Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 20 July 2022

The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence
- Joanna Moncrieff 1 , 2 ,
- Ruth E. Cooper 3 ,
- Tom Stockmann 4 ,
- Simone Amendola 5 ,
- Michael P. Hengartner 6 &
- Mark A. Horowitz 1 , 2
Molecular Psychiatry volume 28 , pages 3243–3256 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
1.27m Accesses
235 Citations
9423 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Diagnostic markers
A Correspondence to this article was published on 16 June 2023
A Comment to this article was published on 16 June 2023
The serotonin hypothesis of depression is still influential. We aimed to synthesise and evaluate evidence on whether depression is associated with lowered serotonin concentration or activity in a systematic umbrella review of the principal relevant areas of research. PubMed, EMBASE and PsycINFO were searched using terms appropriate to each area of research, from their inception until December 2020. Systematic reviews, meta-analyses and large data-set analyses in the following areas were identified: serotonin and serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, concentrations in body fluids; serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor binding; serotonin transporter (SERT) levels measured by imaging or at post-mortem; tryptophan depletion studies; SERT gene associations and SERT gene-environment interactions. Studies of depression associated with physical conditions and specific subtypes of depression (e.g. bipolar depression) were excluded. Two independent reviewers extracted the data and assessed the quality of included studies using the AMSTAR-2, an adapted AMSTAR-2, or the STREGA for a large genetic study. The certainty of study results was assessed using a modified version of the GRADE. We did not synthesise results of individual meta-analyses because they included overlapping studies. The review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020207203). 17 studies were included: 12 systematic reviews and meta-analyses, 1 collaborative meta-analysis, 1 meta-analysis of large cohort studies, 1 systematic review and narrative synthesis, 1 genetic association study and 1 umbrella review. Quality of reviews was variable with some genetic studies of high quality. Two meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining the serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, showed no association with depression (largest n = 1002). One meta-analysis of cohort studies of plasma serotonin showed no relationship with depression, and evidence that lowered serotonin concentration was associated with antidepressant use ( n = 1869). Two meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining the 5-HT 1A receptor (largest n = 561), and three meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining SERT binding (largest n = 1845) showed weak and inconsistent evidence of reduced binding in some areas, which would be consistent with increased synaptic availability of serotonin in people with depression, if this was the original, causal abnormaly. However, effects of prior antidepressant use were not reliably excluded. One meta-analysis of tryptophan depletion studies found no effect in most healthy volunteers ( n = 566), but weak evidence of an effect in those with a family history of depression ( n = 75). Another systematic review ( n = 342) and a sample of ten subsequent studies ( n = 407) found no effect in volunteers. No systematic review of tryptophan depletion studies has been performed since 2007. The two largest and highest quality studies of the SERT gene, one genetic association study ( n = 115,257) and one collaborative meta-analysis ( n = 43,165), revealed no evidence of an association with depression, or of an interaction between genotype, stress and depression. The main areas of serotonin research provide no consistent evidence of there being an association between serotonin and depression, and no support for the hypothesis that depression is caused by lowered serotonin activity or concentrations. Some evidence was consistent with the possibility that long-term antidepressant use reduces serotonin concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Genetic contributions to brain serotonin transporter levels in healthy adults
The kynurenine pathway in major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of 101 studies
The complex clinical response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in depression: a network perspective
Introduction.
The idea that depression is the result of abnormalities in brain chemicals, particularly serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT), has been influential for decades, and provides an important justification for the use of antidepressants. A link between lowered serotonin and depression was first suggested in the 1960s [ 1 ], and widely publicised from the 1990s with the advent of the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. Although it has been questioned more recently [ 5 , 6 ], the serotonin theory of depression remains influential, with principal English language textbooks still giving it qualified support [ 7 , 8 ], leading researchers endorsing it [ 9 , 10 , 11 ], and much empirical research based on it [ 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 ]. Surveys suggest that 80% or more of the general public now believe it is established that depression is caused by a ‘chemical imbalance’ [ 15 , 16 ]. Many general practitioners also subscribe to this view [ 17 ] and popular websites commonly cite the theory [ 18 ].
It is often assumed that the effects of antidepressants demonstrate that depression must be at least partially caused by a brain-based chemical abnormality, and that the apparent efficacy of SSRIs shows that serotonin is implicated. Other explanations for the effects of antidepressants have been put forward, however, including the idea that they work via an amplified placebo effect or through their ability to restrict or blunt emotions in general [ 19 , 20 ].
Despite the fact that the serotonin theory of depression has been so influential, no comprehensive review has yet synthesised the relevant evidence. We conducted an ‘umbrella’ review of the principal areas of relevant research, following the model of a similar review examining prospective biomarkers of major depressive disorder [ 21 ]. We sought to establish whether the current evidence supports a role for serotonin in the aetiology of depression, and specifically whether depression is associated with indications of lowered serotonin concentrations or activity.
Search strategy and selection criteria
The present umbrella review was reported in accordance with the 2009 PRISMA statement [ 22 ]. The protocol was registered with PROSPERO in December 2020 (registration number CRD42020207203) ( https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=207203 ). This was subsequently updated to reflect our decision to modify the quality rating system for some studies to more appropriately appraise their quality, and to include a modified GRADE to assess the overall certainty of the findings in each category of the umbrella review.
In order to cover the different areas and to manage the large volume of research that has been conducted on the serotonin system, we conducted an ‘umbrella’ review. Umbrella reviews survey existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses relevant to a research question and represent one of the highest levels of evidence synthesis available [ 23 ]. Although they are traditionally restricted to systematic reviews and meta-analyses, we aimed to identify the best evidence available. Therefore, we also included some large studies that combined data from individual studies but did not employ conventional systematic review methods, and one large genetic study. The latter used nationwide databases to capture more individuals than entire meta-analyses, so is likely to provide even more reliable evidence than syntheses of individual studies.
We first conducted a scoping review to identify areas of research consistently held to provide support for the serotonin hypothesis of depression. Six areas were identified, addressing the following questions: (1) Serotonin and the serotonin metabolite 5-HIAA–whether there are lower levels of serotonin and 5-HIAA in body fluids in depression; (2) Receptors - whether serotonin receptor levels are altered in people with depression; (3) The serotonin transporter (SERT) - whether there are higher levels of the serotonin transporter in people with depression (which would lower synaptic levels of serotonin); (4) Depletion studies - whether tryptophan depletion (which lowers available serotonin) can induce depression; (5) SERT gene – whether there are higher levels of the serotonin transporter gene in people with depression; (6) Whether there is an interaction between the SERT gene and stress in depression.
We searched for systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and large database studies in these six areas in PubMed, EMBASE and PsycINFO using the Healthcare Databases Advanced Search tool provided by Health Education England and NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence). Searches were conducted until December 2020.
We used the following terms in all searches: (depress* OR affective OR mood) AND (systematic OR meta-analysis), and limited searches to title and abstract, since not doing so produced numerous irrelevant hits. In addition, we used terms specific to each area of research (full details are provided in Table S1 , Supplement). We also searched citations and consulted with experts.
Inclusion criteria were designed to identify the best available evidence in each research area and consisted of:
Research synthesis including systematic reviews, meta-analysis, umbrella reviews, individual patient meta-analysis and large dataset analysis.
Studies that involve people with depressive disorders or, for experimental studies (tryptophan depletion), those in which mood symptoms are measured as an outcome.
Studies of experimental procedures (tryptophan depletion) involving a sham or control condition.
Studies published in full in peer reviewed literature.
Where more than five systematic reviews or large analyses exist, the most recent five are included.
Exclusion criteria consisted of:
Animal studies.
Studies exclusively concerned with depression in physical conditions (e.g. post stroke or Parkinson’s disease) or exclusively focusing on specific subtypes of depression such as postpartum depression, depression in children, or depression in bipolar disorder.
No language or date restrictions were applied. In areas in which no systematic review or meta-analysis had been done within the last 10 years, we also selected the ten most recent studies at the time of searching (December 2020) for illustration of more recent findings. We performed this search using the same search string for this domain, without restricting it to systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Data analysis
Each member of the team was allocated one to three domains of serotonin research to search and screen for eligible studies using abstract and full text review. In case of uncertainty, the entire team discussed eligibility to reach consensus.
For included studies, data were extracted by two reviewers working independently, and disagreement was resolved by consensus. Authors of papers were contacted for clarification when data was missing or unclear.
We extracted summary effects, confidence intervals and measures of statistical significance where these were reported, and, where relevant, we extracted data on heterogeneity. For summary effects in the non-genetic studies, preference was given to the extraction and reporting of effect sizes. Mean differences were converted to effect sizes where appropriate data were available.
We did not perform a meta-analysis of the individual meta-analyses in each area because they included overlapping studies [ 24 ]. All extracted data is presented in Table 1 . Sensitivity analyses were reported where they had substantial bearing on interpretation of findings.
The quality rating of systematic reviews and meta-analyses was assessed using AMSTAR-2 (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews) [ 25 ]. For two studies that did not employ conventional systematic review methods [ 26 , 27 ] we used a modified version of the AMSTAR-2 (see Table S3 ). For the genetic association study based on a large database analysis we used the STREGA assessment (STrengthening the REporting of Genetic Association Studies) (Table S4 ) [ 28 ]. Each study was rated independently by at least two authors. We report ratings of individual items on the relevant measure, and the percentage of items that were adequately addressed by each study (Table 1 , with further detail in Tables S3 and S4 ).
Alongside quality ratings, two team members (JM, MAH) rated the certainty of the results of each study using a modified version of the GRADE guidelines [ 29 ]. Following the approach of Kennis et al. [ 21 ], we devised six criteria relevant to the included studies: whether a unified analysis was conducted on original data; whether confounding by antidepressant use was adequately addressed; whether outcomes were pre-specified; whether results were consistent or heterogeneity was adequately addressed if present; whether there was a likelihood of publication bias; and sample size. The importance of confounding by effects of current or past antidepressant use has been highlighted in several studies [ 30 , 31 ]. The results of each study were scored 1 or 0 according to whether they fulfilled each criteria, and based on these ratings an overall judgement was made about the certainty of evidence across studies in each of the six areas of research examined. The certainty of each study was based on an algorithm that prioritised sample size and uniform analysis using original data (explained more fully in the supplementary material), following suggestions that these are the key aspects of reliability [ 27 , 32 ]. An assessment of the overall certainty of each domain of research examining the role of serotonin was determined by consensus of at least two authors and a direction of effect indicated.
Search results and quality rating
Searching identified 361 publications across the 6 different areas of research, among which seventeen studies fulfilled inclusion criteria (see Fig. 1 and Table S1 for details of the selection process). Included studies, their characteristics and results are shown in Table 1 . As no systematic review or meta-analysis had been performed within the last 10 years on serotonin depletion, we also identified the 10 latest studies for illustration of more recent research findings (Table 2 ).
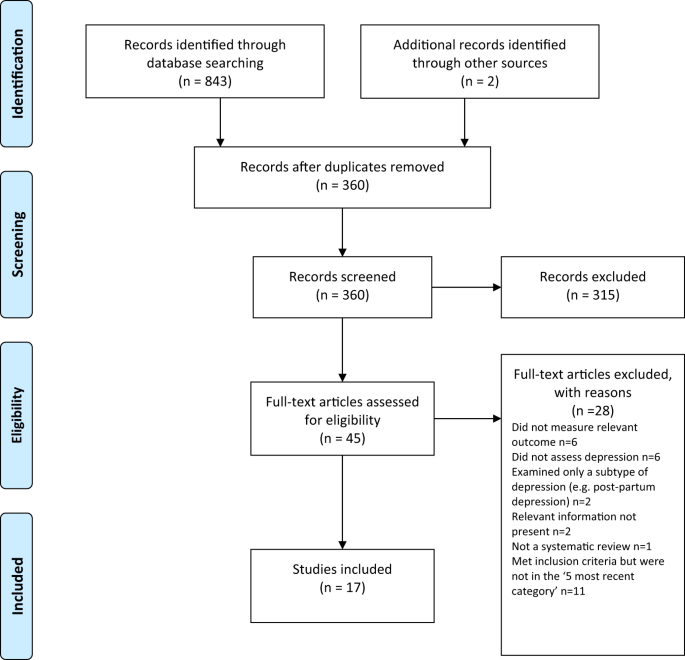
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagramme.
Quality ratings are summarised in Table 1 and reported in detail in Tables S2 – S3 . The majority (11/17) of systematic reviews and meta-analyses satisfied less than 50% of criteria. Only 31% adequately assessed risk of bias in individual studies (a further 44% partially assessed this), and only 50% adequately accounted for risk of bias when interpreting the results of the review. One collaborative meta-analysis of genetic studies was considered to be of high quality due to the inclusion of several measures to ensure consistency and reliability [ 27 ]. The large genetic analysis of the effect of SERT polymorphisms on depression, satisfied 88% of the STREGA quality criteria [ 32 ].
Serotonin and 5-HIAA
Serotonin can be measured in blood, plasma, urine and CSF, but it is rapidly metabolised to 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). CSF is thought to be the ideal resource for the study of biomarkers of putative brain diseases, since it is in contact with brain interstitial fluid [ 33 ]. However, collecting CSF samples is invasive and carries some risk, hence large-scale studies are scarce.
Three studies fulfilled inclusion criteria (Table 1 ). One meta-analysis of three large observational cohort studies of post-menopausal women, revealed lower levels of plasma 5-HT in women with depression, which did not, however, reach statistical significance of p < 0.05 after adjusting for multiple comparisons. Sensitivity analyses revealed that antidepressants were strongly associated with lower serotonin levels independently of depression.
Two meta-analyses of a total of 19 studies of 5-HIAA in CSF (seven studies were included in both) found no evidence of an association between 5-HIAA concentrations and depression.
Fourteen different serotonin receptors have been identified, with most research on depression focusing on the 5-HT 1A receptor [ 11 , 34 ]. Since the functions of other 5-HT receptors and their relationship to depression have not been well characterised, we restricted our analysis to data on 5-HT 1A receptors [ 11 , 34 ]. 5-HT 1A receptors, known as auto-receptors, inhibit the release of serotonin pre-synaptically [ 35 ], therefore, if depression is the result of reduced serotonin activity caused by abnormalities in the 5-HT 1A receptor, people with depression would be expected to show increased activity of 5-HT 1A receptors compared to those without [ 36 ].
Two meta-analyses satisfied inclusion criteria, involving five of the same studies [ 37 , 38 ] (see Table 1 ). The majority of results across the two analyses suggested either no difference in 5-HT 1A receptors between people with depression and controls, or a lower level of these inhibitory receptors, which would imply higher concentrations or activity of serotonin in people with depression. Both meta-analyses were based on studies that predominantly involved patients who were taking or had recently taken (within 1–3 weeks of scanning) antidepressants or other types of psychiatric medication, and both sets of authors commented on the possible influence of prior or current medication on findings. In addition, one analysis was of very low quality [ 37 ], including not reporting on the numbers involved in each analysis and using one-sided p-values, and one was strongly influenced by three studies and publication bias was present [ 38 ].
The serotonin transporter (SERT)
The serotonin transporter protein (SERT) transports serotonin out of the synapse, thereby lowering the availability of serotonin in the synapse [ 39 , 40 ]. Animals with an inactivated gene for SERT have higher levels of extra-cellular serotonin in the brain than normal [ 41 , 42 , 43 ] and SSRIs are thought to work by inhibiting the action of SERT, and thus increasing levels of serotonin in the synaptic cleft [ 44 ]. Although changes in SERT may be a marker for other abnormalities, if depression is caused by low serotonin availability or activity, and if SERT is the origin of that deficit, then the amount or activity of SERT would be expected to be higher in people with depression compared to those without [ 40 ]. SERT binding potential is an index of the concentration of the serotonin transporter protein and SERT concentrations can also be measured post-mortem.
Three overlapping meta-analyses based on a total of 40 individual studies fulfilled inclusion criteria (See Table 1 ) [ 37 , 39 , 45 ]. Overall, the data indicated possible reductions in SERT binding in some brain areas, although areas in which effects were detected were not consistent across the reviews. In addition, effects of antidepressants and other medication cannot be ruled out, since most included studies mainly or exclusively involved people who had a history of taking antidepressants or other psychiatric medications. Only one meta-analysis tested effects of antidepressants, and although results were not influenced by the percentage of drug-naïve patients in each study, numbers were small so it is unlikely that medication-related effects would have been reliably detected [ 45 ]. All three reviews cited evidence from animal studies that antidepressant treatment reduces SERT [ 46 , 47 , 48 ]. None of the analyses corrected for multiple testing, and one review was of very low quality [ 37 ]. If the results do represent a positive finding that is independent of medication, they would suggest that depression is associated with higher concentrations or activity of serotonin.
Depletion studies
Tryptophan depletion using dietary means or chemicals, such as parachlorophenylalanine (PCPA), is thought to reduce serotonin levels. Since PCPA is potentially toxic, reversible tryptophan depletion using an amino acid drink that lacks tryptophan is the most commonly used method and is thought to affect serotonin within 5–7 h of ingestion. Questions remain, however, about whether either method reliably reduces brain serotonin, and about other effects including changes in brain nitrous oxide, cerebrovascular changes, reduced BDNF and amino acid imbalances that may be produced by the manipulations and might explain observed effects independent of possible changes in serotonin activity [ 49 ].
One meta-analysis and one systematic review fulfilled inclusion criteria (see Table 1 ). Data from studies involving volunteers mostly showed no effect, including a meta-analysis of parallel group studies [ 50 ]. In a small meta-analysis of within-subject studies involving 75 people with a positive family history, a minor effect was found, with people given the active depletion showing a larger decrease in mood than those who had a sham procedure [ 50 ]. Across both reviews, studies involving people diagnosed with depression showed slightly greater mood reduction following tryptophan depletion than sham treatment overall, but most participants had taken or were taking antidepressants and participant numbers were small [ 50 , 51 ].
Since these research syntheses were conducted more than 10 years ago, we searched for a systematic sample of ten recently published studies (Table 2 ). Eight studies conducted with healthy volunteers showed no effects of tryptophan depletion on mood, including the only two parallel group studies. One study presented effects in people with and without a family history of depression, and no differences were apparent in either group [ 52 ]. Two cross-over studies involving people with depression and current or recent use of antidepressants showed no convincing effects of a depletion drink [ 53 , 54 ], although one study is reported as positive mainly due to finding an improvement in mood in the group given the sham drink [ 54 ].
SERT gene and gene-stress interactions
A possible link between depression and the repeat length polymorphism in the promoter region of the SERT gene (5-HTTLPR), specifically the presence of the short repeats version, which causes lower SERT mRNA expression, has been proposed [ 55 ]. Interestingly, lower levels of SERT would produce higher levels of synaptic serotonin. However, more recently, this hypothesis has been superseded by a focus on the interaction effect between this polymorphism, depression and stress, with the idea that the short version of the polymorphism may only give rise to depression in the presence of stressful life events [ 55 , 56 ]. Unlike other areas of serotonin research, numerous systematic reviews and meta-analyses of genetic studies have been conducted, and most recently a very large analysis based on a sample from two genetic databanks. Details of the five most recent studies that have addressed the association between the SERT gene and depression, and the interaction effect are detailed in Table 1 .
