argumentative essay
What is argumentative essay definition, usage, and literary examples, argumentative essay definition.
An argumentative essay [ahr-gyuh-MEN-tuh-tiv ess-ay] is an essay in which the writer uses thorough research to defend their position on a disputable topic. An argumentative essay contains a thesis, multiple body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The body can also include a counterargument.

Roots in Ancient Rhetoric
The argumentative essay format has roots in ancient rhetoric , which Greco-Romans considered the “art of persuasion .” While ancient societies primarily used speech to persuade their audiences, modern academics most often use written arguments based on the ancient orators’ classical argument structure.
As detailed in Plato’s On Rhetoric , a classical argument—similar to an argumentative essay—begins with an introduction ( exordium ), gives necessary context ( narratio ), offers the writer’s position and thesis ( proposito and partitio ), presents supporting research to confirm the writer’s argument or refute other positions ( confirmatio and refutatio ), and ends with a conclusion ( peroration ).
The Five-Part Argumentative Essay
- Thesis and Introduction: Often only a sentence long, the thesis concisely describes the writer’s position, and the introductory paragraph provides context.
- Body Paragraphs and Counterargument: There are generally three body paragraphs used to present research that supports the writer’s thesis. They can also include a counterargument that details and refutes opposing positions.
- Conclusion: This summarizes the writer’s evidential findings and reiterates the thesis.
Classic Models
There are two main models of argumentation: the Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
The Toulmin Model
British philosopher Stephen Toulmin founded the Toulmin model in his book The Uses of Argument (1958). This style of argumentation, an expansion of the classical model, has six major components:
- Claim: The thesis
- Data : The research supporting the thesis
- Warrant: An explanation that connects the data and the thesis
- Backing: Support for the warrant
- Modality: Confirmation of the arguer’s conviction in the thesis
- Rebuttal : A counterargument or exceptions to the thesis
The Rogerian Model
Psychotherapist Carl Rogers developed the Rogerian model as a form of rhetoric that favored empathy and multiple perspectives . This model attempts to weigh each option fairly before persuading its audience. The model consists of the following components:
- Introduction: Introduction of the topic as a mutual problem
- Opposing Position: An explanation of the writer’s position that recognizes opposing positions
- Context for Opposing Position: An outline of the opposing position and confirmation of its validity
- Argued Position: A presentation of the writer’s position
- Context for Position: This offers data that validates writer’s position
- Benefits: An explanation of how the writer’s position benefits the opposition
Argumentative vs. Expository Essays
Similar to an argumentative essay, an expository essay uses evidence to inform its readers. It teaches readers how to do something, analyzes a topic, gives step-by-step instructions, or describes an event.
Expository essays differ from argumentative essays in that they’re often assigned within a classroom structure, restricting the amount of outside research. The aim of an expository essay is more often to explain something rather than persuade its audience.
Argumentative Essays in Education
Argumentative essays appear primarily as assignments in education and academia. Writing in this form requires that students understand alternative opinions, learn the value of thorough research, and learn to persuade their audiences using evidence.
Examples of Argumentative Essays
1. Matthew L. Sanders, “ Becoming a Learner ”
“Becoming a Learner: Realizing the Opportunity of Education” is a 2018 essay by Matthew L. Sanders. In the essay, Sanders argues against the traditional understanding of a college education and suggests students seek out critical and creative thinking skills rather than job marketability. Sanders outlines his thesis clearly:
The primary purpose of college isn’t learning a specific set of professional skills; the primary purpose of college is to become a learner.
2. Margaret Fuller, “ The Great Lawsuit ”
In Fuller’s 1843 essay, she compares the plight of women to that of slaves and argues that women should have the same rights as men:
As men become aware that all men have not had a fair chance, they are inclined to say that no women have had a fair chance.
3. Nicholas Carr, “ Is Google Making us Stupid? ”
In his 2008 essay, Carr uses mostly anecdotal evidence to support his thesis. He posits that having access to the internet’s trove of information contributes to an inability to read longer-form materials. In the following excerpt, he presents current research that supports his thesis:
They [University College London] found that people using the sites exhibited “a form of skimming activity,” hopping from on source to another and rarely returning to any source they’d already visited. They typically read no more than one or two pages of an article or book before they would “bounce” out to another site.
Further Research on Argumentative Essays
The Purdue Online Writing Lab outlines effective argumentative essays.
Find examples of argumentative essays on LiteraryDevices.net and Prepscholar.com .
Masterclass.com has an argumentative essay step-by-step writing guide available.
Related Terms
- Expository Essay
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Argumentative Essay
Definition of argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay is a type of essay that presents arguments about both sides of an issue. It could be that both sides are presented equally balanced, or it could be that one side is presented more forcefully than the other. It all depends on the writer, and what side he supports the most. The general structure of an argumentative essay follows this format:
- Introduction : Attention Grabber/ hook , Background Information , Thesis Statement
- Body : Three body paragraphs (three major arguments)
- Counterargument : An argument to refute earlier arguments and give weight to the actual position
- Conclusion : Rephrasing the thesis statement , major points, call to attention, or concluding remarks .
Models for Argumentative Essays
There are two major models besides this structure given above, which is called a classical model. Two other models are the Toulmin and Rogerian models.
Toulmin model is comprised of an introduction with a claim or thesis, followed by the presentation of data to support the claim. Warrants are then listed for the reasons to support the claim with backing and rebuttals. However, the Rogerian model asks to weigh two options, lists the strengths and weaknesses of both options, and gives a recommendation after an analysis.
Five Types of Argument Claims in Essay Writing
There are five major types of argument claims as given below.
- A claim of definition
- A claim about values
- A claim about the reason
- A claim about comparison
- A claim about policy or position
A writer makes a claim about these issues and answers the relevant questions about it with relevant data and evidence to support the claim.
Three Major Types of Argument and How to Apply Them
Classical argument.
This model of applying argument is also called the Aristotelian model developed by Aristotle. This type of essay introduces the claim, with the opinion of the writer about the claim, its both perspectives, supported by evidence, and provides a conclusion about the better perspective . This essay includes an introduction, a body having the argument and support, a counter-argument with support, and a conclusion.
Toulmin Argument
This model developed by Stephen Toulmin is based on the claim followed by grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier, and rebuttal . Its structure comprises, an introduction having the main claim, a body with facts and evidence, while its rebuttal comprises counter-arguments and a conclusion.
Rogerian Argument
The third model by Carl Rogers has different perspectives having proof to support and a conclusion based on all the available perspectives. Its structure comprises an introduction with a thesis, the opposite point of view and claim, a middle-ground for both or more perspectives, and a conclusion.
Four Steps to Outline and Argumentative Essay
There are four major steps to outlining an argumentative essay.
- Introduction with background, claim, and thesis.
- Body with facts, definition, claim, cause and effect, or policy.
- The opposing point of view with pieces of evidence.
Examples of Argumentative Essay in Literature
Example #1: put a little science in your life by brian greene.
“When we consider the ubiquity of cellphones, iPods, personal computers and the Internet, it’s easy to see how science (and the technology to which it leads) is woven into the fabric of our day-to-day activities . When we benefit from CT scanners, M.R.I. devices, pacemakers and arterial stents, we can immediately appreciate how science affects the quality of our lives. When we assess the state of the world, and identify looming challenges like climate change, global pandemics, security threats and diminishing resources, we don’t hesitate in turning to science to gauge the problems and find solutions. And when we look at the wealth of opportunities hovering on the horizon—stem cells, genomic sequencing, personalized medicine, longevity research, nanoscience, brain-machine interface, quantum computers, space technology—we realize how crucial it is to cultivate a general public that can engage with scientific issues; there’s simply no other way that as a society we will be prepared to make informed decisions on a range of issues that will shape the future.”
These two paragraphs present an argument about two scientific fields — digital products and biotechnology. It has also given full supporting details with names.
Example #2: Boys Here, Girls There: Sure, If Equality’s the Goal by Karen Stabiner
“The first objections last week came from the National Organization for Women and the New York Civil Liberties Union, both of which opposed the opening of TYWLS in the fall of 1996. The two groups continue to insist—as though it were 1896 and they were arguing Plessy v. Ferguson—that separate can never be equal. I appreciate NOW ’s wariness of the Bush administration’s endorsement of single-sex public schools, since I am of the generation that still considers the label “feminist” to be a compliment—and many feminists still fear that any public acknowledgment of differences between the sexes will hinder their fight for equality .”
This paragraph by Karen Stabiner presents an objection to the argument of separation between public schools. It has been fully supported with evidence of the court case.
Example #3: The Flight from Conversation by Sherry Turkle
“We’ve become accustomed to a new way of being “ alone together.” Technology-enabled, we are able to be with one another, and also elsewhere, connected to wherever we want to be. We want to customize our lives. We want to move in and out of where we are because the thing we value most is control over where we focus our attention. We have gotten used to the idea of being in a tribe of one, loyal to our own party.”
This is an argument by Sherry Turkle, who beautifully presented it in the first person plural dialogues . However, it is clear that this is part of a greater argument instead of the essay.
Function of Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay presents both sides of an issue. However, it presents one side more positively or meticulously than the other one, so that readers could be swayed to the one the author intends. The major function of this type of essay is to present a case before the readers in a convincing manner, showing them the complete picture.
Synonyms of Argumentative Essay
Argumentative Essay synonyms are as follows: persuasive essays, research essays, analytical essays, or even some personal essays.
Related posts:
- Elements of an Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Types of Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay

4-minute read
- 30th April 2022
An argumentative essay is a structured, compelling piece of writing where an author clearly defines their stance on a specific topic. This is a very popular style of writing assigned to students at schools, colleges, and universities. Learn the steps to researching, structuring, and writing an effective argumentative essay below.
Requirements of an Argumentative Essay
To effectively achieve its purpose, an argumentative essay must contain:
● A concise thesis statement that introduces readers to the central argument of the essay
● A clear, logical, argument that engages readers
● Ample research and evidence that supports your argument
Approaches to Use in Your Argumentative Essay
1. classical.
● Clearly present the central argument.
● Outline your opinion.
● Provide enough evidence to support your theory.
2. Toulmin
● State your claim.
● Supply the evidence for your stance.
● Explain how these findings support the argument.
● Include and discuss any limitations of your belief.
3. Rogerian
● Explain the opposing stance of your argument.
● Discuss the problems with adopting this viewpoint.
● Offer your position on the matter.
● Provide reasons for why yours is the more beneficial stance.
● Include a potential compromise for the topic at hand.
Tips for Writing a Well-Written Argumentative Essay
● Introduce your topic in a bold, direct, and engaging manner to captivate your readers and encourage them to keep reading.
● Provide sufficient evidence to justify your argument and convince readers to adopt this point of view.
● Consider, include, and fairly present all sides of the topic.
● Structure your argument in a clear, logical manner that helps your readers to understand your thought process.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Discuss any counterarguments that might be posed.
● Use persuasive writing that’s appropriate for your target audience and motivates them to agree with you.
Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay
Follow these basic steps to write a powerful and meaningful argumentative essay :
Step 1: Choose a topic that you’re passionate about
If you’ve already been given a topic to write about, pick a stance that resonates deeply with you. This will shine through in your writing, make the research process easier, and positively influence the outcome of your argument.
Step 2: Conduct ample research to prove the validity of your argument
To write an emotive argumentative essay , finding enough research to support your theory is a must. You’ll need solid evidence to convince readers to agree with your take on the matter. You’ll also need to logically organize the research so that it naturally convinces readers of your viewpoint and leaves no room for questioning.
Step 3: Follow a simple, easy-to-follow structure and compile your essay
A good structure to ensure a well-written and effective argumentative essay includes:
Introduction
● Introduce your topic.
● Offer background information on the claim.
● Discuss the evidence you’ll present to support your argument.
● State your thesis statement, a one-to-two sentence summary of your claim.
● This is the section where you’ll develop and expand on your argument.
● It should be split into three or four coherent paragraphs, with each one presenting its own idea.
● Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that indicates why readers should adopt your belief or stance.
● Include your research, statistics, citations, and other supporting evidence.
● Discuss opposing viewpoints and why they’re invalid.
● This part typically consists of one paragraph.
● Summarize your research and the findings that were presented.
● Emphasize your initial thesis statement.
● Persuade readers to agree with your stance.
We certainly hope that you feel inspired to use these tips when writing your next argumentative essay . And, if you’re currently elbow-deep in writing one, consider submitting a free sample to us once it’s completed. Our expert team of editors can help ensure that it’s concise, error-free, and effective!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Argumentative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Modes of Discourse—Exposition, Description, Narration, Argumentation (EDNA)—are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes. Although these genres have been criticized by some composition scholars, the Purdue OWL recognizes the wide spread use of these approaches and students’ need to understand and produce them.
What is an argumentative essay?
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner.
Please note : Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative essay differs from the expository essay in the amount of pre-writing (invention) and research involved. The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
Argumentative essay assignments generally call for extensive research of literature or previously published material. Argumentative assignments may also require empirical research where the student collects data through interviews, surveys, observations, or experiments. Detailed research allows the student to learn about the topic and to understand different points of view regarding the topic so that she/he may choose a position and support it with the evidence collected during research. Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning.
The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
In the first paragraph of an argument essay, students should set the context by reviewing the topic in a general way. Next the author should explain why the topic is important ( exigence ) or why readers should care about the issue. Lastly, students should present the thesis statement. It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse. Transitions should wrap up the idea from the previous section and introduce the idea that is to follow in the next section.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the discussion of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. In addition, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph. Some paragraphs will directly support the thesis statement with evidence collected during research. It is also important to explain how and why the evidence supports the thesis ( warrant ).
However, argumentative essays should also consider and explain differing points of view regarding the topic. Depending on the length of the assignment, students should dedicate one or two paragraphs of an argumentative essay to discussing conflicting opinions on the topic. Rather than explaining how these differing opinions are wrong outright, students should note how opinions that do not align with their thesis might not be well informed or how they might be out of date.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
The argumentative essay requires well-researched, accurate, detailed, and current information to support the thesis statement and consider other points of view. Some factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal evidence should support the thesis. However, students must consider multiple points of view when collecting evidence. As noted in the paragraph above, a successful and well-rounded argumentative essay will also discuss opinions not aligning with the thesis. It is unethical to exclude evidence that may not support the thesis. It is not the student’s job to point out how other positions are wrong outright, but rather to explain how other positions may not be well informed or up to date on the topic.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students may begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize the information presented in the body of the essay. Restate why the topic is important, review the main points, and review your thesis. You may also want to include a short discussion of more research that should be completed in light of your work.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of World War II and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the argument in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the conflict. Therefore, the argumentative essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph essay
A common method for writing an argumentative essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of (a) an introductory paragraph (b) three evidentiary body paragraphs that may include discussion of opposing views and (c) a conclusion.
Longer argumentative essays
Complex issues and detailed research call for complex and detailed essays. Argumentative essays discussing a number of research sources or empirical research will most certainly be longer than five paragraphs. Authors may have to discuss the context surrounding the topic, sources of information and their credibility, as well as a number of different opinions on the issue before concluding the essay. Many of these factors will be determined by the assignment.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)

We define an argumentative essay as a type of essay that presents arguments about both sides of an issue. The purpose is to convince the reader to accept a particular viewpoint or action. In an argumentative essay, the writer takes a stance on a controversial or debatable topic and supports their position with evidence, reasoning, and examples. The essay should also address counterarguments, demonstrating a thorough understanding of the topic.
Table of Contents
- What is an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay structure
- Argumentative essay outline
- Types of argument claims
How to write an argumentative essay?
- Argumentative essay writing tips
- Good argumentative essay example
How to write a good thesis
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents a coherent and logical analysis of a specific topic. 1 The goal is to convince the reader to accept the writer’s point of view or opinion on a particular issue. Here are the key elements of an argumentative essay:
- Thesis Statement : The central claim or argument that the essay aims to prove.
- Introduction : Provides background information and introduces the thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph addresses a specific aspect of the argument, presents evidence, and may include counter arguments.
Articulate your thesis statement better with Paperpal. Start writing now!
- Evidence : Supports the main argument with relevant facts, examples, statistics, or expert opinions.
- Counterarguments : Anticipates and addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen the overall argument.
- Conclusion : Summarizes the main points, reinforces the thesis, and may suggest implications or actions.

Argumentative essay structure
Aristotelian, Rogerian, and Toulmin are three distinct approaches to argumentative essay structures, each with its principles and methods. 2 The choice depends on the purpose and nature of the topic. Here’s an overview of each type of argumentative essay format.
Have a looming deadline for your argumentative essay? Write 2x faster with Paperpal – Start now!
Argumentative essay outline
An argumentative essay presents a specific claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning. Here’s an outline for an argumentative essay, along with examples for each section: 3
1. Introduction :
- Hook : Start with a compelling statement, question, or anecdote to grab the reader’s attention.
Example: “Did you know that plastic pollution is threatening marine life at an alarming rate?”
- Background information : Provide brief context about the issue.
Example: “Plastic pollution has become a global environmental concern, with millions of tons of plastic waste entering our oceans yearly.”
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position.
Example: “We must take immediate action to reduce plastic usage and implement more sustainable alternatives to protect our marine ecosystem.”
2. Body Paragraphs :
- Topic sentence : Introduce the main idea of each paragraph.
Example: “The first step towards addressing the plastic pollution crisis is reducing single-use plastic consumption.”
- Evidence/Support : Provide evidence, facts, statistics, or examples that support your argument.
Example: “Research shows that plastic straws alone contribute to millions of tons of plastic waste annually, and many marine animals suffer from ingestion or entanglement.”
- Counterargument/Refutation : Acknowledge and refute opposing viewpoints.
Example: “Some argue that banning plastic straws is inconvenient for consumers, but the long-term environmental benefits far outweigh the temporary inconvenience.”
- Transition : Connect each paragraph to the next.
Example: “Having addressed the issue of single-use plastics, the focus must now shift to promoting sustainable alternatives.”
3. Counterargument Paragraph :
- Acknowledgement of opposing views : Recognize alternative perspectives on the issue.
Example: “While some may argue that individual actions cannot significantly impact global plastic pollution, the cumulative effect of collective efforts must be considered.”
- Counterargument and rebuttal : Present and refute the main counterargument.
Example: “However, individual actions, when multiplied across millions of people, can substantially reduce plastic waste. Small changes in behavior, such as using reusable bags and containers, can have a significant positive impact.”
4. Conclusion :
- Restatement of thesis : Summarize your main argument.
Example: “In conclusion, adopting sustainable practices and reducing single-use plastic is crucial for preserving our oceans and marine life.”
- Call to action : Encourage the reader to take specific steps or consider the argument’s implications.
Example: “It is our responsibility to make environmentally conscious choices and advocate for policies that prioritize the health of our planet. By collectively embracing sustainable alternatives, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier future.”

