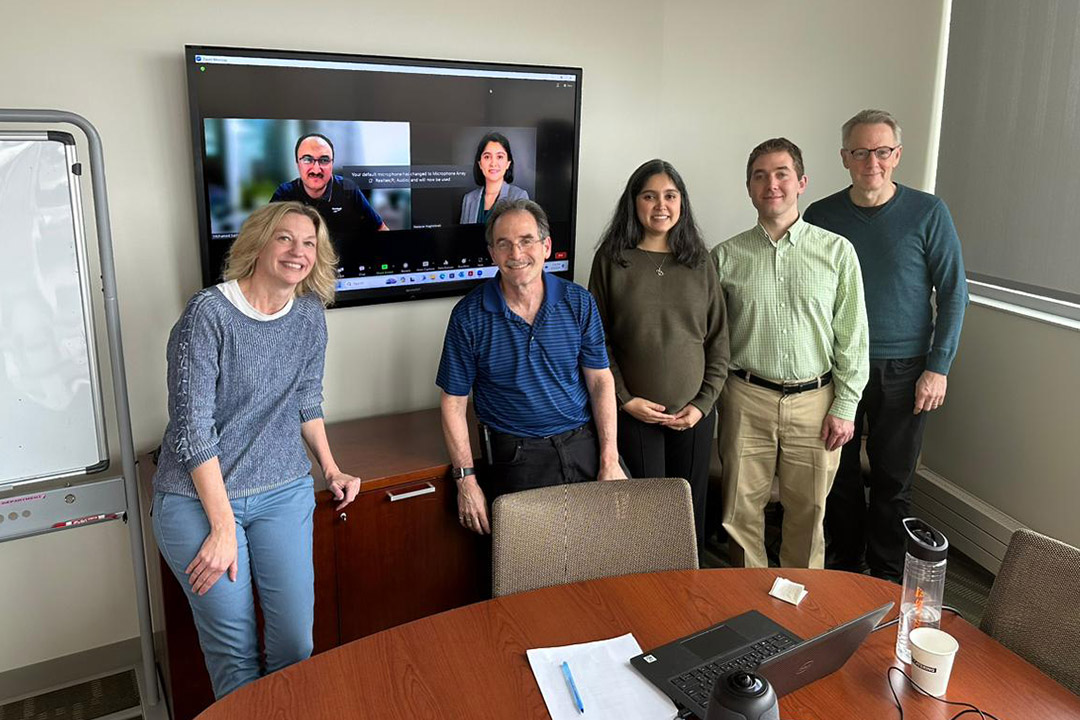

Nastaran Nagshineh, center, defended her Ph.D. thesis at RIT in April. Faculty from RIT’s Rochester and Dubai campuses served on her thesis committee and include, from left to right, Kathleen Lamkin-Kennard, Steven Weinstein, Nathaniel Barlow, and David Kofke (a professor at the University at Buffalo). Mohamed Samaha participated remotely and appears on the video screen behind the group and alongside Nagshineh’s picture.
Nastaran Nagshineh is one of the first Ph.D. candidates to bridge RIT’s Rochester and Dubai campuses. Her accomplishment creates a path for future students at the university’s international campuses.
Nagshineh completed her Ph.D. in mathematical modeling while working full time as a mathematics lecturer at RIT Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, teaching as many as five classes a semester. She described her Ph.D. journey as “an exercise in perseverance” due to competing demands and long days. Rochester is eight hours behind Dubai, and the time difference meant many late-night classes and meetings.
“I saw this collaboration as an opportunity, rather than as a challenge, because my primary adviser, Dr. Steven Weinstein (RIT professor of chemical engineering), and my co-adviser, Dr. Mohamed Samaha (RIT Dubai associate professor of mechanical engineering), both have the same area of research interest,” she said. “They both worked toward my success.”