Although some earlier meta-analyses of case-control studies showed a statistically significant association between the 5-HTTLPR and depression in some ethnic groups [ 57 , 58 ], two recent large, high quality studies did not find an association between the SERT gene polymorphism and depression [ 27 , 32 ]. These two studies consist of by far the largest and most comprehensive study to date [ 32 ] and a high-quality meta-analysis that involved a consistent re-analysis of primary data across all conducted studies, including previously unpublished data, and other comprehensive quality checks [ 27 , 59 ] (see Table 1 ).
Similarly, early studies based on tens of thousands of participants suggested a statistically significant interaction between the SERT gene, forms of stress or maltreatment and depression [ 60 , 61 , 62 ], with a small odds ratio in the only study that reported this (1.18, 95% CI 1.09 to 1.28) [ 62 ]. However, the two recent large, high-quality studies did not find an interaction between the SERT gene and stress in depression (Border et al [ 32 ] and Culverhouse et al.) [ 27 ] (see Table 1 ).
Overall results
Table 3 presents the modified GRADE ratings for each study and the overall rating of the strength of evidence in each area. Areas of research that provided moderate or high certainty of evidence such as the studies of plasma serotonin and metabolites and the genetic and gene-stress interaction studies all showed no association between markers of serotonin activity and depression. Some other areas suggested findings consistent with increased serotonin activity, but evidence was of very low certainty, mainly due to small sample sizes and possible residual confounding by current or past antidepressant use. One area - the tryptophan depletion studies - showed very low certainty evidence of lowered serotonin activity or availability in a subgroup of volunteers with a family history of depression. This evidence was considered very low certainty as it derived from a subgroup of within-subject studies, numbers were small, and there was no information on medication use, which may have influenced results. Subsequent research has not confirmed an effect with numerous negative studies in volunteers.
Our comprehensive review of the major strands of research on serotonin shows there is no convincing evidence that depression is associated with, or caused by, lower serotonin concentrations or activity. Most studies found no evidence of reduced serotonin activity in people with depression compared to people without, and methods to reduce serotonin availability using tryptophan depletion do not consistently lower mood in volunteers. High quality, well-powered genetic studies effectively exclude an association between genotypes related to the serotonin system and depression, including a proposed interaction with stress. Weak evidence from some studies of serotonin 5-HT 1A receptors and levels of SERT points towards a possible association between increased serotonin activity and depression. However, these results are likely to be influenced by prior use of antidepressants and its effects on the serotonin system [ 30 , 31 ]. The effects of tryptophan depletion in some cross-over studies involving people with depression may also be mediated by antidepressants, although these are not consistently found [ 63 ].
The chemical imbalance theory of depression is still put forward by professionals [ 17 ], and the serotonin theory, in particular, has formed the basis of a considerable research effort over the last few decades [ 14 ]. The general public widely believes that depression has been convincingly demonstrated to be the result of serotonin or other chemical abnormalities [ 15 , 16 ], and this belief shapes how people understand their moods, leading to a pessimistic outlook on the outcome of depression and negative expectancies about the possibility of self-regulation of mood [ 64 , 65 , 66 ]. The idea that depression is the result of a chemical imbalance also influences decisions about whether to take or continue antidepressant medication and may discourage people from discontinuing treatment, potentially leading to lifelong dependence on these drugs [ 67 , 68 ].
As with all research synthesis, the findings of this umbrella review are dependent on the quality of the included studies, and susceptible to their limitations. Most of the included studies were rated as low quality on the AMSTAR-2, but the GRADE approach suggested some findings were reasonably robust. Most of the non-genetic studies did not reliably exclude the potential effects of previous antidepressant use and were based on relatively small numbers of participants. The genetic studies, in particular, illustrate the importance of methodological rigour and sample size. Whereas some earlier, lower quality, mostly smaller studies produced marginally positive findings, these were not confirmed in better-conducted, larger and more recent studies [ 27 , 32 ]. The identification of depression and assessment of confounders and interaction effects were limited by the data available in the original studies on which the included reviews and meta-analyses were based. Common methods such as the categorisation of continuous measures and application of linear models to non-linear data may have led to over-estimation or under-estimation of effects [ 69 , 70 ], including the interaction between stress and the SERT gene. The latest systematic review of tryptophan depletion studies was conducted in 2007, and there has been considerable research produced since then. Hence, we provided a snapshot of the most recent evidence at the time of writing, but this area requires an up to date, comprehensive data synthesis. However, the recent studies were consistent with the earlier meta-analysis with little evidence for an effect of tryptophan depletion on mood.
Although umbrella reviews typically restrict themselves to systematic reviews and meta-analyses, we aimed to provide the most comprehensive possible overview. Therefore, we chose to include meta-analyses that did not involve a systematic review and a large genetic association study on the premise that these studies contribute important data on the question of whether the serotonin hypothesis of depression is supported. As a result, the AMSTAR-2 quality rating scale, designed to evaluate the quality of conventional systematic reviews, was not easily applicable to all studies and had to be modified or replaced in some cases.
One study in this review found that antidepressant use was associated with a reduction of plasma serotonin [ 26 ], and it is possible that the evidence for reductions in SERT density and 5-HT 1A receptors in some of the included imaging study reviews may reflect compensatory adaptations to serotonin-lowering effects of prior antidepressant use. Authors of one meta-analysis also highlighted evidence of 5-HIAA levels being reduced after long-term antidepressant treatment [ 71 ]. These findings suggest that in the long-term antidepressants might produce compensatory changes [ 72 ] that are opposite to their acute effects [ 73 , 74 ]. Lowered serotonin availability has also been demonstrated in animal studies following prolonged antidepressant administration [ 75 ]. Further research is required to clarify the effects of different drugs on neurochemical systems, including the serotonin system, especially during and after long-term use, as well as the physical and psychological consequences of such effects.
This review suggests that the huge research effort based on the serotonin hypothesis has not produced convincing evidence of a biochemical basis to depression. This is consistent with research on many other biological markers [ 21 ]. We suggest it is time to acknowledge that the serotonin theory of depression is not empirically substantiated.
Data availability
All extracted data is available in the paper and supplementary materials. Further information about the decision-making for each rating for categories of the AMSTAR-2 and STREGA are available on request.
Coppen A. The biochemistry of affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 1967;113:1237–64.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
American Psychiatric Association. What Is Psychiatry? 2021. https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/what-is-psychiatry-menu .
GlaxoSmithKline. Paxil XR. 2009. www.Paxilcr.com (site no longer available). Last accessed 27th Jan 2009.
Eli Lilly. Prozac - How it works. 2006. www.prozac.com/how_prozac/how_it_works.jsp?reqNavId=2.2 . (site no longer available). Last accessed 10th Feb 2006.
Healy D. Serotonin and depression. BMJ: Br Med J. 2015;350:h1771.
Article Google Scholar
Pies R. Psychiatry’s New Brain-Mind and the Legend of the “Chemical Imbalance.” 2011. https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/psychiatrys-new-brain-mind-and-legend-chemical-imbalance . Accessed March 2, 2021.
Geddes JR, Andreasen NC, Goodwin GM. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2020.
Book Google Scholar
Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Kaplan & Sadock’s Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. 10th Editi. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW); 2017.
Cowen PJ, Browning M. What has serotonin to do with depression? World Psychiatry. 2015;14:158–60.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Harmer CJ, Duman RS, Cowen PJ. How do antidepressants work? New perspectives for refining future treatment approaches. Lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4:409–18.
Yohn CN, Gergues MM, Samuels BA. The role of 5-HT receptors in depression. Mol Brain. 2017;10:28.
Hahn A, Haeusler D, Kraus C, Höflich AS, Kranz GS, Baldinger P, et al. Attenuated serotonin transporter association between dorsal raphe and ventral striatum in major depression. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35:3857–66.
Amidfar M, Colic L, Kim MWAY-K. Biomarkers of major depression related to serotonin receptors. Curr Psychiatry Rev. 2018;14:239–44.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Albert PR, Benkelfat C, Descarries L. The neurobiology of depression—revisiting the serotonin hypothesis. I. Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367:2378–81.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pilkington PD, Reavley NJ, Jorm AF. The Australian public’s beliefs about the causes of depression: associated factors and changes over 16 years. J Affect Disord. 2013;150:356–62.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pescosolido BA, Martin JK, Long JS, Medina TR, Phelan JC, Link BG. A disease like any other? A decade of change in public reactions to schizophrenia, depression, and alcohol dependence. Am J Psychiatry. 2010;167:1321–30.
Read J, Renton J, Harrop C, Geekie J, Dowrick C. A survey of UK general practitioners about depression, antidepressants and withdrawal: implementing the 2019 Public Health England report. Therapeutic Advances in. Psychopharmacology. 2020;10:204512532095012.
Google Scholar
Demasi M, Gøtzsche PC. Presentation of benefits and harms of antidepressants on websites: A cross-sectional study. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2020;31:53–65.
Jakobsen JC, Gluud C, Kirsch I. Should antidepressants be used for major depressive disorder? BMJ Evidence-Based. Medicine. 2020;25:130–130.
Moncrieff J, Cohen D. Do antidepressants cure or create abnormal brain states? PLoS Med. 2006;3:e240.
Kennis M, Gerritsen L, van Dalen M, Williams A, Cuijpers P, Bockting C. Prospective biomarkers of major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25:321–38.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Fusar-Poli P, Radua J. Ten simple rules for conducting umbrella reviews. Evid Based Ment Health. 2018;21:95–100.
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Becker LA, Pieper D, Hartling L. Chapter V: Overviews of Reviews. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al., editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2,. version 6.Cochrane; 2021.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Huang T, Balasubramanian R, Yao Y, Clish CB, Shadyab AH, Liu B, et al. Associations of depression status with plasma levels of candidate lipid and amino acid metabolites: a meta-analysis of individual data from three independent samples of US postmenopausal women. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-00870-9 .
Culverhouse RC, Saccone NL, Horton AC, Ma Y, Anstey KJ, Banaschewski T, et al. Collaborative meta-analysis finds no evidence of a strong interaction between stress and 5-HTTLPR genotype contributing to the development of depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:133–42.
Little J, Higgins JPT, Ioannidis JPA, Moher D, Gagnon F, von Elm E, et al. STrengthening the REporting of Genetic Association Studies (STREGA)— An Extension of the STROBE Statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000022.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Schünemann HJ. What is quality of evidence and why is it important to clinicians? BMJ. 2008;336:995–8.
Yoon HS, Hattori K, Ogawa S, Sasayama D, Ota M, Teraishi T, et al. Relationships of cerebrospinal fluid monoamine metabolite levels with clinical variables in major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78:e947–56.
Kugaya A, Seneca NM, Snyder PJ, Williams SA, Malison RT, Baldwin RM, et al. Changes in human in vivo serotonin and dopamine transporter availabilities during chronic antidepressant administration. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:413–20.
Border R, Johnson EC, Evans LM, Smolen A, Berley N, Sullivan PF, et al. No support for historical candidate gene or candidate gene-by-interaction hypotheses for major depression across multiple large samples. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:376–87.
Ogawa S, Tsuchimine S, Kunugi H. Cerebrospinal fluid monoamine metabolite concentrations in depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of historic evidence. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;105:137–46.
Nautiyal KM, Hen R. Serotonin receptors in depression: from A to B. F1000Res. 2017;6:123.
Rojas PS, Neira D, Muñoz M, Lavandero S, Fiedler JL. Serotonin (5‐HT) regulates neurite outgrowth through 5‐HT1A and 5‐HT7 receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2014;92:1000–9.
Kaufman J, DeLorenzo C, Choudhury S, Parsey RV. The 5-HT1A receptor in Major Depressive Disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;26:397–410.
Nikolaus S, Müller H-W, Hautzel H. Different patterns of 5-HT receptor and transporter dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders – a comparative analysis of in vivo imaging findings. Rev Neurosci. 2016;27:27–59.
Wang L, Zhou C, Zhu D, Wang X, Fang L, Zhong J, et al. Serotonin-1A receptor alterations in depression: A meta-analysis of molecular imaging studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2016;16:1–9.
Kambeitz JP, Howes OD. The serotonin transporter in depression: Meta-analysis of in vivo and post mortem findings and implications for understanding and treating depression. J Affect Disord. 2015;186:358–66.
Meyer JH. Imaging the serotonin transporter during major depressive disorder and antidepressant treatment. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007;32:86–102.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mathews TA, Fedele DE, Coppelli FM, Avila AM, Murphy DL, Andrews AM. Gene dose-dependent alterations in extraneuronal serotonin but not dopamine in mice with reduced serotonin transporter expression. J Neurosci Methods. 2004;140:169–81.
Shen H-W, Hagino Y, Kobayashi H, Shinohara-Tanaka K, Ikeda K, Yamamoto H, et al. Regional differences in extracellular dopamine and serotonin assessed by in vivo microdialysis in mice lacking dopamine and/or serotonin transporters. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:1790–9.
Hagino Y, Takamatsu Y, Yamamoto H, Iwamura T, Murphy DL, Uhl GR, et al. Effects of MDMA on extracellular dopamine and serotonin levels in mice lacking dopamine and/or serotonin transporters. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011;9:91–5.
Zhou Z, Zhen J, Karpowich NK, Law CJ, Reith MEA, Wang D-N. Antidepressant specificity of serotonin transporter suggested by three LeuT-SSRI structures. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:652–7.
Gryglewski G, Lanzenberger R, Kranz GS, Cumming P. Meta-analysis of molecular imaging of serotonin transporters in major depression. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34:1096–103.
Benmansour S, Owens WA, Cecchi M, Morilak DA, Frazer A. Serotonin clearance in vivo is altered to a greater extent by antidepressant-induced downregulation of the serotonin transporter than by acute blockade of this transporter. J Neurosci. 2002;22:6766–72.
Benmansour S, Cecchi M, Morilak DA, Gerhardt GA, Javors MA, Gould GG, et al. Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments on serotonin transporter function, density, and mRNA level. J Neurosci. 1999;19:10494–501.
Horschitz S, Hummerich R, Schloss P. Down-regulation of the rat serotonin transporter upon exposure to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Neuroreport. 2001;12:2181–4.
Young SN. Acute tryptophan depletion in humans: a review of theoretical, practical and ethical aspects. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013;38:294–305.
Ruhe HG, Mason NS, Schene AH. Mood is indirectly related to serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine levels in humans: a meta-analysis of monoamine depletion studies. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12:331–59.
Fusar-Poli P, Allen P, McGuire P, Placentino A, Cortesi M, Perez J. Neuroimaging and electrophysiological studies of the effects of acute tryptophan depletion: A systematic review of the literature. Psychopharmacology. 2006;188:131–43.
Hogenelst K, Schoevers RA, Kema IP, Sweep FCGJ, aan het Rot M. Empathic accuracy and oxytocin after tryptophan depletion in adults at risk for depression. Psychopharmacology. 2016;233:111–20.
Weinstein JJ, Rogers BP, Taylor WD, Boyd BD, Cowan RL, Shelton KM, et al. Effects of acute tryptophan depletion on raphé functional connectivity in depression. Psychiatry Res. 2015;234:164–71.
Moreno FA, Erickson RP, Garriock HA, Gelernter J, Mintz J, Oas-Terpstra J, et al. Association study of genotype by depressive response during tryptophan depletion in subjects recovered from major depression. Mol. Neuropsychiatry. 2015;1:165–74.
Munafò MR. The serotonin transporter gene and depression. Depress Anxiety. 2012;29:915–7.
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, et al. Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 2003;301:386–9.
Kiyohara C, Yoshimasu K. Association between major depressive disorder and a functional polymorphism of the 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) transporter gene: A meta-analysis. Psychiatr Genet. 2010;20:49–58.
Oo KZ, Aung YK, Jenkins MA, Win AK. Associations of 5HTTLPR polymorphism with major depressive disorder and alcohol dependence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust N. Z J Psychiatry. 2016;50:842–57.
Culverhouse RC, Bowes L, Breslau N, Nurnberger JI, Burmeister M, Fergusson DM, et al. Protocol for a collaborative meta-analysis of 5-HTTLPR, stress, and depression. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:1–12.
Karg K, Burmeister M, Shedden K, Sen S. The serotonin transporter promoter variant (5-HTTLPR), stress, and depression meta-analysis revisited. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2011;68:444.
Sharpley CF, Palanisamy SKA, Glyde NS, Dillingham PW, Agnew LL. An update on the interaction between the serotonin transporter promoter variant (5-HTTLPR), stress and depression, plus an exploration of non-confirming findings. Behav Brain Res. 2014;273:89–105.
Bleys D, Luyten P, Soenens B, Claes S. Gene-environment interactions between stress and 5-HTTLPR in depression: A meta-analytic update. J Affect Disord. 2018;226:339–45.
Delgado PL. Monoamine depletion studies: implications for antidepressant discontinuation syndrome. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67:22–26.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kemp JJ, Lickel JJ, Deacon BJ. Effects of a chemical imbalance causal explanation on individuals’ perceptions of their depressive symptoms. Behav Res Ther. 2014;56:47–52.
Lebowitz MS, Ahn W-K, Nolen-Hoeksema S. Fixable or fate? Perceptions of the biology of depression. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2013;81:518.
Zimmermann M, Papa A. Causal explanations of depression and treatment credibility in adults with untreated depression: Examining attribution theory. Psychol Psychother. 2020;93:537–54.
Maund E, Dewar-Haggart R, Williams S, Bowers H, Geraghty AWA, Leydon G, et al. Barriers and facilitators to discontinuing antidepressant use: A systematic review and thematic synthesis. J Affect Disord. 2019;245:38–62.
Eveleigh R, Speckens A, van Weel C, Oude Voshaar R, Lucassen P. Patients’ attitudes to discontinuing not-indicated long-term antidepressant use: barriers and facilitators. Therapeutic Advances in. Psychopharmacology. 2019;9:204512531987234.
Harrell FE Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis. Springer, Cham; 2015.
Schafer JL, Kang J. Average causal effects from nonrandomized studies: a practical guide and simulated example. Psychol Methods. 2008;13:279–313.
Pech J, Forman J, Kessing LV, Knorr U. Poor evidence for putative abnormalities in cerebrospinal fluid neurotransmitters in patients with depression versus healthy non-psychiatric individuals: A systematic review and meta-analyses of 23 studies. J Affect Disord. 2018;240:6–16.
Fava GA. May antidepressant drugs worsen the conditions they are supposed to treat? The clinical foundations of the oppositional model of tolerance. Therapeutic Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020;10:2045125320970325.
Kitaichi Y, Inoue T, Nakagawa S, Boku S, Kakuta A, Izumi T, et al. Sertraline increases extracellular levels not only of serotonin, but also of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of rats. Eur J Pharm. 2010;647:90–6.
Gartside SE, Umbers V, Hajós M, Sharp T. Interaction between a selective 5‐HT1Areceptor antagonist and an SSRI in vivo: effects on 5‐HT cell firing and extracellular 5‐HT. Br J Pharmacol. 1995;115:1064–70.
Bosker FJ, Tanke MAC, Jongsma ME, Cremers TIFH, Jagtman E, Pietersen CY, et al. Biochemical and behavioral effects of long-term citalopram administration and discontinuation in rats: role of serotonin synthesis. Neurochem Int. 2010;57:948–57.