Types of argument claims
A claim is a statement or proposition a writer puts forward with evidence to persuade the reader. 4 Here are some common types of argument claims, along with examples:
- Fact Claims : These claims assert that something is true or false and can often be verified through evidence. Example: “Water boils at 100°C at sea level.”
- Value Claims : Value claims express judgments about the worth or morality of something, often based on personal beliefs or societal values. Example: “Organic farming is more ethical than conventional farming.”
- Policy Claims : Policy claims propose a course of action or argue for a specific policy, law, or regulation change. Example: “Schools should adopt a year-round education system to improve student learning outcomes.”
- Cause and Effect Claims : These claims argue that one event or condition leads to another, establishing a cause-and-effect relationship. Example: “Excessive use of social media is a leading cause of increased feelings of loneliness among young adults.”
- Definition Claims : Definition claims assert the meaning or classification of a concept or term. Example: “Artificial intelligence can be defined as machines exhibiting human-like cognitive functions.”
- Comparative Claims : Comparative claims assert that one thing is better or worse than another in certain respects. Example: “Online education is more cost-effective than traditional classroom learning.”
- Evaluation Claims : Evaluation claims assess the quality, significance, or effectiveness of something based on specific criteria. Example: “The new healthcare policy is more effective in providing affordable healthcare to all citizens.”
Understanding these argument claims can help writers construct more persuasive and well-supported arguments tailored to the specific nature of the claim.
If you’re wondering how to start an argumentative essay, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with the argumentative essay format and writing process.
- Choose a Topic: Select a topic that you are passionate about or interested in. Ensure that the topic is debatable and has two or more sides.
- Define Your Position: Clearly state your stance on the issue. Consider opposing viewpoints and be ready to counter them.
- Conduct Research: Gather relevant information from credible sources, such as books, articles, and academic journals. Take notes on key points and supporting evidence.
- Create a Thesis Statement: Develop a concise and clear thesis statement that outlines your main argument. Convey your position on the issue and provide a roadmap for the essay.
- Outline Your Argumentative Essay: Organize your ideas logically by creating an outline. Include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis.
- Write the Introduction: Start with a hook to grab the reader’s attention (a quote, a question, a surprising fact). Provide background information on the topic. Present your thesis statement at the end of the introduction.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that relates to the thesis. Support your points with evidence and examples. Address counterarguments and refute them to strengthen your position. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs.
- Address Counterarguments: Acknowledge and respond to opposing viewpoints. Anticipate objections and provide evidence to counter them.
- Write the Conclusion: Summarize the main points of your argumentative essay. Reinforce the significance of your argument. End with a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking statement.
- Revise, Edit, and Share: Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency. Check for grammatical and spelling errors. Share your essay with peers, friends, or instructors for constructive feedback.
- Finalize Your Argumentative Essay: Make final edits based on feedback received. Ensure that your essay follows the required formatting and citation style.
Struggling to start your argumentative essay? Paperpal can help – try now!
Argumentative essay writing tips
Here are eight strategies to craft a compelling argumentative essay:
- Choose a Clear and Controversial Topic : Select a topic that sparks debate and has opposing viewpoints. A clear and controversial issue provides a solid foundation for a strong argument.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather relevant information from reputable sources to support your argument. Use a variety of sources, such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert opinions, to strengthen your position.
- Create a Strong Thesis Statement : Clearly articulate your main argument in a concise thesis statement. Your thesis should convey your stance on the issue and provide a roadmap for the reader to follow your argument.
- Develop a Logical Structure : Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on a specific point of evidence that contributes to your overall argument. Ensure a logical flow from one point to the next.
- Provide Strong Evidence : Support your claims with solid evidence. Use facts, statistics, examples, and expert opinions to support your arguments. Be sure to cite your sources appropriately to maintain credibility.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counterarguments. Addressing and refuting alternative perspectives strengthens your essay and demonstrates a thorough understanding of the issue. Be mindful of maintaining a respectful tone even when discussing opposing views.
- Use Persuasive Language : Employ persuasive language to make your points effectively. Avoid emotional appeals without supporting evidence and strive for a respectful and professional tone.
- Craft a Compelling Conclusion : Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and leave a lasting impression in your conclusion. Encourage readers to consider the implications of your argument and potentially take action.

Good argumentative essay example
Let’s consider a sample of argumentative essay on how social media enhances connectivity:
In the digital age, social media has emerged as a powerful tool that transcends geographical boundaries, connecting individuals from diverse backgrounds and providing a platform for an array of voices to be heard. While critics argue that social media fosters division and amplifies negativity, it is essential to recognize the positive aspects of this digital revolution and how it enhances connectivity by providing a platform for diverse voices to flourish. One of the primary benefits of social media is its ability to facilitate instant communication and connection across the globe. Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram break down geographical barriers, enabling people to establish and maintain relationships regardless of physical location and fostering a sense of global community. Furthermore, social media has transformed how people stay connected with friends and family. Whether separated by miles or time zones, social media ensures that relationships remain dynamic and relevant, contributing to a more interconnected world. Moreover, social media has played a pivotal role in giving voice to social justice movements and marginalized communities. Movements such as #BlackLivesMatter, #MeToo, and #ClimateStrike have gained momentum through social media, allowing individuals to share their stories and advocate for change on a global scale. This digital activism can shape public opinion and hold institutions accountable. Social media platforms provide a dynamic space for open dialogue and discourse. Users can engage in discussions, share information, and challenge each other’s perspectives, fostering a culture of critical thinking. This open exchange of ideas contributes to a more informed and enlightened society where individuals can broaden their horizons and develop a nuanced understanding of complex issues. While criticisms of social media abound, it is crucial to recognize its positive impact on connectivity and the amplification of diverse voices. Social media transcends physical and cultural barriers, connecting people across the globe and providing a platform for marginalized voices to be heard. By fostering open dialogue and facilitating the exchange of ideas, social media contributes to a more interconnected and empowered society. Embracing the positive aspects of social media allows us to harness its potential for positive change and collective growth.
- Clearly Define Your Thesis Statement: Your thesis statement is the core of your argumentative essay. Clearly articulate your main argument or position on the issue. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Provide Strong Supporting Evidence: Back up your thesis with solid evidence from reliable sources and examples. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, anecdotes, or real-life examples. Make sure your evidence is relevant to your argument, as it impacts the overall persuasiveness of your thesis.
- Anticipate Counterarguments and Address Them: Acknowledge and address opposing viewpoints to strengthen credibility. This also shows that you engage critically with the topic rather than presenting a one-sided argument.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay with Paperpal?
Writing a winning argumentative essay not only showcases your ability to critically analyze a topic but also demonstrates your skill in persuasively presenting your stance backed by evidence. Achieving this level of writing excellence can be time-consuming. This is where Paperpal, your AI academic writing assistant, steps in to revolutionize the way you approach argumentative essays. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Paperpal to write your essay:
- Sign Up or Log In: Begin by creating an account or logging into paperpal.com .
- Navigate to Paperpal Copilot: Once logged in, proceed to the Templates section from the side navigation bar.
- Generate an essay outline: Under Templates, click on the ‘Outline’ tab and choose ‘Essay’ from the options and provide your topic to generate an outline.
- Develop your essay: Use this structured outline as a guide to flesh out your essay. If you encounter any roadblocks, click on Brainstorm and get subject-specific assistance, ensuring you stay on track.
- Refine your writing: To elevate the academic tone of your essay, select a paragraph and use the ‘Make Academic’ feature under the ‘Rewrite’ tab, ensuring your argumentative essay resonates with an academic audience.
- Final Touches: Make your argumentative essay submission ready with Paperpal’s language, grammar, consistency and plagiarism checks, and improve your chances of acceptance.
Paperpal not only simplifies the essay writing process but also ensures your argumentative essay is persuasive, well-structured, and academically rigorous. Sign up today and transform how you write argumentative essays.
The length of an argumentative essay can vary, but it typically falls within the range of 1,000 to 2,500 words. However, the specific requirements may depend on the guidelines provided.
You might write an argumentative essay when: 1. You want to convince others of the validity of your position. 2. There is a controversial or debatable issue that requires discussion. 3. You need to present evidence and logical reasoning to support your claims. 4. You want to explore and critically analyze different perspectives on a topic.
Argumentative Essay: Purpose : An argumentative essay aims to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a specific point of view or argument. Structure : It follows a clear structure with an introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, counterarguments and refutations, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is formal and relies on logical reasoning, evidence, and critical analysis. Narrative/Descriptive Essay: Purpose : These aim to tell a story or describe an experience, while a descriptive essay focuses on creating a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. Structure : They may have a more flexible structure. They often include an engaging introduction, a well-developed body that builds the story or description, and a conclusion. Tone : The tone is more personal and expressive to evoke emotions or provide sensory details.
- Gladd, J. (2020). Tips for Writing Academic Persuasive Essays. Write What Matters .
- Nimehchisalem, V. (2018). Pyramid of argumentation: Towards an integrated model for teaching and assessing ESL writing. Language & Communication , 5 (2), 185-200.
- Press, B. (2022). Argumentative Essays: A Step-by-Step Guide . Broadview Press.
- Rieke, R. D., Sillars, M. O., & Peterson, T. R. (2005). Argumentation and critical decision making . Pearson/Allyn & Bacon.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
Make Your Research Paper Error-Free with Paperpal’s Online Spell Checker
The do’s & don’ts of using generative ai tools ethically in academia, you may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid....

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
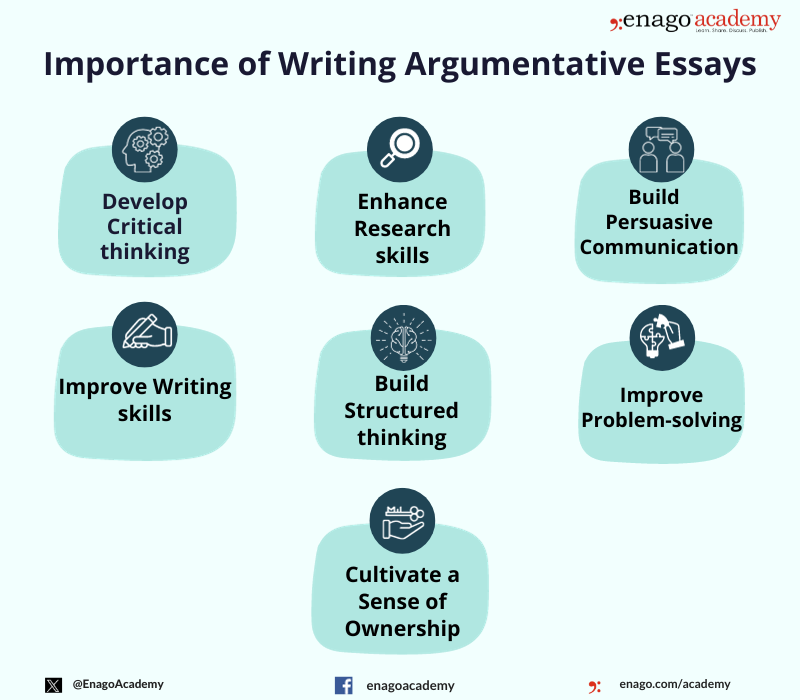
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,
“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…

- Career Corner
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 6 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Argumentative Essay Examples to Inspire You (+ Free Formula)
.webp)
Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Have you ever been asked to explain your opinion on a controversial issue?
- Maybe your family got into a discussion about chemical pesticides
- Someone at work argues against investing resources into your project
- Your partner thinks intermittent fasting is the best way to lose weight and you disagree
Proving your point in an argumentative essay can be challenging, unless you are using a proven formula.
Argumentative essay formula & example
In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments. Then, again, development of the rebuttal. This is followed by an example, and ends with a summary. This is a very basic structure, but it gives you a bird-eye-view of how a proper argumentative essay can be built.

Writing an argumentative essay (for a class, a news outlet, or just for fun) can help you improve your understanding of an issue and sharpen your thinking on the matter. Using researched facts and data, you can explain why you or others think the way you do, even while other reasonable people disagree.
Free AI argumentative essay generator > Free AI argumentative essay generator >
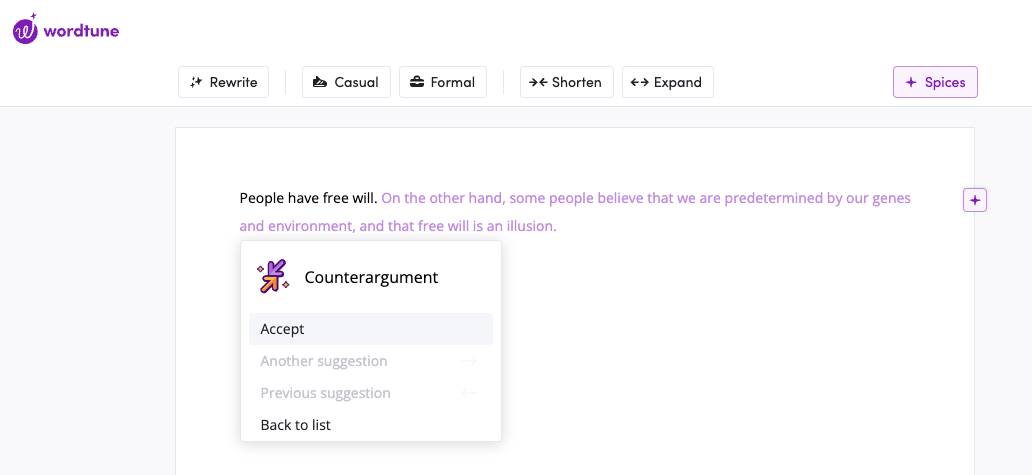
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an explanatory essay that takes a side.
Instead of appealing to emotion and personal experience to change the reader’s mind, an argumentative essay uses logic and well-researched factual information to explain why the thesis in question is the most reasonable opinion on the matter.
Over several paragraphs or pages, the author systematically walks through:
- The opposition (and supporting evidence)
- The chosen thesis (and its supporting evidence)
At the end, the author leaves the decision up to the reader, trusting that the case they’ve made will do the work of changing the reader’s mind. Even if the reader’s opinion doesn’t change, they come away from the essay with a greater understanding of the perspective presented — and perhaps a better understanding of their original opinion.
All of that might make it seem like writing an argumentative essay is way harder than an emotionally-driven persuasive essay — but if you’re like me and much more comfortable spouting facts and figures than making impassioned pleas, you may find that an argumentative essay is easier to write.
Plus, the process of researching an argumentative essay means you can check your assumptions and develop an opinion that’s more based in reality than what you originally thought. I know for sure that my opinions need to be fact checked — don’t yours?
So how exactly do we write the argumentative essay?
How do you start an argumentative essay
First, gain a clear understanding of what exactly an argumentative essay is. To formulate a proper topic sentence, you have to be clear on your topic, and to explore it through research.
Students have difficulty starting an essay because the whole task seems intimidating, and they are afraid of spending too much time on the topic sentence. Experienced writers, however, know that there is no set time to spend on figuring out your topic. It's a real exploration that is based to a large extent on intuition.
6 Steps to Write an Argumentative Essay (Persuasion Formula)
Use this checklist to tackle your essay one step at a time:

1. Research an issue with an arguable question
To start, you need to identify an issue that well-informed people have varying opinions on. Here, it’s helpful to think of one core topic and how it intersects with another (or several other) issues. That intersection is where hot takes and reasonable (or unreasonable) opinions abound.
I find it helpful to stage the issue as a question.
For example:
Is it better to legislate the minimum size of chicken enclosures or to outlaw the sale of eggs from chickens who don’t have enough space?
Should snow removal policies focus more on effectively keeping roads clear for traffic or the environmental impacts of snow removal methods?
Once you have your arguable question ready, start researching the basic facts and specific opinions and arguments on the issue. Do your best to stay focused on gathering information that is directly relevant to your topic. Depending on what your essay is for, you may reference academic studies, government reports, or newspaper articles.
Research your opposition and the facts that support their viewpoint as much as you research your own position . You’ll need to address your opposition in your essay, so you’ll want to know their argument from the inside out.
2. Choose a side based on your research
You likely started with an inclination toward one side or the other, but your research should ultimately shape your perspective. So once you’ve completed the research, nail down your opinion and start articulating the what and why of your take.
What: I think it’s better to outlaw selling eggs from chickens whose enclosures are too small.
Why: Because if you regulate the enclosure size directly, egg producers outside of the government’s jurisdiction could ship eggs into your territory and put nearby egg producers out of business by offering better prices because they don’t have the added cost of larger enclosures.
This is an early form of your thesis and the basic logic of your argument. You’ll want to iterate on this a few times and develop a one-sentence statement that sums up the thesis of your essay.
Thesis: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with cramped living spaces is better for business than regulating the size of chicken enclosures.
Now that you’ve articulated your thesis , spell out the counterargument(s) as well. Putting your opposition’s take into words will help you throughout the rest of the essay-writing process. (You can start by choosing the counter argument option with Wordtune Spices .)

Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers, making the low-cost protein source harder to afford — especially for low-income consumers.
There may be one main counterargument to articulate, or several. Write them all out and start thinking about how you’ll use evidence to address each of them or show why your argument is still the best option.
3. Organize the evidence — for your side and the opposition
You did all of that research for a reason. Now’s the time to use it.
Hopefully, you kept detailed notes in a document, complete with links and titles of all your source material. Go through your research document and copy the evidence for your argument and your opposition’s into another document.
List the main points of your argument. Then, below each point, paste the evidence that backs them up.
If you’re writing about chicken enclosures, maybe you found evidence that shows the spread of disease among birds kept in close quarters is worse than among birds who have more space. Or maybe you found information that says eggs from free-range chickens are more flavorful or nutritious. Put that information next to the appropriate part of your argument.
Repeat the process with your opposition’s argument: What information did you find that supports your opposition? Paste it beside your opposition’s argument.
You could also put information here that refutes your opposition, but organize it in a way that clearly tells you — at a glance — that the information disproves their point.
Counterargument: Outlawing the sale of eggs from chickens with too small enclosures will immediately drive up egg prices for consumers.
BUT: Sicknesses like avian flu spread more easily through small enclosures and could cause a shortage that would drive up egg prices naturally, so ensuring larger enclosures is still a better policy for consumers over the long term.
As you organize your research and see the evidence all together, start thinking through the best way to order your points.
Will it be better to present your argument all at once or to break it up with opposition claims you can quickly refute? Would some points set up other points well? Does a more complicated point require that the reader understands a simpler point first?
Play around and rearrange your notes to see how your essay might flow one way or another.
4. Freewrite or outline to think through your argument
Is your brain buzzing yet? At this point in the process, it can be helpful to take out a notebook or open a fresh document and dump whatever you’re thinking on the page.
Where should your essay start? What ground-level information do you need to provide your readers before you can dive into the issue?
Use your organized evidence document from step 3 to think through your argument from beginning to end, and determine the structure of your essay.