Nagshineh is one of 67 RIT Ph.D. students who defended their thesis this academic year and who will earn their doctorate. RIT awarded 63 Ph.D. degrees in 2023.
In 2020-2021, RIT’s Graduate School met and surpassed the university’s goal of conferring 50 Ph.D. degrees during an academic year. That number will continue to grow as students cycle through the seven new Ph.D. programs that RIT has added since 2017, said Diane Slusarski , dean of RIT’s Graduate School.
Meeting these goals puts RIT on a path toward achieving an “R1,” or research-intensive designation, from the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Learning. RIT is currently ranked as an R2 institution . Many factors go into changing a university’s status, including research investment and maintaining a three-year average of 70 Ph.D. degrees awarded per year, according to Slusarski.
“We have met the goals of the strategic plan, and now we look forward to contributing to the research innovation in the future,” Slusarski said. “We want to help the new programs thrive and win national research awards.”
RIT’s emphasis on high-level research is seen in Nagshineh’s Ph.D. work. She applies mathematical modeling to the field of fluid dynamics. Her research has been published in top-tier journals and has gained notice, said Weinstein, her thesis adviser.
Weinstein describes Nagshineh’s accomplishments as “a testament to a fantastic work ethic and commitment” and is inspirational to younger students at Rochester and Dubai.
“The collaboration between RIT Dubai/Rochester has continued,” he said. “Another paper was submitted a few weeks ago with Mohamed Samaha and Nate Barlow (RIT associate professor in the School of Mathematics and Statistics) as co-authors, as well as Cade Reinberger, a younger Ph.D. student in my research group.”
Mathematical modeling is one of RIT’s newer Ph.D. degree programs, and Nagshineh is among its earliest graduates. The program has doubled in size since it began accepting students in 2017, Slusarski said. This past fall, the mathematical modeling program had 35 students, with two graduating this year.
Altogether, RIT has 13 Ph.D. degree programs currently enrolling 438 students, with computing and information sciences accounting for the largest with 117 students. RIT’s other Ph.D. programs include astrophysical sciences and technology , biomedical and chemical engineering , business administration , color science , electrical and computer engineering, imaging science , mechanical and industrial engineering , microsystems engineering , and sustainability .
New programs in cognitive science and physics will launch in the fall.
The growth in RIT graduate education—with more than 3,000 master’s and doctoral students—reflects a demographic change in the student population, Slusarski said. “We have a higher percentage of women in the graduate programs than we have for RIT undergraduate programs.”
RIT’s graduate programs enroll 42 percent women, according to Christie Leone , assistant dean for the Graduate School.
Nagshineh, who also holds an MS in electrical engineering from RIT Dubai, welcomes her role as a mentor to other women students on both campuses.
“As a young woman in an Arabic country, the power of women is often underestimated and undervalued, and I hope to serve as a role model to female students, especially those that question their path,” Nagshineh said.
She plans to continue in her career as a professor and a researcher. “I would like to pursue a research program where I can advise my own students and teach them more deeply.”
Recommended News
May 13, 2024

Ceramics and Illustration graduate Emma Herz Thakur travels to France as a Fulbright awardee
Emma Herz Thakur ’24 feels fortunate that at RIT she met people who have won major grants, had their work featured in museums, and are connected with scholars from around the world. Now, she is one of them.

New graduate Peyton D’Anthony wins Fulbright award to teach in Kosovo
Peyton D’Anthony enjoys identifying patterns and creating new connections. Those are just two of the skills she hopes to instill in her students as a teacher in Kosovo this fall.

Graduate Joseph Casale ready to return to Malaysia as a Fulbright awardee
Joseph Casale had hardly been on a plane when he traveled to Malaysia to do research a year ago. Now, he gets the opportunity to do it again.

Mikkael Lamoca receives Fulbright scholarship to complete cutting-edge STEM cell research
Conducting hands-on research was a hallmark of the time Mikkael Lamoca ‘24 (biomedical engineering), ‘24 MS (science, technology, and public policy) spent at RIT. A Fulbright award presents him a new opportunity to conduct cutting-edge research at one of the top universities in Asia.