Download references
There was no specific funding for this review. MAH is supported by a Clinical Research Fellowship from North East London NHS Foundation Trust (NELFT). This funder had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Psychiatry, University College London, London, UK
Joanna Moncrieff & Mark A. Horowitz
Research and Development Department, Goodmayes Hospital, North East London NHS Foundation Trust, Essex, UK
Faculty of Education, Health and Human Sciences, University of Greenwich, London, UK
Ruth E. Cooper
Psychiatry-UK, Cornwall, UK
Tom Stockmann
Department of Dynamic and Clinical Psychology, and Health Studies, Faculty of Medicine and Psychology, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
Simone Amendola
Department of Applied Psychology, Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Zurich, Switzerland
Michael P. Hengartner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JM conceived the idea for the study. JM, MAH, MPH, TS and SA designed the study. JM, MAH, MPH, TS, and SA screened articles and abstracted data. JM drafted the first version of the manuscript. JM, MAH, MPH, TS, SA, and REC contributed to the manuscript’s revision and interpretation of findings. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joanna Moncrieff .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
All authors have completed the Unified Competing Interest form at http://www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding author). SA declares no conflicts of interest. MAH reports being co-founder of a company in April 2022, aiming to help people safely stop antidepressants in Canada. MPH reports royalties from Palgrave Macmillan, London, UK for his book published in December, 2021, called “Evidence-biased Antidepressant Prescription.” JM receives royalties for books about psychiatric drugs, reports grants from the National Institute of Health Research outside the submitted work, that she is co-chairperson of the Critical Psychiatry Network (an informal group of psychiatrists) and a board member of the unfunded organisation, the Council for Evidence-based Psychiatry. Both are unpaid positions. TS is co-chairperson of the Critical Psychiatry Network. RC is an unpaid board member of the International Institute for Psychiatric Drug Withdrawal.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary tables, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Moncrieff, J., Cooper, R.E., Stockmann, T. et al. The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Mol Psychiatry 28 , 3243–3256 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01661-0
Download citation
Received : 21 June 2021
Revised : 31 May 2022
Accepted : 07 June 2022
Published : 20 July 2022
Issue Date : August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01661-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
The involvement of serotonin in major depression: nescience in disguise.
- Danilo Arnone
- Catherine J. Harmer
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
Serotonin effects on human iPSC-derived neural cell functions: from mitochondria to depression
- Iseline Cardon
- Sonja Grobecker
- Christian H. Wetzel
Neither serotonin disorder is at the core of depression nor dopamine at the core of schizophrenia; still these are biologically based mental disorders
- Konstantinos N. Fountoulakis
- Eva Maria Tsapakis
The impact of adult neurogenesis on affective functions: of mice and men
- Mariana Alonso
- Anne-Cécile Petit
- Pierre-Marie Lledo
Biallelic variants identified in 36 Pakistani families and trios with autism spectrum disorder
- Ricardo Harripaul
- John B. Vincent
Scientific Reports (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Nih research matters.
April 23, 2024
Research in Context: Treating depression
Finding better approaches.
While effective treatments for major depression are available, there is still room for improvement. This special Research in Context feature explores the development of more effective ways to treat depression, including personalized treatment approaches and both old and new drugs.

Everyone has a bad day sometimes. People experience various types of stress in the course of everyday life. These stressors can cause sadness, anxiety, hopelessness, frustration, or guilt. You may not enjoy the activities you usually do. These feelings tend to be only temporary. Once circumstances change, and the source of stress goes away, your mood usually improves. But sometimes, these feelings don’t go away. When these feelings stick around for at least two weeks and interfere with your daily activities, it’s called major depression, or clinical depression.
In 2021, 8.3% of U.S. adults experienced major depression. That’s about 21 million people. Among adolescents, the prevalence was much greater—more than 20%. Major depression can bring decreased energy, difficulty thinking straight, sleep problems, loss of appetite, and even physical pain. People with major depression may become unable to meet their responsibilities at work or home. Depression can also lead people to use alcohol or drugs or engage in high-risk activities. In the most extreme cases, depression can drive people to self-harm or even suicide.
The good news is that effective treatments are available. But current treatments have limitations. That’s why NIH-funded researchers have been working to develop more effective ways to treat depression. These include finding ways to predict whether certain treatments will help a given patient. They're also trying to develop more effective drugs or, in some cases, find new uses for existing drugs.
Finding the right treatments
The most common treatments for depression include psychotherapy, medications, or a combination. Mild depression may be treated with psychotherapy. Moderate to severe depression often requires the addition of medication.
Several types of psychotherapy have been shown to help relieve depression symptoms. For example, cognitive behavioral therapy helps people to recognize harmful ways of thinking and teaches them how to change these. Some researchers are working to develop new therapies to enhance people’s positive emotions. But good psychotherapy can be hard to access due to the cost, scheduling difficulties, or lack of available providers. The recent growth of telehealth services for mental health has improved access in some cases.
There are many antidepressant drugs on the market. Different drugs will work best on different patients. But it can be challenging to predict which drugs will work for a given patient. And it can take anywhere from 6 to 12 weeks to know whether a drug is working. Finding an effective drug can involve a long period of trial and error, with no guarantee of results.
If depression doesn’t improve with psychotherapy or medications, brain stimulation therapies could be used. Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, uses electrodes to send electric current into the brain. A newer technique, transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), stimulates the brain using magnetic fields. These treatments must be administered by specially trained health professionals.
“A lot of patients, they kind of muddle along, treatment after treatment, with little idea whether something’s going to work,” says psychiatric researcher Dr. Amit Etkin.
One reason it’s difficult to know which antidepressant medications will work is that there are likely different biological mechanisms that can cause depression. Two people with similar symptoms may both be diagnosed with depression, but the causes of their symptoms could be different. As NIH depression researcher Dr. Carlos Zarate explains, “we believe that there’s not one depression, but hundreds of depressions.”
Depression may be due to many factors. Genetics can put certain people at risk for depression. Stressful situations, physical health conditions, and medications may contribute. And depression can also be part of a more complicated mental disorder, such as bipolar disorder. All of these can affect which treatment would be best to use.
Etkin has been developing methods to distinguish patients with different types of depression based on measurable biological features, or biomarkers. The idea is that different types of patients would respond differently to various treatments. Etkin calls this approach “precision psychiatry.”
One such type of biomarker is electrical activity in the brain. A technique called electroencephalography, or EEG, measures electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. When Etkin was at Stanford University, he led a research team that developed a machine-learning algorithm to predict treatment response based on EEG signals. The team applied the algorithm to data from a clinical trial of the antidepressant sertraline (Zoloft) involving more than 300 people.

EEG data for the participants were collected at the outset. Participants were then randomly assigned to take either sertraline or an inactive placebo for eight weeks. The team found a specific set of signals that predicted the participants’ responses to sertraline. The same neural “signature” also predicted which patients with depression responded to medication in a separate group.
Etkin’s team also examined this neural signature in a set of patients who were treated with TMS and psychotherapy. People who were predicted to respond less to sertraline had a greater response to the TMS/psychotherapy combination.
Etkin continues to develop methods for personalized depression treatment through his company, Alto Neuroscience. He notes that EEG has the advantage of being low-cost and accessible; data can even be collected in a patient’s home. That’s important for being able to get personalized treatments to the large number of people they could help. He’s also working on developing antidepressant drugs targeted to specific EEG profiles. Candidate drugs are in clinical trials now.
“It’s not like a pie-in-the-sky future thing, 20–30 years from now,” Etkin explains. “This is something that could be in people’s hands within the next five years.”
New tricks for old drugs
While some researchers focus on matching patients with their optimal treatments, others aim to find treatments that can work for many different patients. It turns out that some drugs we’ve known about for decades might be very effective antidepressants, but we didn’t recognize their antidepressant properties until recently.
One such drug is ketamine. Ketamine has been used as an anesthetic for more than 50 years. Around the turn of this century, researchers started to discover its potential as an antidepressant. Zarate and others have found that, unlike traditional antidepressants that can take weeks to take effect, ketamine can improve depression in as little as one day. And a single dose can have an effect for a week or more. In 2019, the FDA approved a form of ketamine for treating depression that is resistant to other treatments.
But ketamine has drawbacks of its own. It’s a dissociative drug, meaning that it can make people feel disconnected from their body and environment. It also has the potential for addiction and misuse. For these reasons, it’s a controlled substance and can only be administered in a doctor’s office or clinic.
Another class of drugs being studied as possible antidepressants are psychedelics. These include lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocybin, the active ingredient in magic mushrooms. These drugs can temporarily alter a person’s mood, thoughts, and perceptions of reality. Some have historically been used for religious rituals, but they are also used recreationally.
In clinical studies, psychedelics are typically administered in combination with psychotherapy. This includes several preparatory sessions with a therapist in the weeks before getting the drug, and several sessions in the weeks following to help people process their experiences. The drugs are administered in a controlled setting.
Dr. Stephen Ross, co-director of the New York University Langone Health Center for Psychedelic Medicine, describes a typical session: “It takes place in a living room-like setting. The person is prepared, and they state their intention. They take the drug, they lie supine, they put on eye shades and preselected music, and two therapists monitor them.” Sessions last for as long as the acute effects of the drug last, which is typically several hours. This is a healthcare-intensive intervention given the time and personnel needed.
In 2016, Ross led a clinical trial examining whether psilocybin-assisted therapy could reduce depression and anxiety in people with cancer. According to Ross, as many as 40% of people with cancer have clinically significant anxiety and depression. The study showed that a single psilocybin session led to substantial reductions in anxiety and depression compared with a placebo. These reductions were evident as soon as one day after psilocybin administration. Six months later, 60-80% of participants still had reduced depression and anxiety.
Psychedelic drugs frequently trigger mystical experiences in the people who take them. “People can feel a sense…that their consciousness is part of a greater consciousness or that all energy is one,” Ross explains. “People can have an experience that for them feels more ‘real’ than regular reality. They can feel transported to a different dimension of reality.”
About three out of four participants in Ross’s study said it was among the most meaningful experiences of their lives. And the degree of mystical experience correlated with the drug’s therapeutic effect. A long-term follow-up study found that the effects of the treatment continued more than four years later.
If these results seem too good to be true, Ross is quick to point out that it was a small study, with only 29 participants, although similar studies from other groups have yielded similar results. Psychedelics haven’t yet been shown to be effective in a large, controlled clinical trial. Ross is now conducting a trial with 200 people to see if the results of his earlier study pan out in this larger group. For now, though, psychedelics remain experimental drugs—approved for testing, but not for routine medical use.
Unlike ketamine, psychedelics aren’t considered addictive. But they, too, carry risks, which certain conditions may increase. Psychedelics can cause cardiovascular complications. They can cause psychosis in people who are predisposed to it. In uncontrolled settings, they have the risk of causing anxiety, confusion, and paranoia—a so-called “bad trip”—that can lead the person taking the drug to harm themself or others. This is why psychedelic-assisted therapy takes place in such tightly controlled settings. That increases the cost and complexity of the therapy, which may prevent many people from having access to it.
Better, safer drugs
Despite the promise of ketamine or psychedelics, their drawbacks have led some researchers to look for drugs that work like them but with fewer side effects.
Depression is thought to be caused by the loss of connections between nerve cells, or neurons, in certain regions of the brain. Ketamine and psychedelics both promote the brain’s ability to repair these connections, a quality called plasticity. If we could understand how these drugs encourage plasticity, we might be able to design drugs that can do so without the side effects.

Dr. David Olson at the University of California, Davis studies how psychedelics work at the cellular and molecular levels. The drugs appear to promote plasticity by binding to a receptor in cells called the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor (5-HT2AR). But many other compounds also bind 5-HT2AR without promoting plasticity. In a recent NIH-funded study, Olson showed that 5-HT2AR can be found both inside and on the surface of the cell. Only compounds that bound to the receptor inside the cells promoted plasticity. This suggests that a drug has to be able to get into the cell to promote plasticity.
Moreover, not all drugs that bind 5-HT2AR have psychedelic effects. Olson’s team has developed a molecular sensor, called psychLight, that can identify which compounds that bind 5-HT2AR have psychedelic effects. Using psychLight, they identified compounds that are not psychedelic but still have rapid and long-lasting antidepressant effects in animal models. He’s founded a company, Delix Therapeutics, to further develop drugs that promote plasticity.
Meanwhile, Zarate and his colleagues have been investigating a compound related to ketamine called hydroxynorketamine (HNK). Ketamine is converted to HNK in the body, and this process appears to be required for ketamine’s antidepressant effects. Administering HNK directly produced antidepressant-like effects in mice. At the same time, it did not cause the dissociative side effects and addiction caused by ketamine. Zarate’s team has already completed phase I trials of HNK in people showing that it’s safe. Phase II trials to find out whether it’s effective are scheduled to begin soon.
“What [ketamine and psychedelics] are doing for the field is they’re helping us realize that it is possible to move toward a repair model versus a symptom mitigation model,” Olson says. Unlike existing antidepressants, which just relieve the symptoms of depression, these drugs appear to fix the underlying causes. That’s likely why they work faster and produce longer-lasting effects. This research is bringing us closer to having safer antidepressants that only need to be taken once in a while, instead of every day.
—by Brian Doctrow, Ph.D.
Related Links
- How Psychedelic Drugs May Help with Depression
- Biosensor Advances Drug Discovery
- Neural Signature Predicts Antidepressant Response
- How Ketamine Relieves Symptoms of Depression
- Protein Structure Reveals How LSD Affects the Brain
- Predicting The Usefulness of Antidepressants
- Depression Screening and Treatment in Adults
- Serotonin Transporter Structure Revealed
- Placebo Effect in Depression Treatment
- When Sadness Lingers: Understanding and Treating Depression
- Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs
References: An electroencephalographic signature predicts antidepressant response in major depression. Wu W, Zhang Y, Jiang J, Lucas MV, Fonzo GA, Rolle CE, Cooper C, Chin-Fatt C, Krepel N, Cornelssen CA, Wright R, Toll RT, Trivedi HM, Monuszko K, Caudle TL, Sarhadi K, Jha MK, Trombello JM, Deckersbach T, Adams P, McGrath PJ, Weissman MM, Fava M, Pizzagalli DA, Arns M, Trivedi MH, Etkin A. Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0397-3. Epub 2020 Feb 10. PMID: 32042166. Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Ross S, Bossis A, Guss J, Agin-Liebes G, Malone T, Cohen B, Mennenga SE, Belser A, Kalliontzi K, Babb J, Su Z, Corby P, Schmidt BL. J Psychopharmacol . 2016 Dec;30(12):1165-1180. doi: 10.1177/0269881116675512. PMID: 27909164. Long-term follow-up of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for psychiatric and existential distress in patients with life-threatening cancer. Agin-Liebes GI, Malone T, Yalch MM, Mennenga SE, Ponté KL, Guss J, Bossis AP, Grigsby J, Fischer S, Ross S. J Psychopharmacol . 2020 Feb;34(2):155-166. doi: 10.1177/0269881119897615. Epub 2020 Jan 9. PMID: 31916890. Psychedelics promote neuroplasticity through the activation of intracellular 5-HT2A receptors. Vargas MV, Dunlap LE, Dong C, Carter SJ, Tombari RJ, Jami SA, Cameron LP, Patel SD, Hennessey JJ, Saeger HN, McCorvy JD, Gray JA, Tian L, Olson DE. Science . 2023 Feb 17;379(6633):700-706. doi: 10.1126/science.adf0435. Epub 2023 Feb 16. PMID: 36795823. Psychedelic-inspired drug discovery using an engineered biosensor. Dong C, Ly C, Dunlap LE, Vargas MV, Sun J, Hwang IW, Azinfar A, Oh WC, Wetsel WC, Olson DE, Tian L. Cell . 2021 Apr 8: S0092-8674(21)00374-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.043. Epub 2021 Apr 28. PMID: 33915107. NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Zanos P, Moaddel R, Morris PJ, Georgiou P, Fischell J, Elmer GI, Alkondon M, Yuan P, Pribut HJ, Singh NS, Dossou KS, Fang Y, Huang XP, Mayo CL, Wainer IW, Albuquerque EX, Thompson SM, Thomas CJ, Zarate CA Jr, Gould TD. Nature . 2016 May 26;533(7604):481-6. doi: 10.1038/nature17998. Epub 2016 May 4. PMID: 27144355.
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH
Primary Care Online Resources and Education
Conclusion depression.
Depression is one of the most common conditions in primary care, but is often unrecognized, undiagnosed, and untreated. Depression has a high rate of morbidity and mortality when left untreated. Most patients suffering from depression do not complain of feeling depressed, but rather anhedonia or vague unexplained symptoms. All physicians should remain alert to effectively screen for depression in their patients. There are several screening tools for depression that are effective and feasible in primary care settings. An appropriate history, physical, initial basic lab evaluation, and mental status examination can assist the physician in diagnosing the patient with the correct depressive spectrum disorder (including bipolar disorder). Primary care physicians should carefully assess depressed patients for suicide. Depression in the elderly is not part of the normal aging process. Patients who are elderly when they have their first episode of depression have a relatively higher likelihood of developing chronic and recurring depression. The prognosis for recovery is equal in young and old patients, although remission may take longer to achieve in older patients. Elderly patients usually start antidepressants at lower doses than their younger counterparts.
Most primary care physician can successfully treat uncomplicated mild or moderate forms of major depression in their settings with careful psychiatric management (e.g., close monitoring of symptoms, side effects, etc.); maintaining a therapeutic alliance with their patient; pharmacotherapy (acute, continuation, and maintenance phases); and / or referral for psychotherapy. The following situations require referral to psychiatrist: suicide risk, bipolar disorder or a manic episode, psychotic symptoms, severe decrease in level of functioning, recurrent depression and chronic depression, depression that is refractory to treatment, cardiac disease that requires tricyclic antidepressants treatment, need for electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), lack of available support system, and any diagnostic or treatment questions.
Antidepressant medications’ effectiveness is generally comparable across classes and within classes of medications. The medications differ in side effect profiles, drug-drug interactions, and cost. The history of a positive response to a particular drug for an individual or a family member, as well as patient preferences, should also be taken into account. Most psychiatrists agree that an SSRI should be the first line choice. The dual action reuptake inhibitors venlafaxine and bupropion are generally regarded as second line agents. Tricyclics and other mixed or dual action inhibitors are third line, and MAOI’s (monoamine oxidase inhibitors) are usually medications of last resort for patients who have not responded to other medications, due to their low tolerability, dietary restrictions, and drug-drug interactions. Most primary care physicians would prefer that a psychiatrist manage patients requiring MAOI’s.
Psychotherapy may be a first line therapy choice for mild depression particularly when associated with psychosocial stress, interpersonal problems, or with concurrent developmental or personality disorders. Psychotherapy in mild to moderate depression is most effective in the acute phase, and in preventing relapse during continuation phase treatment. Psychotherapy is not appropriate alone for severe depression, psychosis, and bipolar disorders. For more severe depression, psychotherapy may be appropriate in combination with the use of medications. The most effective forms of psychotherapy are those with structured and brief approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy, and certain problem solving therapies. Regardless of the psychotherapy initiated, “psychiatric management” must be integrated at the same time.