There are three typical structures for argumentative essays:
- Make your argument and tackle opposition claims one by one, as they come up in relation to the points of your argument - In this approach, the whole essay — from beginning to end — focuses on your argument, but as you make each point, you address the relevant opposition claims individually. This approach works well if your opposition’s views can be quickly explained and refuted and if they directly relate to specific points in your argument.
- Make the bulk of your argument, and then address the opposition all at once in a paragraph (or a few) - This approach puts the opposition in its own section, separate from your main argument. After you’ve made your case, with ample evidence to convince your readers, you write about the opposition, explaining their viewpoint and supporting evidence — and showing readers why the opposition’s argument is unconvincing. Once you’ve addressed the opposition, you write a conclusion that sums up why your argument is the better one.
- Open your essay by talking about the opposition and where it falls short. Build your entire argument to show how it is superior to that opposition - With this structure, you’re showing your readers “a better way” to address the issue. After opening your piece by showing how your opposition’s approaches fail, you launch into your argument, providing readers with ample evidence that backs you up.
As you think through your argument and examine your evidence document, consider which structure will serve your argument best. Sketch out an outline to give yourself a map to follow in the writing process. You could also rearrange your evidence document again to match your outline, so it will be easy to find what you need when you start writing.
5. Write your first draft
You have an outline and an organized document with all your points and evidence lined up and ready. Now you just have to write your essay.
In your first draft, focus on getting your ideas on the page. Your wording may not be perfect (whose is?), but you know what you’re trying to say — so even if you’re overly wordy and taking too much space to say what you need to say, put those words on the page.
Follow your outline, and draw from that evidence document to flesh out each point of your argument. Explain what the evidence means for your argument and your opposition. Connect the dots for your readers so they can follow you, point by point, and understand what you’re trying to say.
As you write, be sure to include:
1. Any background information your reader needs in order to understand the issue in question.
2. Evidence for both your argument and the counterargument(s). This shows that you’ve done your homework and builds trust with your reader, while also setting you up to make a more convincing argument. (If you find gaps in your research while you’re writing, Wordtune Spices can source statistics or historical facts on the fly!)

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. A conclusion that sums up your overall argument and evidence — and leaves the reader with an understanding of the issue and its significance. This sort of conclusion brings your essay to a strong ending that doesn’t waste readers’ time, but actually adds value to your case.
6. Revise (with Wordtune)
The hard work is done: you have a first draft. Now, let’s fine tune your writing.
I like to step away from what I’ve written for a day (or at least a night of sleep) before attempting to revise. It helps me approach clunky phrases and rough transitions with fresh eyes. If you don’t have that luxury, just get away from your computer for a few minutes — use the bathroom, do some jumping jacks, eat an apple — and then come back and read through your piece.
As you revise, make sure you …
- Get the facts right. An argument with false evidence falls apart pretty quickly, so check your facts to make yours rock solid.
- Don’t misrepresent the opposition or their evidence. If someone who holds the opposing view reads your essay, they should affirm how you explain their side — even if they disagree with your rebuttal.
- Present a case that builds over the course of your essay, makes sense, and ends on a strong note. One point should naturally lead to the next. Your readers shouldn’t feel like you’re constantly changing subjects. You’re making a variety of points, but your argument should feel like a cohesive whole.
- Paraphrase sources and cite them appropriately. Did you skip citations when writing your first draft? No worries — you can add them now. And check that you don’t overly rely on quotations. (Need help paraphrasing? Wordtune can help. Simply highlight the sentence or phrase you want to adjust and sort through Wordtune’s suggestions.)
- Tighten up overly wordy explanations and sharpen any convoluted ideas. Wordtune makes a great sidekick for this too 😉

Words to start an argumentative essay
The best way to introduce a convincing argument is to provide a strong thesis statement . These are the words I usually use to start an argumentative essay:
- It is indisputable that the world today is facing a multitude of issues
- With the rise of ____, the potential to make a positive difference has never been more accessible
- It is essential that we take action now and tackle these issues head-on
- it is critical to understand the underlying causes of the problems standing before us
- Opponents of this idea claim
- Those who are against these ideas may say
- Some people may disagree with this idea
- Some people may say that ____, however
When refuting an opposing concept, use:
- These researchers have a point in thinking
- To a certain extent they are right
- After seeing this evidence, there is no way one can agree with this idea
- This argument is irrelevant to the topic
Are you convinced by your own argument yet? Ready to brave the next get-together where everyone’s talking like they know something about intermittent fasting , chicken enclosures , or snow removal policies?
Now if someone asks you to explain your evidence-based but controversial opinion, you can hand them your essay and ask them to report back after they’ve read it.
Share This Article:

Preparing for Graduate School: 8 Tips to Know
How to Master Concise Writing: 9 Tips to Write Clear and Crisp Content

Title Case vs. Sentence Case: How to Capitalize Your Titles
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
Argumentative Essay – Outline, Form, and Examples

What is an argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay requires the writer to investigate a specific topic by collecting and evaluating evidence to establish a position on the subject matter.
When preparing to compose a good argumentative essay, utilize the following steps:
Step 1: Select a topic.
Step 2: Identify a position.
Step 3: Locate appropriate resources.
Step 4: Identify evidence supporting the position. ( NOTE: If there is little evidence in support of the claim, consider re-examining the main argument.)

When gathering evidence, use credible sources . To determine the credibility of the source, consider authority, currency, accuracy, and objectivity:
Who is the author ? Are they an expert in the field? Has a reputable publisher published the work?
How current is the information in the source? Does the currency of the source matter? Does the age of the source impact the content? Is there newer information that disproves the source’s information?
Can other sources verify the accuracy of the information? Does the information contradict that found in other commonly accepted sources?
Is there any evidence of bias, or is the source objective ? Is the research sponsored by an organization that may skew the information?
The following are typically recognized as providing appropriate, credible research material:
Peer-reviewed journals/research papers
Government agencies
Professional organizations
Library databases
Reference books

Writers should avoid using the following sources:
Social media posts
Out-of-date materials
Step 5: Utilize the research to determine a thesis statement that identifies the topic, position, and support(s).
Step 6: Use the evidence to construct an outline, detailing the main supports and relevant evidence.

Argumentative essay outline
After gathering all of the necessary research, the next step in composing an argumentative essay focuses on organizing the information through the use of an outline:
Introduction
Attention Grabber/Hook
Background Information: Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the reader needs to know to understand the argument.
Thesis: State the position in connection to the main topic and identify the supports that will help prove the argument.
Topic sentence
Identify evidence in support of the claim in the topic sentence
Explain how the evidence supports the argument
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 2 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Invite the audience to take a specific action.
Identify the overall importance of the topic and position.

How to write an argumentative essay
Regardless of the writer’s topic or point of view, an argumentative essay should include an introductory paragraph, body paragraphs, a conclusion, and works cited.
Background information
Body Paragraphs
Analysis of evidence
Rephrased thesis
Review of main ideas
Call to action
Works Cited

Argumentative essay introduction
The introduction sets the tone for the entire paper and introduces the argument. In general, the first paragraph(s) should attract the reader’s attention, provide relevant context, and conclude with a thesis statement.
To attract the reader's attention , start with an introductory device. There are several attention-grabbing techniques, the most common of which consist of the following:
The writer can emphasize the topic’s importance by explaining the current interest in the topic or indicating that the subject is influential.
Pertinent statistics give the paper an air of authority.
There are many reasons for a stimulating statement to surprise a reader. Sometimes it is joyful; sometimes it is shocking; sometimes it is surprising because of who said it.
An interesting incident or anecdote can act as a teaser to lure the reader into the remainder of the essay. Be sure that the device is appropriate for the subject and focus of what follows.
Provide the reader with relevant context and background information necessary to understand the topic.
Conclude with a thesis statement that identifies the overall purpose of the essay (topic and position). Writers can also include their support directly in the thesis, which outlines the structure of the essay for the reader.
Avoid the following when writing the introduction to argumentative writing:
Starting with dictionary definitions is too overdone and unappealing.
Do not make an announcement of the topic like “In this paper I will…” or “The purpose of this essay is to….”
Evidence supporting or developing the thesis should be in the body paragraphs, not the introduction.
Beginning the essay with general or absolute statements such as “throughout history...” or “as human beings we always...” or similar statements suggest the writer knows all of history or that all people behave or think in the same way.
Argumentative essay thesis
The thesis statement is the single, specific claim the writer sets out to prove and is typically positioned as the last sentence of the introduction . It is the controlling idea of the entire argument that identifies the topic, position, and reasoning.
When constructing a thesis for an argumentative paper, make sure it contains a side of the argument, not simply a topic. An argumentative thesis identifies the writer’s position on a given topic. If a position cannot be taken, then it is not argumentative thesis:
Topic: Capital punishment is practiced in many states.
Thesis: Capital punishment should be illegal.
While not always required, the thesis statement can include the supports the writer will use to prove the main claim. Therefore, a thesis statement can be structured as follows:
TOPIC + POSITION (+ SUPPORTS)
No Supports: College athletes (TOPIC) should be financially compensated (POSITION).
Supports: College athletes (TOPIC) should be financially compensated (POSITION) because they sacrifice their minds and bodies (SUPPORT 1), cannot hold
Argumentative essay body paragraphs
Body paragraphs can be of varying lengths, but they must present a coherent argument unified under a single topic. They are rarely ever longer than one page, double-spaced; usually they are much shorter.
Lengthy paragraphs indicate a lack of structure. Identify the main ideas of a lengthy paragraph to determine if they make more sense as separate topics in separate paragraphs.
Shorter paragraphs usually indicate a lack of substance; there is not enough evidence or analysis to prove the argument. Develop the ideas more or integrate the information into another paragraph.
The structure of an argumentative paragraph should include a topic sentence, evidence, and a transition.
The topic sentence is the thesis of the paragraph that identifies the arguable point in support of the main argument. The reader should know exactly what the writer is trying to prove within the paragraph by reading the first sentence.
The supporting evidence and analysis provide information to support the claim. There should be a balance between the evidence (facts, quotations, summary of events/plot, etc.) and analysis (interpretation of evidence). If the paragraph is evidence-heavy, there is not much of an argument; if it is analysis-heavy, there is not enough evidence in support of the claim.
The transition can be at the beginning or the end of a paragraph. However, it is much easier to combine the transition with the concluding observation to help the paragraphs flow into one another. Transitions in academic writing should tell the reader where you were, where you are going, and relate to the thesis.
Some essays may benefit from the inclusion of rebuttals to potential counterarguments of the writer’s position.
Argumentative essay conclusion
The conclusion should make readers glad they read the paper. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest readers but also enrich their understanding in some way. There are three aspects to follow when constructing the conclusion: rephrase the thesis, synthesize information, and call the reader to action.
Rephrased the thesis in the first sentence of the conclusion. It must be in different words; do not simply write it verbatim.
Synthesize the argument by showing how the paper's main points support the argument.
Propose a course of action or a solution to an issue. This can redirect the reader's thought process to apply the ideas to their life or to see the broader implications of the topic.
Avoid the following when constructing the conclusion:
Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as "in conclusion," "in summary," or "in closing;" although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as trite in writing
Introducing a new idea or subtopic in the conclusion
Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of the paper
Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper
Argumentative essay examples
Examples of argumentative essays vary depending upon the type:
Academic essays differ based upon the topic and position. These essays follow a more traditional structure and are typically assigned in high school or college. Examples of academic argumentative essay topics include the following:
Advantages or disadvantages of social media
Animal testing
Art education
Benefit or detriment of homework
Capital punishment
Class warfare
Immigration
School uniforms
Universal healthcare
Violence in video games
Argumentative literary essays are typically more informal and do not follow the same structure as an academic essay. The following are popular examples of argumentative literary essays:
“Letter from Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King, Jr.
“Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf
“Shooting an Elephant” by George Orwell
“Thoughts for the Times on War and Death” by Sigmund Freud
“Does the Truth Matter? Science, Pseudoscience, and Civilization” by Carl Sagan
“Self-Reliance” by Ralph Waldo Emerson
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays.
While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to demonstrate their research and analytical skills. The secret of a successful paper lies behind strong arguments and counterarguments. So, the writer should focus on facts and data rather than personal values and beliefs.
Besides, a good argumentative essay should be structured appropriately:
- The introduction and conclusion have to create a frame for the entire essay.
- The body paragraphs are supposed to cover the essential points.
- Supporting evidence should make a paper more professional and reputable.
Are you still wondering what an argumentative essay is and how to write it? Check out the sections below prepared by our experts . Here, you can find the most valuable info, helpful tips, and useful examples.
📜 Classic Strategy
📋 toulmin strategy, 🗣️ rogerian strategy, ✒️ fill in the blanks, 🔍 edit and proofread, 🔗 references, 📌 argumentative essay in a nutshell.
Are you trying to figure out what an argumentative essay is? It’s a type of academic paper that covers both sides of a given issue. An author can decide whether they aim to present both sides equally or support one side more dynamically.
One of the mistakes among students is the confusion of argumentative and persuasive essays . Do you want to figure out the differences? Take a look at the following table.
Before writing an argument essay, it would be helpful to choose an appropriate model to rely on. There are three strategies to consider: Classical, Toulmin, and Rogerian.
Look at the following sections and choose the most suitable one for you.
Are you wondering how to write an argumentative essay? Consider using the classical approach. It is the most popular way of composing an argumentative paper.
Under the classical strategy, the author has to follow these rules:
- research the issue;
- present both sides;
- express own opinion;
- prove the reader the validity of the conclusion.
It is up to the audience to decide whether your position is right or wrong. Yet, you should try to convince the readers of the effectiveness of your opinion.
Usually, the classical argument paper is structured in the following way:
- Introduction . Use the hook to catch the readers’ attention. State the problem and explain why your topic is relatable to the audience.
- General background. Introduce the general info and several facts about your issue.
- Thesis statement . State your position clearly and concisely.
- The central argument. Provide valid evidence and appropriate examples to support your position. Refer only to reliable sources.
- Rebuttal . Include a counter paragraph in your essay, presenting the opposing arguments. Provide specific examples to make the reader understand your position. Also, explain to the audience why the counterclaims are incorrect.
- Conclusion . Synthesize your arguments and counterarguments. Give the readers a question for further investigation of your problem. To make your essay more impressive, compose a memorable concluding sentence.
Toulmin strategy is the most suitable for the discussion of controversial issues. This model aims to find common ground through clear logic and valid evidence. Besides, the Toulmin strategy eliminates unnecessary things and limits the points to agree upon.
An argumentative essay written by the Toulmin model includes the following elements:
- Claim . A viewpoint that the author aims to prove.
- Evidence . Supportive facts from reliable resources that highlight the significance of the claim.
- Warrant . An element that connects the claim and that evidence.
- Backing . Additional reasoning that underlines the warrant’s validity.
- Rebuttal . Counterarguments that contradict the author’s position.
- Qualifier . An additional element (usually, a word or a short phrase) that narrows the claim’s capacity. Several examples of qualifiers: “typically,” “usually,” “occasionally,” etc.
- Exceptions . Specific limitations that indicate the cases where that claim may not be valid.
Like the Toulmin approach, Rogerian strategy attempts to find common ground between two sides of one issue. However, the technique is slightly different.
The Rogerian model is often used in highly controversial debates when the parties do not accept each other’s position. Thus, the given strategy focuses on finding the agreement by proving the validity of the opposing arguments.
Below, you can find the primary outline for the Rogerian argumentative essay:
- Introduce the problem. Present the issue clearly and explain why it is worth the readers’ attention.
- Summarize and analyze the counterarguments. Take into consideration all the possible counterpoints and look at them from different perspectives. Discuss the cases in which the opposing claims could be valid. Demonstrate your open-mindedness. This will make the opposite party more loyal to you.
- Present your position. After discussing the counterpoints, state your opinion. Convince the audience about the validity of your points.
- Prove the advantages of your position. Explain to the opposite party how the acceptance and adoption of your points will benefit them.
🧐 How to Write an Argumentative Essay
Before working on your essay, carefully read the assignment. Make sure you understand all the instructor’s requirements and the purpose of the paper.
- Pay enough attention to the task. Did your professor assign you a topic? Or do you need to choose it yourself ? Make sure you have an idea that will turn into an outstanding essay.
- Select the strategy you are going to apply. An argumentative essay format will depend on the model you choose to compose your paper. Analyze the issue you will arise and decide what strategy is the most suitable. Is it the Classical model, the Toulmin, or the Rogerian one?
After that, start composing your argumentative essay. Check out the following sections. We have a lot of insightful info to share with you!
📚 Research the Topic
The first step of writing an argumentative paper is an in-depth investigation of the topic. To validate your arguments, you have to refer to credible resources. The essay will look more professional if you use reliable sources in it.