Demystifying Math 55
By anastasia yefremova.
Few undergraduate level classes have the distinction of nation-wide recognition that Harvard University’s Math 55 has. Officially comprised of Mathematics 55A “Studies in Algebra and Group Theory” and Mathematics 55B “Studies in Real and Complex Analysis,” it is technically an introductory level course. It is also a veritable legend among high schoolers and college students alike, renowned as — allegedly — the hardest undergraduate math class in the country. It has been mentioned in books and articles, has its own Wikipedia page, and has been the subject of countless social media posts and videos.
Most recently, Harvard junior Mahad Khan created a TikTok video dedicated to Math 55 that has received over 360,000 views to date. His is only one of many — his older brother created one, too — but it has the distinction of an insider’s perspective. “I thought it would be interesting if I cleared up the misconceptions about Math 55,” Khan said. While he hadn’t taken the course himself, he wanted to go beyond its reputation. “I wanted to get a real perspective by interviewing a former student and current course assistant.”
Over the years, perception of Math 55 has become based less on the reality of the course itself and more on a cumulative collection of lore and somewhat sensationalist rumors. It’s tempting to get swept up in the thrill of hearsay but while there might be kernels of truth to some of the stories, many of them are outdated and taken out of context. At the end of the day, however, Math 55 is a class like any other. Below, we take a stab at busting some of the more well known and persistent myths about the class. Or, at the very least, offering an extra layer of clarity.
Myth #1: Math 55 is only for high school math geniuses
Most articles or mentions of Math 55 refer to it as filled with math competition champions and genius-level wunderkinds. The class is supposedly legendary among high school math prodigies, who hear terrifying stories about it in their computer camps and at the International Math Olympiad. There are even rumors of a special test students have to take before they are even allowed into Math 55. But while familiarity with proof-based mathematics is considered a plus for those interested in the course, there is no prerequisite for competition or research experience.
In fact students whose only exposure to advanced math has been through olympiads and summer research programs can have a harder time adjusting. Their approach to the material tends to be understandably more solitary and that can be a disadvantage for the level of collaboration higher level mathematics require. “It has become a lot more open to people with different backgrounds,” said Professor Denis Auroux , who teaches Math 55,. “Our slogan is, if you’re reasonably good at math, you love it, and you have lots of time to devote to it, then Math 55 is completely fine for you.”
Also, there is no extra test to get into the class.
Myth #2: Just take a graduate class, instead
Math 55 is hard. Whether you’re just 55-curious, or a past or present student in the class, this is something everyone agrees on. The course condenses four years of math into two semesters, after all. “For the first semester, you work on linear and abstract algebra with a bit of representation theory,” said sophomore math concentrator Dora Woodruff. “The second semester is real and complex analysis, and a little bit of algebraic topology. That’s almost the whole undergraduate curriculum.” Woodruff — incidentally, the student Khan interviewed — took Math 55 as a freshman and returned her second year as a course assistant. She is intimately familiar with the course’s difficulty level.
So why not just take an upper level undergraduate course to begin with or even one at a graduate level, if you’re really looking for a challenge? What justifies the existence of a class with the difficulty level of Math 55? One argument is that the course helps structure and systemize the knowledge with which many students come to Harvard. It gives them a firm background in preparation for the rest of their math education. Math 55 is difficult and it is purposefully structured that way as it’s meant to help students mature as mathematicians rather than as simple course takers.
But more importantly, “it’s just not true that Math 55 is at the level of a graduate class,” Auroux said. “It goes through several upper division undergraduate math classes with maybe a bit more advanced digressions into material here and there, but it sticks very close to what is taught in 100-level classes. The difference is we go through it at a faster pace, maybe with more challenging homework, and ideally as a community of people bringing our heads together.”