Patients, who live with depression, and their family and friends, have enormous challenges to overcome. Primary care physicians can provide compassionate care, important education, psychiatric monitoring, social support, reassurance, and advocacy for these patients and their loved ones.
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
A major aim of this course was to shed some light on the aetiology of depression and anxiety. At the end of it you should have some idea of the complexity of this enterprise. We have focused on one of the best-studied and hence best-understood contributors to psychopathology – stress. This has biological, social and psychological significance, and its operation can be studied and understood at all these levels.
The clear message you should take away is that interaction between these levels is enormously important in aetiology. Biological factors, such as dysregulation of the HPA axis and its consequences, possible abnormalities in brain neurotransmitter systems, the effects of stress on the developing brain at different ages, and the kinds of genes that an individual carries, appear to play an important part in the development and maintenance of emotional disorders such as depression and anxiety. However, these biological factors cannot be divorced from factors that are thought of as psychosocial, such as abuse in childhood, or stressful events and how we perceive them. This is very evident from the most recent developments in genetics, which show how, via epigenetic processes, experiences are translated into the activity (or expression) of genes, which then modify the workings of the brain in ways that affect mood.
Research into epigenetic influences on mental health and ill-health is burgeoning and is likely to make a very significant contribution to our understanding of aetiology in the years to come. If so, it should also help clarify how existing treatments, both pharmacological and psychotherapeutic, for emotional disorders work, or suggest new approaches that would work more effectively.
The HPA axis is overactive in those with depression and anxiety, suggesting a role for chronic stress. Elevated levels of glucocorticoids such as cortisol and corticosterone, resulting from chronic stress, have toxic effects in some areas of the brain and promote neurogenesis in others.
The monoamine hypothesis of mood disorders has been influential in trying to explain the causes of depression. However the picture is now more complex and the view of a simple chemical imbalance as a cause of depression is outdated.
Hypotheses such as the neurotrophic hypothesis and the network hypothesis have been developed to try to account for the complex effects of antidepressant treatments on the brain.
The life-cycle model of stress links brain development with stress effects over the lifetime.
The cognitive approach concentrates on particular ways of thinking and how these cause and sustain depression.
Genetic and other vulnerabilities (also called predispositions or diatheses) can interact with environmental factors, which include psychosocial stressors such as stressful life events and early life stress (including child abuse) to cause emotional disorders such as depression.
Epigenetic processes add another layer of complexity to the interaction between genes and environment. There is increasingly evidence of the importance of epigenetic processes in the aetiology of mood disorders.
Depression and Suicide Risk Screening: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force
Affiliations.
- 1 Kaiser Permanente Evidence-based Practice Center, Kaiser Permanente Center for Health Research, Portland, Oregon.
- 2 Gillings School of Global Public Health, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill.
- PMID: 37338873
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.7787
Importance: Depression is common and associated with substantial burden. Suicide rates have increased over the past decade, and both suicide attempts and deaths have devastating effects on individuals and families.
Objective: To review the benefits and harms of screening and treatment for depression and suicide risk and the accuracy of instruments to detect these conditions among primary care patients.
Data sources: MEDLINE, PsychINFO, Cochrane library through September 7, 2022; references of existing reviews; ongoing surveillance for relevant literature through November 25, 2022.
Study selection: English-language studies of screening or treatment compared with control conditions, or test accuracy of screening instruments (for depression, instruments were selected a priori; for suicide risk, all were included). Existing systematic reviews were used for treatment and test accuracy for depression.
Data extraction and synthesis: One investigator abstracted data; a second checked accuracy. Two investigators independently rated study quality. Findings were synthesized qualitatively, including reporting of meta-analysis results from existing systematic reviews; meta-analyses were conducted on original research when evidence was sufficient.
Main outcomes and measures: Depression outcomes; suicidal ideation, attempts, and deaths; sensitivity and specificity of screening tools.
Results: For depression, 105 studies were included: 32 original studies (N=385 607) and 73 systematic reviews (including ≈2138 studies [N ≈ 9.8 million]). Depression screening interventions, many of which included additional components beyond screening, were associated with a lower prevalence of depression or clinically important depressive symptomatology after 6 to 12 months (pooled odds ratio, 0.60 [95% CI, 0.50-0.73]; reported in 8 randomized clinical trials [n=10 244]; I2 = 0%). Several instruments demonstrated adequate test accuracy (eg, for the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire at a cutoff of 10 or greater, the pooled sensitivity was 0.85 [95% CI, 0.79-0.89] and specificity was 0.85 [95% CI, 0.82-0.88]; reported in 47 studies [n = 11 234]). A large body of evidence supported benefits of psychological and pharmacologic treatment of depression. A pooled estimate from trials used for US Food and Drug Administration approval suggested a very small increase in the absolute risk of a suicide attempt with second-generation antidepressants (odds ratio, 1.53 [95% CI, 1.09-2.15]; n = 40 857; 0.7% of antidepressant users had a suicide attempt vs 0.3% of placebo users; median follow-up, 8 weeks). Twenty-seven studies (n = 24 826) addressed suicide risk. One randomized clinical trial (n=443) of a suicide risk screening intervention found no difference in suicidal ideation after 2 weeks between primary care patients who were and were not screened for suicide risk. Three studies of suicide risk test accuracy were included; none included replication of any instrument. The included suicide prevention studies generally did not demonstrate an improvement over usual care, which typically included specialty mental health treatment.
Conclusions and relevance: Evidence supported depression screening in primary care settings, including during pregnancy and postpartum. There are numerous important gaps in the evidence for suicide risk screening in primary care settings.
Publication types
- Meta-Analysis
- Research Support, U.S. Gov't, P.H.S.
- Systematic Review
- Antidepressive Agents / therapeutic use
- Depression* / diagnosis
- Depression* / therapy
- Mass Screening* / adverse effects
- Mass Screening* / methods
- Meta-Analysis as Topic
- Psychotherapy
- Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic
- Risk Assessment
- Sensitivity and Specificity
- Suicide, Attempted / prevention & control
- United States
- Antidepressive Agents
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Validation of depression, anxiety, and stress scales (DASS-21) among Thai nursing students in an online learning environment during the COVID-19 outbreak: A multi-center study
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliations Movement Science and Exercise Research Center-Walailak University (MoveSE-WU), Walailak University, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand, School of Allied Health Sciences, Walailak University, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
Roles Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Faculty of Nursing, Roi Et Rajabhat University, Roi Et, Thailand
Roles Investigation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Faculty of Physical Therapy, Huachiew Chalermprakiet University, Bangkok, Thailand
Roles Writing – review & editing
Affiliation School of Medicine, Walailak University, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
Roles Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Faculty of Nursing, Ratchathani University, Udonthani Campus, Udonthani, Thailand
Roles Investigation, Writing – original draft
Affiliation Faculty of Nursing, Chalermkarnchana University, Srisaket Campus, Srisaket, Thailand
Affiliation Faculty of Nursing, University of Jember, Jember, Indonesia
- Yuwadee Wittayapun,
- Ueamporn Summart,
- Panicha Polpanadham,
- Thanyaporn Direksunthorn,
- Raweewan Paokanha,
- Naruk Judabood,
- Muhamad Zulfatul A’la

- Published: June 30, 2023
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
The Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-21), an introductory scale used to identify common mental disorders (CMDs) among adults, was validated across cultures in Asian populations; nevertheless, its capacity for screening these disorders may be limited for some specified groups, including nursing students. This study attempted to investigate the psychometric scale’s unique features of DASS-21 for Thai nursing students in an online learning environment during the COVID-19 outbreak. A cross-sectional study using the multistage sampling technique recruited 3,705 nursing students from 18 universities located in south and northeast Thailand. The data were gathered using an online web-based survey, and then all respondents were divided into 2 groups (group 1, n = 2,000, group 2, n = 1,705). After using the statistical methods to reduce items, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) using group 1 was performed to investigate the factor structure of the DASS-21. Finally, group 2 used confirmatory factor analysis to verify the modified structure proposed by the EFA and assess the construct validity of the DASS-21. A total of 3,705 Thai nursing students were enrolled. For the factorial construct validity, a three-factor model was initially suggested containing 18 items (DASS-18) spread across 3 components: anxiety (7 items), depression (7 items) and stress (4 items). The internal consistency reliability was acceptable with Cronbach’s alpha in the range of 0.73–0.92for either the total or its subscales. For convergent validity, average variance extracted (AVE) showed that all the DASS-18 subscales achieved convergence effect with AVE in the range of 0.50–0.67. The psychometric features of the DASS-18 will support Thai psychologists and researchers to screen CMDs more easily among undergraduate nursing students in tertiary institutions who enrolled in an online learning environment during the COVID-19 outbreak.
Citation: Wittayapun Y, Summart U, Polpanadham P, Direksunthorn T, Paokanha R, Judabood N, et al. (2023) Validation of depression, anxiety, and stress scales (DASS-21) among Thai nursing students in an online learning environment during the COVID-19 outbreak: A multi-center study. PLoS ONE 18(6): e0288041. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041
Editor: Omar M. Khraisat, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, JORDAN
Received: November 11, 2022; Accepted: June 18, 2023; Published: June 30, 2023
Copyright: © 2023 Wittayapun et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting information files. We have already generated our minimal data set 2,000 datasets out of the total (3,705) (D1.XLSX).
Funding: This study was supported by The Walailak University's Individual Research Grants provided funding for the study (Grant Number WU-IRG-65-015). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Depression and anxiety are common mental health disorders (CMDs), leading causes of disability and have gained prominence due to their growing global burden [ 1 ]. Individually, these disorders contribute to poor psychological wellbeing, which interferes with learning and inhibits students’ academic performance [ 2 ]. Early screening for anxiety and depression in primary care and academic settings necessitates an assessment strategy that is rapid and easy to apply and has proven psychometric properties [ 2 ].
During the COVID-19 pandemic, undergraduate students also reported their anxiety or stress [ 3 , 4 ]. According to a network study, 932 nursing students were included. More than one third of these students reported at least moderate symptoms of worry or stress, and almost one half of these students presented at least mild symptoms of depression [ 5 ]. Due to a quick shift from face-to-face to an online learning environment during university lock downs, undergraduate nursing and midwifery curricula had trouble adjusting to "remote learning" that relies on the use of electronic technologies and media sources to conduct learning outside of the traditional classroom [ 6 ]. Thus, being unable to participate in extensive training such as clinical settings make students feel as though they are passing up a good opportunity to learn these abilities that may have decreased students’ mental health [ 5 , 7 ]. In addition, anxiety and depression may occur more commonly among low experienced apprentices including nursing students [ 8 ]. Moreover, this current study also discovered that the levels of anxiety and depression were higher among nursing students than among those students from other disciplines, regarding their probably high risk of infection exposure and fear of communicable diseases [ 8 ]. Currently, rare evidence is available concerning the mental health of Thai nursing students encountering an instant psychological response in relation to COVID-19. To provide psychiatric interventions to people experiencing these negative emotional states, early diagnosis of these diseases is essential [ 2 ]. Early assessment, using an effective screening instrument (such as a rating scale), provides a rapid indicator of the client’s emotional well-being and is helpful for further clinical judgment and early treatment. Likewise, self-reported questionnaires and clinician-rated scales are two commonly used methods to assess CMDs [ 9 ].
The Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale (DASS) is a common scale frequently used to detect CMDs [ 10 ]. Both the DASS-42 and its shortened version, the DASS-21, are frequently used to assess depression, anxiety, and stress among adults, and are considered superior to other psychometric tools to identify these CMDs and screen for psychological abnormalities [ 11 ]. Moreover, DASS-21 has several advantages over the original 42-item version (DASS-42), such as fewer items, cleaner factor structure and smaller interfactor correlations [ 12 ]. Data analyses among adults using this measure produced consistent results regarding its psychometric properties [ 2 , 7 , 12 – 14 ]. Findings regarding the DASS-21’s factor structure are contradictory, ranging from one to four factors structures [ 15 – 17 ]. Results from a prior study in Asia, conducted among nursing students in Brunei, have validated the DASS-21 used the final model, including a nine-item scale across three components [ 18 ]. However, this study encountered limitations because this representative sample (n = 126) was the smallest compared with other studies.
In the Thai context, DASS-21 has been validated across cultures among Asian residents from various projects and research objectives such as assessing the work-related stress and coping strategies among employees in the education and health care sectors [ 19 ], so its ability in detecting these mental health problems may be limited for specific groups including undergraduate nursing students. Another study enrolled preclinical medical students to explore psychometric properties of DASS-21, but this study also used this tool as dependent variable and did not report the constructed validity or the Cronbach alpha coefficient [ 20 ]. Insufficient data are available to validate the DASS-21’s psychometric properties in specific Thai populations, which could constitute considerable variation concerning sociocultural backgrounds and political differences among groups.
To date, regarding the context of online learning, no research, concerning factor structures and convergent validity of DASS-21, has been conducted among Thai nursing students. Applying the original subscales scoring for all adulthood categories to only young adult age groups (approximately ages 18 to 26 years) without comprehending the instrument’s psychometric properties could lead to inaccurate conclusions [ 21 ]. This study aimed to examine the psychometric scale‐specific features of DASS-21 for Thai nursing students concerning an online learning situation during the COVID-19 outbreak.
Materials and methods
Study design and population.
This constituted cross-sectional research, obtaining data from one part of the larger multi-center study, aiming to assess the effects of online learning on the prevalence and factors associated with musculoskeletal disorders among Thai, Indonesian, Vietnamese, and Lao faculty members and students during the COVID-19 outbreak. After this study is completed, they recruit some samples and send them the survey of DASS-21. The target population of this study comprised Thai nursing students nationwide undertaken using a multistage sampling technique. Altogether, 96 nursing institutes in Thailand are spread across five regions. Using a simple random sampling technique, two of the five regions, the south and the northeast, were chosen in the first stage. In these areas, 37 nursing institutes are located. Then using a nonproportional stratified sampling technique, 15 nursing institutes were chosen. In addition, three nursing faculties from the Central Region were conveniently sampled, providing a total of 18 institutes. Totally, 5395 students were able to receive participant information sheets online from us. Prior to collecting data, administrators’ approval was obtained after a thorough description of the study’s objective. Before the survey began, a statement of consent was obtained from all participants by permitting only those who pressed "I consent" to go to the questionnaires. A total of 5136 participants indicated their willingness to join the study. Code numbers were created to protect students’ privacy. Finally, nonproportional stratified sampling was used on 4,618 undergraduate students, and 3705 became eligible respondents. Individual student data is only accessible to the authors of this study. These samples were employed to access study participants using an online web-based survey. Recruiting participants and collecting data occurred from April 2022 to June 2022.
Study instruments
The DASS-21 assesses depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms [ 10 ], and is divided into three subscales, each with seven items including depression (DASS 21-D), anxiety (DASS 21-A) and stress (DASS 21-S) (DASS 21S). The translation of this tool from English to Thai was carried out during the cross-culture translation procedure [ 19 ]. Each item is graded on a four-point Likert scale ranging from 0 (“did not apply to me at all”) to 3 (“applied to me a lot”). Because the DASS-21 is a shortened version of the DASS (42 items), the final score of each scale was multiplied by two before being compared with the original DASS scale. Higher scores and response values reflect greater levels of the condition being evaluated. In this study we used the Thai version of the DASS-21 with the original author’s permission [ 19 ]. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of depression, anxiety, and stress for The Thai version are 0.82, 0.78, and 0.69, respectively [ 19 ].
The Visual Analog Scale to Evaluate Fatigue Severity (VAS-F) [ 22 ] has 18 components all related to one’s perception of exhaustion. Each question asks respondents to place an “X" along a VAS line that runs between two extremes, such as "not at all fatigued" and "very tired," to identify what they are feeling right now. The score goes from 0 to 100 and is recorded using a vertical line of 10 cm. The line from "No fatigue" to the subject’s stated point indicating their level of fatigue, was measured to obtain the score; the higher the VAFS score, the greater the level of fatigue [ 23 ]. The Cronbach’s alpha for the fatigue subscale was 0.91 and the value of energy subscale was 0.94, respectively [ 22 ]. In addition, questions about general information of the participants, i.e., gender, age, study year, online learning, were included.
Sample size calculation
The sample size was calculated using the formula "sample size = number of items X number of participants," which is an extensively used formula in survey development research. We estimated the minimum sample size based on one item to ten participants [ 24 ]. Therefore, the minimum acceptable sample size, based on 21 items of DASS-21, was 210 respondents. However, our research enrolled 3,705 nursing students from 18 universities mainly located in south and northeast Thailand. Hence, larger sample size could provide more meaningful factor loadings and yield more generalizable results. The inclusion criteria for the participants were age at least 17 years, a nursing student at the institute during the study period more than six months and engaged in the online learning. Individuals who do not fill the administered questionnaire or submit an incompletely filled questionnaire such as responding to only a part of general information in the Thai Version of DASS-21, and nursing students with existing CMDs were excluded from this study. To avoid model overfitting, the exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analyses (CFA) were organized on a random split of the total 3705 subjects in two group samples (group 1, n = 2000, and group 2, n = 1705).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analysis in this study was conducted using IBM SPSS and AMOS version 20. Descriptive statistics with means and standard deviation for continuous variables and counts and percentages for categorical data were used to describe the participant’s demographic characteristics.
To investigate the number of components in the EFA for the DASS-21 measuring model, parallel analysis (based on principle component analysis) was undertaken using sample group 1. Then the structure of factors was investigated using principal axis factoring with varimax rotation. Factor loadings less than 0.5 were suppressed, and item cross loadings more than 0.2 were removed one at a time. Furthermore, factor loadings were used to calculate average variance extracted (AVE) and composite reliability (CR). Regarding the findings of the principal axis factoring, a CFA was applied to the remaining held-out participants. The measurement model was fitted using an unweighted least square estimate CFA, and model fit was evaluated using the cumulative fit index (CFI), adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI), root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA), and Tucker-Lewis’s index (TLI) [ 19 , 25 , 26 ]. Likewise, Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) with a p-value less than 0.08 was considered to indicate a good model fit, so it was reported and used in this investigation for the sake of convention. Along with the CFA, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy and the Bartlett’s test of sphericity were developed to provide additional construct validity evidence [ 27 ].
CR and Cronbach’s alpha were used to assess reliability. CR is acceptable when the values for the three subscales are greater than 0.6 [ 28 ]. Cronbach’s alpha was used to assess internal consistency reliability, and Cronbach’s alpha above 0.7 for all the subscales was considered to be an acceptable reliability [ 28 ]. In addition, the relationship between each of the DASS items and its own DASS subscale with that item removed is known as the corrected item-total correlations of the three subscales.
We investigated the convergent validity of DASS-18 using the AVE. To indicate convergent validity, the AVE must be equal to or greater than 0.50, indicating that the construct’s variance accounts for more than 50% of its variation [ 26 ]. Furthermore, the discriminant validity determined whether the three indicators of depression, anxiety and stress domains were distinct factors from one another. Pearson’s correlation (r) lower than 0.85 among variables verified their discriminant validity [ 26 ] Pearson correlations were calculated to investigate the intercorrelations matrix, the temporal stability of DASS-18 subscale scores and the relationship between DASS-18 and VAS-F.