To research like a professional , do the following:
- Use only credible sources. You can refer to the books, research articles, materials from academic databases, or Google Scholar. Webpages registered as governmental or educational institutions (.gov, .edu.) and widely-known news websites (New York Times, BBC, CNBC) are also considered appropriate. Avoid using blog posts, outdated materials, and any other data from unreliable sources. You may get into huge trouble, taking information from random websites, since it may be invalid.
- Pay attention to the publishing date . You may be required to use the sources released no later than five years ago. Yet, it is not always the case, especially when you’re dealing with historical documents. Thus, double-check your instructions regarding recommended sources.
- Keep your topic in mind. Concentrate on what you are writing about and select the sources for your exact issue. Avoid sources that provide too general information and look for more limited ones. If your idea is World War II’s economic consequences, the history book from ancient times to modern days will not be the best option.
- Become an expert. Take enough time to investigate the issue you are writing about. Read numerous articles, compare and contrast the scientists’ opinions. Prove your reader that you are a reliable person who selected the best sources.
📝 Outline Your Essay
The majority of students tend to underestimate the power of outlining. Don’t do this! An argumentative essay outline is a helpful tool for planning, structuring, and composing.
Firstly , a well-developed outline helps the writer to put all their thoughts in an appropriate order. None of the essential points will be lost if the student plans the essay before writing.
Secondly , it lets the writer figure out what evidence suits what argument most. Before writing, draft your essay first. Put examples, facts, etc. in the right parts of the paper. Then, write the entire text.
Thirdly , an outline provides a perfect opportunity to change the essay’s parts without rewriting the paper. Are you unsure of specific details? Not a problem. Change them in the outline without ruining the text.
There are essential elements that your outline should contain. Check out the following section to see them.
Introduction
How to start an argumentative essay? First and foremost, include an argumentative essay introduction in your outline.
This part should grab the readers’ attention from the first words. Thus, put enough effort into composing a compelling hook . What can it be? An impressive statistic or an exciting fact? Be creative – decide yourself! But make sure that your intro is catchy enough.
After the hook, introduce your topic’s general background . Prove the readers the significance of your issue and gradually come to the thesis statement .
The concept of studying abroad is becoming increasingly popular in both developed and developing countries. Students around the globe strive to explore the world and broaden their minds, and studying in a foreign country is an excellent opportunity to do so. Such experience may be extremely beneficial because meeting new people and discovering foreign cultures help students to gain valuable knowledge and see the world from a new perspective. However, while presenting significant opportunities for personal growth, it may also bring about some challenges.
Thesis Statement
A thesis is an essential part of your argumentative essay. It should state your position regarding the issue clearly and concisely. Avoid general statements, vague words, and be as specific and possible. Your thesis statement should guide the readers throughout the main points of the paper.
The location of the thesis in the essay plays a crucial role. The most appropriate place for it is the last sentence of the introductory paragraph.
Although students face difficulties such as loneliness while studying abroad, it is a worthy experience to introduce them to new knowledge, people, and culture and promote their independence.
Body Paragraphs
The body of your paper is supposed to develop your position, provide valid evidence and examples. Each paragraph has to focus only on one idea. This will ensure the logical structure of your argumentative essay.
A body paragraph should start from the topic sentence and end with the concluding sentence . Such a frame around every section will make your readers stay concentrated on your ideas and get your opinion.
- The topic sentence is the first sentence of the passage. It should reflect its point and correspond to the thesis statement.
- The concluding sentence aims to wrap up the author’s thoughts. Thus, make sure that the last sentence of a paragraph is insightful enough.
Each body paragraph should include an argument (or a counterargument) with supporting evidence. Get your proof from credible sources and ensure that it directly corresponds to the point.
An example of a topic sentence :
The benefits of education abroad are almost innumerable, prominent examples being gaining new knowledge, making friends with people who have different mindsets, and discovering new cultures.
An example of a concluding sentence:
Participants of student exchange programs usually return more driven and eager to develop both themselves and their country.
A conclusion plays a critical role in understanding the entire paper. It summarizes the body and leaves the final impression. Besides, it may push the readers on further investigation of the issue.
- To make your argumentative essay conclusion powerful, it is not enough just to summarize the arguments. It has to synthesize your ideas and show the connection between them. In other words, your points should be summarized and analyzed.
- Moreover, a conclusion refers to the thesis statement . A mere restatement of the central idea is not the most successful way of finishing your paper. You should try to develop it to demonstrate the reason you’ve written the previous paragraphs.
One more tip:
- Give the audience an incentive to explore the topic more in-depth. Insert the questions for further investigation at the end of your essay. It would play a significant role in making an impressive conclusion.
To sum up, studying abroad is beneficial as it helps a person evolve and perceive a world from new perspectives. It is an opportunity for a participant to explore the world, meet new people, gain valuable knowledge and experience, and broaden their horizons. Education abroad might pose problems like homesickness, loneliness, and trouble with getting accustomed to a new environment. However, all of them can be easily overcome if a student is flexible and eager to become autonomous and independent.
The list of references is a crucial part of any argumentative essay. It should contain all the sources the writer uses in the paper.
Before organizing your reference list , double-check your argumentative essay format. Is it written in MLA, APA, or maybe in Chicago style? How many references does the professor expect you to include? What kind of sources are you required to use?
After figuring out these issues, move to the format requirements of the writing style you use for your paper. The most popular ones are APA (7th edition), MLA, and ChicagoAD (author-date) styles. Below, you can find the examples of a reference for the same book in different formatting styles.
Did you develop a good outline? Congratulations! You are almost done with the essay. Now, you need to fill in the blanks and create a final version of your paper. Here is where you need to demonstrate a high level of your writing skills.
- Make sure your paper has no logical fallacies. Information from an untrustworthy source, a hasty generalization, or a false conclusion may put your reliability as an author under threat. So double-check all the data you include in your essay. Moreover, make sure all your statements are well-developed and supported by valid evidence.
- Check your argumentative essay structure . All the arguments should refer to the thesis statement and must be presented in the logical sequence. The supporting evidence and examples have to be inserted in the text logically, according to the arguments.
- Pay enough attention to the citations. References and in-text citations are incredibly tricky. Always check every detail according to your essay format. If you are unsure of specific issues, refer to a citation guide and make your paper free of formatting mistakes.
- Ensure the coherence of your argumentative essay. Often, the paper’s material seems raw only because it is presented without a logical connection. To ensure a smooth connection between the ideas, use transitions between the paragraphs and linking words inside them. Insert them in the text to connect the points. As a result, you will have a coherent essay with the logical flow of the arguments.

The final step of your writing process is editing and proofreading. Although it is not that energy and time consuming, it still plays a critical role in the work’s success.
While writing your argumentative paper, plan your time accordingly. This will provide you with an opportunity to polish your essay before submitting it. And take a look at our checklist and always use it to improve your papers:
- NO first and second person. Use only the third person in your argumentative essay. It is a general requirement for any kind of academic paper.
- NO slang. The word choice is an essential part of the essay writing process. Ensure you use only formal vocabulary and avoid using informal language (jargon, slang, etc.).
- NO unchecked words. Sometimes, words can raise questions and lead to misunderstandings. If you are unsure whether the term is used appropriately, double-check its meaning or replace it with another.
- NO plagiarism. While proofreading, make sure your citations are either properly paraphrased or taken in quotation marks. You can change the sentence structure to avoid plagiarism.
- NO minor mistakes. Grammar, spelling, punctuation play a crucial role. Want to make your paper look professional? Make sure it is free of minor mistakes then.
Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should student-athletes benefit from sports?
- Do celebrities really have influence on people behavior?
- Will decriminalization of drugs increase drug menace?
- Does social and environmental reporting promote organizations’ financial success?
- Should online learning be promoted?
- Can space exploration resolve human problems?
- Is success really the outcome of hard work?
- Is there discrimination against women in sports?
- Will banning tobacco sales promote public health?
- Is euthanasia a clemency?
- Should college education be free and accessible for every student?
- Should football be banned for being too dangerous?
- Is it time to change social norms ?
- Should public servants’ strikes be prohibited?
- Does media create a negative image of ageing and older people?
- Is capitalism the best economic system?
- Can children under 18 make an appropriate decision on getting tattoo ?
- Should net neutrality be protected?
- Can an improper use of social media provoke a family crisis?
- Is it right to use animals in biomedical research ?
- Does the climate change affect our indoor environment?
- Are children’s crimes a result of poor parenting?
- Should health care be universal?
- Does the increased use of technology hurt students’ efficiency?
- Is transformative education a key to the system modernization?
- Why should patients have access to truthful information?
- How does language barrier affect health care access?
- Would allowing adoption by same-sex couples benefit the country’s child welfare system?
- Is spanking children a proper way to improve their behavior?
- Does gun control law lowers crime rates?
- Will ban on spamming improve users’ internet experience?
- Should behavior be made illegal because it’s immoral?
- Is globalization really a progress?
- Does aid to developing countries bring more harm than good?
- Can parents improve children mental health by restricting internet use ?
- Is trusting our senses the best way to get the truth?
- Why parents should not have the right to choose their children based on genetics.
- Is college education really worth it?
- Will wearing a body camera by police officer enhance public trust?
- Immigration : a benefit or a threat?
- Is it a duty of adult children to take care of their elderly parents?
- Should abortions be legal?
- Are agents an integral part of professional sports?
- Will ban of cellphones while driving decrease the car accident rates?
- Should marijuana be legal for medical use?
- Is veganism diet universally beneficial?
- Should museums return artefacts?
- Is water birth beneficial for women’s health?
- Will paying people to stay healthy benefit the nation in the long-term perspective?
- Is obesity a disease or a choice?
It is up to you to decide how many parts to include in your essay. However, the 5 paragraph structure is the most appropriate model for an argumentative paper. So, write an introduction, a conclusion, and three body paragraphs.
The pronoun “you” is acceptable for informal writing. Yet, in academic papers, avoid using the second person. The same situation is with the first person. Generally, academic papers require the use of the third person.
A hook aims to grab the readers’ attention. Thus, you could start your essay with an interesting fact about your issue. Another way to create a catchy hook is to prove the audience the relatability of your topic. Make the readers want to explore your essay by demonstrating the significance of your issue.
Yes, you can. A question might become a compelling hook. Just make sure that it is profound, thought-provocative, and concise. A too broad or complicated question will only confuse your readers.
A title is an essential part of the essay since it causes the first impression. While selecting a heading, take into consideration the following points:
1. The title must be catchy.
2. It has to be not too long (5-12 words).
3. The title has to reflect the topic of the paper.
4. It should not be too complicated: the simpler – the better.
Thank you for visiting our page! We hope the information was helpful and insightful. Do you have friends who seek help with writing an argumentative essay? Share our article with them. And don’t forget to leave your comments!
- Sample Argument Essays: Mesa Community College
- Argument: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- Tips for Organizing an Argumentative Essay: Judith L., Beumer Writing Center, Valparaiso University
- Argumentative Essay: Oya Ozagac, Bogazici University, Online Writing Lab
- Argumentative Essays: Purdue Online Writing Lab, College of Liberal Arts, Purdue University
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay Step by Step: Virginia Kearney, Owlcation
- Counterargument: Gordon Harvey for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Basic Steps in the Research Process: North Hennepin Community College, Minnesota
- How to Recognize Plagiarism, Overview: School of Education, Indiana University Bloomington
- 15 Steps to Good Research: Georgetown University Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![literature argumentative essay How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![literature argumentative essay How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![literature argumentative essay How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...

Sorry to disappoint you, but if you think that your high scores and grades would be enough to get accepted into the university of your dreams, you’re wrong… The best colleges worldwide, such as the Ivy League schools receive applications from thousands and thousands of talented students. You gotta stand...

Often when you’re completing academic writing, especially essays, you need to use pronouns. In academic writing, the use of the word you is unacceptable. You can find yourself in a sticky situation, deciding upon gender-neutral pronouns in your academic writing. How can students deal with it? In most situations today,...

A divorce is a life-changing experience that affects spouses and their children (if there are any). Since divorce rates are relatively high in modern society, more and more people face this problem nowadays. When you are assigned to compose an argumentative essay about divorce, you should be as careful as...
![literature argumentative essay How to Stop Corruption Essay: Guide & Topics [+4 Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/close-up-two-hands-while-paying-money-284x153.jpeg)
Corruption is an abuse of power that was entrusted to a person or group of people for personal gain. It can appear in various settings and affect different social classes, leading to unemployment and other economic issues. This is why writing an essay on corruption can become a challenge. One...

Do you have to write an essay for the first time? Or maybe you’ve only written essays with less than 1000 words? Someone might think that writing a 1000-word essay is a rather complicated and time-consuming assignment. Others have no idea how difficult thousand-word essays can be. Well, we have...

To write an engaging “If I Could Change the World” essay, you have to get a few crucial elements: The questions that define this paper type: What? How? Whom? When? Where? The essay structure that determines where each answer should be; Some tips that can make your writing unique and original. Let us...
![literature argumentative essay Why I Want to be a Pharmacist Essay: How to Write [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/cut-out-medicament-drug-doctor-medical-1-284x153.jpg)
Why do you want to be a pharmacist? An essay on this topic can be challenging, even when you know the answer. The most popular reasons to pursue this profession are the following:

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 strong argumentative essay examples, analyzed.
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Writing
Course: praxis core writing > unit 1, argumentative essay | quick guide.
- Source-based essay | Quick guide
- Revision in context | Quick guide
- Within-sentence punctuation | Quick guide
- Subordination and coordination | Quick guide
- Independent and dependent Clauses | Video lesson
- Parallel structure | Quick guide
- Modifier placement | Quick guide
- Shifts in verb tense | Quick guide
- Pronoun clarity | Quick guide
- Pronoun agreement | Quick guide
- Subject-verb agreement | Quick guide
- Noun agreement | Quick guide
- Frequently confused words | Quick guide
- Conventional expressions | Quick guide
- Logical comparison | Quick guide
- Concision | Quick guide
- Adjective/adverb confusion | Quick guide
- Negation | Quick guide
- Capitalization | Quick guide
- Apostrophe use | Quick guide
- Research skills | Quick guide
Argumentative essay (30 minutes)
- states or clearly implies the writer’s position or thesis
- organizes and develops ideas logically, making insightful connections between them
- clearly explains key ideas, supporting them with well-chosen reasons, examples, or details
- displays effective sentence variety
- clearly displays facility in the use of language
- is generally free from errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- organizes and develops ideas clearly, making connections between them
- explains key ideas, supporting them with relevant reasons, examples, or details
- displays some sentence variety
- displays facility in the use of language
- states or implies the writer’s position or thesis
- shows control in the organization and development of ideas
- explains some key ideas, supporting them with adequate reasons, examples, or details
- displays adequate use of language
- shows control of grammar, usage, and mechanics, but may display errors
- limited in stating or implying a position or thesis
- limited control in the organization and development of ideas
- inadequate reasons, examples, or details to explain key ideas
- an accumulation of errors in the use of language
- an accumulation of errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- no clear position or thesis
- weak organization or very little development
- few or no relevant reasons, examples, or details
- frequent serious errors in the use of language
- frequent serious errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics
- contains serious and persistent writing errors or
- is incoherent or
- is undeveloped or
- is off-topic
How should I build a thesis?
- (Choice A) Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable. A Kids should find role models that are worthier than celebrities because celebrities may be famous for reasons that aren't admirable.
- (Choice B) Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans. B Because they profit from the admiration of youths, celebrities have a moral responsibility for the reactions their behaviors provoke in fans.
- (Choice C) Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person. C Celebrities may have more imitators than most people, but they hold no more responsibility over the example they set than the average person.
- (Choice D) Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models. D Notoriety is not always a choice, and some celebrities may not want to be role models.
- (Choice E) Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children. E Parents have a moral responsibility to serve as immediate role models for their children.
How should I support my thesis?
- (Choice A) As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. A As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids.
- (Choice B) Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths.
- (Choice C) Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products. C Many celebrities, like Kylie Jenner with her billion-dollar cosmetics company, profit directly from being imitated by fans who purchase sponsored products.
- (Choice D) My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers. D My ten-year-old nephew may love Drake's music, but his behaviors are more similar to those of the adults he interacts with on a daily basis, like his parents and teachers.
- (Choice E) It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities. E It's very common for young people to wear fashions similar to those of their favorite celebrities.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: Step By Step Guide
10 May, 2020
9 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Being able to present your argument and carry your point in a debate or a discussion is a vital skill. No wonder educational establishments make writing compositions of such type a priority for all students. If you are not really good at delivering a persuasive message to the audience, this guide is for you. It will teach you how to write an argumentative essay successfully step by step. So, read on and pick up the essential knowledge.