A core goal of Math 55, according to Auroux, is to build a sense of community. Other schools might encourage advanced first-year students to take upper level undergraduate or even graduate classes, but Math 55 helps build a cohort of like-minded people who really like math, are good at it, and want to do a lot of it during their time at Harvard. That’s the experience Woodruff had, as well. “The community can be very strong,” she said. “You meet a lot of other people very interested in math and stay friends with them for the rest of college.”
Myth #3: Homework takes between 24 and 60 hours
Horror stories of endless homework are synonymous with the class. You’ll read or hear about “24 to 60 hours per week on homework” in almost every reference to Math 55. But one, there is a world of difference between 24 and 60 hours that is never explained, and two, this timeframe is quite misaligned with reality.
Auroux frequently sends out surveys to his students asking how long homework takes them and the average for most is closer to 15 hours a week. Those with more extensive prior math backgrounds can take as little as five to ten hours. The key factor is collaboration. “This class doesn’t lend itself to self-study,” Auroux stressed. Once they have thought about each problem set on their own, students are welcome and encouraged to talk to their friends and collaborate. “As soon as I see that something took over 30 hours I ask the student, do you know you’re supposed to be working with people and come ask me questions when you’re stuck?”
It is true that between reviewing lectures, digesting the material, and solving the problem sets, students usually end up devoting between 20 and 30 hours a week to the class. However, that includes the time dedicated to homework. So while students are discouraged from taking too many difficult classes and extracurriculars in the same semester as Math 55, they are also not expected to spend the time equivalent to a full-time job on their problem sets every week.
Myth #4: less than half of the class makes it to the second semester
Math 55 is just as infamous for its attrition rate as it is for its difficulty. Most sources like to cite the 1970 class, which began with 75 students and — between the advanced nature of the material and the time-constraints under which students had to work — ended with barely 20. Since then, the rumor has been that the Math 55 class shrinks by half its original size or more before the first semester is over. The reality is much less shocking and a bit more complicated.
Enrollment in this past fall semester’s Math 55A peaked at (ironically) 55 students. Well into the spring semester’s Math 55B, 47 students were still enrolled in the course. “On average, a drop of about 10-15 percent is much closer to what I would expect,” Auroux said. And those numbers become even more flexible if one takes into consideration the weeks math students have at the beginning of each semester to try out different classes and “shop” around before they have to commit to anything. This means students find their way in and out of Math 55 in a variety of ways over the course of the academic year.
According to Auroux, some students shop Math 55 in the fall and switch to the less intense Math 25 for the remainder of the semester. Others start out in Math 25 and, if not sufficiently challenged, switch to Math 55. Even people who end up in academia are not exempt from this. During his time as a student, our own Department of Mathematics’ Professor Emeritus Benedict Gross switched to the lower level Math 21 after two weeks in Math 55. In fact, those two weeks almost made him reconsider his desire to pursue mathematics. “By the beginning of sophomore year, I had decided to major in physics,” he recalled. “But during shopping period that fall, I walked past a math class taught by Andrew Gleason and stopped in to listen. It turned out to be Math 55.” He enrolled and by the end of the semester had found his vocation in mathematics.
All this means that Auroux sees student numbers vacillate up and down throughout the academic year. “There are about four or five students in this spring semester’s Math 55 that took Math 25 or even Math 22 in the fall, and they’re doing mostly fine,” he said. “It’s a lot of work, but I think they’re having a great time.”
Myth #5: 55-er culture is cult-y and exclusionary
Even though her experience with Math 55 was a positive one, Woodruff is very aware of the unhealthy culture the class has been rumored to cultivate. It’s easy for students to form exclusionary cliques that consist only of other Math 55 students, and some look down on anyone taking lower level math classes. But Woodruff also stressed that the instructors are very aware of this and actively take steps to curb that kind of toxic behavior. She said Auroux frequently brings up the importance of keeping the Math 55 community inclusive through Slack messages and lecture references.