Ethics considerations
This study was examined and authorized by Walailak University’s institutional review board (Ref. No. WUEC-22-007-01) and the Center for Ethics in Human Research, Khon Kaen University (Ref. No. HE652094).
General information of the participants
The details of participant characteristics are described in Table 1 . Most completing the questionnaire were females (94.2%) with a mean age of 20 (SD = 1.26) years. Almost two thirds of these participants (67.2%) were experiencing some semesters of online learning at the time of collecting data.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
(n = 3705).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.t001
Exploratory factor analysis
After randomizing the 2000 participants for EFA, firstly, parallel analysis of the matrix indicated that a three-factor solution could be extracted. Secondly, the rotational factor loading matrix was statistically significant. Three factors having eigenvalues over one were created by the initial analyses of the Group 1 sample. To ascertain the factorial structure of DASS-21 and the underlying dimensions comprising its 21 items. The initial analysis revealed a three-factor structure that explained 69.31% of the original data’s variance. Three items (S8, S11, S12) from the stress scale were found to be loading on multiple factors; therefore, these items were removed from this analysis. The three factors resembled the original structure (9) with a reduced factor in stress component; however, the three-factor component (eigenvalues = 9.82; 1.74; and 1.23) was revealed by the scree plot and the eigenvalues higher than one requirement, and this model accounted for 71.31% of the variance. The result of the KMO test was 0.965 (χ2 = 30932; p<0.001), showing that the model was highly adequate. The factor loadings for each DASS- 18 item are shown in Table 2 , with factor loadings >0.50 indicating acceptable loading ( Table 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.t002
Confirmatory factor analysis
Three items from the stress scale were eliminated (the remaining 18 items of DASS, thus DASS-18). The DASS-18 measuring model, which included 18 items distributed across three components including DASS-18-A (7 items), DASS-18-D (7 items) and DASS-18-S (4 items) was fitted using an unweighted least square CFA. Based on the five specified fit criteria, the model demonstrated an acceptable fit to the data (CMIN/df = 3.082; p = 0.001; CFI = 0.98; RMSEA = 0.032; GFI = 0.98 and NFI = 0.99. The effect of the large sample size may have prevented the chi-square tests from providing acceptable assessments of model fit, whereas other indices indicated that these models remained well-fitted for the data. In addition, except for each factor-constraint item, so that no significant test could be archived, all model items were significantly loaded a long with their concurrent factors (all p-values <0.05) ( Fig 1 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.g001
In all cases, the Pearson’s correlation coefficients between DASS-18-D, DASS-18-A and DASS-18-S presented moderate to remarkably elevated levels (0.52 to 0.92) indicating that these scales were moderately to highly discriminatory.
Convergent validity
AVE calculations showed all the DASS-18 subscales achieved a convergence effect (with the AVE of depression = 0.504; the AVE of anxiety = 0.674 and the AVE of stress = 0.551).

Discriminant validity
The magnitude of the correlations among depression, anxiety and stress domains determined the discriminant validity of the variables ( Fig 1 ). The variables showed correlations (r) lower than 0.85 except the correlation between depression and stress domains (r = 0.91).
Association of the DASS-18 scores among demographic characteristic and VAS-F
The total scale of DASS-18 showed a statistically significant positive and fair to moderate association with the VAS-F total score, sex and online learning. Additionally, the DASS-18 total score showed a moderately positive significance correlated to VAS-F in the anticipated direction, confirming the association between higher levels of fatigue and higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress ( Table 3 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.t003
Reliability analysis
The CR of the three domains of DASS-18 ranging from 0.830 to 0.935 indicated evidence of acceptable reliability. Regarding Cronbach alpha values of 0.92 for the overall scale, 0.87 for depression, 0.79 for anxiety and 0.73 for stress, the DASS-18 exhibited adequate internal consistency reliability. Similarly, the internal consistency of this scale was good, as evidenced by the item-rest correlations for all three subscales being better than 0.3 and the corrected item-rest correlation for the entire scale ranging from 0.53 to 0.91 ( Table 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.t004
Product moment intercorrelations matrix values were determined between the three domains of DASS-18 and VAS-F. These intercorrelations values were found to be moderately strong the subscales of depression and anxiety showed the strongest intercorrelation among the three (r = 0.735), which was also statistically significant. These results could imply that the stress domain of DASS-18 moderately and positively correlated to VAS-F (r = 0.445) ( Table 5 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.t005
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the psychometric properties of DASS-21 among Thai nursing students experiencing online classes during the COVID-19 outbreak. For the results of the factorial construct validity of the DASS-18, a three-factor model showed satisfactory conformity to the psychometric construct of the DASS-21 original version [ 10 ], and these results support the fact that the DASS-18 instrument for this cohort contained 18 items spread across three components as follows: anxiety (seven items), depression (seven items) and stress (four items). The three factors were comparable to the structure found by prior studies exploring the psychometric features and generalization of the DASS-21 for use in Asian nations [ 19 ]. This investigation showed that the DASS-18 is a promising and psychometrically sound tool, ideally suited for determining the frequency and intensity of symptoms associated with negative affective states for these participants. Furthermore, the two-week temporal stability was good for all DASS-18 scale scores; in particular, the DASS-18 stress subscale showed the highest correlation values across time and they had a great internal consistency reliability, agreeing with our hypotheses. The consequences of reducing three items from the stress scale are the reasons for the lower Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of this scale than that of Lovibond and Lovibond’ s original version [ 10 ]. These differences might have resulted from the DASS-18 having fewer items because the quantity of items creates an impact on how Cronbach’s alpha is calculated [ 19 ].
According to our results, only minimal changes were observed between the original DASS-stress (seven items) and our DASS-stress (four items) scales. These disparities might be explained by how diverse culture’s view perception of some items that could be interpreted as besides the stress context cultural factors and the response of the participants may influence how individuals understand item of the DASS-stress scales, but not on the DASS-depression and DASS-anxiety scale as we found no significant cultural problem with these two scales and no concerns were noted regarding the EFA findings as demonstrated by the statistical results of this study. Therefore, the DASS-18 factor structure clearly demonstrated three factors, as in the original DASS-21 scale [ 10 ]. Likewise, one study reported that no invariances were discovered in their multi-group analysis across the six countries [ 19 ]. In addition, findings from this previous study on the correlations of the three subscales with those of other psychiatric instruments measuring similar constructs offered support for the validity of the DASS-18 subscales and were generally favorable [ 19 ]. Moreover, the depression and anxiety subscales of the DASS-18 exhibited specific relationships with the relevant measures of these disorders, indicating that using these constructs was appropriate.
Cronbach’s alpha coefficient from our study revealed that total DASS-18 scores and its subscales exhibited good internal consistency. This coefficient ranged from good to excellent in prior studies comprising both nonclinical and clinical adult samples [ 2 , 9 , 10 , 19 , 21 , 29 – 31 ]. Hence, the data collectively proved that the DASS-18 demonstrated strong internal consistency across a variety of demographics and languages. Moreover, the results of the item analysis indicated that the items in each scale had good discrimination indices (corrected item-total correction). These indices suggested that the DASS-18 Thai version items would be effective at distinguishing between high and low scorers on this scale. Related research has also revealed that this assessment tool provides a good item discrimination index [ 13 , 18 ].
The relationships between demographic characteristics and DASS-18 scale scores were also investigated. This study found a weak positive statistically significant relationship between DASS-18 and sex. Despite the concerns about future endurance and competency aspect, female participants expressed more depression, anxiety, and stress than males. This may be because female nursing students usually have commitments outside of the classroom, such as taking care of their family members and performing chores [ 7 , 32 ]. Our results indicated that online learning moderately, positively correlated to the total DASS-18 score because high standards for performance, learning habits, and training may negative impact students’ mental health [ 7 ]. Similarly, clinical courses in nursing programs call for specialized cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor abilities typically following specialized theoretical courses. Because of being unable to take part in clinical settings, these students felt as though they were missing out on a great opportunity to acquire these abilities [ 6 , 20 ]. Thus, these students may have felt unprepared for learning in a clinical setting due to the extremely brief on campus learning time before lockdown, and the pandemic made it more difficult for nursing students to advance in their practical training [ 6 ]. When lockdowns ended, nursing students had greater opportunity to contract an illness by themselves or face patients with COVID-19 experiencing significant effects [ 5 ].
The internal consistency of the DASS-18 was adequate and consistent with the related Asian research [ 7 , 19 ]. The Thai version’s convergent validity is supported by favorable correlations with the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI); correlations in this direction were anticipated to measure the same construct [ 19 ]. These results demonstrated the validity and reliability of the Thai DASS-18 version as a tool for measuring negative emotional states. This indicated that this scale could prove beneficial for screening CMDs among clinical undergraduate students including nursing students.
The convergent validity of the DASS-18 was examined using the AVE calculation of all three subscales. The results revealed that all sub-scales’ AVE were greater than 0.50, corresponding to the convergent validity acceptance criteria. These findings were also compatible with the findings of a study that aimed to validate the DASS-21 among Vietnam students in an e-learning environment [ 7 ]. Regarding the discriminant validity, factors of this stress subscale also highly correlated to each other, which were higher than the values suggested by Hu and Bentler [ 26 ]. These higher correlations indicated significant overlapping in the content of the DASS-18 scales, indicating a general construct, such as affective distress. One related study also reported a higher correlation among these subscales [ 13 ].
When comparing depression, anxiety and stress scales, anxiety items had higher factor loadings, eigenvalues, and percentage of variation than the other domains. Depression and anxiety continued to have the highest inter-correlations, with a value of 0.708 indicating significant overlap between the two domains. Despite the overlap between domains, they could still be separated. An extraordinarily strong and positive association was noted between these domains. The Thai nursing students’ symptoms of stress, anxiety and depression were all positively connected, according to these positive correlation values. The DASS-18’s correlation coefficients showed beneficial correlations between the two instruments in this regard. Likewise, these coefficients also showed that the subjects’ anxiety and depression were present at the same time. The DASS-18 was thus shown to measure depression and anxiety among the responders in a simultaneous and unique manner. These findings were in line with studies in other countries [ 21 , 29 ].
Strengths and limitations
The strength of this study is the fact that the structure and psychometric features of the DASS-21 were examined for the first time in a large sample of undergraduate nursing students in Thailand. Because the participant-to-questionnaire-item ratio was satisfactory, the prerequisites for component analysis were met, and bias resulting from the number of observations was reduced.
Our study encountered limitations regarding the nursing students comprising our subjects. They could not accurately be generalized to other nonclinical undergraduate students due to their diverse qualities because they may be privileged in terms of socioeconomic status, freedom, and health. The study was cross-sectional; hence, the data were unable to show test-retest reliability over time. The study was limited in terms of criterion validity because we did not test any other parameters besides VAS-F.
The study ‘s main findings demonstrate that the DASS-18 is a valid instrument for detecting CMDs among Thai nursing students enrolled in online courses during the COVID-19 outbreak. The three-factor structure with 18 items proposed in the initial study was supported by the findings. Therefore, the availability of the DASS-18’s psychometric features will enhance performance of Thai psychologists and researchers in effectively screening the population of undergraduate nursing students for CMDs at tertiary institutions.
Supporting information
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0288041.s001
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all nursing institutions for supporting students’ data collection. The research collaborators at all involved nursing institutes are thanked by the authors for helping with sample recruitment and data gathering. All nursing students joining this study are gratefully acknowledged.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 28. Kline P. Handbook of psychological testing: Routledge; 2013.
Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Psychiatry & Mental Health — Depression
Essays About Depression
Depression essay topic examples.
Explore topics like the impact of stigma on depression, compare it across age groups or in literature and media, describe the emotional journey of depression, discuss how education can help, and share personal stories related to it. These essay ideas offer a broad perspective on depression, making it easier to understand and engage with this important subject.
Argumentative Essays
Argumentative essays require you to analyze and present arguments related to depression. Here are some topic examples:
- 1. Argue whether mental health stigma contributes to the prevalence of depression in society.
- 2. Analyze the effectiveness of different treatment approaches for depression, such as therapy versus medication.
Example Introduction Paragraph for an Argumentative Essay: Depression is a pervasive mental health issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This essay delves into the complex relationship between mental health stigma and the prevalence of depression in society, examining the barriers to seeking help and the consequences of this stigma.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for an Argumentative Essay: In conclusion, the analysis of mental health stigma's impact on depression underscores the urgent need to challenge and dismantle the stereotypes surrounding mental health. As we reflect on the far-reaching consequences of stigma, we are called to create a society that fosters empathy, understanding, and open dialogue about mental health.
Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays enable you to examine similarities and differences within the context of depression. Consider these topics:
- 1. Compare and contrast the symptoms and risk factors of depression in adolescents and adults.
- 2. Analyze the similarities and differences between the portrayal of depression in literature and its depiction in modern media.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Compare and Contrast Essay: Depression manifests differently in various age groups and mediums of expression. This essay embarks on a journey to compare and contrast the symptoms and risk factors of depression in adolescents and adults, shedding light on the unique challenges faced by each demographic.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Compare and Contrast Essay: In conclusion, the comparison and contrast of depression in adolescents and adults highlight the importance of tailored interventions and support systems. As we contemplate the distinct challenges faced by these age groups, we are reminded of the need for age-appropriate mental health resources and strategies.
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays allow you to vividly depict aspects of depression, whether it's the experience of the individual or the societal impact. Here are some topic ideas:
- 1. Describe the emotional rollercoaster of living with depression, highlighting the highs and lows of the experience.
- 2. Paint a detailed portrait of the consequences of untreated depression on an individual's personal and professional life.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Descriptive Essay: Depression is a complex emotional journey that defies easy characterization. This essay embarks on a descriptive exploration of the emotional rollercoaster that individuals with depression experience, delving into the profound impact it has on their daily lives.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Descriptive Essay: In conclusion, the descriptive portrayal of the emotional rollercoaster of depression underscores the need for empathy and support for those grappling with this condition. Through this exploration, we are reminded of the resilience of the human spirit and the importance of compassionate understanding.
Persuasive Essays
Persuasive essays involve arguing a point of view related to depression. Consider these persuasive topics:
- 1. Persuade your readers that incorporating mental health education into the school curriculum can reduce the prevalence of depression among students.
- 2. Argue for or against the idea that employers should prioritize the mental well-being of their employees to combat workplace depression.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay: The prevalence of depression underscores the urgent need for proactive measures to address mental health. This persuasive essay asserts that integrating mental health education into the school curriculum can significantly reduce the prevalence of depression among students, offering them the tools to navigate emotional challenges.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay: In conclusion, the persuasive argument for mental health education in schools highlights the potential for early intervention and prevention. As we consider the well-being of future generations, we are called to prioritize mental health education as an essential component of a holistic education system.
Narrative Essays
Narrative essays offer you the opportunity to tell a story or share personal experiences related to depression. Explore these narrative essay topics:
- 1. Narrate a personal experience of overcoming depression or supporting a loved one through their journey.
- 2. Imagine yourself in a fictional scenario where you advocate for mental health awareness and destigmatization on a global scale.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Narrative Essay: Personal experiences with depression can be transformative and enlightening. This narrative essay delves into a personal journey of overcoming depression, highlighting the challenges faced, the support received, and the lessons learned along the way.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Narrative Essay: In conclusion, the narrative of my personal journey through depression reminds us of the resilience of the human spirit and the power of compassion and understanding. As we reflect on our own experiences, we are encouraged to share our stories and contribute to the ongoing conversation about mental health.
Critical Appraisal of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Treating Depression
Ileana chivescu case study, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Depression is Depression an Actual Illness
The epidemic of depression among students and teenagers, the effects of depression in your body and its treatment, the issue of depression and its reality nowadays, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Overview of Biological Predispositions and Risk Factors Associated with Depression
How to overcome depression and anxiety, depression: definition, risks, symptoms and treatment, the best way to help someone who is depressed, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Issue of Depression: Mental Battle
What is a depression, living in depression: a firsthand account, teen depression - symptoms and causes, adolescent depression and its contribution to teenage suicides, the issue of depression and its affect in an emerging adulthood, depression: definition and ways of resolving caused problems, depression in teenagers: causes and ways to overcome, depression and its main causes, genetic disorder report: clinical depression, the way teachers can help their students to overcome anxiety and depression, depression and its effects of mind and body, the effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy (cbt) for treating individuals with depression and anxiety, how to overcome teenage depression, depression as the reason of serious health problems and suicide, a depressing world with different obstacles, the link between self-esteem and adolescent depression, darwinian psychology and depression: the gender differential hypothesis, prevention of depression, anxiety and burnout in resident doctors – a systematic review, dysregulated processing of negative and positive responses in depression.
Depression, known as major depressive disorder or clinical depression, is a psychological condition characterized by enduring feelings of sadness and a significant loss of interest in activities. It is a mood disorder that affects a person's emotional state, thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being.
Its origin can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where melancholia was described as a state of sadness and melancholy. In the 19th century, depression began to be studied more systematically, and terms such as "melancholic depression" and "nervous breakdown" emerged. The understanding and classification of depression have evolved over time. In the early 20th century, Sigmund Freud and other psychoanalysts explored the role of unconscious conflicts in the development of depression. In the mid-20th century, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) was established, providing a standardized criteria for diagnosing depressive disorders.
Biological Factors: Genetic predisposition plays a role in depression, as individuals with a family history of the disorder are at a higher risk. Psychological Factors: These may include a history of trauma or abuse, low self-esteem, pessimistic thinking patterns, and a tendency to ruminate on negative thoughts. Environmental Factors: Adverse life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial difficulties, relationship problems, or chronic stress, can increase the risk of depression. Additionally, living in a socioeconomically disadvantaged area or lacking access to social support can be contributing factors. Health-related Factors: Chronic illnesses, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and chronic pain, are associated with a higher risk of depression. Substance abuse and certain medications can also increase vulnerability to depression. Developmental Factors: Certain life stages, including adolescence and the postpartum period, bring about unique challenges and changes that can contribute to the development of depression.
Depression is characterized by a range of symptoms that affect an individual's emotional, cognitive, and physical well-being. These characteristics can vary in intensity and duration but generally include persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed. One prominent characteristic of depression is a noticeable change in mood, which can manifest as a constant feeling of sadness or emptiness. Individuals may also experience a significant decrease or increase in appetite, leading to weight loss or gain. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or excessive sleepiness, are common as well. Depression can impact cognitive functioning, causing difficulties in concentration, decision-making, and memory recall. Negative thoughts, self-criticism, and feelings of guilt or worthlessness are also common cognitive symptoms. Furthermore, physical symptoms may arise, including fatigue, low energy levels, and a general lack of motivation. Physical aches and pains, without an apparent medical cause, may also be present.
The treatment of depression typically involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. It is important to note that the most effective treatment may vary for each individual, and a personalized approach is often necessary. One common form of treatment is psychotherapy, which involves talking to a mental health professional to explore and address the underlying causes and triggers of depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with depression. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage depressive symptoms. Antidepressant medications work by balancing neurotransmitters in the brain that are associated with mood regulation. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage that suits an individual's needs. Additionally, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing depression. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress reduction techniques can all contribute to improving mood and overall well-being. In severe cases of depression, when other treatments have not been effective, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be considered. ECT involves administering controlled electric currents to the brain to induce a brief seizure, which can have a positive impact on depressive symptoms.
1. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 264 million people worldwide suffer from depression, making it one of the leading causes of disability globally. 2. Depression can affect people of all ages, including children and adolescents. In fact, the prevalence of depression in young people is increasing, with an estimated 3.3 million adolescents in the United States experiencing at least one major depressive episode in a year. 3. Research has shown that there is a strong link between depression and other physical health conditions. People with depression are more likely to experience chronic pain, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders, among other medical conditions.
The topic of depression holds immense significance and should be explored through essays due to its widespread impact on individuals and society as a whole. Understanding and raising awareness about depression is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, depression affects a significant portion of the global population, making it a pressing public health issue. Exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can contribute to better mental health outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Additionally, writing an essay about depression can help combat the stigma surrounding mental health. By promoting open discussions and providing accurate information, essays can challenge misconceptions and foster empathy and support for those experiencing depression. Furthermore, studying depression allows for a deeper examination of its complex nature, including its psychological, biological, and sociocultural factors. Lastly, essays on depression can highlight the importance of early detection and intervention, promoting timely help-seeking behaviors and reducing the burden of the condition on individuals and healthcare systems. By shedding light on this critical topic, essays have the potential to educate, inspire action, and contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and society.
1. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing. 2. World Health Organization. (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. World Health Organization. 3. Kessler, R. C., Bromet, E. J., & Quinlan, J. (2013). The burden of mental disorders: Global perspectives from the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Cambridge University Press. 4. Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. Guilford Press. 5. Nierenberg, A. A., & DeCecco, L. M. (2001). Definitions and diagnosis of depression. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 62(Suppl 22), 5-9. 6. Greenberg, P. E., Fournier, A. A., Sisitsky, T., Pike, C. T., & Kessler, R. C. (2015). The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2005 and 2010). Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 76(2), 155-162. 7. Cuijpers, P., Berking, M., Andersson, G., Quigley, L., Kleiboer, A., & Dobson, K. S. (2013). A meta-analysis of cognitive-behavioural therapy for adult depression, alone and in comparison with other treatments. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 58(7), 376-385. 8. Hirschfeld, R. M. A. (2014). The comorbidity of major depression and anxiety disorders: Recognition and management in primary care. Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders, 16(2), PCC.13r01611. 9. Rush, A. J., Trivedi, M. H., Wisniewski, S. R., Nierenberg, A. A., Stewart, J. W., Warden, D., ... & Fava, M. (2006). Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163(11), 1905-1917. 10. Kendler, K. S., Kessler, R. C., Walters, E. E., MacLean, C., Neale, M. C., Heath, A. C., & Eaves, L. J. (1995). Stressful life events, genetic liability, and onset of an episode of major depression in women. American Journal of Psychiatry, 152(6), 833-842.
Relevant topics
- Mental Health
- Eating Disorders
- Drug Addiction
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Efficacy of psilocybin...
Efficacy of psilocybin for treating symptoms of depression: systematic review and meta-analysis
Linked editorial.
Psilocybin for depression
- Related content
- Peer review
This article has a correction. Please see:
- EXPRESSION OF CONCERN: Efficacy of psilocybin for treating symptoms of depression: systematic review and meta-analysis - May 04, 2024
- Athina-Marina Metaxa , masters graduate researcher 1 ,
- Mike Clarke , professor 2
- 1 Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford OX2 6GG, UK
- 2 Northern Ireland Methodology Hub, Centre for Public Health, ICS-A Royal Hospitals, Belfast, Ireland, UK
- Correspondence to: A-M Metaxa athina.metaxa{at}hmc.ox.ac.uk (or @Athina_Metaxa12 on X)
- Accepted 6 March 2024
Objective To determine the efficacy of psilocybin as an antidepressant compared with placebo or non-psychoactive drugs.
Design Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data sources Five electronic databases of published literature (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Medline, Embase, Science Citation Index and Conference Proceedings Citation Index, and PsycInfo) and four databases of unpublished and international literature (ClinicalTrials.gov, WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global, and PsycEXTRA), and handsearching of reference lists, conference proceedings, and abstracts.
Data synthesis and study quality Information on potential treatment effect moderators was extracted, including depression type (primary or secondary), previous use of psychedelics, psilocybin dosage, type of outcome measure (clinician rated or self-reported), and personal characteristics (eg, age, sex). Data were synthesised using a random effects meta-analysis model, and observed heterogeneity and the effect of covariates were investigated with subgroup analyses and metaregression. Hedges’ g was used as a measure of treatment effect size, to account for small sample effects and substantial differences between the included studies’ sample sizes. Study quality was appraised using Cochrane’s Risk of Bias 2 tool, and the quality of the aggregated evidence was evaluated using GRADE guidelines.
Eligibility criteria Randomised trials in which psilocybin was administered as a standalone treatment for adults with clinically significant symptoms of depression and change in symptoms was measured using a validated clinician rated or self-report scale. Studies with directive psychotherapy were included if the psychotherapeutic component was present in both experimental and control conditions. Participants with depression regardless of comorbidities (eg, cancer) were eligible.
Results Meta-analysis on 436 participants (228 female participants), average age 36-60 years, from seven of the nine included studies showed a significant benefit of psilocybin (Hedges’ g=1.64, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.55 to 2.73, P<0.001) on change in depression scores compared with comparator treatment. Subgroup analyses and metaregressions indicated that having secondary depression (Hedges’ g=3.25, 95% CI 0.97 to 5.53), being assessed with self-report depression scales such as the Beck depression inventory (3.25, 0.97 to 5.53), and older age and previous use of psychedelics (metaregression coefficient 0.16, 95% CI 0.08 to 0.24 and 4.2, 1.5 to 6.9, respectively) were correlated with greater improvements in symptoms. All studies had a low risk of bias, but the change from baseline metric was associated with high heterogeneity and a statistically significant risk of small study bias, resulting in a low certainty of evidence rating.
Conclusion Treatment effects of psilocybin were significantly larger among patients with secondary depression, when self-report scales were used to measure symptoms of depression, and when participants had previously used psychedelics. Further research is thus required to delineate the influence of expectancy effects, moderating factors, and treatment delivery on the efficacy of psilocybin as an antidepressant.
Systematic review registration PROSPERO CRD42023388065.

- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Introduction
Depression affects an estimated 300 million people around the world, an increase of nearly 20% over the past decade. 1 Worldwide, depression is also the leading cause of disability. 2
Drugs for depression are widely available but these seem to have limited efficacy, can have serious adverse effects, and are associated with low patient adherence. 3 4 Importantly, the treatment effects of antidepressant drugs do not appear until 4-7 weeks after the start of treatment, and remission of symptoms can take months. 4 5 Additionally, the likelihood of relapse is high, with 40-60% of people with depression experiencing a further depressive episode, and the chance of relapse increasing with each subsequent episode. 6 7
Since the early 2000s, the naturally occurring serotonergic hallucinogen psilocybin, found in several species of mushrooms, has been widely discussed as a potential treatment for depression. 8 9 Psilocybin’s mechanism of action differs from that of classic selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and might improve the treatment response rate, decrease time to improvement of symptoms, and prevent relapse post-remission. Moreover, more recent assessments of harm have consistently reported that psilocybin generally has low addictive potential and toxicity and that it can be administered safely under clinical supervision. 10
The renewed interest in psilocybin’s antidepressive effects led to several clinical trials on treatment resistant depression, 11 12 major depressive disorder, 13 and depression related to physical illness. 14 15 16 17 These trials mostly reported positive efficacy findings, showing reductions in symptoms of depression within a few hours to a few days after one dose or two doses of psilocybin. 11 12 13 16 17 18 These studies reported only minimal adverse effects, however, and drug harm assessments in healthy volunteers indicated that psilocybin does not induce physiological toxicity, is not addictive, and does not lead to withdrawal. 19 20 Nevertheless, these findings should be interpreted with caution owing to the small sample sizes and open label design of some of these studies. 11 21
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses since the early 2000s have investigated the use of psilocybin to treat symptoms of depression. Most found encouraging results, but as well as people with depression some included healthy volunteers, 22 and most combined data from studies of multiple serotonergic psychedelics, 23 24 25 even though each compound has unique neurobiological effects and mechanisms of action. 26 27 28 Furthermore, many systematic reviews included non-randomised studies and studies in which psilocybin was tested in conjunction with psychotherapeutic interventions, 25 29 30 31 32 which made it difficult to distinguish psilocybin’s treatment effects. Most systematic reviews and meta-analyses did not consider the impact of factors that could act as moderators to psilocybin’s effects, such as type of depression (primary or secondary), previous use of psychedelics, psilocybin dosage, type of outcome measure (clinician rated or self-reported), and personal characteristics (eg, age, sex). 25 26 29 30 31 32 Lastly, systematic reviews did not consider grey literature, 33 34 which might have led to a substantial overestimation of psilocybin’s efficacy as a treatment for depression. In this review we focused on randomised trials that contained an unconfounded evaluation of psilocybin in adults with symptoms of depression, regardless of country and language of publication.
In this systematic review and meta-analysis of indexed and non-indexed randomised trials we investigated the efficacy of psilocybin to treat symptoms of depression compared with placebo or non-psychoactive drugs. The protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (see supplementary Appendix A). The study overall did not deviate from the pre-registered protocol; one clarification was made to highlight that any non-psychedelic comparator was eligible for inclusion, including placebo, niacin, micro doses of psychedelics, and drugs that are considered the standard of care in depression (eg, SSRIs).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Double blind and open label randomised trials with a crossover or parallel design were eligible for inclusion. We considered only studies in humans and with a control condition, which could include any type of non -active comparator, such as placebo, niacin, or micro doses of psychedelics.
Eligible studies were those that included adults (≥18 years) with clinically significant symptoms of depression, evaluated using a clinically validated tool for depression and mood disorder outcomes. Such tools included the Beck depression inventory, Hamilton depression rating scale, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale, profile of mood states, and quick inventory of depressive symptomatology. Studies of participants with symptoms of depression and comorbidities (eg, cancer) were also eligible. We excluded studies of healthy participants (without depressive symptomatology).
Eligible studies investigated the effect of psilocybin as a standalone treatment on symptoms of depression. Studies with an active psilocybin condition that involved micro dosing (ie, psilocybin <100 μg/kg, according to the commonly accepted convention 22 35 ) were excluded. We included studies with directive psychotherapy if the psychotherapeutic component was present in both the experimental and the control conditions, so that the effects of psilocybin could be distinguished from those of psychotherapy. Studies involving group therapy were also excluded. Any non-psychedelic comparator was eligible for inclusion, including placebo, niacin, and micro doses of psychedelics.
Changes in symptoms, measured by validated clinician rated or self-report scales, such as the Beck depression inventory, Hamilton depression rating scale, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale, profile of mood states, and quick inventory of depressive symptomatology were considered. We excluded outcomes that were measured less than three hours after psilocybin had been administered because any reported changes could be attributed to the transient cognitive and affective effects of the substance being administered. Aside from this, outcomes were included irrespective of the time point at which measurements were taken.
Search strategy
We searched major electronic databases and trial registries of psychological and medical research, with no limits on the publication date. Databases were the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials via the Cochrane Library, Embase via Ovid, Medline via Ovid, Science Citation Index and Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science via Web of Science, and PsycInfo via Ovid. A search through multiple databases was necessary because each database includes unique journals. Supplementary Appendix B shows the search syntax used for the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, which was slightly modified to comply with the syntactic rules of the other databases.
Unpublished and grey literature were sought through registries of past and ongoing trials, databases of conference proceedings, government reports, theses, dissertations, and grant registries (eg, ClinicalTrials.gov, WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global, and PsycEXTRA). The references and bibliographies of eligible studies were checked for relevant publications. The original search was done in January 2023 and updated search was performed on 10 August 2023.
Data collection, extraction, and management
The results of the literature search were imported to the Endnote X9 reference management software, and the references were imported to the Covidence platform after removal of duplicates. Two reviewers (AM and DT) independently screened the title and abstract of each reference and then screened the full text of potentially eligible references. Any disagreements about eligibility were resolved through discussion. If information was insufficient to determine eligibility, the study’s authors were contacted. The reviewers were not blinded to the studies’ authors, institutions, or journal of publication.
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram shows the study selection process and reasons for excluding studies that were considered eligible for full text screening. 36
Critical appraisal of individual studies and of aggregated evidence
The methodological quality of eligible studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool (RoB 2) for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. 37 In addition to the criteria specified by RoB 2, we considered the potential impact of industry funding and conflicts of interest. The overall methodological quality of the aggregated evidence was evaluated using GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation). 38
If we found evidence of heterogeneity among the trials, then small study biases, such as publication bias, were assessed using a funnel plot and asymmetry tests (eg, Egger’s test). 39
We used a template for data extraction (see supplementary Appendix C) and summarised the extracted data in tabular form, outlining personal characteristics (age, sex, previous use of psychedelics), methodology (study design, dosage), and outcome related characteristics (mean change from baseline score on a depression questionnaire, response rates, and remission rates) of the included studies. Response conventionally refers to a 50% decrease in symptom severity based on scores on a depression rating scale, whereas remission scores are specific to a questionnaire (eg, score of ≤5 on the quick inventory of depressive symptomatology, score of ≤10 on the Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale, 50% or greater reduction in symptoms, score of ≤7 on the Hamilton depression rating scale, or score of ≤12 on the Beck depression inventory). Across depression scales, higher scores signify more severe symptoms of depression.
Continuous data synthesis
From each study we extracted the baseline and post-intervention means and standard deviations (SDs) of the scores between comparison groups for the depression questionnaires and calculated the mean differences and SDs of change. If means and SDs were not available for the included studies, we extracted the values from available graphs and charts using the Web Plot Digitizer application ( https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer/ ). If it was not possible to calculate SDs from the graphs or charts, we generated values by converting standard errors (SEs) or confidence intervals (CIs), depending on availability, using formulas in the Cochrane Handbook (section 7.7.3.2). 40
Standardised mean differences were calculated for each study. We chose these rather than weighted mean differences because, although all the studies measured depression as the primary outcome, they did so with different questionnaires that score depression based on slightly different items. 41 If we had used weighted mean differences, any variability among studies would be assumed to reflect actual methodological or population differences and not differences in how the outcome was measured, which could be misleading. 40
The Hedges’ g effect size estimate was used because it tends to produce less biased results for studies with smaller samples (<20 participants) and when sample sizes differ substantially between studies, in contrast with Cohen’s d. 42 According to the Cochrane Handbook, the Hedges’ g effect size measure is synonymous with the standardised mean difference, 40 and the terms may be used interchangeably. Thus, a Hedges’ g of 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, or 1.2 corresponds to a small, medium, large, or very large effect, respectively. 40
Owing to variation in the participants’ personal characteristics, psilocybin dosage, type of depression investigated (primary or secondary), and type of comparators, we used a random effects model with a Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman modification. 43 This model also allowed for heterogeneity and within study variability to be incorporated into the weighting of the results of the included studies. 44 Lastly, this model could help to generalise the findings beyond the studies and patient populations included, making the meta-analysis more clinically useful. 45 We chose the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment in favour of more widely used random effects models (eg, DerSimonian and Laird) because it allows for better control of type 1 errors, especially for studies with smaller samples, and provides a better estimation of between study variance by accounting for small sample sizes. 46 47
For studies in which multiple treatment groups were compared with a single placebo group, we split the placebo group to avoid multiplicity. 48 Similarly, if studies included multiple primary outcomes (eg, change in depression at three weeks and at six weeks), we split the treatment groups to account for overlapping participants. 40
Prediction intervals (PIs) were calculated and reported to show the expected effect range of a similar future study, in a different setting. In a random effects model, within study measures of variability, such as CIs, can only show the range in which the average effect size could lie, but they are not informative about the range of potential treatment effects given the heterogeneity between studies. 49 Thus, we used PIs as an indication of variation between studies.
Heterogeneity and sensitivity analysis
Statistical heterogeneity was tested using the χ 2 test (significance level P<0.1) and I 2 statistic, and heterogeneity among included studies was evaluated visually and displayed graphically using a forest plot. If substantial or considerable heterogeneity was found (I 2 ≥50% or P<0.1), 50 we considered the study design and characteristics of the included studies. Sources of heterogeneity were explored by subgroup analysis, and the potential effects on the results are discussed.
Planned sensitivity analyses to assess the effect of unpublished studies and studies at high risk of bias were not done because all included studies had been published and none were assessed as high risk of bias. Exclusion sensitivity plots were used to display graphically the impact of individual studies and to determine which studies had a particularly large influence on the results of the meta-analysis. All sensitivity analyses were carried out with Stata 16 software.
Subgroup analysis
To reduce the risk of errors caused by multiplicity and to avoid data fishing, we planned subgroup analyses a priori and limited to: (1) patient characteristics, including age and sex; (2) comorbidities, such as a serious physical condition (previous research indicates that the effects of psilocybin may be less strong for such participants, compared with participants with no comorbidities) 33 ; (3) number of doses and amount of psilocybin administered, because some previous meta-analyses found that a higher number of doses and a higher dose of psilocybin both predicted a greater reduction in symptoms of depression, 34 whereas others reported the opposite 33 ; (4) psilocybin administered alongside psychotherapeutic guidance or as a standalone treatment; (5) severity of depressive symptoms (clinical v subclinical symptomatology); (6) clinician versus patient rated scales; and (7) high versus low quality studies, as determined by RoB 2 assessment scores.
Metaregression
Given that enough studies were identified (≥10 distinct observations according to the Cochrane Handbook’s suggestion 40 ), we performed metaregression to investigate whether covariates, or potential effect modifiers, explained any of the statistical heterogeneity. The metaregression analysis was carried out using Stata 16 software.
Random effects metaregression analyses were used to determine whether continuous variables such as participants’ age, percentage of female participants, and percentage of participants who had previously used psychedelics modified the effect estimate, all of which have been implicated in differentially affecting the efficacy of psychedelics in modifying mood. 51 We chose this approach in favour of converting these continuous variables into categorical variables and conducting subgroup analyses for two primary reasons; firstly, the loss of any data and subsequent loss of statistical power would increase the risk of spurious significant associations, 51 and, secondly, no cut-offs have been agreed for these factors in literature on psychedelic interventions for mood disorders, 52 making any such divisions arbitrary and difficult to reconcile with the findings of other studies. The analyses were based on within study averages, in the absence of individual data points for each participant, with the potential for the results to be affected by aggregate bias, compromising their validity and generalisability. 53 Furthermore, a group level analysis may not be able to detect distinct interactions between the effect modifiers and participant subgroups, resulting in ecological bias. 54 As a result, this analysis should be considered exploratory.
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was performed to determine if choice of analysis method affected the primary findings of meta-analysis. Specifically, we reanalysed the data on change in depression score using a random effects Dersimonian and Laird model without the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman modification and compared the results with those of the originally used model. This comparison is particularly important in the presence of substantial heterogeneity and the potential of small study effects to influence the intervention effect estimate. 55
Patient and public involvement
Research on novel depression treatments is of great interest to both patients and the public. Although patients and members of the public were not directly involved in the planning or writing of this manuscript owing to a lack of available funding for recruitment and researcher training, patients and members of the public read the manuscript after submission.