What is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is a paper that gets the reader to recognize the author’s side of the argument as valid. The purpose of this specific essay is to pose a question and answer it with compelling evidence. At its core, this essay type works to champion a specific viewpoint. The key, however, is that the topic of the argumentative essay has multiple sides, which can be explained, weighed, and judged by relevant sources.
Check out our ultimate argumentative essay topics list!
This essay often explores common questions associated with any type of argument including:

Argumentative VS Persuasive Essay
It’s important not to confuse argumentative essay with a persuasive essay – while they both seem to follow the same goal, their methods are slightly different. While the persuasive essay is here to convince the reader (to pick your side), the argumentative essay is here to present information that supports the claim.
In simple words, it explains why the author picked this side of the argument, and persuasive essay does its best to persuade the reader to agree with your point of view.
Now that we got this straight, let’s get right to our topic – how to write an argumentative essay. As you can easily recognize, it all starts with a proper argument. First, let’s define the types of argument available and strategies that you can follow.
Types of Argument
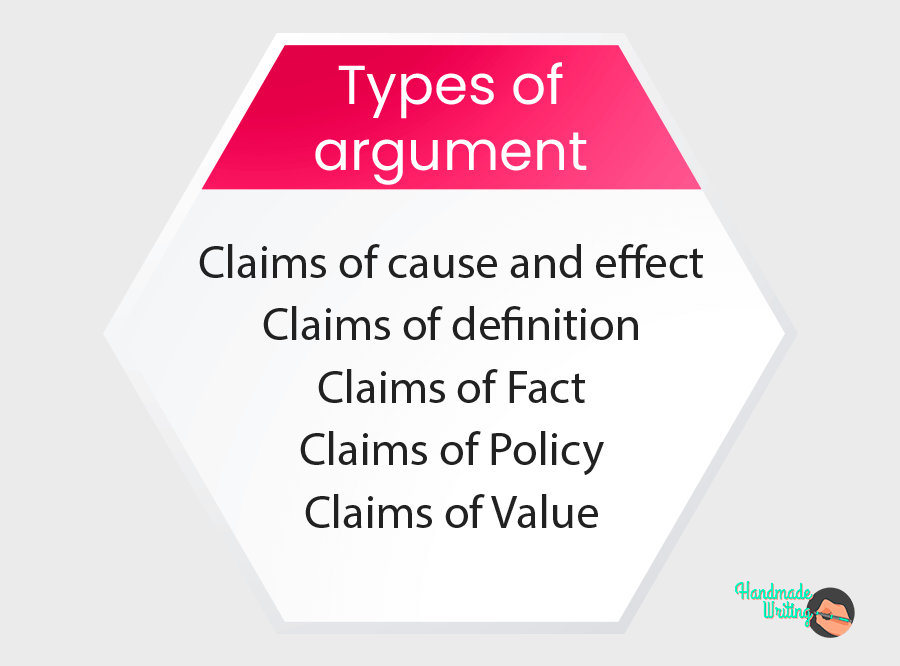
When delving into the types of argument, the vocabulary suddenly becomes quite “lawyerish”; and that makes sense since lawyers stake their whole livelihood on their ability to win arguments. So step into your lawyer shoes, and learn about the five kinds of arguments that you could explore in an argumentative paper:
Claims of cause and effect
This paper focuses on answering what caused the issue(s), and what the resulting effects have been.
Claims of definition
This paper explores a controversial interpretation of a particular definition; the paper delves into what the world really means and how it could be interpreted in different ways.
Claims of Fact
This argumentative paper examines whether a particular fact is accurate; it often looks at several sources reporting a fact and examines their veracity.
Claims of Policy
This is a favorite argumentative essay in government and sociology classes; this paper explores a particular policy, who it affects, and what (if anything) should be done about it.
Claims of Value
This essay identifies a particular value or belief and then examines how and why it is important to a particular cohort or a larger, general population.
The aim of argument, or of discussion, should not be victory, but progress. Joseph Joubert
Argument Strategies
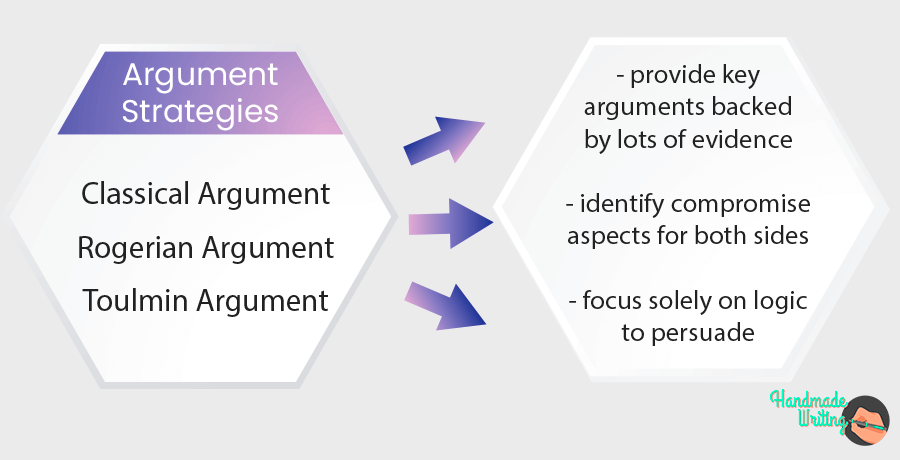
When mulling over how to approach your argumentative assignment, you should be aware that three main argument strategies exist regarding how exactly to argue an issue: classical, Rogerian, Toulmin.
Classical Argument
This argument structure dates back to the ancient Greeks and Romans. In this strategy, the arguer introduces the issue, provides context, clearly states their claim, provides key arguments backed by lots of evidence, and nullifies opposing arguments with valid data.
Rogerian Argument
Hate conflict? This may be the argumentative paper strategy for you. At its core, this strategy works to identify compromise aspects for both sides; this approach works to find commonality and an ultimate agreement between two sides rather than proclaiming a winner or loser. The focus in this argument is compromise and respect of all sides.
Toulmin Argument
Remember Spock? This is his type of strategy; the Toulmin approach focuses solely on logic to persuade the audience. It is heavy on data and often relies on qualities to narrow the focus of a claim and strengthen the writer’s stance. This approach also tends to rely on exceptions, which clearly set limits on the parameters of an argument, thus making a particular stance easier to agree with.
With that in mind, we can now organize our argument into the essay structure.
Have no time to write your essay? You can buy argumentative essay tasks at Handmade Writing. Our service is available 24/7.
Argumentative essay Example
Organizing the argumentative essay outline.
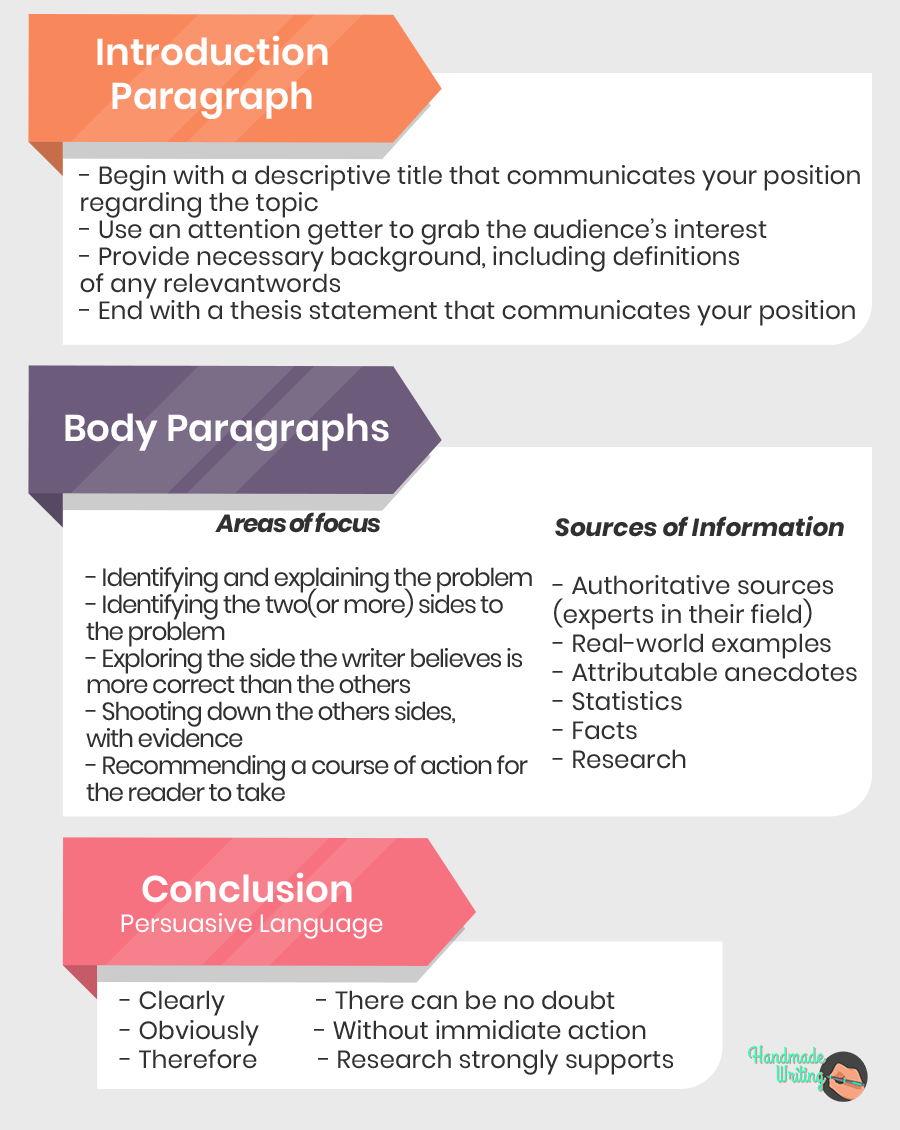
An argumentative essay follows the typical essay format: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. However, the body paragraphs are structured a bit differently from other body paragraphs. Surely, not something you can see in a cause and effect essay outline .
While the introduction should still begin with an attention-grabbing sentence that catches the reader’s interest and compels him or her to continue reading and provides key background information, the following paragraphs focus on specific aspects of the argument.
Let’s begin with the introduction.
Related Post: How to write an Essay Introduction ?
Introduction Paragraph
As its name suggests, this paragraph provides all the background information necessary for a reader unfamiliar with the argumentative essay topic to understand what it’s about. A solid introduction should:
- Begin with a descriptive title that communicates your position regarding the topic
- Rhetorical question
- Personal anecdote
- Provide necessary background, including definitions of any relevant words
- End with a thesis statement that communicates your position
Stuck with your essay task? No more struggle! HandMadeWriting is the top essay writing service. Our online essay writer service not only guides you on writing papers, it can write a high-quality essay for you.
Body Paragraphs

Body paragraphs can range in size from six to fifteen or more sentences. The goal of these paragraphs is to support the thesis statement. Recommended areas of focus for the body paragraphs within an argumentative paper include:
- Identifying and explaining the problem
- Identifying the two (or more) sides to the problem
- Exploring the side the writer believes is more appropriate than the others
- Shooting down the other sides, with evidence
- Recommending a course of action for the reader
One important way how this essay differs from other kinds is its specific nature. At the end of reading such an essay, the audience should clearly understand the issue or controversy and have enough information to make an informed decision regarding the issue. But what compels an audience make an informed decision? Several things!
- Authoritative sources (experts in their field)
- Real-world examples
- Attributable anecdotes

In this paragraph, often the shortest of all the paragraphs, the writer reviews his or her most compelling reasons for taking a particular stance on an issue. The persuasion should be strong here, and the writer should use combative language including examples such as:
- “then” statements
- There can be no doubt
- Without immediate action
- Research strongly supports
It is also appropriate to refute potential opposition in the conclusion. By stating the objections readers could have, and show why they should be dismissed; the conclusion resonates more strongly with the reader.
Check our guide if you have any other questions on academic paper writing!
Argumentative Essay Sample
Be sure to check the sample essay, completed by our writers. Use it as an example to write your own argumentative essay. Link: Argumentative essay on white rappers’ moral rights to perform .
Remember : the key to winning any argument should be reliable sources — the better, the more trustworthy your sources, the more likely the audience will consider a viewpoint different from their own.
And while you may feel a deep passion towards a particular topic, keep in mind that emotions can be messy; this essay should present all sides to the argument respectfully and with a clear intention to portray each of them fairly.
Let the data, statistics, and facts speak loudly and clearly for themselves. And don’t forget to use opinionated language — using such diction is a must in any strong argumentative writing!

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
130 New Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Questions on everything from mental health and sports to video games and dating. Which ones inspire you to take a stand?

By The Learning Network
Note: We have an updated version of this list, with 300 new argumentative writing prompts .
What issues do you care most about? What topics do you find yourself discussing passionately, whether online, at the dinner table, in the classroom or with your friends?
In Unit 5 of our free yearlong writing curriculum and related Student Editorial Contest , we invite students to research and write about the issues that matter to them, whether that’s Shakespeare , health care , standardized testing or being messy .
But with so many possibilities, where does one even begin? Try our student writing prompts.
In 2017, we compiled a list of 401 argumentative writing prompts , all drawn from our daily Student Opinion column . Now, we’re rounding up 130 more we’ve published since then ( available here as a PDF ). Each prompt links to a free Times article as well as additional subquestions that can help you think more deeply about it.
You might use this list to inspire your own writing and to find links to reliable resources about the issues that intrigue you. But even if you’re not participating in our contest, you can use these prompts to practice the kind of low-stakes writing that can help you hone your argumentation skills.
So scroll through the list below with questions on everything from sports and mental health to dating and video games and see which ones inspire you to take a stand.
Please note: Many of these prompts are still open to comment by students 13 and up.
Technology & Social Media
1. Do Memes Make the Internet a Better Place? 2. Does Online Public Shaming Prevent Us From Being Able to Grow and Change? 3. How Young Is Too Young to Use Social Media? 4. Should the Adults in Your Life Be Worried by How Much You Use Your Phone? 5. Is Your Phone Love Hurting Your Relationships? 6. Should Kids Be Social Media Influencers? 7. Does Grammar Still Matter in the Age of Twitter? 8. Should Texting While Driving Be Treated Like Drunken Driving? 9. How Do You Think Technology Affects Dating?
10. Are Straight A’s Always a Good Thing? 11. Should Schools Teach You How to Be Happy? 12. How Do You Think American Education Could Be Improved? 13. Should Schools Test Their Students for Nicotine and Drug Use? 14. Can Social Media Be a Tool for Learning and Growth in Schools? 15. Should Facial Recognition Technology Be Used in Schools? 16. Should Your School Day Start Later? 17. How Should Senior Year in High School Be Spent? 18. Should Teachers Be Armed With Guns? 19. Is School a Place for Self-Expression? 20. Should Students Be Punished for Not Having Lunch Money? 21. Is Live-Streaming Classrooms a Good Idea? 22. Should Gifted and Talented Education Be Eliminated? 23. What Are the Most Important Things Students Should Learn in School? 24. Should Schools Be Allowed to Censor Student Newspapers? 25. Do You Feel Your School and Teachers Welcome Both Conservative and Liberal Points of View? 26. Should Teachers and Professors Ban Student Use of Laptops in Class? 27. Should Schools Teach About Climate Change? 28. Should All Schools Offer Music Programs? 29. Does Your School Need More Money? 30. Should All Schools Teach Cursive? 31. What Role Should Textbooks Play in Education? 32. Do Kids Need Recess?
College & Career
33. What Is Your Reaction to the College Admissions Cheating Scandal? 34. Is the College Admissions Process Fair? 35. Should Everyone Go to College? 36. Should College Be Free? 37. Are Lavish Amenities on College Campuses Useful or Frivolous? 38. Should ‘Despised Dissenters’ Be Allowed to Speak on College Campuses? 39. How Should the Problem of Sexual Assault on Campuses Be Addressed? 40. Should Fraternities Be Abolished? 41. Is Student Debt Worth It?
Mental & Physical Health
42. Should Students Get Mental Health Days Off From School? 43. Is Struggle Essential to Happiness? 44. Does Every Country Need a ‘Loneliness Minister’? 45. Should Schools Teach Mindfulness? 46. Should All Children Be Vaccinated? 47. What Do You Think About Vegetarianism? 48. Do We Worry Too Much About Germs? 49. What Advice Should Parents and Counselors Give Teenagers About Sexting? 50. Do You Think Porn Influences the Way Teenagers Think About Sex?
Race & Gender
51. How Should Parents Teach Their Children About Race and Racism? 52. Is America ‘Backsliding’ on Race? 53. Should All Americans Receive Anti-Bias Education? 54. Should All Companies Require Anti-Bias Training for Employees? 55. Should Columbus Day Be Replaced With Indigenous Peoples Day? 56. Is Fear of ‘The Other’ Poisoning Public Life? 57. Should the Boy Scouts Be Coed? 58. What Is Hard About Being a Boy?
59. Can You Separate Art From the Artist? 60. Are There Subjects That Should Be Off-Limits to Artists, or to Certain Artists in Particular? 61. Should Art Come With Trigger Warnings? 62. Should Graffiti Be Protected? 63. Is the Digital Era Improving or Ruining the Experience of Art? 64. Are Museums Still Important in the Digital Age? 65. In the Age of Digital Streaming, Are Movie Theaters Still Relevant? 66. Is Hollywood Becoming More Diverse? 67. What Stereotypical Characters Make You Cringe? 68. Do We Need More Female Superheroes? 69. Do Video Games Deserve the Bad Rap They Often Get? 70. Should Musicians Be Allowed to Copy or Borrow From Other Artists? 71. Is Listening to a Book Just as Good as Reading It? 72. Is There Any Benefit to Reading Books You Hate?
73. Should Girls and Boys Sports Teams Compete in the Same League? 74. Should College Athletes Be Paid? 75. Are Youth Sports Too Competitive? 76. Is It Selfish to Pursue Risky Sports Like Extreme Mountain Climbing? 77. How Should We Punish Sports Cheaters? 78. Should Technology in Sports Be Limited? 79. Should Blowouts Be Allowed in Youth Sports? 80. Is It Offensive for Sports Teams and Their Fans to Use Native American Names, Imagery and Gestures?
81. Is It Wrong to Focus on Animal Welfare When Humans Are Suffering? 82. Should Extinct Animals Be Resurrected? If So, Which Ones? 83. Are Emotional-Support Animals a Scam? 84. Is Animal Testing Ever Justified? 85. Should We Be Concerned With Where We Get Our Pets? 86. Is This Exhibit Animal Cruelty or Art?
Parenting & Childhood
87. Who Should Decide Whether a Teenager Can Get a Tattoo or Piercing? 88. Is It Harder to Grow Up in the 21st Century Than It Was in the Past? 89. Should Parents Track Their Teenager’s Location? 90. Is Childhood Today Over-Supervised? 91. How Should Parents Talk to Their Children About Drugs? 92. What Should We Call Your Generation? 93. Do Other People Care Too Much About Your Post-High School Plans? 94. Do Parents Ever Cross a Line by Helping Too Much With Schoolwork? 95. What’s the Best Way to Discipline Children? 96. What Are Your Thoughts on ‘Snowplow Parents’? 97. Should Stay-at-Home Parents Be Paid? 98. When Do You Become an Adult?
Ethics & Morality
99. Why Do Bystanders Sometimes Fail to Help When They See Someone in Danger? 100. Is It Ethical to Create Genetically Edited Humans? 101. Should Reporters Ever Help the People They Are Covering? 102. Is It O.K. to Use Family Connections to Get a Job? 103. Is $1 Billion Too Much Money for Any One Person to Have? 104. Are We Being Bad Citizens If We Don’t Keep Up With the News? 105. Should Prisons Offer Incarcerated People Education Opportunities? 106. Should Law Enforcement Be Able to Use DNA Data From Genealogy Websites for Criminal Investigations? 107. Should We Treat Robots Like People?
Government & Politics
108. Does the United States Owe Reparations to the Descendants of Enslaved People? 109. Do You Think It Is Important for Teenagers to Participate in Political Activism? 110. Should the Voting Age Be Lowered to 16? 111. What Should Lawmakers Do About Guns and Gun Violence? 112. Should Confederate Statues Be Removed or Remain in Place? 113. Does the U.S. Constitution Need an Equal Rights Amendment? 114. Should National Monuments Be Protected by the Government? 115. Should Free Speech Protections Include Self Expression That Discriminates? 116. How Important Is Freedom of the Press? 117. Should Ex-Felons Have the Right to Vote? 118. Should Marijuana Be Legal? 119. Should the United States Abolish Daylight Saving Time? 120. Should We Abolish the Death Penalty? 121. Should the U.S. Ban Military-Style Semiautomatic Weapons? 122. Should the U.S. Get Rid of the Electoral College? 123. What Do You Think of President Trump’s Use of Twitter? 124. Should Celebrities Weigh In on Politics? 125. Why Is It Important for People With Different Political Beliefs to Talk to Each Other?
Other Questions
126. Should the Week Be Four Days Instead of Five? 127. Should Public Transit Be Free? 128. How Important Is Knowing a Foreign Language? 129. Is There a ‘Right Way’ to Be a Tourist? 130. Should Your Significant Other Be Your Best Friend?