Some students come to Harvard just for the opportunity to take Math 55. Some view enrolling in the class as proof of their mathematical gumption and competence. A Harvard Independent article called Math 55 the “premiere mathematical challenge for overachieving and…ridiculously mathy freshmen” and a piece in The Harvard Crimson referred to it as “a bit of a status thing as far as math majors here are concerned.” Over the years, the Harvard Department of Mathematics has taken steps to correct these assumptions.
For one thing, neither the Math 55A nor the Math 55B official course descriptions boast the dubious honor of referring to it as “probably the most difficult undergraduate math class in the country” (don’t trust everything you read on Wikipedia). For another, “we’re trying to emphasize that there’s no magic to Math 55,” Auroux said. “It contains the same material as some of the other classes we have. People who take it are not intrinsically better or smarter than the ones who don’t.”
Myth #6: You have to take Math 55 if you’re serious about going into academia
One reason math concentrators could feel pressured to enroll in Math 55 is because they view it as a prerequisite for a career in academia. It’s a sort of badge of honor and proof of their commitment to the field of mathematics. It is true that quite a few graduates of the course have gone on to pursue a career in mathematics. Woodruff herself believes that will be the most likely path for her, and several faculty members in our own Department of Mathematics took Math 55 during their days as Harvard freshmen.
“Several times in my research career when I understood something fundamental, I would realize that this was what Math 55 was trying to teach us,” Gross said. “It was an amazing introduction to the whole of mathematics and it was transformative for me.” In fact, Gross met Higgins Professor of Mathematics Joe Harris when they took the class together, forging a lifelong friendship. When they returned to Harvard as faculty, they took turns teaching Math 25 and Math 55.
However, Auroux is quick to point out that while many graduates of the course do end up in academia, most professional mathematicians have likely never even heard of Math 55. “I would like to think that it’s a success story if people end up doing math, because the goal of Math 55 is to show students how beautiful math can be,” he said. “If they love it enough to go to grad school and become mathematicians, that’s wonderful. And if they want to take that math knowledge and do something else with their life, that’s just as wonderful.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revlong57. •. Honestly, if you're looking at doing a PhD in applied math, it will probably have value in a future career outside of academia. Pure math is basically only useful for academic jobs. Now, let's look at the pros and cons of getting a PhD in applied math. Source, I'm getting a PhD in an applied math area.
The PhD was quite hard and taxing on my mental health. Having a rather theoretic topic, you sit at your desk all day and try to come up with an idea. ... A theoretical math PhD is (obviously) extremely difficult and most of the topics in it tend not be directly beneficial towards future employment in anything but more work in abstract ...
Guide to Graduate Studies. The Ph.D. program of the Harvard Department of Mathematics is designed to help motivated students develop their understanding and enjoyment of mathematics. Enjoyment and understanding of the subject, as well as enthusiasm in teaching it, are greater when one is actively thinking about mathematics in one's own way.
0. Roughly: good grades (3.8+ GPA) in difficult courses, good test scores (80+ percentile on math GRE subject test [not the regular GRE math, which you should get a ~perfect score on without studying]), strong research background and good letters corresponding to it. That will get you into schools in the top ~30.
Noam Elkies finished his PhD in math at the age of 20. The average graduate student would probably take anywhere from 4 - 5 years. That doesn't mean Noam was a god among graduate students when he was a graduate student, and that's the reason he was able to finish his thesis faster than Joe Schmoe (though he is quite exceptional) and Joe Schmoe ...
Admissions. Financial Support. Graduate Program Administrator. Marjorie Bell (she/her) 617-496-5211. [email protected]. Science Center Room 331. 1 Oxford Street. Cambridge, MA 02138.
The application deadline for fall 2024 admission has passed. Applications for fall 2025 admission will open in September 2024. For information on admissions and financial support, please visit the Harvard Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. Harvard Griffin GSAS is committed to ensuring that our application fee does ...