Figure 1 presents the flow of studies through the systematic review and meta-analysis. 56 A total of 4884 titles were retrieved from the five databases of published literature, and a further 368 titles were identified from the databases of unpublished and international literature in February 2023. After the removal of duplicate records, we screened the abstracts and titles of 875 reports. A further 12 studies were added after handsearching of reference lists and conference proceedings and abstracts. Overall, nine studies totalling 436 participants were eligible. The average age of the participants ranged from 36-60 years. During an updated search on 10 August 2023, no further studies were identified.

Flow of studies in systematic review and meta-analysis
After screening of the title and abstract, 61 titles remained for full text review. Native speakers helped to translate papers in languages other than English. The most common reasons for exclusion were the inclusion of healthy volunteers, absence of control groups, and use of a survey based design rather than an experimental design. After full text screening, nine studies were eligible for inclusion, and 15 clinical trials prospectively registered or underway as of August 2023 were noted for potential future inclusion in an update of this review (see supplementary Appendix D).
We sent requests for further information to the authors of studies by Griffiths et al, 57 Barrett, 58 and Benville et al, 59 because these studies appeared to meet the inclusion criteria but were only provided as summary abstracts online. A potentially eligible poster presentation from the 58th annual meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology was identified but the lead author (Griffiths) clarified that all information from the presentation was included in the studies by Davis et al 13 and Gukasyan et al 60 ; both of which we had already deemed ineligible.
Barrett 58 reported the effects of psilocybin on the cognitive flexibility and verbal reasoning of a subset of patients with major depressive disorder from Griffith et al’s trial, 61 compared with a waitlist group, but when contacted, Barrett explained that the results were published in the study by Doss et al, 62 which we had already screened and judged ineligible (see supplementary Appendix E). Benville et al’s study 59 presented a follow-up of Ross et al’s study 17 on a subset of patients with cancer and high suicidal ideation and desire for hastened death at baseline. Measures of antidepressant effects of psilocybin treatment compared with niacin were taken before and after treatment crossover, but detailed results are not reported. Table 1 describes the characteristics of the included studies and table 2 lists the main findings of the studies.
Characteristics of included studies
- View inline
Main findings of included studies
Side effects and adverse events
Side effects reported in the included studies were minor and transient (eg, short term increases in blood pressure, headache, and anxiety), and none were coded as serious. Cahart-Harris et al noted one instance of abnormal dreams and insomnia. 63 This side effect profile is consistent with findings from other meta-analyses. 30 68 Owing to the different scales and methods used to catalogue side effects and adverse events across trials, it was not possible to combine these data quantitatively (see supplementary Appendix F).
Risk of bias
The Cochrane RoB 2 tools were used to evaluate the included studies ( table 3 ). RoB 2 for randomised trials was used for the five reports of parallel randomised trials (Carhart-Harris et al 63 and its secondary analysis Barba et al, 64 Goodwin et al 18 and its secondary analysis Goodwin et al, 65 and von Rotz et al 66 ) and RoB 2 for crossover trials was used for the four reports of crossover randomised trials (Griffiths et al, 14 Grob et al, 15 and Ross et al 17 and its follow-up Ross et al 67 ). Supplementary Appendix G provides a detailed explanation of the assessment of the included studies.
Summary risk of bias assessment of included studies, based on domains in Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool
Quality of included studies
Confidence in the quality of the evidence for the meta-analysis was assessed using GRADE, 38 through the GRADEpro GDT software program. Figure 2 shows the results of this assessment, along with our summary of findings.

GRADE assessment outputs for outcomes investigated in meta-analysis (change in depression scores and response and remission rates). The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). BDI=Beck depression inventory; CI=confidence interval; GRADE=Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation; HADS-D=hospital anxiety and depression scale; HAM-D=Hamilton depression rating scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale; QIDS=quick inventory of depressive symptomatology; RCT=randomised controlled trial; SD=standard deviation
Meta-analyses
Continuous data, change in depression scores —Using a Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman modified random effects meta-analysis, change in depression scores was significantly greater after treatment with psilocybin compared with active placebo. The overall Hedges’ g (1.64, 95% CI 0.55 to 2.73) indicated a large effect size favouring psilocybin ( fig 3 ). PIs were, however, wide and crossed the line of no difference (95% CI −1.72 to 5.03), indicating that there could be settings or populations in which psilocybin intervention would be less efficacious.

Forest plot for overall change in depression scores from before to after treatment. CI=confidence interval; DL=DerSimonian and Laird; HKSJ=Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman
Exploring publication bias in continuous data —We used Egger’s test and a funnel plot to examine the possibility of small study biases, such as publication bias. Statistical significance of Egger’s test for small study effects, along with the asymmetry in the funnel plot ( fig 4 ), indicates the presence of bias against smaller studies with non-significant results, suggesting that the pooled intervention effect estimate is likely to be overestimated. 69 An alternative explanation, however, is that smaller studies conducted at the early stages of a new psychotherapeutic intervention tend to include more high risk or responsive participants, and psychotherapeutic interventions tend to be delivered more effectively in smaller trials; both of these factors can exaggerate treatment effects, resulting in funnel plot asymmetry. 70 Also, because of the relatively small number of included studies and the considerable heterogeneity observed, test power may be insufficient to distinguish real asymmetry from chance. 71 Thus, this analysis should be considered exploratory.

Funnel plot assessing publication bias among studies measuring change in depression scores from before to after treatment. CI=confidence interval; θ IV =estimated effect size under inverse variance random effects model
Dichotomous data
We extracted response and remission rates for each group when reported directly, or imputed information when presented graphically. Two studies did not measure response or remission and thus did not contribute data for this part of the analysis. 15 18 The random effects model with a Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman modification was used to allow for heterogeneity to be incorporated into the weighting of the included studies’ results, and to provide a better estimation of between study variance accounting for small sample sizes.
Response rate —Overall, the likelihood of psilocybin intervention leading to treatment response was about two times greater (risk ratio 2.02, 95% CI 1.33 to 3.07) than with placebo. Despite the use of different scales to measure response, the heterogeneity between studies was not significant (I 2 =25.7%, P=0.23). PIs were, however, wide and crossed the line of no difference (−0.94 to 3.88), indicating that there could be settings or populations in which psilocybin intervention would be less efficacious.
Remission rate —Overall, the likelihood of psilocybin intervention leading to remission of depression was nearly three times greater than with placebo (risk ratio 2.71, 95% CI 1.75 to 4.20). Despite the use of different scales to measure response, no statistical heterogeneity was found between studies (I 2 =0.0%, P=0.53). PIs were, however, wide and crossed the line of no difference (0.87 to 2.32), indicating that there could be settings or populations in which psilocybin intervention would be less efficacious.
Exploring publication bias in response and remission rates data —We used Egger’s test and a funnel plot to examine whether response and remission estimates were affected by small study biases. The result for Egger’s test was non-significant (P>0.05) for both response and remission estimates, and no substantial asymmetry was observed in the funnel plots, providing no indication for the presence of bias against smaller studies with non-significant results.
Heterogeneity: subgroup analyses and metaregression
Heterogeneity was considerable across studies exploring changes in depression scores (I 2 =89.7%, P<0.005), triggering subgroup analyses to explore contributory factors. Table 4 and table 5 present the results of the heterogeneity analyses (subgroup analyses and metaregression, respectively). Also see supplementary Appendix H for a more detailed description and graphical representation of these results.
Subgroup analyses to explore potential causes of heterogeneity among included studies
Metaregression analyses to explore potential causes of heterogeneity among included studies
Cumulative meta-analyses
We used cumulative meta-analyses to investigate how the overall estimates of the outcomes of interest changed as each study was added in chronological order 72 ; change in depression scores and likelihood of treatment response both increased as the percentage of participants with past use of psychedelics increased across studies, as expected based on the metaregression analysis (see supplementary Appendix I). No other significant time related patterns were found.
We reanalysed the data for change in depression scores using a random effects Dersimonian and Laird model without the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman modification and compared the results with those of the original model. All comparisons found to be significant using the Dersimonian and Laird model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment were also significant without the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment, and confidence intervals were only slightly narrower. Thus, small study effects do not appear to have played a major role in the treatment effect estimate.
Additionally, to estimate the accuracy and robustness of the estimated treatment effect, we excluded studies from the meta-analysis one by one; no important differences in the treatment effect, significance, and heterogeneity levels were observed after the exclusion of any study (see supplementary Appendix J).
In our meta-analysis we found that psilocybin use showed a significant benefit on change in depression scores compared with placebo. This is consistent with other recent meta-analyses and trials of psilocybin as a standalone treatment for depression 73 74 or in combination with psychological support. 24 25 29 30 31 32 68 75 This review adds to those finding by exploring the considerable heterogeneity across the studies, with subsequent subgroup analyses showing that the type of depression (primary or secondary) and the depression scale used (Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale, quick inventory of depressive symptomatology, or Beck depression inventory) had a significant differential effect on the outcome. High between study heterogeneity has been identified by some other meta-analyses of psilocybin (eg, Goldberg et al 29 ), with a higher treatment effect in studies with patients with comorbid life threatening conditions compared with patients with primary depression. 22 Although possible explanations, including personal factors (eg, patients with life threatening conditions being older) or depression related factors (eg, secondary depression being more severe than primary depression) could be considered, these hypotheses are not supported by baseline data (ie, patients with secondary depression do not differ substantially in age or symptom severity from patients with primary depression). The differential effects from assessment scales used have not been examined in other meta-analyses of psilocybin, but this review’s finding that studies using the Beck depression inventory showed a higher treatment effect than those using the Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale and quick inventory of depressive symptomatology is consistent with studies in the psychological literature that have shown larger treatment effects when self-report scales are used (eg, Beck depression inventory). 76 77 This finding may be because clinicians tend to overestimate the severity of depression symptoms at baseline assessments, leading to less pronounced differences between before and after treatment identified in clinician assessed scales (eg, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale, quick inventory of depressive symptomatology). 78
Metaregression analyses further showed that a higher average age and a higher percentage of participants with past use of psychedelics both correlated with a greater improvement in depression scores with psilocybin use and explained a substantial amount of between study variability. However, the cumulative meta-analysis showed that the effects of age might be largely an artefact of the inclusion of one specific study, and alternative explanations are worth considering. For instance, Studerus et al 79 identified participants’ age as the only personal variable significantly associated with psilocybin response, with older participants reporting a higher “blissful state” experience. This might be because of older people’s increased experience in managing negative emotions and the decrease in 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A receptor density associated with older age. 80 Furthermore, Rootman et al 81 reported that the cognitive performance of older participants (>55 years) improved significantly more than that of younger participants after micro dosing with psilocybin. Therefore, the higher decrease in depressive symptoms associated with older age could be attributed to a decrease in cognitive difficulties experienced by older participants.
Interestingly, a clear pattern emerged for past use of psychedelics—the higher the proportion of study participants who had used psychedelics in the past, the higher the post-psilocybin treatment effect observed. Past use of psychedelics has been proposed to create an expectancy bias among participants and amplify the positive effects of psilocybin 82 83 84 ; however, this important finding has not been examined in other meta-analyses and may highlight the role of expectancy in psilocybin research.
Limitations of this study
Generalisability of the findings of this meta-analysis was limited by the lack of racial and ethnic diversity in the included studies—more than 90% of participants were white across all included trials, resulting in a homogeneous sample that is not representative of the general population. Moreover, it was not possible to distinguish between subgroups of participants who had never used psilocybin and those who had taken psilocybin more than a year before the start of the trial, as these data were not provided in the included studies. Such a distinction would be important, as the effects of psilocybin on mood may wane within a year after being administered. 21 85 Also, how psychological support was conceptualised was inconsistent within studies of psilocybin interventions; many studies failed to clearly describe the type of psychological support participants received, and others used methods ranging from directive guidance throughout the treatment session to passive encouragement or reassurance (eg, Griffiths et al, 14 Carhart-Harris et al 63 ). The included studies also did not gather evidence on participants’ previous experiences with treatment approaches, which could influence their response to the trials’ intervention. Thus, differences between participant subgroups related to past use of psilocybin or psychotherapy may be substantial and could help interpret this study’s findings more accurately. Lastly, the use of graphical extraction software to estimate the findings of studies where exact numerical data were not available (eg, Goodwin et al, 18 Grob et al 15 ), may have affected the robustness of the analyses.
A common limitation in studies of psilocybin is the likelihood of expectancy effects augmenting the treatment effect observed. Although some studies used low dose psychedelics as comparators to deal with this problem (eg, Carhart-Harris et al, 63 Goodwin et al, 18 Griffiths et al 14 ) or used a niacin placebo that can induce effects similar to those of psilocybin (eg, Grob et al, 15 Ross et al 17 ), the extent to which these methods were effective in blinding participants is not known. Other studies have, however, reported that participants can accurately identify the study groups to which they had been assigned 70-85% of the time, 84 86 indicating a high likelihood of insufficient blinding. This is especially likely for studies in which a high proportion of participants had previously used psilocybin and other hallucinogens, making the identification of the drug’s acute effects easier (eg, Griffiths et al, 14 Grob et al, 15 Ross et al 17 ). Patients also have expectations related to the outcome of their treatment, expecting psilocybin to improve their symptoms of depression, and these positive expectancies are strong predictors of actual treatment effects. 87 88 Importantly, the effect of outcome expectations on treatment effect is particularly strong when patient reported measures are used as primary outcomes, 89 which was the case in several of the included studies (eg, Griffiths et al, 14 Grob et al, 15 Ross et al 17 ). Unfortunately, none of the included studies recorded expectations before treatment, so it is not possible to determine the extent to which this factor affected the findings.
Implications for clinical practice
Although this review’s findings are encouraging for psilocybin’s potential as an effective antidepressant, a few areas about its applicability in clinical practice remain unexplored. Firstly, it is unclear whether the protocols for psilocybin interventions in clinical trials can be reliably and safely implemented in clinical practice. In clinical trials, patients receive psilocybin in a non-traditional medical setting, such as a specially designed living room, while they may be listening to curated calming music and are isolated from most external stimuli by wearing eyeshades and external noise-cancelling earphones. A trained therapist closely supervises these sessions, and the patient usually receives one or more preparatory sessions before the treatment commences. Standardising an intervention setting with so many variables is unlikely to be achievable in routine practice, and consensus is considerably lacking on the psychotherapeutic training and accreditations needed for a therapist to deliver such treatment. 90 The combination of these elements makes this a relatively complex and expensive intervention, which could make it challenging to gain approval from regulatory agencies and to gain reimbursement from insurance companies and others. Within publicly funded healthcare systems, the high cost of treatment may make psilocybin treatment inaccessible. The high cost associated with the intervention also increases the risk that unregulated clinics may attempt to cut costs by making alterations to the protocol and the therapeutic process, 91 92 which could have detrimental effects for patients. 92 93 94 Thus, avoiding the conflation of medical and commercial interests is a primary concern that needs to be dealt with before psilocybin enters mainstream practice.
Implications for future research
More large scale randomised trials with long follow-up are needed to fully understand psilocybin’s treatment potential, and future studies should aim to recruit a more diverse population. Another factor that would make clinical trials more representative of routine practice would be to recruit patients who are currently using or have used commonly prescribed serotonergic antidepressants. Clinical trials tend to exclude such participants because many antidepressants that act on the serotonin system modulate the 5-hydroxytryptamine type 2A receptor that psilocybin primarily acts upon, with prolonged use of tricyclic antidepressants associated with more intense psychedelic experiences and use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors or SSRIs inducing weaker responses to psychedelics. 95 96 97 Investigating psilocybin in such patients would, however, provide valuable insight on how psilocybin interacts with commonly prescribed drugs for depression and would help inform clinical practice.
Minimising the influence of expectancy effects is another core problem for future studies. One strategy would be to include expectancy measures and explore the level of expectancy as a covariate in statistical analysis. Researchers should also test the effectiveness of condition masking. Another proposed solution would be to adopt a 2×2 balanced placebo design, where both the drug (psilocybin or placebo) and the instructions given to participants (told they have received psilocybin or told they have received placebo) are crossed. 98 Alternatively, clinical trials could adopt a three arm design that includes both an inactive placebo (eg, saline) and active placebo (eg, niacin, lower psylocibin dose), 98 allowing for the effects of psilocybin to be separated from those of the placebo.
Overall, future studies should explore psilocybin’s exact mechanism of treatment effectiveness and outline how its physiological effects, mystical experiences, dosage, treatment setting, psychological support, and relationship with the therapist all interact to produce a synergistic antidepressant effect. Although this may be difficult to achieve using an explanatory randomised trial design, pragmatic clinical trial designs may be better suited to psilocybin research, as their primary objective is to achieve high external validity and generalisability. Such studies may include multiple alternative treatments rather than simply an active and placebo treatment comparison (eg, psilocybin v SSRI v serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor), and participants would be recruited from broader clinical populations. 99 100 Although such studies are usually conducted after a drug’s launch, 100 earlier use of such designs could help assess the clinical effectiveness of psilocybin more robustly and broaden patient access to a novel type of antidepressant treatment.
Conclusions
This review’s findings on psilocybin’s efficacy in reducing symptoms of depression are encouraging for its use in clinical practice as a drug intervention for patients with primary or secondary depression, particularly when combined with psychological support and administered in a supervised clinical environment. However, the highly standardised treatment setting, high cost, and lack of regulatory guidelines and legal safeguards associated with psilocybin treatment need to be dealt with before it can be established in clinical practice.
What is already known on this topic
Recent research on treatments for depression has focused on psychedelic agents that could have strong antidepressant effects without the drawbacks of classic antidepressants; psilocybin being one such substance
Over the past decade, several clinical trials, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews have investigated the use of psilocybin for symptoms of depression, and most have found that psilocybin can have antidepressant effects
Studies published to date have not investigated factors that may moderate psilocybin’s effects, including type of depression, past use of psychedelics, dosage, outcome measures, and publication biases
What this study adds
This review showed a significantly greater efficacy of psilocybin among patients with secondary depression, patients with past use of psychedelics, older patients, and studies using self-report measures for symptoms of depression
Efficacy did not appear to be homogeneous across patient types—for example, those with depression and a life threatening illness appeared to benefit more from treatment
Further research is needed to clarify the factors that maximise psilocybin’s treatment potential for symptoms of depression
Ethics statements
Ethical approval.
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Oxford Nuffield Department of Medicine, which waived the need for ethical approval and the need to obtain consent for the collection, analysis, and publication of the retrospectively obtained anonymised data for this non-interventional study.
Data availability statement
The relevant aggregated data and statistical code will be made available on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank DT who acted as an independent secondary reviewer during the study selection and data review process.
Contributors: AMM contributed to the design and implementation of the research, analysis of the results, and writing of the manuscript. MC was involved in planning and supervising the work and contributed to the writing of the manuscript. AMM and MC are the guarantors. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted.
Funding: None received.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at https://www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest/ and declare: no support from any organisation for the submitted work; AMM is employed by IDEA Pharma, which does consultancy work for pharmaceutical companies developing drugs for physical and mental health conditions; MC was the supervisor for AMM’s University of Oxford MSc dissertation, which forms the basis for this paper; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Transparency: The corresponding author (AMM) affirms that the manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported; that no important aspects of the study have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the study as registered have been explained.