Tips on essay planning and writing
What is an essay, brainstorm your topic by creating a mind map, check you understand what your essay question is asking you, academic writing style, signposting, building an argument and summarising other people's ideas, what is paraphrasing, essay structure, useful links.

Traditional academic essays are pieces of writing which are designed to demonstrate the following points:
- that you understand a particular subject
- that you have undertaken some kind of research
- that you can produce a clear and coherent argument
This means that you have to combine important ideas, examples, and interpretations from other writers with your own. All of these have to be put together in a linear, written format (making one point, then moving on to the next), which persuades the reader that your line of argument is a convincing one.
Note : There may be variations in the approach you need to take depending on the discipline you are studying. Check with your tutor/department for discipline specific guidelines.
When you choose, or are assigned, an essay question, you are asked to focus on something very specific. It's not just a case of writing down everything you know about the subject. An essay question instructs you to do something with the knowledge you have, and to put it into a certain context, which will allow you to demonstrate the range of your critical thinking.
Essay questions therefore have instructional verbs to determine what your approach should be. These are words such as: discuss, analyse, argue, compare, review, evaluate, examine, outline, illustrate .... These tell you how to answer the question and what your essay should do. It is important that you understand exactly what these words mean so that you don’t misinterpret a question.

- For more examples check 'Terms that may be used in essays or examinations'
You will usually be expected to write using academic language and specialist vocabulary from your subject area. Academic writing normally contains these features:
- Formal writing in an impersonal or objective style and often takes the 'passive' voice. Passive constructions can be used to avoid using 'I' in essays, e.g. 'It can be argued...'
- Vocabulary appropriate for particular academic contexts is used which may include technical and specialist words.
- Contains references to other writers’ publications which are used to support the arguments in the text
- You may notice that cautious language is frequently used in reporting research and making claims. 'Cautious language' indicates reservations or tentativeness about the conclusions that may be drawn from the evidence presented. Useful phrases are: 'it may be concluded', and 'we can assume'.

Major Signposting
Major signposting is used to signal the introduction of key sections or aspects of the work. These might include the aim, purpose, or structure.
In the introduction:
- This essay will…
- The aim of this essay is to…
- The major issue being discussed is…
- This essay will define and describe…
- This essay will critically examine…
- This essay will first define…then discuss…before making recommendations for…
- This essay is organised in the following way;
In the conclusion:
- To conclude,
- In conclusion,
- To summarise,
- It is evident that
Minor Signposting
Minor signposting are linking words and phrases that make connections for your reader and move them through the text.
- They may be as simple as: First, second, third, next, then, last, lastly, finally
- To offer a counterpoint: However, although, though, yet, alternatively, nevertheless
- To indicate an example: For example, notably, for instance, in this case
Linking words and phrases help give your writing more fluidity. Linking words and phrases will help the flow of your academic writing.
Linking words are particularly useful for use in comparing and contrasting ideas and to move from one idea to another.
Check these resources for examples of linking words and phrases:
- Examples of linking words and phrases (University of Reading via Future Learn)
- Transitional devices (Purdue University)
- Signposting (Queen's University Belfast)
Source: Academic Writing Skills by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
Illustrations vector created by stories - www.freepik.com