A number of recent graduates have won prestigious fellowships including the Clay Fellowship, the Simons Fellowship, and NSF Graduate Research Fellowship. Others now have jobs in industry. Additional information on the graduate program is available from the Department of Mathematics and requirements for the degree are detailed in Policies.
a Secondary Field (which is similar to a "minor" subject area). SEAS offers PhD Secondary Field programs in Data Science and in Computational Science and Engineering. GSAS lists secondary fields offered by other programs. a Master of Science (S.M.) degree conferred en route to the Ph.D in one of several of SEAS's subject areas.
Students who entered the program in Autumn 2023 or later. To qualify for the Ph.D. in Mathematics, students must choose and pass examinations in two of the following four areas: algebra. real analysis. geometry and topology. applied mathematics. The exams each consist of two parts. Students are given three hours for each part.
In outline, to earn the PhD in either Mathematics or Applied Mathematics, the candidate must meet the following requirements. During the first year of the Ph.D. program: Take at least 4 courses, 2 or more of which are graduate courses offered by the Department of Mathematics. Pass the six-hour written Preliminary Examination covering calculus ...
The Ph.D. program in the Department of Mathematics provides students with in-depth knowledge and rigorous training in all the subject areas of mathematics. A core feature is the first-year program, which helps bring students to the forefront of modern mathematics. Students work closely with faculty and each other and participate fully in both ...
PhD Program. More information and a full list of requirements for the PhD program in Mathematics can be found in the University Bulletin. During their first year in the program, students typically engage in coursework and seminars which prepare them for the Qualifying Examinations . Currently, these two exams test the student's breadth of ...
The department runs tutorials and offers several introductory graduate courses (e.g. Math 212a, 213a, 230a, 231a, and 232a) to help students acquire the necessary broad basic background in mathematics to pass the exam. The exam consists of three, three-hour papers held on consecutive afternoons. Each paper has six questions, one each on the ...
website creator . Program of Study. The Department of Mathematics offers a program leading to the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. The PhD program is an intensive course of study designed for the full-time student planning a career in research and teaching at the university level or in quantitative research and development in industry or government.
4+ weeks before your first deadline, email and/or talk to your potential letter writers to let them know you would like to request a letter of recommendation for PhD programs (or REUs or whatever). Potentially set up a meeting to discuss the process with them. Be polite, respectful, organized, and efficient.
Description. The graduate program in the field of mathematics at Cornell leads to the Ph.D. degree, which takes most students five to six years of graduate study to complete. One feature that makes the program at Cornell particularly attractive is the broad range of interests of the faculty. The department has outstanding groups in the areas of ...
I had to escape 'grad student guilt'. To make it through my Ph.D., I had to escape 'grad student guilt'. A version of this story appeared in Science, Vol 384, Issue 6695. For just a moment, my mind was quiet. The incessant, bleak internal monologue was silenced. Clinging to the climbing wall by my fingers and toes, using every muscle to ...
RIT awarded 63 Ph.D. degrees in 2023. In 2020-2021, RIT's Graduate School met and surpassed the university's goal of conferring 50 Ph.D. degrees during an academic year. That number will continue to grow as students cycle through the seven new Ph.D. programs that RIT has added since 2017, said Diane Slusarski, dean of RIT's Graduate School.
Myth #2: Just take a graduate class, instead. Math 55 is hard. Whether you're just 55-curious, or a past or present student in the class, this is something everyone agrees on. The course condenses four years of math into two semesters, after all. "For the first semester, you work on linear and abstract algebra with a bit of representation ...
"Today marks a significant milestone in your journey, and it is no doubt the culmination of a lot of hard work, dedication and determination." The College of Engineering, Mathematics and Science recognized over 300 candidates, including 19 graduate degree candidates. ... The College of Liberal Arts and Education recognized more than 260 ...