Dissemination to participants and related patient and public communities: To disseminate our findings and increase the impact of our research, we plan on writing several social media posts and blog posts outlining the main conclusions of our paper. These will include blog posts on the websites of the University of Oxford’s Department of Primary Care Health Sciences and Department for Continuing Education, as well as print publications, which are likely to reach a wider audience. Furthermore, we plan to present our findings and discuss them with the public in local mental health related events and conferences, which are routinely attended by patient groups and advocacy organisations.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
- ↵ World Health Organization. Depressive Disorder (Depression); 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression .
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators
- Cipriani A ,
- Furukawa TA ,
- Salanti G ,
- Trivedi MH ,
- Wisniewski SR ,
- Mitchell AJ
- Bockting CL ,
- Hollon SD ,
- Jarrett RB ,
- Nierenberg AA ,
- Petersen TJ ,
- Páleníček T ,
- Carbonaro TM ,
- Bradstreet MP ,
- Barrett FS ,
- Carhart-Harris RL ,
- Bolstridge M ,
- Griffiths RR ,
- Johnson MW ,
- Carducci MA ,
- Danforth AL ,
- Chopra GS ,
- Kraehenmann R ,
- Preller KH ,
- Scheidegger M ,
- Goodwin GM ,
- Aaronson ST ,
- Alvarez O ,
- Bogenschutz MP ,
- Podrebarac SK ,
- Roseman L ,
- Galvão-Coelho NL ,
- Gonzalez M ,
- Dos Santos RG ,
- Osório FL ,
- Crippa JA ,
- Zuardi AW ,
- Cleare AJ ,
- Martelli C ,
- Benyamina A
- Vollenweider FX ,
- Demetriou L ,
- Carhart-Harris RL
- Timmermann C ,
- Giribaldi B ,
- Goldberg SB ,
- Nicholas CR ,
- Raison CL ,
- Irizarry R ,
- Winczura A ,
- Dimassi O ,
- Dhillon N ,
- Griffiths RR
- Castro Santos H ,
- Gama Marques J
- Moreno FA ,
- Wiegand CB ,
- Taitano EK ,
- Liberati A ,
- Tetzlaff J ,
- Altman DG ,
- PRISMA Group
- Sterne JAC ,
- Savović J ,
- Guyatt GH ,
- Schünemann HJ ,
- Tugwell P ,
- Knottnerus A
- Sterne JA ,
- Sutton AJ ,
- Ioannidis JP ,
- Higgins JPT ,
- Chandler J ,
- Borenstein M ,
- Hedges LV ,
- Higgins JP ,
- Rothstein HR
- DerSimonian R ,
- ↵ Borenstein M, Hedges L, Rothstein H. Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects. Meta-analysis. com. 2007;1-62.
- IntHout J ,
- Rovers MM ,
- Gøtzsche PC
- Spineli LM ,
- ↵ Higgins JP, Green S. Identifying and measuring heterogeneity. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 2011;5(0).
- Austin PC ,
- O’Donnell KC ,
- Mennenga SE ,
- Bogenschutz MP
- Sander SD ,
- Berlin JA ,
- Santanna J ,
- Schmid CH ,
- Szczech LA ,
- Feldman HI ,
- Anti-Lymphocyte Antibody Induction Therapy Study Group
- ↵ Iyengar S, Greenhouse J. Sensitivity analysis and diagnostics. Handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. Russell Sage Foundation, 2009:417-33.
- McKenzie JE ,
- Bossuyt PM ,
- ↵ Griffiths R, Barrett F, Johnson M, Mary C, Patrick F, Alan D. Psilocybin-Assisted Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder: Results From a Randomized Trial. Proceedings of the ACNP 58th Annual Meeting: Poster Session II. In Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:230-384.
- ↵ Barrett F. ACNP 58th Annual Meeting: Panels, Mini-Panels and Study Groups. [Abstract.] Neuropsychopharmacology 2019;44:1-77. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0544-z . OpenUrl CrossRef
- Benville J ,
- Agin-Liebes G ,
- Roberts DE ,
- Gukasyan N ,
- Hurwitz ES ,
- Považan M ,
- Rosenberg MD ,
- Carhart-Harris R ,
- Buehler S ,
- Kettner H ,
- von Rotz R ,
- Schindowski EM ,
- Jungwirth J ,
- Vargas AS ,
- Barroso M ,
- Gallardo E ,
- Isojarvi J ,
- Lefebvre C ,
- Glanville J
- Sukpraprut-Braaten S ,
- Narlesky M ,
- Strayhan RC
- Prouzeau D ,
- Conejero I ,
- Voyvodic PL ,
- Becamel C ,
- Lopez-Castroman J
- Więckiewicz G ,
- Stokłosa I ,
- Gorczyca P ,
- John Mann J ,
- Currier D ,
- Zimmerman M ,
- Friedman M ,
- Boerescu DA ,
- Attiullah N
- Borgherini G ,
- Conforti D ,
- Studerus E ,
- Kometer M ,
- Vollenweider FX
- Pinborg LH ,
- Rootman JM ,
- Kryskow P ,
- Turner EH ,
- Rosenthal R
- Bershad AK ,
- Schepers ST ,
- Bremmer MP ,
- Sepeda ND ,
- Hurwitz E ,
- Horvath AO ,
- Del Re AC ,
- Flückiger C ,
- Rutherford BR ,
- Pearson C ,
- Husain SF ,
- Harris KM ,
- George JR ,
- Michaels TI ,
- Sevelius J ,
- Williams MT
- Collins A ,
- Bonson KR ,
- Buckholtz JW ,
- Yamauchi M ,
- Matsushima T ,
- Coleshill MJ ,
- Colloca L ,
- Zachariae R ,
- Colagiuri B
- Heifets BD ,
- Pratscher SD ,
- Bradley E ,
- Sugarman J ,

Tackling Treatment Resistant Depression with Multiple Tools
Ketamine changed lives and opened minds, but it's no panacea..
Posted May 6, 2024 | Reviewed by Kaja Perina
- What Is Depression?
- Find counselling to overcome depression
- Ketamine changed lives and opened minds to alternative treatments for mental health.
- Yet Ketamine is no panacea for treatment-resistant depression and other debilitating mental health conditions.
- Other solutions exist that are helping to make treatment-resistant conditions more treatable than ever before.
After administering more than 23,000 ketamine treatments over the past 5 years, we obviously believe in the drug’s importance—saving and changing lives of many patients who suffer from intractable mental health disease.
.png.jpg?itok=RwuuG0-x)
But ketamine is no panacea for treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and other debilitating mental health conditions. Other solutions exist that are helping to make treatment-resistant conditions more treatable than ever before. And while the explosion of ketamine-for-cash clinics did a lot to build awareness of ketamine, it also provided a myopic, wonder-drug view that overlooks alternatives.
In this blog, we will provide a quick overview of a few key treatments that are helping to make the term treatment-resistant somewhat archaic. We will omit treatments that are currently illegal or require hospitalization.
TMS–a non-drug, non-invasive alternative
Transcranial magnetic stimulation has long been a mainstay of our mental health practice. It’s been a completely noninvasive, non-drug, FDA-approved treatment for depression and OCD for nearly 15 years. According to a study published by the Journal of Neuropsychiatry , “Response to [TMS] treatment is variable, with response rates reported between 45% and 60% and remission rates between 30% and 40%.”
Why we choose this alternative: When a patient is treatment-resistant, having failed at least two traditional antidepressants , we often try TMS rather than continue to trial additional antidepressant medications. TMS is an important treatment for patients needing to avoid medications due to pregnancy or side effects.
Over the years, the technology and research behind TMS has steadily improved. Recently, researchers found that one of the many impacts TMS has on the brain is to correct the flow of brain signals. Researchers at Stanford Medicine studied 33 individuals with major depressive disorder and found that their brain signals were traveling in the wrong direction. After treating the participants with TMS, the flow of neural activity reversed directions and resulted in a lift in mood.
While not everyone with depression has an abnormal flow of neural activity, this is one possible cause of depression. In fact, we often begin our treatment intervention with TMS because it is well tolerated with minimal side effects and non-invasive.
Vagal Nerve Stimulation–an implantable option
Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) is an FDA-approved, non- medication treatment option for severe or bipolar depression. Like ketamine, it has a 70% success rate when used for TRD, meaning the patient hasn’t responded to traditional antidepressants.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation for depression involves implanting a small device just below the skin in the upper chest, similar to a pacemaker. VNS stimulates the vagus nerve, triggering its natural process of sending electrical pulses to parts of the brain that control mood.
Why we use this alternative: One thing to note is that VNS is considered an adjunct treatment, meaning it is typically used in tandem with an antidepressant or other treatment. We believe VNS could be the ‘ketamine reduction’ device providing a safe, enduring treatment beyond medication options. It gives mental health patients another vital option that works with your body’s natural means of controlling mood.
VNS is a proven treatment that has been around for more than 25 years and has been used in over 130,000 people. With recent advancements in the VNS technology and implantable devices, it has become much more accessible to the patients who need it most.
A small 2022 study of TRD patients in China found that, after 9 months of treatment with VNS, the response and remission were 85.7% and 57.1%, respectively. Meanwhile, a much larger clinical trial is underway since 2019 and will run until 2028 to “determine whether active VNS Therapy treatment is superior to a no stimulation control in producing a reduction in baseline depressive symptom severity.”
Though VNS is not as fast acting as most other antidepressant treatments, it can be used safely in combination with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), and common antidepressant medications to provide patients an added boost to break through their symptoms.
Dextromethorphan/bupropion–a (not so new) drug alternative
A new oral antidepressant, Auvelity, was approved by the FDA in 2022 following a phase 3 clinical trial study titled: Efficacy and Safety of AXS-05 (Dextromethorphan-Bupropion) in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder . According to clinical trial data, MDD patients treated with dextromethorphan-bupropion showed significant improvements in depressive symptoms compared to a placebo :

“Remission was achieved by 39.5% of patients with dextromethorphan-bupropion versus 17.3% with placebo (treatment difference, 22.2; 95% CI, 11.7 to 32.7; P < .001), and clinical response by 54.0% versus 34.0%, respectively (treatment difference, 20.0%; 95% CI, 8.4%, 31.6%; P < .001), at week 6.”
The drug is a combination of dextromethorphan (the active ingredient in Robitussin) and Wellbutrin (bupropion), an antidepressant. This was an important development that substantiated what was believed for some time; namely that dextromethorphan may have an impact on mood by affecting similar receptors to ketamine, working differently than other antidepressants.
As with ketamine, the generic ingredients can be just as powerful and more affordable. In fact, we may combine generic dextromethorphan with alternative antidepressants if a patient doesn’t tolerate Wellbutrin due to side effects or allergies.
Why we use this alternative: Ketamine must be administered in a clinic setting, due to its short-lived hallucinogenic effects and the potential for abuse. Dextromethorphan, on the other hand can be prescribed, along with an antidepressant, as an at-home regimen for patients.
We should note that the trial did not include TRD and risk of suicide among its criteria for patient selection. This is called out in an editorial by Alan F. Schatzberg, M.D. in The American Journal of Psychiatry which cautioned that early enthusiasm over Dextromethorphan/bupropion “needs to be tempered until further clinical experience is gained and more studies in patients with treatment-resistant depression are accomplished.” And Psychiatry News said, “An Axsome-sponsored trial conducted solely in patients with treatment-resistant depression failed to detect a difference between Auvelity and placebo after six weeks.”
So with the jury still out, we’re happy (if not enthusiastic) to see promising results from some of our own TRD patients with dextromethorphan as an antidepressant adjunct treatment.
Although ketamine and esketamine have certainly changed lives and opened minds to alternative treatments for mental health. With a number of other advancements, we hope that the term treatment-resistant becomes a thing of the past.
Iosifescu DV, Jones A, O’Gorman C, et al. Efficacy and safety of AXS-05 (dextromethorphan-bupropion) in patients with major depressive disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial (GEMINI). J Clin Psychiatry . 2022;83(4):21m14345.
Nina Bai, Researchers treat depression by reversing brain signals traveling the wrong way. Stanford Medicine News Center. Retrieved May 15, 2023, from: https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2023/05/depression-reverse-brain…
Zhang X, Qing MJ, Rao YH, Guo YM. Adjunctive Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression: a Quantitative Analysis. Psychiatr Q. 2020 Sep;91(3):669-679. doi: 10.1007/s11126-020-09726-5. PMID: 32144640.
Zhang X, Guo YM, Ning YP, Cao LP, Rao YH, Sun JQ, Qing MJ, Zheng W. Adjunctive vagus nerve stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a preliminary study. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2022 Nov;26(4):337-342. doi: 10.1080/13651501.2021.2019789. Epub 2022 Jan 13. PMID: 35023429.
Schatzberg , M.D., Alan F. Understanding the Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of a Dextromethorphan-Bupropion Combination: Where Does It Fit in the NMDA Versus mu-Opioid Story? American Journal of Psychiatry. Jul 2022 Retrieved April 17, from: https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.20220434
Kelly MS, Oliveira-Maia AJ, Bernstein M, Stern AP, Press DZ, Pascual-Leone A, Boes AD. Initial Response to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Treatment for Depression Predicts Subsequent Response. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Spring;29(2):179-182. doi: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.16100181. Epub 2016 Nov 30. PMID: 27899052; PMCID: PMC5592731.

Brian H. Johns, M.D., specializes in treatment-resistant depression and other mood disorders that haven't responded to traditional interventions.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conclusions. We have reviewed the determinants of depression and recognize that there are a multitude of risk and protective factors at the individual and wider ecologic levels. These determinants are interlinked and influence one another. ... This paper discusses key areas in depression research; however, an exhaustive discussion of all the ...
VOL. 390 NO. 17. In this first episode of a four-part Double Take video miniseries on depression from the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Scott-Vernaglia recounts her personal experiences ...
Abstract. Major depression is a mood disorder characterized by a sense of inadequacy, despondency, decreased activity, pessimism, anhedonia and sadness where these symptoms severely disrupt and ...
A relationship network of depression research was established, highlighting the highly influential countries, journals, categories, authors, institutions, cited articles, and keywords in this research field. ... In conclusion, depression is associated with an increased risk of lung, oral, prostate, and skin cancers, an increased risk of cancer ...
Depression is a disorder that increasingly affects different populations, with an estimated prevalence rate of 4.4% worldwide 1.This condition is defined as a mental disorder characterized by a ...
Over the past 16 years, we have developed a 'Meta-analytic Research Domain' (MARD) of all randomized trials of psychological treatments of depression. A MARD is a living systematic review of a research field, that cannot be otherwise covered by one (network) meta-analysis and includes multiple PICOs.
The causes of depression are manifold and complex. But biologically definable factors are starting to come to light. One theory that is gaining support is that the culprit might be a slowdown in ...
The idea that depression is the result of abnormalities in brain chemicals, particularly serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT), has been influential for decades, and provides an important ...
Our lack of knowledge cannot be put down to a scarcity of research in existing treatments. In the past decades, more than 500 randomised trials have examined the effects of antidepressant medications, and more than 600 trials have examined the effects of psychotherapies for depression (although comparatively few are conducted for early-onset depression).
Abstract. Cognitive science has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the onset, maintenance, and treatment of depression. Research conducted over the last 50 years supports the proposition that depression and risk for depression are characterized by the operation of negative biases, and often by a lack of positive biases, in self ...
This special Research in Context feature explores the development of more effective ways to treat depression, including personalized treatment approaches and both old and new drugs. Choat / Adobe Stock. Everyone has a bad day sometimes. People experience various types of stress in the course of everyday life. These stressors can cause sadness ...
To improve our understanding, some research has been undertaken in which YP themselves are asked about their experience of depression. In a questionnaire study involving adolescents with depression in New Zealand, the researchers identified the aforementioned irritability as the most common characteristic alongside interpersonal problems and ...
Conclusion depression. Depression is one of the most common conditions in primary care, but is often unrecognized, undiagnosed, and untreated. Depression has a high rate of morbidity and mortality when left untreated. Most patients suffering from depression do not complain of feeling depressed, but rather anhedonia or vague unexplained symptoms ...
In addition, initial presentation with social phobia was associated with a 5.7-fold increased risk of developing major depressive disorder. These associations between anxiety and depression can be traced back even earlier in life. For example, childhood behavioral inhibition in response to novelty or strangers, or an extreme anxious temperament ...
In conclusion, the literature on cognition in depression strongly supports the hypothesis that negative affective states can induce negative cognitive biases and beliefs, but
Conclusion Depression in adolescence is a relevant condition to the medical community, due to its uncertain clinical course and underdiagnosis worldwide. ... This Research Topic is a collection of ...
In this systematic review, we aimed to summarize the current state of brain biomarker research for NIBS in depression, ... Conclusions. This systematic review has identified 4 robust neuroimaging biomarkers that have reached a sufficient level for testing in prospective trials to evaluate their feasibility and clinical actionability.
Conclusion. A major aim of this course was to shed some light on the aetiology of depression and anxiety. At the end of it you should have some idea of the complexity of this enterprise. We have focused on one of the best-studied and hence best-understood contributors to psychopathology - stress. This has biological, social and psychological ...
Depression: The Latest Research. If you're one of more than 17 million adults or 3.2 million teens in the United States with major depression, you may know that treatment often falls short. The ...
Conclusion. Depression is a highly recurrent chronic condition that causes substantial suffering and results in increased mortality risk. 44, 51 The World Health Organization has identified depression as a leading cause of disability worldwide and a major contributor to the overall burden of disease. 52 The SCMH was administered from September ...
Evidence supported depression screening in primary care settings, including during pregnancy and postpartum. ... meta-analyses were conducted on original research when evidence was sufficient. Main outcomes and measures: Depression outcomes; suicidal ideation, attempts ... Conclusions and relevance: ...
Conclusion. In patients with anxiety and/or depression, hypomentalization as measured by the RFQ-6 is not a major problem, but emotion regulation is. It seems that these two, theoretically related constructs, do not necessarily co-occur. Alternatively, the RFQ-6 scale might not capture the mentalization construct in a valid way.
The Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-21), an introductory scale used to identify common mental disorders (CMDs) among adults, was validated across cultures in Asian populations; nevertheless, its capacity for screening these disorders may be limited for some specified groups, including nursing students. This study attempted to investigate the psychometric scale's unique features of ...
Depression is a pervasive mental health issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This essay delves into the complex relationship between mental health stigma and the prevalence of depression in society, examining the barriers to seeking help and the consequences of this stigma. Example Conclusion Paragraph for an Argumentative Essay:
Conclusion Treatment effects of psilocybin were significantly larger among patients with secondary depression, when self-report scales were used to measure symptoms of depression, and when participants had previously used psychedelics. ... Research on novel depression treatments is of great interest to both patients and the public. Although ...
Vagal Nerve Stimulation-an implantable option. Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) is an FDA-approved, non- medication treatment option for severe or bipolar depression. Like ketamine, it has a 70% ...
Background: Postpartum depression (PPD) is a significant mental health concern affecting mothers globally. However, research on PPD prevalence and risk factors in Najran City, Saudi Arabia, is limited. Study Aim: this cross-sectional study aimed to determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with PPD among mothers in Najran City. Methodology: A questionnaire-based study was conducted ...