Often the clearest way to combine different points of view and to show that you have understood those points of view is to summarise them. Each summary of a different viewpoint can include direct and indirect quotations of key points, plus your understanding of what they mean and a comment on the weaknesses and strengths of the idea or viewpoint. Having described, interpreted and analysed other people's ideas, you can then go on to describe your own point of view and explain why you have chosen it.
Writing which ignores any of the parts described above, can become unbalanced. For example, if there are none of your own ideas, the piece becomes a review of everyone else's work. In these circumstances you could be accused of being uncritical. If the writing does not refer to other people's ideas (directly or indirectly), there is a problem of being too personal and non-academic (this partly depends on your subject). Neither of these would be persuasive arguments.
Paraphrasing is expressing someone else’s writing in your own choice of words, while keeping the same essential meaning. As Pears and Shields (2019, p. 15) explain, it is ‘an alternative way of referring to an author’s ideas or arguments without using direct quotations from their text’.
Paraphrasing is generally more highly valued by academics than direct quoting because it allows you to demonstrate a greater understanding of your source and helps you to maintain your personal writing style and the smooth flow of your essay.
Don’t forget to include in-text citations (author and date) in the text of your assignment and full references at the end of your assignment every time you paraphrase someone else’s words or ideas.
- Paraphrasing - an overview A guide on paraphrasing, academic writing, citing and referencing
- Introduction
- The main body
- Bibliography
The introduction is the official start of the essay and it usually includes some or all of the following:
- a statement introducing the topic
- an explanation of why it is important
- a brief mention of work on the same topic written by other writers
- a gap or problem in previous related work which will be solved or answered in this essay
- an outline of the structure of the essay
- definitions of key terms
- an anecdote or vignette (short story) which highlights the main point of the essay
The body is the largest part of your writing and this is where you guide your reader through your main ideas and arguments. These ideas and arguments come from your brainstorming and research. It is therefore a mixture of other people’s ideas and your own. These points should be organised into a logical order which allows your reader to follow your train of thought.
The balance of discussion between your own ideas and information and those from external sources is crucial to the development of your argument. Without this balance, the writing can become either a summary of other people's ideas and theories, or a description of your personal ideas and experiences with no evidence of research. Both of these would lack analysis, a core component of a good essay. It is therefore vitally important to ensure that a mixture of positions are presented.
Each main point will be described, supported and analysed using examples from your own experiences, and information and theories from external sources (books, journals, websites, lectures, etc.). The main points should be clearly organised by using paragraphs.
In short pieces of writing (< 3,000 words), there will be groups of paragraphs which together form one part of your argument. Usually these sections in "short" essays do not have specific headings. However, they can be clearly identified by using linking phrases which show for example:
- how many elements the section consists of:
There are four main reasons why ...
- the connection of additional points:
Another important point to consider is ... A further issue of importance is ... Moving on the the issue of ...
- or the introduction of a contrasting point:
On the other hand, ... In contrast to the above, ... An alternative understanding of the issue is ...
Longer pieces of writing and dissertations
In long pieces of writing (> 3,000 words) it is sometimes useful to identify clear sections by using sub-headings. Each section (or chapter of a dissertation or thesis) with a sub-heading is like a short essay which could stand alone. The sub-headings may come from your brainstorm and/or your research. However, the best order for the sections in long essays may only become clear after you have started writing them. When the best order becomes clear, chapter introductions and conclusions can be written in each section.
A short chapter introduction should briefly outline the contents of each section and where possible, should also refer back to the sections before and explain how they are related. Similarly, each section needs a conclusion. This should summarise what has been written in this part and should again make connections to other sections. In particular, it should describe the relationship between this part and the next. These are crucial in order to tell the reader what each part is about and how it fits with the other sections. It is like tying knots between separate pieces of string in order to make a single, stronger cord: your argument.
The conclusion is the closing part of the essay and, like the i ntroduction, connects the body of the essay to the title. However, whereas the introduction often starts generally, becomes more focussed and often includes an outline of the main points; the conclusion attempts to summarise the main ideas and arguments, then leads to a final statement.
It should not include new ideas which have not been mentioned before, although you can join ideas you have mentioned in a new way. You may also want to restate questions which you could not answer in your essay, but which you think deserve further study. As the final part of the essay, the conclusion is the last thing which the reader sees. Therefore, it should tie together the different points you have made.
Conclusions often include the following elements:
- language 'markers' showing that this is the conclusion (e.g. to conclude, in summary, this essay has given an account of...)
- a summary of the ideas in the main body
- a comment about the limitations of the scope of the essay / study
- a glance to the future: a prediction, recommendations for action, suggestions for further research, implications for future policy
A bibliography (or reference list) comes after the conclusion (or appendices and final figures) and includes all the information about the sources you have mentioned in the essay. For more information on referencing please see the Write it Right guide.
- Academic Writing Basics (Author: Megan Robertson)
- Academic Writing Essays in English (© 2021 UEfAP)
- Academic Writing Handbook
- OWL Purdue Online Writing Lab
- The Writing Process by English Language Studies group at the MIT Understanding and using the information on this site should make writing not only less anxiety-provoking and more efficient and effective for you, but ultimately it should also help you feel more creative and more satisfied with the products of your writing efforts and learn more in your classes as well.
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 10:13 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/tips-writing-essays
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
50 Argumentative Essay Topics
Illustration by Catherine Song. ThoughtCo.
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
An argumentative essay requires you to decide on a topic and take a position on it. You'll need to back up your viewpoint with well-researched facts and information as well. One of the hardest parts is deciding which topic to write about, but there are plenty of ideas available to get you started.
Choosing a Great Argumentative Essay Topic
Students often find that most of their work on these essays is done before they even start writing. This means that it's best if you have a general interest in your subject, otherwise you might get bored or frustrated while trying to gather information. (You don't need to know everything, though.) Part of what makes this experience rewarding is learning something new.
It's best if you have a general interest in your subject, but the argument you choose doesn't have to be one that you agree with.
The subject you choose may not necessarily be one that you are in full agreement with, either. You may even be asked to write a paper from the opposing point of view. Researching a different viewpoint helps students broaden their perspectives.
Ideas for Argument Essays
Sometimes, the best ideas are sparked by looking at many different options. Explore this list of possible topics and see if a few pique your interest. Write those down as you come across them, then think about each for a few minutes.
Which would you enjoy researching? Do you have a firm position on a particular subject? Is there a point you would like to make sure to get across? Did the topic give you something new to think about? Can you see why someone else may feel differently?
50 Possible Topics
A number of these topics are rather controversial—that's the point. In an argumentative essay, opinions matter and controversy is based on opinions, which are, hopefully, backed up by facts. If these topics are a little too controversial or you don't find the right one for you, try browsing through persuasive essay and speech topics as well.
- Is global climate change caused by humans?
- Is the death penalty effective?
- Is our election process fair?
- Is torture ever acceptable?
- Should men get paternity leave from work?
- Are school uniforms beneficial?
- Do we have a fair tax system?
- Do curfews keep teens out of trouble?
- Is cheating out of control?
- Are we too dependent on computers?
- Should animals be used for research?
- Should cigarette smoking be banned?
- Are cell phones dangerous?
- Are law enforcement cameras an invasion of privacy?
- Do we have a throwaway society?
- Is child behavior better or worse than it was years ago?
- Should companies market to children?
- Should the government have a say in our diets?
- Does access to condoms prevent teen pregnancy?
- Should members of Congress have term limits?
- Are actors and professional athletes paid too much?
- Are CEOs paid too much?
- Should athletes be held to high moral standards?
- Do violent video games cause behavior problems?
- Should creationism be taught in public schools?
- Are beauty pageants exploitative ?
- Should English be the official language of the United States?
- Should the racing industry be forced to use biofuels?
- Should the alcohol drinking age be increased or decreased?
- Should everyone be required to recycle?
- Is it okay for prisoners to vote (as they are in some states)?
- Is it good that same-sex couples are able to marry?
- Are there benefits to attending a single-sex school ?
- Does boredom lead to trouble?
- Should schools be in session year-round ?
- Does religion cause war?
- Should the government provide health care?
- Should abortion be illegal?
- Are girls too mean to each other?
- Is homework harmful or helpful?
- Is the cost of college too high?
- Is college admission too competitive?
- Should euthanasia be illegal?
- Should the federal government legalize marijuana use nationally ?
- Should rich people be required to pay more taxes?
- Should schools require foreign language or physical education?
- Is affirmative action fair?
- Is public prayer okay in schools?
- Are schools and teachers responsible for low test scores?
- Is greater gun control a good idea?
- Preparing an Argument Essay: Exploring Both Sides of an Issue
- Controversial Speech Topics
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Bad Essay Topics for College Admissions
- 25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
- Topic In Composition and Speech
- MBA Essay Tips
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- 61 General Expository Essay Topic Ideas to Practice Academic Writing
- 40 Writing Topics for Argumentative and Persuasive Essays
- Expository Essay Genre With Suggested Prompts
- Middle School Debate Topics
- Topical Organization Essay
- Supporting Detail in Composition and Speech
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 12 April 2024
Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?
- Seyyed Kazem Banihashem 1 , 2 ,
- Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman 3 ,
- Omid Noroozi 2 ,
- Jewoong Moon 4 &
- Hendrik Drachsler 1 , 5
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 21 , Article number: 23 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Peer feedback is introduced as an effective learning strategy, especially in large-size classes where teachers face high workloads. However, for complex tasks such as writing an argumentative essay, without support peers may not provide high-quality feedback since it requires a high level of cognitive processing, critical thinking skills, and a deep understanding of the subject. With the promising developments in Artificial Intelligence (AI), particularly after the emergence of ChatGPT, there is a global argument that whether AI tools can be seen as a new source of feedback or not for complex tasks. The answer to this question is not completely clear yet as there are limited studies and our understanding remains constrained. In this study, we used ChatGPT as a source of feedback for students’ argumentative essay writing tasks and we compared the quality of ChatGPT-generated feedback with peer feedback. The participant pool consisted of 74 graduate students from a Dutch university. The study unfolded in two phases: firstly, students’ essay data were collected as they composed essays on one of the given topics; subsequently, peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback data were collected through engaging peers in a feedback process and using ChatGPT as a feedback source. Two coding schemes including coding schemes for essay analysis and coding schemes for feedback analysis were used to measure the quality of essays and feedback. Then, a MANOVA analysis was employed to determine any distinctions between the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. Additionally, Spearman’s correlation was utilized to explore potential links between the essay quality and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. The results showed a significant difference between feedback generated by ChatGPT and peers. While ChatGPT provided more descriptive feedback including information about how the essay is written, peers provided feedback including information about identification of the problem in the essay. The overarching look at the results suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. Regarding the relationship between the quality of essays and the quality of the feedback provided by ChatGPT and peers, we found no overall significant relationship. These findings imply that the quality of the essays does not impact both ChatGPT and peer feedback quality. The implications of this study are valuable, shedding light on the prospective use of ChatGPT as a feedback source, particularly for complex tasks like argumentative essay writing. We discussed the findings and delved into the implications for future research and practical applications in educational contexts.
Introduction
Feedback is acknowledged as one of the most crucial tools for enhancing learning (Banihashem et al., 2022 ). The general and well-accepted definition of feedback conceptualizes it as information provided by an agent (e.g., teacher, peer, self, AI, technology) regarding aspects of one’s performance or understanding (e.g., Hattie & Timplerely, 2007 ). Feedback serves to heighten students’ self-awareness concerning their strengths and areas warranting improvement, through providing actionable steps required to enhance performance (Ramson, 2003 ). The literature abounds with numerous studies that illuminate the positive impact of feedback on diverse dimensions of students’ learning journey including increasing motivation (Amiryousefi & Geld, 2021 ), fostering active engagement (Zhang & Hyland, 2022 ), promoting self-regulation and metacognitive skills (Callender et al., 2016 ; Labuhn et al., 2010 ), and enriching the depth of learning outcomes (Gan et al., 2021 ).
Normally, teachers have primarily assumed the role of delivering feedback, providing insights into students’ performance on specific tasks or their grasp of particular subjects (Konold et al., 2004 ). This responsibility has naturally fallen upon teachers owing to their expertise in the subject matter and their competence to offer constructive input (Diezmann & Watters, 2015 ; Holt-Reynolds, 1999 ; Valero Haro et al., 2023 ). However, teachers’ role as feedback providers has been challenged in recent years as we have witnessed a growth in class sizes due to the rapid advances in technology and the widespread use of digital technologies that resulted in flexible and accessible education (Shi et al., 2019 ). The growth in class sizes has translated into an increased workload for teachers, leading to a pertinent predicament. This situation has directly impacted their capacity to provide personalized and timely feedback to each student, a capability that has encountered limitations (Er et al., 2021 ).
In response to this challenge, various solutions have emerged, among which peer feedback has arisen as a promising alternative instructional approach (Er et al., 2021 ; Gao et al., 2024 ; Noroozi et al., 2023 ; Kerman et al., 2024 ). Peer feedback entails a process wherein students assume the role of feedback providers instead of teachers (Liu & Carless, 2006 ). Involving students in feedback can add value to education in several ways. First and foremost, research indicates that students delve into deeper and more effective learning when they take on the role of assessors, critically evaluating and analyzing their peers’ assignments (Gielen & De Wever, 2015 ; Li et al., 2010 ). Moreover, involving students in the feedback process can augment their self-regulatory awareness, active engagement, and motivation for learning (e.g., Arguedas et al., 2016 ). Lastly, the incorporation of peer feedback not only holds the potential to significantly alleviate teachers’ workload by shifting their responsibilities from feedback provision to the facilitation of peer feedback processes but also nurtures a dynamic learning environment wherein students are actively immersed in the learning journey (e.g., Valero Haro et al., 2023 ).
Despite the advantages of peer feedback, furnishing high-quality feedback to peers remains a challenge. Several factors contribute to this challenge. Primarily, generating effective feedback necessitates a solid understanding of feedback principles, an element that peers often lack (Latifi et al., 2023 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ). Moreover, offering high-quality feedback is inherently a complex task, demanding substantial cognitive processing to meticulously evaluate peers’ assignments, identify issues, and propose constructive remedies (King, 2002 ; Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Furthermore, the provision of valuable feedback calls for a significant level of domain-specific expertise, which is not consistently possessed by students (Alqassab et al., 2018 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ).
In recent times, advancements in technology, coupled with the emergence of fields like Learning Analytics (LA), have presented promising avenues to elevate feedback practices through the facilitation of scalable, timely, and personalized feedback (Banihashem et al., 2023 ; Deeva et al., 2021 ; Drachsler, 2023 ; Drachsler & Kalz, 2016 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ; Zawacki-Richter et al., 2019 ; Rüdian et al., 2020 ). Yet, a striking stride forward in the field of educational technology has been the advent of a novel Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool known as “ChatGPT,” which has sparked a global discourse on its potential to significantly impact the current education system (Ray, 2023 ). This tool’s introduction has initiated discussions on the considerable ways AI can support educational endeavors (Bond et al., 2024 ; Darvishi et al., 2024 ).
In the context of feedback, AI-powered ChatGPT introduces what is referred to as AI-generated feedback (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ). While the literature suggests that ChatGPT has the potential to facilitate feedback practices (Dai et al., 2023 ; Katz et al., 2023 ), this literature is very limited and mostly not empirical leading us to realize that our current comprehension of its capabilities in this regard is quite restricted. Therefore, we lack a comprehensive understanding of how ChatGPT can effectively support feedback practices and to what degree it can improve the timeliness, impact, and personalization of feedback, which remains notably limited at this time.
More importantly, considering the challenges we raised for peer feedback, the question is whether AI-generated feedback and more specifically feedback provided by ChatGPT has the potential to provide quality feedback. Taking this into account, there is a scarcity of knowledge and research gaps regarding the extent to which AI tools, specifically ChatGPT, can effectively enhance feedback quality compared to traditional peer feedback. Hence, our research aims to investigate the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT within the context of essay writing and to juxtapose its quality with that of feedback generated by students.
This study carries the potential to make a substantial contribution to the existing body of recent literature on the potential of AI and in particular ChatGPT in education. It can cast a spotlight on the quality of AI-generated feedback in contrast to peer-generated feedback, while also showcasing the viability of AI tools like ChatGPT as effective automated feedback mechanisms. Furthermore, the outcomes of this study could offer insights into mitigating the feedback-related workload experienced by teachers through the intelligent utilization of AI tools (e.g., Banihashem et al., 2022 ; Er et al., 2021 ; Pardo et al., 2019 ).
However, there might be an argument regarding the rationale for conducting this study within the specific context of essay writing. Addressing this potential query, it is crucial to highlight that essay writing stands as one of the most prevalent yet complex tasks for students (Liunokas, 2020 ). This task is not without its challenges, as evidenced by the extensive body of literature that indicates students often struggle to meet desired standards in their essay composition (e.g., Bulqiyah et al., 2021 ; Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Latifi et al., 2023 ).
Furthermore, teachers frequently express dissatisfaction with the depth and overall quality of students’ essay writing (Latifi et al., 2023 ). Often, these teachers lament that their feedback on essays remains superficial due to the substantial time and effort required for critical assessment and individualized feedback provision (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ). Regrettably, these constraints prevent them from delving deeper into the evaluation process (Kerman et al., 2022 ).
Hence, directing attention towards the comparison of peer-generated feedback quality and AI-generated feedback quality within the realm of essay writing bestows substantial value upon both research and practical application. This study enriches the academic discourse and informs practical approaches by delivering insights into the adequacy of feedback quality offered by both peers and AI for the domain of essay writing. This investigation serves as a critical step in determining whether the feedback imparted by peers and AI holds the necessary caliber to enhance the craft of essay writing.
The ramifications of addressing this query are noteworthy. Firstly, it stands to significantly alleviate the workload carried by teachers in the process of essay evaluation. By ascertaining the viability of feedback from peers and AI, teachers can potentially reduce the time and effort expended in reviewing essays. Furthermore, this study has the potential to advance the quality of essay compositions. The collaboration between students providing feedback to peers and the integration of AI-powered feedback tools can foster an environment where essays are not only better evaluated but also refined in their content and structure.With this in mind, we aim to tackle the following key questions within the scope of this study:
RQ1. To what extent does the quality of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback differ in the context of essay writing?
Rq2. does a relationship exist between the quality of essay writing performance and the quality of feedback generated by peers and chatgpt, context and participant.
This study was conducted in the academic year of 2022–2023 at a Dutch university specializing in life sciences. In total, 74 graduate students from food sciences participated in this study in which 77% of students were female ( N = 57) and 23% were male ( N = 17).
Study design and procedure
This empirical study has an exploratory nature and it was conducted in two phases. An online module called “ Argumentative Essay Writing ” (AEW) was designed to be followed by students within the Brightspace platform. The purpose of the AEW module was to improve students’ essay writing skills by engaging them in a peer learning process where students were invited to provide feedback on each other’s essays. After designing the module, the study was implemented in two weeks and followed in two phases.
In week one (phase one), students were asked to write an essay on given topics. The topics for the essay were controversial and included “ Scientists with affiliations to the food industry should abstain from participating in risk assessment processes ”, “ powdered infant formula must adhere to strict sterility standards ”, and “ safe food consumption is the responsibility of the consumer ”. The given controversial topics were directly related to the course content and students’ area of study. Students had time for one week to write their essays individually and submit them to the Brightspace platform.
In week two (phase two), students were randomly invited to provide two sets of written/asynchronous feedback on their peers’ submitted essays. We gave a prompt to students to be used for giving feedback ( Please provide feedback to your peer and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ). To be able to engage students in the online peer feedback activity, we used the FeedbackFruits app embedded in the Brightspace platform. FeedbackFruits functions as an external educational technology tool seamlessly integrated into Brightspace, aimed at enhancing student engagement via diverse peer collaboration approaches. Among its features are peer feedback, assignment evaluation, skill assessment, automated feedback, interactive videos, dynamic documents, discussion tasks, and engaging presentations (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). In this research, our focus was on the peer feedback feature of the FeedbackFruits app, which empowers teachers to design tasks that enable students to offer feedback to their peers.
In addition, we used ChatGPT as another feedback source on peers’ essays. To be consistent with the criteria for peer feedback, we gave the same feedback prompt question with a minor modification to ChatGPT and asked it to give feedback on the peers’ essays ( Please read and provide feedback on the following essay and explain the extent to which she/he has presented/elaborated/justified various elements of an argumentative essay. What are the problems and what are your suggestions to improve each element of the essay? Your feedback must be between 250 and 350 words ).
Following this design, we were able to collect students’ essay data, peer feedback data, and feedback data generated by ChatGPT. In the next step, we used two coding schemes to analyze the quality of the essays and feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
Measurements
Coding scheme to assess the quality of essay writing.
In this study, a coding scheme proposed by Noroozi et al. ( 2016 ) was employed to assess students’ essay quality. This coding system was constructed based on the key components of high-quality essay composition, encompassing eight elements: introduction pertaining to the subject, taking a clear stance on the subject, presenting arguments in favor of the chosen position, providing justifications for the arguments supporting the position, counter-arguments, justifications for counter-arguments, responses to counter-arguments, and concluding with implications. Each element in the coding system is assigned a score ranging from zero (indicating the lowest quality level) to three (representing the highest quality level). The cumulative scores across all these elements were aggregated to determine the overall quality score of the student’s written essays. Two experienced coders in the field of education collaborated to assess the quality of the written essays, and their agreement level was measured at 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.70–0.81]; z = 25.05; p < 0.001), signifying a significant level of consensus between the coders.
Coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT
To assess the quality of feedback provided by both peers and ChatGPT, we employed a coding scheme developed by Noroozi et al. ( 2022 ). This coding framework dissects the characteristics of feedback, encompassing three key elements: the affective component, which considers the inclusion of emotional elements such as positive sentiments like praise or compliments, as well as negative emotions such as anger or disappointment; the cognitive component, which includes description (a concise summary of the essay), identification (pinpointing and specifying issues within the essay), and justification (providing explanations and justifications for the identified issues); and the constructive component, which involves offering recommendations, albeit not detailed action plans for further enhancements. Ratings within this coding framework range from zero, indicating poor quality, to two, signifying good quality. The cumulative scores were tallied to determine the overall quality of the feedback provided to the students. In this research, as each essay received feedback from both peers and ChatGPT, we calculated the average score from the two sets of feedback to establish the overall quality score for the feedback received, whether from peers or ChatGPT. The same two evaluators were involved in the assessment. The inter-rater reliability between the evaluators was determined to be 75% (Cohen’s Kappa = 0.75 [95% confidence interval: 0.66–0.84]; z = 17.52; p < 0.001), showing a significant level of agreement between them.
The logic behind choosing these coding schemes was as follows: Firstly, from a theoretical standpoint, both coding schemes were developed based on robust and well-established theories. The coding scheme for evaluating essay quality draws on Toulmin’s argumentation model ( 1958 ), a respected framework for essay writing. It encompasses all elements essential for high-quality essay composition and aligns well with the structure of essays assigned in the chosen course for this study. Similarly, the feedback coding scheme is grounded in prominent works on identifying feedback features (e.g., Nelson & Schunn, 2009 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ; Wu & Schunn, 2020 ), enabling the identification of key features of high-quality feedback (Noroozi et al., 2022 ). Secondly, from a methodological perspective, both coding schemes feature a transparent scoring method, mitigating coder bias and bolstering the tool’s credibility.
To ensure the data’s validity and reliability for statistical analysis, two tests were implemented. Initially, the Levene test assessed group homogeneity, followed by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to evaluate data normality. The results confirmed both group homogeneity and data normality. For the first research question, gender was considered as a control variable, and the MANCOVA test was employed to compare the variations in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Addressing the second research question involved using Spearman’s correlation to examine the relationships among original argumentative essays, peer feedback, and ChatGPT-generated feedback.
The results showed a significant difference in feedback quality between peer feedback and ChatGPT-generated feedback. Peers provided feedback of higher quality compared to ChatGPT. This difference was mainly due to the descriptive and identification of the problem features of feedback. ChatGPT tended to produce more extensive descriptive feedback including a summary statement such as the description of the essay or taken action, while students performed better in pinpointing and identifying the issues in the feedback provided (see Table 1 ).
A comprehensive list featuring selected examples of feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT is presented in Fig 1 . This table additionally outlines examples of how the generated feedback was coded based on the coding scheme to assess the quality of feedback.
A comparative list of selected examples of peer-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback
Overall, the results indicated that there was no significant relationship between the quality of essay writing and the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT. However, a positive correlation was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by ChatGPT, while a negative relationship was observed between the quality of the essay and the affective feature of feedback generated by peers. This finding means that as the quality of the essay improves, ChatGPT tends to provide more affective feedback, while peers tend to provide less affective feedback (see Table 2 ).
This study was an initial effort to explore the potential of ChatGPT as a feedback source in the context of essay writing and to compare the extent to which the quality of feedback generated by ChatGPT differs from the feedback provided by peers. Below we discuss our findings for each research question.
Discussion on the results of RQ1
For the first research question, the results revealed a disparity in feedback quality when comparing peer-generated feedback to feedback generated by ChatGPT. Peer feedback demonstrated higher quality compared to ChatGPT-generated feedback. This discrepancy is attributed primarily to variations in the descriptive and problem-identification features of the feedback.
ChatGPT tended to provide more descriptive feedback, often including elements such as summarizing the content of the essay. This inclination towards descriptive feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to analyze and synthesize textual information effectively. Research on ChatGPT further supports this notion, demonstrating the AI tool’s capacity to offer a comprehensive overview of the provided content, therefore potentially providing insights and a holistic perspective on the content (Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ).
ChatGPT’s proficiency in providing extensive descriptive feedback could be seen as a strength. It might be particularly valuable for summarizing complex arguments or providing comprehensive overviews, which could aid students in understanding the overall structure and coherence of their essays.
In contrast, students’ feedback content entailed high quality regarding identifying specific issues and areas for improvement. Peers outperformance compared to ChatGPT in identifying problems within the essays could be related to humans’ potential in cognitive skills, critical thinking abilities, and contextual understanding (e.g., Korteling et al., 2021 ; Lamb et al., 2019 ). This means that students, with their contextual knowledge and critical thinking skills, may be better equipped to identify issues within the essays that ChatGPT may overlook.
Furthermore, a detailed look at the findings of the first research question discloses that the feedback generated by ChatGPT comprehensively encompassed all essential components characterizing high-quality feedback, including affective, cognitive, and constructive dimensions (Kerman et al., 2022 ; Patchan et al., 2016 ). This comprehensive observation could be an indication of the fact that ChatGPT-generated feedback could potentially serve as a viable source of feedback. This observation is supported by previous studies where a positive role for AI-generated feedback and automated feedback in enhancing educational outcomes has been recognized (e.g., Bellhäuser et al., 2023 ; Gombert et al., 2024 ; Huang et al., 2023 ; Xia et al., 2022 ).
Finally, an overarching look at the results of the first research question suggests a potential complementary role for ChatGPT and students in the feedback process. This means that using these two feedback sources together creates a synergistic relationship that could result in better feedback outcomes.
Discussion on the results of RQ2
Results for the second research question revealed no observations of a significant correlation between the quality of the essays and the quality of the feedback generated by both peers and ChatGPT. These findings carry a consequential implication, suggesting that the inherent quality of the essays under scrutiny exerts negligible influence over the quality of feedback furnished by both students and the ChatGPT.
In essence, these results point to a notable degree of independence between the writing prowess exhibited in the essays and the efficacy of the feedback received from either source. This disassociation implies that the ability to produce high-quality essays does not inherently translate into a corresponding ability to provide equally insightful feedback, neither for peers nor for ChatGPT. This decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality highlighted the multifaceted nature of these evaluative processes, where proficiency in constructing a coherent essay does not necessarily guarantee an equally adept capacity for evaluating and articulating constructive commentary on peers’ work.
The implications of these findings are both intriguing and defy conventional expectations, as they deviate somewhat from the prevailing literature’s stance. The existing body of scholarly work generally posits a direct relationship between the quality of an essay and the subsequent quality of generated feedback (Noroozi et al., 2016 ;, 2022 ; Kerman et al., 2022 ; Vale Haro et al., 2023 ). This line of thought contends that essays of inferior quality might serve as a catalyst for more pronounced error detection among students, encompassing grammatical intricacies, depth of content, clarity, and coherence, as well as the application of evidence and support. Conversely, when essays are skillfully crafted, the act of pinpointing areas for enhancement becomes a more complex task, potentially necessitating a heightened level of subject comprehension and nuanced evaluation.
However, the present study’s findings challenge this conventional wisdom. The observed decoupling of essay quality from feedback quality suggests a more nuanced interplay between the two facets of assessment. Rather than adhering to the anticipated pattern, wherein weaker essays prompt clearer identification of deficiencies, and superior essays potentially render the feedback process more challenging, the study suggests that the process might be more complex than previously thought. It hints at a dynamic in which the act of evaluating essays and providing constructive feedback transcends a simple linear connection with essay quality.
These findings, while potentially unexpected, are an indication of the complex nature of essay assignments and feedback provision highlighting the complexity of cognitive processes that underlie both tasks, and suggesting that the relationship between essay quality and feedback quality is not purely linear but influenced by a multitude of factors, including the evaluator’s cognitive framework, familiarity with the subject matter, and critical analysis skills.
Despite this general observation, a closer examination of the affective features within the feedback reveals a different pattern. The positive correlation between essay quality and the affective features present in ChatGPT-generated feedback could be related to ChatGPT’s capacity to recognize and appreciate students’ good work. As the quality of the essay increases, ChatGPT might be programmed to offer more positive and motivational feedback to acknowledge students’ progress (e.g., Farrokhnia et al., 2023 ; Ray, 2023 ). In contrast, the negative relationship between essay quality and the affective features in peer feedback may be attributed to the evolving nature of feedback from peers (e.g., Patchan et al., 2016 ). This suggests that as students witness improvements in their peers’ essay-writing skills and knowledge, their feedback priorities may naturally evolve. For instance, students may transition from emphasizing emotional and affective comments to focusing on cognitive and constructive feedback, with the goal of further enhancing the overall quality of the essays.
Limitations and implications for future research and practice
We acknowledge the limitations of this study. Primarily, the data underpinning this investigation was drawn exclusively from a singular institution and a solitary course, featuring a relatively modest participant pool. This confined scope inevitably introduces certain constraints that need to be taken into consideration when interpreting the study’s outcomes and generalizing them to broader educational contexts. Under this constrained sampling, the findings might exhibit a degree of contextual specificity, potentially limiting their applicability to diverse institutional settings and courses with distinct curricular foci. The diverse array of academic environments, student demographics, and subject matter variations existing across educational institutions could potentially yield divergent patterns of results. Therefore, while the current study’s outcomes provide insights within the confines of the studied institution and course, they should be interpreted and generalized with prudence. Recognizing these limitations, for future studies, we recommend considering a large-scale participant pool with a diverse range of variables, including individuals from various programs and demographics. This approach would enrich the depth and breadth of understanding in this domain, fostering a more comprehensive comprehension of the complex dynamics at play.
In addition, this study omitted an exploration into the degree to which students utilize feedback provided by peers and ChatGPT. That is to say that we did not investigate the effects of such feedback on essay enhancements in the revision phase. This omission inherently introduces a dimension of uncertainty and places a constraint on the study’s holistic understanding of the feedback loop. By not addressing these aspects, the study’s insights are somewhat partial, limiting the comprehensive grasp of the potential influences that these varied feedback sources wield on students’ writing enhancement processes. An analysis of the feedback assimilation patterns and their subsequent effects on essay refinement would have unveiled insights into the practical utility and impact of the feedback generated by peers and ChatGPT.
To address this limitation, future investigations could be structured to encompass a more thorough examination of students’ feedback utilization strategies and the resulting implications for the essay revision process. By shedding light on the complex interconnection between feedback reception, its integration into the revision process, and the ultimate outcomes in terms of essay improvement, a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamics involved could be attained.
Furthermore, in this study, we employed identical question prompts for both peers and ChatGPT. However, there is evidence indicating that ChatGPT is sensitive to how prompts are presented to it (e.g., Cao et al., 2023 ; White et al., 2023 ; Zuccon & Koopman, 2023 ). This suggests that variations in the wording, structure, or context of prompts might influence the responses generated by ChatGPT, potentially impacting the comparability of its outputs with those of peers. Therefore, it is essential to carefully consider and control for prompt-related factors in future research when assessing ChatGPT’s performance and capabilities in various tasks and contexts.
In addition, We acknowledge that ChatGPT can potentially generate inaccurate results. Nevertheless, in the context of this study, our examination of the results generated by ChatGPT did not reveal a significant inaccuracies that would warrant inclusion in our findings.
From a methodological perspective, we reported the interrater reliability between the coders to be 75%. While this level of agreement was statistically significant, signifying the reliability of our coders’ analyses, it did not reach the desired level of precision. We acknowledge this as a limitation of the study and suggest enhancing interrater reliability through additional coder training.
In addition, it is worth noting that the advancement of Generative AI like ChatGPT, opens new avenues in educational feedback mechanisms. Beyond just generating feedback, these AI models have the potential to redefine how feedback is presented and assimilated. In the realm of research on adaptive learning systems, the findings of this study also echo the importance of adaptive learning support empowered by AI and ChatGPT (Rummel et al., 2016 ). It can pave the way for tailored educational experiences that respond dynamically to individual student needs. This is not just about the feedback’s content but its delivery, timing, and adaptability. Further exploratory data analyses, such as sequential analysis and data mining, may offer insights into the nuanced ways different adaptive learning supports can foster student discussions (Papamitsiou & Economides, 2014 ). This involves dissecting the feedback dynamics, understanding how varied feedback types stimulate discourse, and identifying patterns that lead to enhanced student engagement.
Ensuring the reliability and validity of AI-empowered feedback is also crucial. The goal is to ascertain that technology-empowered learning support genuinely enhances students’ learning process in a consistent and unbiased manner. Given ChatGPT’s complex nature of generating varied responses based on myriad prompts, the call for enhancing methodological rigor through future validation studies becomes both timely and essential. For example, in-depth prompt validation and blind feedback assessment studies could be employed to meticulously probe the consistency and quality of ChatGPT’s responses. Also, comparative analysis with different AI models can be useful.
From an educational standpoint, our research findings advocate for the integration of ChatGPT as a feedback resource with peer feedback within higher education environments for essay writing tasks since there is a complementary role potential for pee-generated and ChatGPT-generated feedback. This approach holds the potential to alleviate the workload burden on teachers, particularly in the context of online courses with a significant number of students.
This study contributes to and adds value to the young existing but rapidly growing literature in two distinct ways. From a research perspective, this study addresses a significant void in the current literature by responding to the lack of research on AI-generated feedback for complex tasks like essay writing in higher education. The research bridges this gap by analyzing the effectiveness of ChatGPT-generated feedback compared to peer-generated feedback, thereby establishing a foundation for further exploration in this field. From a practical perspective of higher education, the study’s findings offer insights into the potential integration of ChatGPT as a feedback source within higher education contexts. The discovery that ChatGPT’s feedback quality could potentially complement peer feedback highlights its applicability for enhancing feedback practices in higher education. This holds particular promise for courses with substantial enrolments and essay-writing components, providing teachers with a feasible alternative for delivering constructive feedback to a larger number of students.
Data availability
The data is available upon a reasonable request.
Alqassab, M., Strijbos, J. W., & Ufer, S. (2018). Training peer-feedback skills on geometric construction tasks: Role of domain knowledge and peer-feedback levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education , 33 (1), 11–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-017-0342-0 .
Article Google Scholar
Amiryousefi, M., & Geld, R. (2021). The role of redressing teachers’ instructional feedback interventions in EFL learners’ motivation and achievement in distance education. Innovation in Language Learning and Teaching , 15 (1), 13–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/17501229.2019.1654482 .
Arguedas, M., Daradoumis, A., & Xhafa Xhafa, F. (2016). Analyzing how emotion awareness influences students’ motivation, engagement, self-regulation and learning outcome. Educational Technology and Society , 19 (2), 87–103. https://www.jstor.org/stable/jeductechsoci.19.2.87 .
Google Scholar
Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., van Ginkel, S., Macfadyen, L. P., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). A systematic review of the role of learning analytics in enhancing feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2022.100489 .
Banihashem, S. K., Dehghanzadeh, H., Clark, D., Noroozi, O., & Biemans, H. J. (2023). Learning analytics for online game-based learning: A systematic literature review. Behaviour & Information Technology , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2023.2255301 .
Bellhäuser, H., Dignath, C., & Theobald, M. (2023). Daily automated feedback enhances self-regulated learning: A longitudinal randomized field experiment. Frontiers in Psychology , 14 , 1125873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1125873 .
Bond, M., Khosravi, H., De Laat, M., Bergdahl, N., Negrea, V., Oxley, E., & Siemens, G. (2024). A meta systematic review of artificial intelligence in higher education: A call for increased ethics, collaboration, and rigour. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 21 (4), 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00436-z .
Bulqiyah, S., Mahbub, M., & Nugraheni, D. A. (2021). Investigating writing difficulties in Essay writing: Tertiary Students’ perspectives. English Language Teaching Educational Journal , 4 (1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.12928/eltej.v4i1.2371 .
Callender, A. A., Franco-Watkins, A. M., & Roberts, A. S. (2016). Improving metacognition in the classroom through instruction, training, and feedback. Metacognition and Learning , 11 (2), 215–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-015-9142-6 .
Cao, J., Li, M., Wen, M., & Cheung, S. C. (2023). A study on prompt design, advantages and limitations of chatgpt for deep learning program repair. arXiv Preprint arXiv:2304 08191 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.08191 .
Dai, W., Lin, J., Jin, F., Li, T., Tsai, Y. S., Gasevic, D., & Chen, G. (2023). Can large language models provide feedback to students? A case study on ChatGPT. https://doi.org/10.35542/osf.io/hcgzj .
Darvishi, A., Khosravi, H., Sadiq, S., Gašević, D., & Siemens, G. (2024). Impact of AI assistance on student agency. Computers & Education , 210 , 104967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104967 .
Deeva, G., Bogdanova, D., Serral, E., Snoeck, M., & De Weerdt, J. (2021). A review of automated feedback systems for learners: Classification framework, challenges and opportunities. Computers & Education , 162 , 104094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104094 .
Diezmann, C. M., & Watters, J. J. (2015). The knowledge base of subject matter experts in teaching: A case study of a professional scientist as a beginning teacher. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education , 13 , 1517–1537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-014-9561-x .
Drachsler, H. (2023). Towards highly informative learning analytics . Open Universiteit. https://doi.org/10.25656/01:26787 .
Drachsler, H., & Kalz, M. (2016). The MOOC and learning analytics innovation cycle (MOLAC): A reflective summary of ongoing research and its challenges. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning , 32 (3), 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12135 .
Er, E., Dimitriadis, Y., & Gašević, D. (2021). Collaborative peer feedback and learning analytics: Theory-oriented design for supporting class-wide interventions. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 46 (2), 169–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1764490 .
Farrokhnia, M., Banihashem, S. K., Noroozi, O., & Wals, A. (2023). A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: Implications for educational practice and research. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Gan, Z., An, Z., & Liu, F. (2021). Teacher feedback practices, student feedback motivation, and feedback behavior: How are they associated with learning outcomes? Frontiers in Psychology , 12 , 697045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.697045 .
Gao, X., Noroozi, O., Gulikers, J. T. M., Biemans, H. J., & Banihashem, S. K. (2024). A systematic review of the key components of online peer feedback practices in higher education. Educational Research Review , 100588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2023.100588 .
Gielen, M., & De Wever, B. (2015). Scripting the role of assessor and assessee in peer assessment in a wiki environment: Impact on peer feedback quality and product improvement. Computers & Education , 88 , 370–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.07.012 .
Gombert, S., Fink, A., Giorgashvili, T., Jivet, I., Di Mitri, D., Yau, J., & Drachsler, H. (2024). From the Automated Assessment of Student Essay Content to highly informative feedback: A case study. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-023-00387-6 .
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research , 77 (1), 81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487 .
Holt-Reynolds, D. (1999). Good readers, good teachers? Subject matter expertise as a challenge in learning to teach. Harvard Educational Review , 69 (1), 29–51. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.69.1.pl5m5083286l77t2 .
Huang, A. Y., Lu, O. H., & Yang, S. J. (2023). Effects of artificial intelligence–enabled personalized recommendations on learners’ learning engagement, motivation, and outcomes in a flipped classroom. Computers & Education , 194 , 104684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104684 .
Katz, A., Wei, S., Nanda, G., Brinton, C., & Ohland, M. (2023). Exploring the efficacy of ChatGPT in analyzing Student Teamwork Feedback with an existing taxonomy. arXiv Preprint arXiv . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.11882 .
Kerman, N. T., Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Online peer feedback patterns of success and failure in argumentative essay writing. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2093914 .
Kerman, N. T., Banihashem, S. K., Karami, M., Er, E., Van Ginkel, S., & Noroozi, O. (2024). Online peer feedback in higher education: A synthesis of the literature. Education and Information Technologies , 29 (1), 763–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12273-8 .
King, A. (2002). Structuring peer interaction to promote high-level cognitive processing. Theory into Practice , 41 (1), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15430421tip4101_6 .
Konold, K. E., Miller, S. P., & Konold, K. B. (2004). Using teacher feedback to enhance student learning. Teaching Exceptional Children , 36 (6), 64–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/004005990403600608 .
Korteling, J. H., van de Boer-Visschedijk, G. C., Blankendaal, R. A., Boonekamp, R. C., & Eikelboom, A. R. (2021). Human-versus artificial intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence , 4 , 622364. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2021.622364 .
Labuhn, A. S., Zimmerman, B. J., & Hasselhorn, M. (2010). Enhancing students’ self-regulation and mathematics performance: The influence of feedback and self-evaluative standards. Metacognition and Learning , 5 , 173–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-010-9056-2 .
Lamb, R., Firestone, J., Schmitter-Edgecombe, M., & Hand, B. (2019). A computational model of student cognitive processes while solving a critical thinking problem in science. The Journal of Educational Research , 112 (2), 243–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1514357 .
Latifi, S., Noroozi, O., & Talaee, E. (2023). Worked example or scripting? Fostering students’ online argumentative peer feedback, essay writing and learning. Interactive Learning Environments , 31 (2), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1799032 .
Li, L., & Liu, X. (2010). Steckelberg. Assessor or assessee: How student learning improves by giving and receiving peer feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 41 (3), 525–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.00968.x .
Liu, N. F., & Carless, D. (2006). Peer feedback: The learning element of peer assessment. Teaching in Higher Education , 11 (3), 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510600680582 .
Liunokas, Y. (2020). Assessing students’ ability in writing argumentative essay at an Indonesian senior high school. IDEAS: Journal on English language teaching and learning. Linguistics and Literature , 8 (1), 184–196. https://doi.org/10.24256/ideas.v8i1.1344 .
Nelson, M. M., & Schunn, C. D. (2009). The nature of feedback: How different types of peer feedback affect writing performance. Instructional Science , 37 , 375–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-008-9053-x .
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Taghizadeh Kerman, N., Parvaneh Akhteh Khaneh, M., Babayi, M., Ashrafi, H., & Biemans, H. J. (2022). Gender differences in students’ argumentative essay writing, peer review performance and uptake in online learning environments. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2022.2034887 .
Noroozi, O., Biemans, H., & Mulder, M. (2016). Relations between scripted online peer feedback processes and quality of written argumentative essay. The Internet and Higher Education , 31, 20-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.05.002
Noroozi, O., Banihashem, S. K., Biemans, H. J., Smits, M., Vervoort, M. T., & Verbaan, C. L. (2023). Design, implementation, and evaluation of an online supported peer feedback module to enhance students’ argumentative essay quality. Education and Information Technologies , 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11683-y .
Papamitsiou, Z., & Economides, A. A. (2014). Learning analytics and educational data mining in practice: A systematic literature review of empirical evidence. Journal of Educational Technology & Society , 17 (4), 49–64. https://doi.org/10.2307/jeductechsoci.17.4.49 . https://www.jstor.org/stable/ .
Pardo, A., Jovanovic, J., Dawson, S., Gašević, D., & Mirriahi, N. (2019). Using learning analytics to scale the provision of personalised feedback. British Journal of Educational Technology , 50 (1), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12592 .
Patchan, M. M., Schunn, C. D., & Correnti, R. J. (2016). The nature of feedback: How peer feedback features affect students’ implementation rate and quality of revisions. Journal of Educational Psychology , 108 (8), 1098. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000103 .
Ramsden, P. (2003). Learning to teach in higher education . Routledge.
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems , 3 , 121–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Rüdian, S., Heuts, A., & Pinkwart, N. (2020). Educational Text Summarizer: Which sentences are worth asking for? In DELFI 2020 - The 18th Conference on Educational Technologies of the German Informatics Society (pp. 277–288). Bonn, Germany.
Rummel, N., Walker, E., & Aleven, V. (2016). Different futures of adaptive collaborative learning support. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education , 26 , 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-016-0102-3 .
Shi, M. (2019). The effects of class size and instructional technology on student learning performance. The International Journal of Management Education , 17 (1), 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2019.01.004 .
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Toulmin, S. (1958). The uses of argument . Cambridge University Press.
Valero Haro, A., Noroozi, O., Biemans, H. J., Mulder, M., & Banihashem, S. K. (2023). How does the type of online peer feedback influence feedback quality, argumentative essay writing quality, and domain-specific learning? Interactive Learning Environments , 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2215822 .
White, J., Fu, Q., Hays, S., Sandborn, M., Olea, C., Gilbert, H., & Schmidt, D. C. (2023). A prompt pattern catalog to enhance prompt engineering with chatgpt. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.11382 . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.11382 .
Wu, Y., & Schunn, C. D. (2020). From feedback to revisions: Effects of feedback features and perceptions. Contemporary Educational Psychology , 60 , 101826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101826 .
Xia, Q., Chiu, T. K., Zhou, X., Chai, C. S., & Cheng, M. (2022). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence , 100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education , 16 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0 .
Zhang, Z. V., & Hyland, K. (2022). Fostering student engagement with feedback: An integrated approach. Assessing Writing , 51 , 100586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2021.100586 .
Zuccon, G., & Koopman, B. (2023). Dr ChatGPT, tell me what I want to hear: How prompt knowledge impacts health answer correctness. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302 .13793. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.13793 .
Download references
No funding has been received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Open Universiteit, Heerlen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Hendrik Drachsler
Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Seyyed Kazem Banihashem & Omid Noroozi
Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran
Nafiseh Taghizadeh Kerman
The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA
Jewoong Moon
DIPE Leibniz Institute, Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany
Hendrik Drachsler
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S. K. Banihashem led this research experiment. N. T. Kerman contributed to the data analysis and writing. O. Noroozi contributed to the designing, writing, and reviewing the manuscript. J. Moon contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript. H. Drachsler contributed to the writing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Seyyed Kazem Banihashem .
Ethics declarations
Declaration of ai-assisted technologies in the writing process.
The authors used generative AI for language editing and took full responsibility.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Banihashem, S.K., Kerman, N.T., Noroozi, O. et al. Feedback sources in essay writing: peer-generated or AI-generated feedback?. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 21 , 23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2023
Accepted : 18 March 2024
Published : 12 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-024-00455-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- AI-generated feedback
- Essay writing
- Feedback sources
- Higher education
- Peer feedback

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Five-Part Argumentative Essay. Thesis and Introduction: Often only a sentence long, the thesis concisely describes the writer's position, and the introductory paragraph provides context. Body Paragraphs and Counterargument: There are generally three body paragraphs used to present research that supports the writer's thesis.They can also include a counterargument that details and ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Establishing an Argument; Logic in Argumentative Writing; Organizing Your Argument Presentation; A good argument in an essay on literature has: A tight, specific focus. Rather than broad sweeping statements, a good argument teases out a single aspect of a piece of literature and analyzes it in minute detail: literature under the microscope.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis, nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Five Types of Argument Claims in Essay Writing. There are five major types of argument claims as given below. A claim of definition. A claim about values. A claim about the reason. A claim about comparison. A claim about policy or position. A writer makes a claim about these issues and answers the relevant questions about it with relevant data ...
An argumentative essay is a structured, compelling piece of writing where an author clearly defines their stance on a specific topic. This is a very popular style of writing assigned to students at schools, colleges, and universities. Learn the steps to researching, structuring, and writing an effective argumentative essay below. Requirements ...
1. Introductory paragraph. The first paragraph of your essay should outline the topic, provide background information necessary to understand your argument, outline the evidence you will present and states your thesis. 2. The thesis statement. This is part of your first paragraph.
The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner. Please note: Some confusion may occur between the argumentative essay and the expository essay. These two genres are similar, but the argumentative ...
inconsistency in your essay. • suggests an answer complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of discussion. If the question is too vague, it won't suggest a line of argument. The question should elicit reflection and argument rather than summary or description. • can be explored using the sources you have available for the assignment,
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
An argumentative essay in academic writing is where one takes a stance on a particular topic, presents arguments to support that stance, and aims to persuade readers to accept the point of view presented. Read this to learn how to write an argumentative essay with examples, create an argumentative essay outline, and gain expert tips for authors.
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
Argumentative essay formula & example. In the image below, you can see a recommended structure for argumentative essays. It starts with the topic sentence, which establishes the main idea of the essay. Next, this hypothesis is developed in the development stage. Then, the rebuttal, or the refutal of the main counter argument or arguments.
When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience. Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your ...
Argumentative literary essays are typically more informal and do not follow the same structure as an academic essay. The following are popular examples of argumentative literary essays: "Letter from Birmingham Jail" by Martin Luther King, Jr. "Death of the Moth" by Virginia Woolf "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
Secondly, it lets the writer figure out what evidence suits what argument most. Before writing, draft your essay first. Put examples, facts, etc. in the right parts of the paper. Then, write the entire text. Thirdly, an outline provides a perfect opportunity to change the essay's parts without rewriting the paper.
Argumentative Essay Example 2. Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to people through female Anopheles mosquitoes. Each year, over half a billion people will become infected with malaria, with roughly 80% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa.
A. As basketball star Charles Barkley stated in a famous advertising campaign for Nike, he was paid to dominate on the basketball court, not to raise your kids. Many celebrities do consider themselves responsible for setting a good example and create non-profit organizations through which they can benefit youths. B.
You can buy argumentative essay tasks at Handmade Writing. Our service is available 24/7. Argumentative essay Example Argumentative essay example Organizing the Argumentative Essay Outline. An argumentative essay follows the typical essay format: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. However, the body paragraphs are structured a bit ...
Try our student writing prompts. In 2017, we compiled a list of 401 argumentative writing prompts, all drawn from our daily Student Opinion column. Now, we're rounding up 130 more we've ...
Essays. In short pieces of writing (< 3,000 words), there will be groups of paragraphs which together form one part of your argument. Usually these sections in "short" essays do not have specific headings. However, they can be clearly identified by using linking phrases which show for example: how many elements the section consists of:
50 Argumentative Essay Topics. Illustration by Catherine Song. ThoughtCo. An argumentative essay requires you to decide on a topic and take a position on it. You'll need to back up your viewpoint with well-researched facts and information as well. One of the hardest parts is deciding which topic to write about, but there are plenty of ideas ...
"The argumentative essay is a genre of writing that requires the student to investigate a topic, collect, generate, and evaluate evidence, and establish a position on the issue." The catch: You don't only establish your position on the topic but also need to prove it and convince a reader that this position is correct.
An online module called "Argumentative Essay Writing" (AEW) was designed to be followed by students within the Brightspace platform. The purpose of the AEW module was to improve students' essay writing skills by engaging them in a peer learning process where students were invited to provide feedback on each other's essays.